Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Question Bank ME14 303 Fluid Mechanics
Enviado por
Sudeesh SudevanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Question Bank ME14 303 Fluid Mechanics
Enviado por
Sudeesh SudevanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
QUESTION BANK
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
Module 1
2 Marks Question
1. Define specific volume.
(NOV 09 2013)
2. Give some examples of surface tension
3. Define Surface tension
4. Define Newtons law of viscosity
(NOV 09 2013)
(OCT 09 2012)
(OCT 09 2011)
5. An oil of specific gravity 0.8 is in a vessel. The height of oil is 30 m. Find the
corresponding height of water at the point?
6. Define centre of buoyancy
7. Define capillarity
(OCT 09 2011)
(DEC 09 2010)
(DEC 09 2010)
5 Marks Questions
1. A flat plate of area 1.5 x 106 mm2 is pulled with a speed of 0.4 m/s relative to
another plate locate at a distance of 0.15 mm from it. Find the force and power
required to maintain this speed, if the fluid separating them is having the viscosity
of 1 poise.
(NOV 09 2013)
2. A right limb of simple U tube manometer containing mercury is open to the
atmosphere while the left limb is connected to a pipe in which a fluid of specific
gravity 0.9 is flowing. The centre of the pipe is 12 cm below the level of mercury
in the right limb. Find the pressure of fluid in the pipe is the difference of mercury
level in the two limbs is 20 cm.
(NOV 09 2013)
3. A rectangular plane surface is 2 m wide and 3 m deep. It lies in vertical plane in
water. Determine the total pressure and position of centre of pressure on the plane
surface when its upper edge is horizontal and coincides with water surface.
(NOV 09 2013)
4. A block of wood of specific gravity 0.7 floats in water. Determine the meta centric
height of the block if its size is 2 m x 1 m x 0.8 m
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
(NOV 09 2013)
Ammini
QUESTION BANK
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
5. Find the height through which water rises by capillary action in a glass tube of 2
mm bore if the surface tension at the prevailing temperature is 0.075 g/cm.
(OCT 09 2012)
6. A plate, 0.025 mm distant from a fixed plate, moves at 60 cm/s and requires a force
of 2 N per unit area i.e., 2 N/m2 to maintain this speed. Determine the fluid
viscosity between the plates.
(OCT 09 2012)
7. Calculate the pressure due to column of. 0.3 m of (a) Water (b) An oil of specific
gravity 0.8. Take density of water, p = 1000 kg/m3.
(OCT 09 2012)
8. What are the gauge pressure and absolute pressure at a point 4 m below the free
surface of a liquid of specific gravity 1.40, if atmospheric pressure is equivalent to
750 mm of mercury
9. State and explain Newtons law of viscosity.
(OCT 09 2011)
(DEC 04 2005, OCT 09 2011)
10.Explain how you would rind the resultant pressure on a curved surface immersed
in a liquid
13.
(DEC 04 2010)
11.Explain the Pascal law.
(DEC 09 2010)
12.Explain absolute, gauge and vacuum pressures
(DEC 09 2010)
Differentiate between :
(i) Dynamic viscosity and kinematic viscosity.
(ii) Absolute and gauge pressure.
14.Define the terms "buoyancy and centre of buoyancy".
(DEC 04 2009)
(DEC 04 2009)
15.Develop the expression for the relationship between the gauge pressure P inside a
droplet of liquid and the surface tension.
(DEC 04 2008)
16.What are the conditions of equilibrium of a floating body and a submerged body ?
(DEC 04 2008)
17.The relative density of a fluid is 1.26 and its dynamic viscosity is 1.50 kg/ms.
Calculate its (i) specific weight (ii) kinematic viscosity.
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
(DEC 04 2007)
Ammini
QUESTION BANK
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
18.Two discs of 20 cm diameter are placed 1mm apart and gap is filled with an oil of
viscosity 8 kg/ms. Determine power required to rotate upper disc at 600 r.p.m. while
holding the lower one stationary.
19.Define viscosity of fluid, what are 'Poise' and 'Stoke' ?
(DEC 04 2007)
(DEC 04 2006, 2010)
20.Define gauge pressure and absolute pressure. How are they related ?
(DEC 04 2006)
3
21.A certain mass of a liquid has a volume of 5 m and a weight of 40 kN. Find the
specific weight, specific gravity and specific volume
(DEC 04 2006)
22.Define specific volume, specific gravity and density of fluid.
(DEC 04 2005)
23.State the hydrostatic law. What is the relation between gauge pressure and absolute
pressure ?
(DEC 04 2005)
24.Prove that the centre of pressure always lies below the centre of gravity on a flat
plate immersed in a liquid at some angle to the free surface.
(DEC 04 2005)
25.What is an inverted U-tube manometer ? Describe the method of pressure
measurement using such a manometer
(DEC 04 2005)
10 Marks Question
1. If the surface-tension of water in contact with air is 0.075 N/m , what correction
need to be applied towards capillary rise in the manometric reading in tube of 3mm
diameter ?
(NOV 09 2013)
2. A solid cylinder of diameter 4 m has a height of 3 m. Find the meta centric height of
the cylinder when it is flowing in water with its axis vertical. The specific gravity of
the cylinder = 0.6.
(NOV 09 2013)
3. If the velocity distribution over a plate is given by u=(2/3)y y2 in which u is the
velocity in meter per second at a distance y meter above the plate, determine the
shear stress at y = 0 and y = 0.15 m. Take dynamic viscosity of fluid as 8.63 poise.
(OCT 09 2012)
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
Ammini
QUESTION BANK
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
4. The pressure intensity at a point in a fluid is given 3.924 N/cm2. Find the
corresponding height of fluid when the fluid is :
specific gravity 0.9.
(a)Water ; and (b) Oil of
(OCT 09 2012)
5. An inverted U-tube differential manometer connects two pressure pipes A and B.
Pipe A contains carbon tetrachloride having a specific gravity 1.5 under a pressure of
11.0 N/cm2 and Pipe B contain oil of specific gravity 0.8 under a pressure of 11.0
N/cm2. The pipe A lies 2.5 m below pipe B. Find the difference of pressure measured
by mercury as fluid filling inverted U-tube.
(OCT 09 2011)
6. A solid cylinder of diameter 5.0 m has a height of 4 m. Find the meta-centric height
of the cylinder when it is floating in water with its axis vertical. The specific gravity
of the cylinder = 0.6.
(OCT 09 2011)
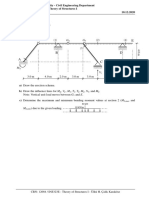
7. A vertical lock gate 6m wide has water to a depth of 8m on one side and to a depth
of 3m on the other. Find the resultant force on the gate and the position of its line of
action. To what position does this line tend as the depth of water on the shallow side
rises to 8m.
(DEC 04 2010)
8. A ship 70m long and 10m broad has a displacement of 19620 kN. A weight of
343.35 kN is moved across the deck through a distance of 6m The ship is tilted
through 60. The moment of inertia of the .ship at water-line about its fore and aft
axis is 75% of MOI. of the circumscribing rectangle. The center of buoyancy is
2.25m below water line. Find the metacentric height and position of centre of gravity
of ship. Specific weight of sea water is 10.104 kN/m3
(DEC 04 2010)
9. If the velocity of a fluid over a plate is a parabolic with the vertex 20 cm from the
plate, where the velocity is 120 cm/s. Calculate the velocity gradients and shear
stresses at a distance of 0, 10 and 20 cm from the plate, if the viscosity of the fluid is
8.5 poise.
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
(DEC 09 2010)
Ammini
QUESTION BANK
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
10.A wooden log of 0.6m diameter and 5m length is floating in river water. Find the
depth of wooden log in water when the specific gravity of the log is 0.7
(DEC 09 2010)
11.Derive an expression for pressure at any point in a incompressible fluid in terms of
the height of that fluid column.
(DEC 04 2009)
12.The dynamic viscosity of an oil used for lubrication between a shaft and sleeve is 6
poise. The shaft is of diameter 0.4 m. and rotates at 190 RPM. Calculate the power
lost in the bearings for a sleeve length of 90 mm. The thickness of oil film is 1.5
mm.
(DEC 04 2009)
13.Derive an expression for the depth of centre of pressure from the free surface of
liquid of an inclined plane surface submerged in the liquid and also the magnitude
of the total force exerted by the liquid on the inclined plane.
(DEC 04 2009)
14.A rectangular pontoon is 5 m. long, 3 m wide and 1.2 m. high. The depth of
immersion of the pontoon is 0.8 m. in sea water (s = 1.025). If the centre of gravity
is 0.6 m. above the bottom of the pontoon, determine the meta centric height.
(DEC 04 2009)
15.Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force due to water acting on a
roller gate of cylindrical form of 4 m diameter, when the gate is placed on the dam
in such a way that water is just going to spill. Take length of the gate as 8 m
(DEC 04 2008)
16.Define compressibility. Prove that compressibility for a gas undergoing isentropic
compression is 1/wp, where w = specific weight of the gas.
(DEC 04 2008)
17.A 15 cm diameter vertical cylinder rotates concentrically inside another cylinder of
diameter 15.1 cm. Both cylinders are 25 cm high. The space between the cylinders
is filled with a liquid whose viscosity is unknown. If the torque of 12.0 Nm is
required to rotate the inner cylinder at 100 rpm, find the viscosity of the fluid.
(DEC 04 2008)
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
Ammini
QUESTION BANK
19.
ME14 303 FLUID MECHANICS
18.Derive the expression for the metacentric height of a floating body.
(DEC 04 2005, 2008)
Derive differential equation of pressure for static fluid
(DEC 04 2007)
20.Find the pressure represented by a column of (i) 10 cm of water (ii) 5 cm of oil of
relative density 0.75 (iii) 2 cm of mercury.
(DEC 04 2007)
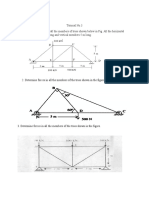
21.A triangular plate 2 m. base and 3 m. altitude is immersed in water. The plane of the
plate is inclined at 300 with the free surface and the base is parallel to and at a depth
of 2 m. below the free water surface. Find the total pressure on one side of the plate
and the centre of pressure.
(DEC 04 2005, 2006)
22.A flat thin plate is dragged at a constant velocity of 4 m/s. on the top of a 5 mm.
deep liquid layer of viscosity 20 centipoise. If the area of the plate is 2 m 2, find the
force required.
(DEC 04 2006)
23.Describe the pressure measurement with manometers. Also explain the various
types of manometers.
Department of Mechanical Engg.
College of Engg.
(DEC 04 2006)
Ammini
Você também pode gostar
- S1 FM Buyyancy T+answersDocumento18 páginasS1 FM Buyyancy T+answersprabathiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Debre Markos University Technology College Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocumento3 páginasDebre Markos University Technology College Mechanical Engineering Departmentanon_293092329Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronics and Communications Engineering: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocumento8 páginasElectronics and Communications Engineering: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesdeevoncAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial #3 #ProblemsDocumento5 páginasTutorial #3 #ProblemsAisha AbuzgaiaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1 2014Documento7 páginasTutorial 1 2014sotdeAinda não há avaliações
- Homeworks 1-10 PDFDocumento95 páginasHomeworks 1-10 PDFWendy LinAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies (4th Year)Documento2 páginasDynamics of Rigid Bodies (4th Year)Jaypee CalambaAinda não há avaliações
- HPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2012Documento20 páginasHPhys Unit 02 BFPM Packet 2012Kelly O'SheaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment II FM2019Documento19 páginasAssignment II FM2019Drkumar SwamyAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IDocumento5 páginasUnit IJackson ..Ainda não há avaliações
- Suresh SirDocumento5 páginasSuresh SirPruthvi PrakashaAinda não há avaliações
- Problems FluidmechanicsDocumento5 páginasProblems Fluidmechanicsanon_182348362Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment No.01 Properties of Fluid: Khamkar U.B ..VAPM ALMALADocumento3 páginasAssignment No.01 Properties of Fluid: Khamkar U.B ..VAPM ALMALAStar Youtuber PrashantAinda não há avaliações
- 07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankDocumento7 páginas07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankAmarkarthik ArunachalamAinda não há avaliações
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDocumento5 páginasDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Mechanical and Industrial Engineeringanon_293092329Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 2Documento8 páginasFluid Mechanics Worksheet 2anon_293092329Ainda não há avaliações
- ENGR207 - Assignment#1Documento5 páginasENGR207 - Assignment#1GendyAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet 4Documento2 páginasSheet 4Mo 16Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 Tutorial Force Sept19Documento6 páginas3 Tutorial Force Sept19hairinnisaAinda não há avaliações
- Newest CompreDocumento5 páginasNewest CompreJohn Dominic B. EugenioAinda não há avaliações
- Study Problems PDFDocumento33 páginasStudy Problems PDFAbdul Hai MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- A Circular Prestressed Concrete Pile Having A Diameter of 40 CM Is To Be Driven in A Layer of Loose SandDocumento2 páginasA Circular Prestressed Concrete Pile Having A Diameter of 40 CM Is To Be Driven in A Layer of Loose SandJay Saberdo CayaAinda não há avaliações
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1) ,) SheetDocumento5 páginasFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1) ,) SheetMo 16Ainda não há avaliações
- CE140-0P (Fluid Mechanics) Problem Set # 2 Name: - Student No.Documento1 páginaCE140-0P (Fluid Mechanics) Problem Set # 2 Name: - Student No.AydinAkhtarpourAinda não há avaliações
- Old Q Paper 10cv35Documento14 páginasOld Q Paper 10cv35Abhijeeth NagarajAinda não há avaliações
- Assign - 5 (Fluid Flow)Documento4 páginasAssign - 5 (Fluid Flow)Mahmoud AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento3 páginasAssignment 1Chanako Dane100% (1)
- Lesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocumento13 páginasLesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Correct Options: D: Welfare Civil&Mech 2017)Documento488 páginasCorrect Options: D: Welfare Civil&Mech 2017)Surya PatanAinda não há avaliações
- ENGR207 - Assignment#2Documento3 páginasENGR207 - Assignment#2Mohamed Khairy100% (1)
- Lesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocumento12 páginasLesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Iii Year 2017-2018Documento109 páginasCivil Iii Year 2017-2018Frank JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocumento3 páginasRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AJeana Rick GallanoAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet 1Documento10 páginasSheet 1lawanAinda não há avaliações
- 603 Quiz 5Documento2 páginas603 Quiz 5Cj SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Questions and Answers1Documento7 páginasHydraulics and Fluid Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Questions and Answers1Palli HemanthAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento1 páginaAssignment 1Frank JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Documento2 páginasReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonAinda não há avaliações
- TS1 PS07 SolutionDocumento2 páginasTS1 PS07 SolutionHasan Selman DoğanAinda não há avaliações
- AM2530 Tutorial3Documento2 páginasAM2530 Tutorial3Ashok YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Practice ProblemsFluidsDocumento4 páginasPractice ProblemsFluidsRitsu TainakaAinda não há avaliações
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering Problems: by GRC - Greywolves Review CenterDocumento383 páginasPower and Industrial Plant Engineering Problems: by GRC - Greywolves Review Centerkristan7Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluids SubjectiveDocumento11 páginasFluids SubjectiveSayantan ChatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics Sheet 8 Momentum ADocumento14 páginasHydraulics Sheet 8 Momentum AMohamed H AliAinda não há avaliações
- Steel ProblemsDocumento7 páginasSteel ProblemsNilava Das100% (1)
- Assignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Documento4 páginasAssignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Rajab AliAinda não há avaliações
- S1 Hyd Thrust T+answersDocumento22 páginasS1 Hyd Thrust T+answersprabathiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrau 4Documento3 páginasHydrau 4Mayya BonaAinda não há avaliações
- Problems On Fluid PropertiesDocumento1 páginaProblems On Fluid PropertiesTOOBA KHALILAinda não há avaliações
- r05220302 Mechanics of FluidsDocumento8 páginasr05220302 Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAinda não há avaliações
- 1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics CompletedDocumento18 páginas1.0-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Completedwaleed AlkaseriAinda não há avaliações
- Coach HGE (Oct 9, 2021)Documento7 páginasCoach HGE (Oct 9, 2021)Glaiza MarieAinda não há avaliações
- GERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeDocumento1 páginaGERTC Review November 2021 Geometry F2F Week 7: Prepared By: Engr. Jobert S. de La Cruz, CeLee Ann CabuquinAinda não há avaliações
- Refresher Module - Engineering Economy 1Documento2 páginasRefresher Module - Engineering Economy 1cat buenafeAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation Set 1: Civil Engineering Department Review in Hydraulics 1st Semester AY 2020-21Documento4 páginasEvaluation Set 1: Civil Engineering Department Review in Hydraulics 1st Semester AY 2020-21Yedda M IlaganAinda não há avaliações
- TrussDocumento5 páginasTrussChaubey AjayAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics sTREngth of MaterialsDocumento1 páginaMechanics sTREngth of MaterialsDenaiya Watton Leeh100% (1)
- Excel Review Center FB 17 - GeasDocumento4 páginasExcel Review Center FB 17 - GeasEmanuel GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFDocumento11 páginasMechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFSuresh Raju100% (2)
- CGM - FM Assignment 1Documento6 páginasCGM - FM Assignment 1charlesgmartinAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics (He304) : Department of Harbour and Ocean EngineeringDocumento21 páginasFluid Mechanics (He304) : Department of Harbour and Ocean EngineeringkhumisoAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid QuestionDocumento20 páginasFluid Questionsaini_sainiAinda não há avaliações
- Grinding MachinesDocumento34 páginasGrinding MachinesSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Diary Scenario Worked Example and Blank TemplateDocumento6 páginasStress Diary Scenario Worked Example and Blank TemplateKavithaAinda não há avaliações
- Francis TurbineDocumento34 páginasFrancis TurbinevishalAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Diary Scenario Worked Example and Blank TemplateDocumento6 páginasStress Diary Scenario Worked Example and Blank TemplateKavithaAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus MET203Documento12 páginasSyllabus MET203Sudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2 Ethics Morals and ValuesDocumento44 páginasModule 2 Ethics Morals and ValuesSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- 1.mechanics of MachineryDocumento12 páginas1.mechanics of Machineryram jrpsAinda não há avaliações
- Reciprocating PumpDocumento43 páginasReciprocating PumpSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture1428641930 PDFDocumento136 páginasLecture1428641930 PDFKrish PavanAinda não há avaliações
- 08 802 Industrial Engineering 2008 Scheme April 2014Documento2 páginas08 802 Industrial Engineering 2008 Scheme April 2014Sudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- 3.3 - 1.1 - Supply Chain ManagementDocumento1 página3.3 - 1.1 - Supply Chain ManagementSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ME404 - Industrial Engineering: Module-IIIDocumento16 páginasME404 - Industrial Engineering: Module-IIISudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Sequencing and Scheduling - An Overview: Chapter-IiDocumento14 páginasSequencing and Scheduling - An Overview: Chapter-IiSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, INDIADocumento15 páginasApj Abdul Kalam Technological University Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, INDIASudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Problem FormulationDocumento5 páginasProblem FormulationSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering Internal Test I - September 2018 Ee 311 - Electrical Drives and Control For AutomationDocumento1 páginaFifth Semester Mechanical Engineering Internal Test I - September 2018 Ee 311 - Electrical Drives and Control For AutomationSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ME Fluid-Mechanics PDFDocumento48 páginasME Fluid-Mechanics PDFSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ME 201 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento3 páginasME 201 Mechanics of SolidsSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- University of Kerala: Syllabus For Iv Semester Mechanical EngineeringDocumento20 páginasUniversity of Kerala: Syllabus For Iv Semester Mechanical EngineeringRahul RetnakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Matlab - Practice ProblemsDocumento5 páginasMatlab - Practice ProblemsSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ME 206 Fluid MachineryDocumento3 páginasME 206 Fluid MachinerySudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Answer To Assignment 1 Questions: 1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (D) 4. (B) 5. (D) 6. (B) 7. (C)Documento2 páginasAnswer To Assignment 1 Questions: 1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (D) 4. (B) 5. (D) 6. (B) 7. (C)Sudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Power Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and BrakesDocumento17 páginasPower Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and Brakesrip111176Ainda não há avaliações
- Quality CircleDocumento33 páginasQuality CircleSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Question PaperDocumento1 páginaQuality Question PaperSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Best IBPS Reasoning Preparation Tips To Follow This YearDocumento7 páginas6 Best IBPS Reasoning Preparation Tips To Follow This YearSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Operations Management Question Bank - Module 1Documento1 páginaOperations Management Question Bank - Module 1Sudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ICSGT 2015 Submission 103 EditDocumento1 páginaICSGT 2015 Submission 103 EditSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- ME09 804 1st SeriesDocumento1 páginaME09 804 1st SeriesSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- "View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter MenuDocumento62 páginas"View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter Menuelty TanAinda não há avaliações
- Dosing Pump DocumentsDocumento7 páginasDosing Pump Documentsbmanojkumar16Ainda não há avaliações
- FrictionDocumento3 páginasFrictiongovind singh nayakAinda não há avaliações
- A Review On CFD Analysis of Control ValvesDocumento4 páginasA Review On CFD Analysis of Control ValvesGRD JournalsAinda não há avaliações
- Re51156 2013-05Documento96 páginasRe51156 2013-05JamesAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Sum1Documento1 páginaSample Sum1Bhargav RawalAinda não há avaliações
- 2022-2023 Fall CE371 HW4 PDFDocumento3 páginas2022-2023 Fall CE371 HW4 PDFMurat EnginAinda não há avaliações
- 09 AE2258 Aerodynamics Lab ManualDocumento26 páginas09 AE2258 Aerodynamics Lab ManualBrandon Spence100% (5)
- Mobile Hydrostatic Test System: MODEL J24352Documento1 páginaMobile Hydrostatic Test System: MODEL J24352contango O&GAinda não há avaliações
- Surge Tank Design Considerations ForDocumento14 páginasSurge Tank Design Considerations ForPatricio Muñoz Proboste100% (1)
- Students Test Mechanical EnggDocumento9 páginasStudents Test Mechanical EnggArnel CdsAinda não há avaliações
- Sol Assign 7Documento6 páginasSol Assign 7John Ray CuevasAinda não há avaliações
- CHEN 2102 Chemical Engineering Fluid MechanicsDocumento5 páginasCHEN 2102 Chemical Engineering Fluid MechanicsSouvik AriAinda não há avaliações
- Coulson & Richardson's Chemical Engineering. Vol. 6, Chemical Engineering Design, 4th Ed-219-223 (1) - 3Documento1 páginaCoulson & Richardson's Chemical Engineering. Vol. 6, Chemical Engineering Design, 4th Ed-219-223 (1) - 3yeri abatamanAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Aerodynamics Class 01 - TWO - LECTURESDocumento101 páginas01 Aerodynamics Class 01 - TWO - LECTUREShaashillAinda não há avaliações
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocumento26 páginas2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25Ainda não há avaliações
- Training Hydraulic Circuits PDFDocumento5 páginasTraining Hydraulic Circuits PDFRICHARDAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Turbomachinery: 1. Coordinate SystemDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To Turbomachinery: 1. Coordinate SystemNah Sr AdAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento32 páginasChapter 6Merlund Rey ZamoraAinda não há avaliações
- Setp1711 Fluid Lab ManualDocumento25 páginasSetp1711 Fluid Lab ManualMohd Aliffazhar SarkawiAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento7 páginasPDFرضا حسنAinda não há avaliações
- FlexTable - Pipe TableDocumento11 páginasFlexTable - Pipe TablecesarAinda não há avaliações
- How Pressure Regulators WorkDocumento22 páginasHow Pressure Regulators WorkAdeel QaiserAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 - Fluid Kinematics STDocumento39 páginasLecture 3 - Fluid Kinematics SToialjarah13Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics Nat ReviewerDocumento15 páginasPhysics Nat ReviewerTeacher Airah FayeAinda não há avaliações
- PumpsDocumento75 páginasPumpsmd junuAinda não há avaliações
- Progress and Future Prospects of CFD in Aerospace - Wind Tunnel and BeyondDocumento16 páginasProgress and Future Prospects of CFD in Aerospace - Wind Tunnel and BeyondIván SuárezAinda não há avaliações
- Flow MeasurementsDocumento18 páginasFlow MeasurementsAbhishek SatheeshAinda não há avaliações