Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Setup and Hold Time": Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3c) - VLSI Concepts
Enviado por
KeerthiKalyanTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Setup and Hold Time": Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3c) - VLSI Concepts
Enviado por
KeerthiKalyanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing
Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c)
How will you calculate the setup and hold values?
How will you analyze setup and hold violation in a circuit?
If you have to improve timing of a circuit then what can you do?
There are few formulas to calculate different parameter ( Theory of those I already
explained in my previous blogs). I am not going to explain those right now. First we will
solve few examples which will give you an basic idea about these formulas, then in the
last I will summarize all those in one place.
I saw a lot of confusion with respect to setup and hold timing calculation. Actually there
are two things.
Timing Specification of a Block/Circuit/Library:
You have a block with input A and output Y. Some combinational logic is there
between A and Y. Now you have to calculate following parameters for that
block
Setup Time Value at input A
Hold Time value at input A.
Maximum operating Clock Frequency or Time Period for that block.
Clock To Y delay value
Input A to Output Y delay value.
Timing Violation of a circuit:
You have to operate a circuit at a particular clock frequency and now you have
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 1 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
to find out whether this circuit has any setup or Hold Violation.
So in second case all the parameters are given and you have to find out whether this
circuit has any violation or not and In first case you have to find out all the parameters
keeping in mind that there should not be any violation.
Lets Discuss in the reverse order.
**********************************************************************************
**********************************************************************************
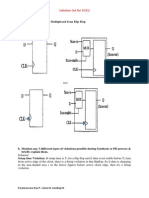
Problem1: In the following Circuit, Find out whether there is any Setup Or
Hold Violation?
Solution:
Hold Analysis:
When a hold check is performed, we have to consider two thingsMinimum Delay along the data path.
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 2 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Maximum Delay along the clock path.
If the difference between the data path and the clock path is negative, then a timing
violation has occurred. ( Note: there are few Exceptions for this- We will discuss that
some other time)
Data path is: CLK->FF1/CLK ->FF1/Q ->Inverter ->FF2/D
Delay in Data path
= min(wire delay to the clock input of FF1) + min(Clk-to-Q delay of FF1) +min(cell delay
of inverter) + min(2 wire delay- "Qof FF1-to-inverter" and "inverter-to-D of FF2")
=Td = 1+9+6+(1+1)=18ns
Clock path is: CLK-> buffer -> FF2/CLK
Clock path Delay
= max(wire delay from CLK to Buffer input) + max(cell delay of Buffer) + max(wire
delay from Buffer output to FF2/CLK pin) + (hold time of FF2)
=Tclk = 3+9+3+2 = 17 ns
Hold Slack = Td - Tclk = 18ns -17ns = 1ns
Since Hold Slack is positive-> No hold Violation.
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 3 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Note: If the hold time had been 4 ns instead of 2 ns, then there would have
been a hold violation.
Td=18ns and Tclk = 3+9+3+4=19ns
So Hold Slack=Td - Tclk = 18ns - 19ns = -1ns (Violation)
Setup Analysis:
When a setup check is performed, we have to consider two thingsMaximum Delay along the data path.
Minimum Delay along the clock path.
If the difference between the clock path and the data path is negative, then a timing
violation has occurred. ( Note: there are few Exceptions for this- We will discuss that
some other time)
Data path is: CLK->FF1/CLK ->FF1/Q ->Inverter ->FF2/D
Delay in Data path
= max(wire delay to the clock input of FF1) + max(Clk-to-Q delay of FF1) +max(cell
delay of inverter) + max(2 wire delay- "Qof FF1-to-inverter" and "inverter-to-D of FF2")
=Td = 2+11+9+(2+2) = 26ns
Note: The first part of the clock path delay (during setup calculation) is the clock
period, which has been set to 15 ns. Hope You remember in last blog, I have mentioned
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 4 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
very clearly that Setup is checked at the next clock cycle. That's the reason for
clock path delay we have to include clock period also.
Clock path is: CLK-> buffer -> FF2/CLK
Clock path Delay
= (Clock period) + min(wire delay from CLK to Buffer input) + min(cell delay of Buffer)
+ min(wire delay from Buffer output to FF2/CLK pin) - (Setup time of FF2)
=Tclk = 15+2+5+2-4=20ns
Setup Slack = Tclk - Td = 20ns - 26ns = -6ns.
Since Setup Slack is negative -> Setup violation.
Note: A bigger clock period or a less maximum delay of the inverter solve
this setup violations in the circuit.
E.g
If Clock period is 22ns then
Tclk = 22+2+5+2-4=31-4=27ns AND Td = 26ns
Setup Slack = Tclk - Td = 27-26=1ns (No Violation)
**********************************************************************************
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 5 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
**********************************************************************************
Problem2: In order to work correctly, what should be the Setup and Hold
time at Input A in the following Circuit. Also find out the maximum
operating frequency for this circuit. (Note: Ignore Wire delay). Where TsuSetup time; Thd-Hold Time; Tc2q- Clock-to-Q delay
Solution:
Step1: Find out the maximum Register to register Delay.
Max Register to Register Delay
= (clk-to-Q delay of U2) + (cell delay of U3) + (all wire delay) + (setup time of U1)
= 5 + 8 + 3 = 16 ns.
Note:
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 6 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
There are 2 register to register paths
U2 -> U3 ->U1 (Delay=5+8+3=16ns)
U1 -> U4 -> U2 ( Delay=5+7+3=15ns)
We have to pick maximum one.
Step2: Find Out Setup Time:
A setup time = Setup time of Flipflop + Max (Data path Delay) - min(Clock path Delay)
= (Setup time of Flipflop + A2D max delay) - (Clk path min delay)
= Tsu + (Tpd U7 + Tpd U3 + wire delay) - Tpd U8
= 3 + (1+8 ) - 2 = 10 ns
Note:
Step3: Find Out Hold Time:
A hold time = Hold time of Flipflop + max(Clock path Delay) - min( Data path delay)
=( Hold time of Flipflop + Clk path max delay) - (A2D max delay)
= Thd + Tpd U8 - (Tpd U7 + Tpd U4+wire delay)
= 4 + 2 - (1+7 ) = -2 ns
Note: Same explanation as for Setup time. For hold time we need minimum data path ,
so we have picked first Data path.
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 7 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Step4: Find out Clock to Out Time:
Clock to Out
= Cell delay of U8 + Clk-to-Q delay of FlipFlop+ Cell delay of U5+ Cell delay of U6+ (all
wire delay)
= Tpd U8+ U2 Tc2q + U5 Tpd + U6 Tpd
= 2 + 5 + 9 + 6 = 22 ns
Note:
There are 2 Clock to Out path- one from Flip flop U1 and other from U2.
Since in this case the Clk-to-Q path for both Flipflop is same, we can consider any
path. But in some other Circuit where the delay is different for both the paths, we
should consider Max delay path.
Step5: Find Pin to Pine Combinational Delay (A to Y delay)
Pin to Pin Combinational Delay (A to Y)
= U7 Tpd + U5 Tpd + U6 Tpd
= 1 + 9 + 6 = 16 ns
Step5: Find Out Max Clock Frequency:
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 8 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Max Clock Freq = 1/ Max (Reg2reg, Clk2Out, Pin2Pin)
= 1/ Max (16, 22, 16)
= 45.5 Mhz
So summery is:
Parameter
Description
Min
Max
Units
Tclk
Clock Period
22
Fclk
Clock Frequency
Atsu
A setup time
10
ns
Athd
A hold time
-2
ns
A2Y
A to Y Tpd
16
ns
Ck2Y
Clock to Y tpd
22
ns
ns
45.5
Mhz
Note: Negative hold times are typically specified as 0 ns.
**********************************************************************************
**********************************************************************************
Problem3: In the above Circuit, Try to improve the timing by adding any
"buffer" or "Register".
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 9 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Solution:
Best way of doing this is Register all Input and Output. We are adding DFF so same
specification (as U2 and U1).
Now follow all those 5 Steps onn by one.
Step1:
Max Register to Register Delay
U2 Tc2q + U5 Tpd + U9 Tsu = 5 + 9 + 3 = 17 ns
Note:
Step2:
A setup time = Tsu + A2D Tpd max - Clk Tpd min
= Tsu + (Tpd U7) - Tpd U8
= 3 + (1) - 2 = 2 ns
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 10 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Note: Only One path between A and D of FF(i.e U8)
Step3:
A hold time = Thd + Clk Tpd max - A2D Tpd min
= Thd + Tpd U8 - (Tpd U7)
= 4 + 2 - ( 1) = 5 ns
Note: Only One path between A and D of FF(i.e U8)
Step4:
Clock to out:
=Tpd U8+ U9 Tc2q + U6 Tpd
=2+5+6 = 13 ns
Step5:
No direct link between A and Y. So Not Applicable.
Step6:
Max Clock Freq = 1/ Max (Reg2reg, Clk2Out, Pin2Pin)
= 1/ Max (17, 13)
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 11 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
=58.8 Mhz
Parameter
Description
Min
Max
Units
Tclk
Clock Period
17
Fclk
Clock Frequency
Atsu
A setup time
ns
Athd
A hold time
ns
Ck2Y
Clock to Y tpd
ns
58.8
13
Mhz
ns
**********************************************************************************
**********************************************************************************
I hope This much will help you. Now its the time to summarize all the important things
and formulas.
Points to remember:
1. Setup is checked at next clock edge.
2. Hold is checked at same clock edge.
3. For Hold Check ( Checking of hold Violation)
Minimum Delay along the data path.
Maximum Delay along the clock path.
4. For SetUp Check ( Checking of Setup Violation)
1. Maximum Delay along the data path.
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 12 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
2. Minimum Delay along the clock path.
Basic 2 FlipFlop circuit.
Calculation of Setup Violation Check: Consider above circuit of 2 FF connected to
each other.
Setup Slack = Required time - Arrival time (since we want data to arrive
before it is required)
Where:
Arrival time (max) = clock delay FF1 (max) +clock-to-Q delay FF1 (max) + comb.
Delay( max)
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 13 of 14
"Examples Of Setup and Hold time" : Static Timing Analysis (STA) basic (Part 3c) |VLSI Concepts
20/06/15 11:55 pm
Required time = clock adjust + clock delay FF2 (min) - set up time FF2
Clock adjust = clock period (since setup is analyzed at next edge)
Calculation of Hold Violation Check: Consider above circuit of 2 FF connected to
each other.
Hold Slack = Arrival Time - Required time (since we want data to arrive
after it is required)
Where:
Arrival time (min) = clock delay FF1 (min) +clock-to-Q delay FF1 (min) + comb.
Delay( min)
Required time = clock adjust + clock delay FF2 (max) + hold time FF2
Clock adjust = 0 (since hold is analyzed at same edge)
Calculation of Maximum Clock Frequency:
Max Clock Freq = 1/ Max (Reg2reg delay, Clk2Out delay, Pin2Pin delay)
Where:
Reg2Reg Delay = Clk-to-Q delay of first FF (max) + conb delay (max) + setup time
of 2nd FF.
Clk2Out Delay = Clock delay w.r.t FF (max) + clock-to-Q delay of FF1 (max) +
comb. delay (max)
Pin2Pin delay = Comb delay between input pin to output pin (max)
http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2011/05/example-of-setup-and-hold-time-static.html
Page 14 of 14
Você também pode gostar
- Examples of Setup and Hold Time - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3c) - VLSI ConceptsDocumento7 páginasExamples of Setup and Hold Time - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3c) - VLSI ConceptsRakesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Examples of Setup and Hold TimeDocumento24 páginasExamples of Setup and Hold TimevpsampathAinda não há avaliações
- STI - FSM - SolutionsDocumento6 páginasSTI - FSM - SolutionsAishwarya GajendrulaAinda não há avaliações
- Timing Analysis: Elec 326 Sequential Circuit TimingDocumento43 páginasTiming Analysis: Elec 326 Sequential Circuit TimingArpit KapoorAinda não há avaliações
- Delay - Timing Path Delay - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 4a) - VLSI ConceptsDocumento6 páginasDelay - Timing Path Delay - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 4a) - VLSI ConceptsAnimesh BiyaniAinda não há avaliações
- CMOS Latches and Flip Flops TutorialDocumento52 páginasCMOS Latches and Flip Flops TutorialGuru VelmathiAinda não há avaliações
- Static Timing Analysis in VLSI CircuitsDocumento16 páginasStatic Timing Analysis in VLSI CircuitseeshgargAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 326 Set12 PDFDocumento17 páginasNotes 326 Set12 PDFEswaran SamyAinda não há avaliações
- A Tutorial On Timing Equations by S Schwartz (TUG 2000 Paper)Documento16 páginasA Tutorial On Timing Equations by S Schwartz (TUG 2000 Paper)domingouclarayAinda não há avaliações
- Timing issues in digital ASIC designDocumento101 páginasTiming issues in digital ASIC designnsai_vs1513Ainda não há avaliações
- Sta Notes 1671631469 PDFDocumento47 páginasSta Notes 1671631469 PDFAathith SaiprasadAinda não há avaliações
- DVD2 JNTU Set1 SolutionsDocumento12 páginasDVD2 JNTU Set1 Solutionsకిరణ్ కుమార్ పగడాలAinda não há avaliações
- TimingDocumento15 páginasTimingSameer BadachiAinda não há avaliações
- Static Timing Analysis: Critical PathsDocumento4 páginasStatic Timing Analysis: Critical PathsNishant SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Clocking Part 2Documento4 páginasClocking Part 2Dmitry LeyzerovichAinda não há avaliações
- STA FinalDocumento66 páginasSTA FinalgauravkshriAinda não há avaliações
- Static Timing AnalysisDocumento32 páginasStatic Timing AnalysisShantanu Sarkar100% (1)
- Step Replace Module Flexi BSC NokiaDocumento19 páginasStep Replace Module Flexi BSC Nokiarudibenget0% (1)
- Equations and Impacts of Setup and Hold Time: SkewDocumento5 páginasEquations and Impacts of Setup and Hold Time: SkewVardhan KarnatiAinda não há avaliações
- Equations and impacts of setup and hold timeDocumento5 páginasEquations and impacts of setup and hold timepavithra reddyAinda não há avaliações
- Equations and Impacts of Setup and Hold TimeDocumento5 páginasEquations and Impacts of Setup and Hold TimeShravan Kumar AshannagariAinda não há avaliações
- DFTDocumento14 páginasDFTRahulAinda não há avaliações
- Clock Skew AnDocumento13 páginasClock Skew AnNimmalapudi SureshAinda não há avaliações
- Setup and Hold TimeDocumento17 páginasSetup and Hold TimeVamsi SomisettyAinda não há avaliações
- CMOS Sequential Circuit Design Lec.-1Documento22 páginasCMOS Sequential Circuit Design Lec.-1Parag ParandkarAinda não há avaliações
- Chip Level Timing: ECE124 Digital Circuits and SystemsDocumento18 páginasChip Level Timing: ECE124 Digital Circuits and SystemspdnoobAinda não há avaliações
- Why timing analysis is important in chip designDocumento58 páginasWhy timing analysis is important in chip designPooja selvamAinda não há avaliações
- FlexCAN bit timing ParametersDocumento8 páginasFlexCAN bit timing Parametersravillakiran56Ainda não há avaliações
- Setup and Hold Time - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3a) - VLSI ConceptsDocumento3 páginasSetup and Hold Time - Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part 3a) - VLSI ConceptsRakesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- STA-Static Timing AnalysisDocumento28 páginasSTA-Static Timing AnalysisNaveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- CtsDocumento13 páginasCtsAnonymous qX2xaKAinda não há avaliações
- Sequential & Combinational Timing AnalysisDocumento8 páginasSequential & Combinational Timing AnalysisSahil SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- StatictimeanalysisDocumento75 páginasStatictimeanalysisAgnathavasiAinda não há avaliações
- Clock Setup and Hold Slack ExplainedDocumento11 páginasClock Setup and Hold Slack Explainedmyforforum0% (1)
- PD Assignments for Timing Analysis and OptimizationDocumento25 páginasPD Assignments for Timing Analysis and OptimizationAnusha ChidagniAinda não há avaliações
- Negative and Positive Clock SkewDocumento27 páginasNegative and Positive Clock SkewSupriya AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- ENG112-Introduction to Electrical and Computer Engineering Fall 2003 Prof. Russell Tessier Understanding Sequential Circuit TimingDocumento8 páginasENG112-Introduction to Electrical and Computer Engineering Fall 2003 Prof. Russell Tessier Understanding Sequential Circuit Timingchuku7Ainda não há avaliações
- STA Basics: Static Timing Analysis OverviewDocumento13 páginasSTA Basics: Static Timing Analysis OverviewMaulin Sheth100% (1)
- DGD 8Documento2 páginasDGD 8Dolores MakaruinaAinda não há avaliações
- OCVstinks MattWeber SLEDocumento21 páginasOCVstinks MattWeber SLEvlsi_asicAinda não há avaliações
- Very ImpDocumento33 páginasVery ImpAkanksha221291Ainda não há avaliações
- NDSU Timer2 Interrupt ExampleDocumento11 páginasNDSU Timer2 Interrupt ExampleCesar Matos100% (2)
- ECE 5263 Digital VLSI Design Clocked Systems Clock SkewDocumento4 páginasECE 5263 Digital VLSI Design Clocked Systems Clock SkewDuy DungAinda não há avaliações
- Virgo+Review1 DAQ Control ElectronicsDocumento14 páginasVirgo+Review1 DAQ Control ElectronicsVladimir NesicAinda não há avaliações
- Timing TutDocumento7 páginasTiming TutKrishna MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Interview QuestionsDocumento23 páginasInterview QuestionsSumanth VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- 11timing Concepts and Physical DesignDocumento42 páginas11timing Concepts and Physical DesignTeja Reddy100% (2)
- Setup and Hold - PDF Version 1Documento15 páginasSetup and Hold - PDF Version 1naniAinda não há avaliações
- UPLOAD - Simile NavasDocumento19 páginasUPLOAD - Simile NavasAnonymous VASS3z0wTHAinda não há avaliações
- MSP Devie ErratasheetDocumento8 páginasMSP Devie ErratasheetmaanviAinda não há avaliações
- Static Timing Analysis - MaharshiDocumento29 páginasStatic Timing Analysis - MaharshiSatish Yada100% (1)
- STA CONSTRAINTS ASSIGNMENTDocumento6 páginasSTA CONSTRAINTS ASSIGNMENTAvas RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Most Asked INterview Questions For Physical DesignDocumento2 páginasMost Asked INterview Questions For Physical DesignAvas RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Clock Tree SynthesisDocumento7 páginasClock Tree Synthesiskaushik vkAinda não há avaliações
- Meta StabilityDocumento16 páginasMeta StabilitySahil SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Timing (3rd Internal)Documento13 páginasTiming (3rd Internal)Utsav ParasharAinda não há avaliações
- Transistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsNo EverandTransistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGAinda não há avaliações
- Fuzzy Neural Networks for Real Time Control Applications: Concepts, Modeling and Algorithms for Fast LearningNo EverandFuzzy Neural Networks for Real Time Control Applications: Concepts, Modeling and Algorithms for Fast LearningAinda não há avaliações
- System Verilog Queue ConceptDocumento5 páginasSystem Verilog Queue ConceptKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- PuzzlesDocumento11 páginasPuzzlesKeerthiKalyan100% (1)
- Latch Time BorrwingDocumento9 páginasLatch Time BorrwingKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- PuzzlesDocumento11 páginasPuzzlesKeerthiKalyan100% (1)
- Higher Education in INDIA: Intel Internship - Procedure and QuestionsDocumento2 páginasHigher Education in INDIA: Intel Internship - Procedure and QuestionsKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- Fault SimulationDocumento18 páginasFault SimulationKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- ASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design: Intel Interview QuestionsDocumento5 páginasASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design: Intel Interview QuestionsKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- Small Signal Analysis of A PMOS Transistor: V V V Cox IDocumento6 páginasSmall Signal Analysis of A PMOS Transistor: V V V Cox IDuc DucAinda não há avaliações
- Fault ModelDocumento42 páginasFault ModelDamon SalvatoreAinda não há avaliações
- Eee590 Ic-Technology SyllabusDocumento2 páginasEee590 Ic-Technology SyllabusKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- Eee590 Ic-Technology SyllabusDocumento2 páginasEee590 Ic-Technology SyllabusKeerthiKalyanAinda não há avaliações
- C++ CLR DocsDocumento1.156 páginasC++ CLR DocsVictor TihoanAinda não há avaliações
- Syntax AnalysisDocumento115 páginasSyntax AnalysisPavan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Sc900a PDFDocumento23 páginasSc900a PDFgoguAinda não há avaliações
- Determinants NotesDocumento3 páginasDeterminants NotesSoham PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Install, 1Documento18 páginasInstall, 1PetzyMarianAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report Course Registration SystemDocumento70 páginasProject Report Course Registration SystemImran Khan Mewati36% (14)
- Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems SolutionsDocumento9 páginasDifferential Equations With Boundary Value Problems SolutionsAbdu Abdoulaye67% (6)
- CPointer HKDocumento37 páginasCPointer HKhardworking_studentAinda não há avaliações
- Linked List: Lab No. 3Documento24 páginasLinked List: Lab No. 3Junaid SaleemAinda não há avaliações
- WSGI Werkzeug and The Challenges of Building A Python Web FrameworkDocumento22 páginasWSGI Werkzeug and The Challenges of Building A Python Web FrameworkIgor Guerrero FonsecaAinda não há avaliações
- CS 253 Binary Search Trees ChapterDocumento28 páginasCS 253 Binary Search Trees ChapterMuhammed Abdel HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Programming Logic and Design Comprehensive 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasProgramming Logic and Design Comprehensive 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Solutions Manualhangingboune82um100% (9)
- Ore TheoremDocumento8 páginasOre Theoremrajananandh72138Ainda não há avaliações
- Problems On Poisson DistributionDocumento4 páginasProblems On Poisson DistributionMomanyi IvyAinda não há avaliações
- Hotel Management Source CodeDocumento11 páginasHotel Management Source CodeDARK JOKERAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento9 páginasProperties of Trigonometric FunctionsMarie Carolaine FameroAinda não há avaliações
- GROUP 3 Image CompressionDocumento31 páginasGROUP 3 Image CompressionPrayerAinda não há avaliações
- ConcreteDrawingProduction ProConcreteS7Documento38 páginasConcreteDrawingProduction ProConcreteS7Lula Caracoleta100% (1)
- IBM Rational Quality Manager 000-823 Practice Exam QuestionsDocumento20 páginasIBM Rational Quality Manager 000-823 Practice Exam QuestionsCahya PerdanaAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Apps Technical Interview Questions Answers GuideDocumento7 páginasOracle Apps Technical Interview Questions Answers GuideJohn StephensAinda não há avaliações
- Zenith ERP Solutions for Staffing, Real Estate and Telecom IndustriesDocumento16 páginasZenith ERP Solutions for Staffing, Real Estate and Telecom IndustriesChinmay MohapatraAinda não há avaliações
- MOE SEP Client Full ProtectionDocumento9 páginasMOE SEP Client Full Protectionhharun_5Ainda não há avaliações
- ISO 10980-1995 ScanDocumento45 páginasISO 10980-1995 ScanAriyandi Yuda PraharaAinda não há avaliações
- Java DocsDocumento144 páginasJava DocsAmit koulAinda não há avaliações
- Support LogDocumento55 páginasSupport LogБарба РискаAinda não há avaliações
- Table Invalid Index DumpDocumento9 páginasTable Invalid Index DumpBac AstonAinda não há avaliações
- Xposed LogDocumento848 páginasXposed LogAnonymous 0lnQB5XTFiAinda não há avaliações
- Burnes 2004Documento18 páginasBurnes 2004Asmadera Mat EsaAinda não há avaliações
- Subject Code:: Data VisualizationDocumento8 páginasSubject Code:: Data VisualizationAmanAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 5: Introduction To Finite Impulse Response Filters: Lastname: - 5digit SSDocumento6 páginasLAB 5: Introduction To Finite Impulse Response Filters: Lastname: - 5digit SSmrithyunjaysivAinda não há avaliações