Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Tropical Design by Froilan Hong
Enviado por
Lawrence TingDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Tropical Design by Froilan Hong
Enviado por
Lawrence TingDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
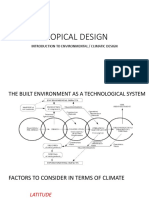
Tropical design is concerned with countries where discomfort due to heat and
humidity are dominant problems.
Classifications of tropical climates :
Warm humid tropical Island
Hot dry maritime dessert
Composite tropical uplands
Characteristics of tropical climates : Warm Humid
DBT High temperature during the day, low diurnal change
RH - relatively high
Precipitation heavy rains especially during monsoon season
Sky cloudy and glaring
Characteristics of tropical climates : Hot dry
DBT very high temperature during the day, large diurnal change
RH Low and very low humidity. Fairly constant throughout the year.
Precipitation Often low or very low
Sky little or no cloud. Cold and non glaring.
Ground Sparse and often bare. Very high glare from ground.
Composite this is a mixture of warm/humid and hot/dry. It has 1/3 to 2/3 ratio of
monsoon period. Can get quite cold in winter.
Macro Climate the climate of a region and or the entire country.
Micro Climate is the climate of the site and its immediate environs.
Dry Bulb Temperature (DRB) this is the measurement of the temperature of the
air and as far as possible excludes any radiant temperature. It is always measured
in the shade.
Relative Humidity (RH) the amount of water in the air.
Hygrometer the instrument in measuring Relative Humudity.
Precipitation mainly rainfall but could also be dew.
Vane Anemometer instrument in measuring high speed winds
Kata Anemometer instrument in measuring low speed winds
The range of the comfort zone will increase in dry and continental climates where
the annual range, is higher.
Condition for Thermal Storage when the difference between average
maximum and minimum temperature during the month is over 10degrees Celsius
and there is medium or low humidity.
Window Size affects
Conduction is the flow of heat through a material by transfer from warmer to
cooler molecules in contact with each other.
Convection is the transfer of heat from one place to another by the flow if
molecules from one place to another.
Radiation is the transfer of energy through space by electromagnetic waves. It
travels through air and the rate of transfer of energy is independent of the
temperature of the air.
Evaporation and Condensation heat can also be absorbed or given out when
materials alter their state, that is from gas to liquid, and from liquid to solid and vice
versa.
Heat loss is considered as the transmission of heat from the air inside the
building to the air outside.
Heat Gain is due mainly to solar radiation at the surface and only a smaller
extent the high air temperatures.
Steady Heat State Flow assumption of a constant external air temperature and
a different constant internal air temperature which rarely exists
Sol-air Temperature is used to find the heating effect of the radiant heat load
and is defined as the temperature of the outside air.
Solar Heat factor is proportional to the inside surface rise in temperature and
this related to the radiant heat from the ceiling walls.
Thermal Capacity the amount of heat required per unit volume per degree rise
in temperature.
Time Constant is defined as the amount of time in hours for the internal
temperature of an element to change by a given percentage of the external
temperature difference when the outside temperature is changed.
Warm Humid Climates : where there are more than 9 months of the year.
Effective temperatures are within or above the comfort zone
Humidities are more that 50%
The difference between day and night temperature is less than 10 degrees
Celsius.
Hot Dry Climates : where there are more than 6 months of the year.
The effective temperatures are within or above the comfort zone
The humidities are less than 70%
The difference between day and night temperature is more than 10 degrees
Celsius.
In composite climates where the hot dry season is three months or more,
heavy walls should be used.
In warm-humid Climate the feeling of discomfort is mainly attributed to high
humidity: the presence of more water vapor in the atmosphere.
WIND FACTOR - is one factor that can negate discomfort in high humidity climate.
Approx. 2.5 to 5.0 meters per second - To experience comfort during periods of
high humidity.
Wind Gradient the variation of speed when wind speeds increase with the height
above the ground, and the smoothness of the ground surface.
Air movement though a building can also prevent an increase in internal air
temperature due to INTERNAL HEAT SOURCE.
The radiation will be greatest when wind speed is lowest, and air movement
through cavities does not affect heat transfer due to radiation.
Above 30% there is positive pressure against the windward slope of a roof.
Air movement is measured in CUBIC METER/MINUTE.
Ventilation is usually measure in AIR CHANGES/HOUR.
Você também pode gostar
- 1 Introduction To Climatic DesignDocumento41 páginas1 Introduction To Climatic DesignNicholas Brian MariñasAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Design: Module O1: IntroductionDocumento15 páginasTropical Design: Module O1: Introductionxilen clevAinda não há avaliações
- Hoa 4Documento8 páginasHoa 4namika marbaAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Design Theories Concepts and STDocumento2 páginasTropical Design Theories Concepts and STZhardei AlysonAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER I. The Problem and Its Background: History Research Library of IntramurosDocumento43 páginasCHAPTER I. The Problem and Its Background: History Research Library of IntramurosAndrea AbundoAinda não há avaliações
- Post World War 2 ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasPost World War 2 ArchitectureMartina Jeunesse FlorendoAinda não há avaliações
- Master of ArchitectureDocumento22 páginasMaster of ArchitectureFrialyn Ermengarde De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Rooftop Garden DesignDocumento2 páginasRooftop Garden DesignEreca NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Architecture in Colonial and Post-Colonial AmericaDocumento49 páginasArchitecture in Colonial and Post-Colonial AmericaJohn Michael AlocAinda não há avaliações
- 003 Archist - Chapter3Documento123 páginas003 Archist - Chapter3arkiosk100% (2)
- Spanish Colonial ArchitectureDocumento8 páginasSpanish Colonial ArchitectureWendell Marc TamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical ArchitectureDocumento5 páginasTropical ArchitectureYen DaAinda não há avaliações
- Philosophy: Francisco "Bobby" MañosaDocumento6 páginasPhilosophy: Francisco "Bobby" MañosaJohnDominicMoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Hoa ReviewerDocumento3 páginasHoa ReviewerRachel Mae BahoyAinda não há avaliações
- Biological MachineDocumento12 páginasBiological MachinePurchiaAinda não há avaliações
- Air Movement in and Around BuildingDocumento41 páginasAir Movement in and Around BuildingJaya Suriya NatesanAinda não há avaliações
- INDMDocumento12 páginasINDMRc RobesoAinda não há avaliações
- Research DesignDocumento21 páginasResearch DesignAbigael Recio Sollorano100% (1)
- American Colonial ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasAmerican Colonial ArchitectureCam DeteraAinda não há avaliações
- Philam Life Building Architectural ValueDocumento3 páginasPhilam Life Building Architectural ValueVann RhymeAinda não há avaliações
- HOA104Documento66 páginasHOA104MR P PinnyAinda não há avaliações
- History of Architecture - PhilippinesDocumento13 páginasHistory of Architecture - PhilippinesJyzel NacuAinda não há avaliações
- ARCH514 Course Guide FSSY20122013Documento3 páginasARCH514 Course Guide FSSY20122013arkioskAinda não há avaliações
- AD6 - Major Plate #1 Research PaperDocumento14 páginasAD6 - Major Plate #1 Research Papervicente3maclangAinda não há avaliações
- FILIPINO Architecture-Modern Jorge RamosDocumento2 páginasFILIPINO Architecture-Modern Jorge Ramosenzong16Ainda não há avaliações
- Proposed Medium-Rise Apartment Building Design AssessmentDocumento17 páginasProposed Medium-Rise Apartment Building Design AssessmentRaynier LigayaAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Design: Introduction To Environmental / Climatic DesignDocumento16 páginasTropical Design: Introduction To Environmental / Climatic DesignSprinklesof Love0% (1)
- Modernism and Post-War ArchitectureDocumento12 páginasModernism and Post-War ArchitectureNiña TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Significant Examples: San Sebastian Church, ManilaDocumento10 páginasSignificant Examples: San Sebastian Church, ManilajezelAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4 - Tropical Design PrelimDocumento41 páginasModule 4 - Tropical Design PrelimJahara N. CuerdoAinda não há avaliações
- Hoa 4Documento6 páginasHoa 4Angelica Portia Forbes RegenciaAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Key-Ecommercial ExamDocumento9 páginasAnswer Key-Ecommercial ExamDonita Ginia AcuinAinda não há avaliações
- Ethnic Houses in the Philippines: A Guide to Traditional ArchitectureDocumento5 páginasEthnic Houses in the Philippines: A Guide to Traditional ArchitectureJohn Laurence Crucena VillaAinda não há avaliações
- American Period PDFDocumento113 páginasAmerican Period PDFJANJHONAinda não há avaliações
- Composite ConstructionDocumento26 páginasComposite ConstructionPatrick MalelangAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Exam-Hoa 4Documento1 páginaMidterm Exam-Hoa 4mhel_almoAinda não há avaliações
- The Mountain Houses - Architecture and Social Class in Cordillera RegionDocumento11 páginasThe Mountain Houses - Architecture and Social Class in Cordillera RegionClarissa LicoAinda não há avaliações
- Requirement Details For Esquisse Number 1 Residential Project Finals Architectural Design 7 Bs Architecture 41e1Documento5 páginasRequirement Details For Esquisse Number 1 Residential Project Finals Architectural Design 7 Bs Architecture 41e1Danica Mae AmicayAinda não há avaliações
- Hoa PH PrelimDocumento33 páginasHoa PH PrelimangerawrrAinda não há avaliações
- Renaissance Architecture in ItalyDocumento5 páginasRenaissance Architecture in ItalyJean Mae DesquitadoAinda não há avaliações
- HOA4 - Lecture 6 - Filipino Arch in The American Commonwealth PeriodDocumento71 páginasHOA4 - Lecture 6 - Filipino Arch in The American Commonwealth Periodhot bloodAinda não há avaliações
- Islamic Architecture Styles & ElementsDocumento18 páginasIslamic Architecture Styles & ElementsAndrea Joyce AngelesAinda não há avaliações
- Golden Age of Philippine Architecture under Marcos RegimeDocumento45 páginasGolden Age of Philippine Architecture under Marcos Regimecyril delfinAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Primitive ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasPhilippine Primitive ArchitectureLeola Vera ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Prewar Modern InfluenceDocumento9 páginasPrewar Modern InfluenceErica PagsAinda não há avaliações
- Postcolonial Modernity in Philippine Architecture 1946-1960sDocumento23 páginasPostcolonial Modernity in Philippine Architecture 1946-1960sKristee Marie O. LagamonAinda não há avaliações
- ESPESO | Passive Cooling Techniques for Tropical DesignDocumento7 páginasESPESO | Passive Cooling Techniques for Tropical DesignBianca EspesoAinda não há avaliações
- Final Esquisse Des 8 Mixed UseDocumento5 páginasFinal Esquisse Des 8 Mixed Usecarlo melgarAinda não há avaliações
- Project # 4-Office Building-StructureDocumento1 páginaProject # 4-Office Building-StructureTobyAinda não há avaliações
- Cambodian ArchitectureDocumento22 páginasCambodian ArchitectureMark Jemuel DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- List of Filipino ArchitectsDocumento12 páginasList of Filipino ArchitectsSheena Lou SangalangAinda não há avaliações
- Project # 3-It CenterDocumento1 páginaProject # 3-It CenterTobyAinda não há avaliações
- Filipino Architecture: 20 C: Modern Islamic Chinese Japanese IndianDocumento57 páginasFilipino Architecture: 20 C: Modern Islamic Chinese Japanese IndianJ VAinda não há avaliações
- Architectural Design 9 - Thesis Research Writing: Palutang Location: Bacoor BayDocumento6 páginasArchitectural Design 9 - Thesis Research Writing: Palutang Location: Bacoor BayJD LupigAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Merged AllDocumento83 páginasAp Merged AllNicole NovesterasAinda não há avaliações
- UAP Past PresidentsDocumento7 páginasUAP Past Presidentsjbvillareal79100% (1)
- Entourage 5th Edition: A Tracing File and Color SourcebookNo EverandEntourage 5th Edition: A Tracing File and Color SourcebookAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Climatic Design FactorsDocumento43 páginasIntroduction To Climatic Design FactorsJireh Grace71% (24)
- Air Masses Fronts and Pressure System PresentationDocumento34 páginasAir Masses Fronts and Pressure System Presentationapi-295900495Ainda não há avaliações
- Air Masses Fronts and Pressure System Presentation 2017Documento36 páginasAir Masses Fronts and Pressure System Presentation 2017api-271661638Ainda não há avaliações
- Cement:: Cemex Holcim Lafarge Northern TaiheiyoDocumento50 páginasCement:: Cemex Holcim Lafarge Northern TaiheiyoLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Ground Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseDocumento1 páginaGround Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Ground Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseDocumento1 páginaGround Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Exterior FinishesDocumento32 páginasExterior FinishesLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Floor FinishesDocumento42 páginasFloor FinishesLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing Practice ProblemsDocumento28 páginasEngineering Drawing Practice Problemsa c s KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Second Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseDocumento1 páginaSecond Floor Plan: Warehouse WarehouseLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Bamboo ScaffoldingDocumento54 páginasBamboo ScaffoldingLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento5 páginasProposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Fire Suppression Systems ExplainedDocumento26 páginasModern Fire Suppression Systems ExplainedLawrence Ting0% (3)
- Proposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento5 páginasProposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Admin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsDocumento9 páginasAdmin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Table of Contents for Proposed MRF PlanDocumento2 páginasTable of Contents for Proposed MRF PlanLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Admin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsDocumento9 páginasAdmin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed MRF Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento2 páginasProposed MRF Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed MRF Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento2 páginasProposed MRF Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff Quarters Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Admin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsDocumento9 páginasAdmin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Admin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsDocumento9 páginasAdmin BLDG Facility Complete Set of DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento5 páginasProposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento5 páginasProposed Pavilion Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Billing - Two Storey Residential RenovationDocumento1 páginaBilling - Two Storey Residential RenovationLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsDocumento10 páginasProposed Staff House Plan Technical DrawingsLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Item No. Particulars Amount: Cost EstimateDocumento5 páginasItem No. Particulars Amount: Cost EstimateLawrence TingAinda não há avaliações
- Sonochemical Synthesis of NanomaterialsDocumento13 páginasSonochemical Synthesis of NanomaterialsMarcos LoredoAinda não há avaliações
- Cases 39 45 PDFDocumento11 páginasCases 39 45 PDFYvette Marie VillaverAinda não há avaliações
- Laptop repair messageDocumento3 páginasLaptop repair messagePonpes Manbaul MaarifAinda não há avaliações
- Alarm Management Second Ed - Hollifield Habibi - IntroductionDocumento6 páginasAlarm Management Second Ed - Hollifield Habibi - IntroductionDavid DuranAinda não há avaliações
- Wall Street Expose: Monkey Business Reveals Investment Banking RealitiesDocumento2 páginasWall Street Expose: Monkey Business Reveals Investment Banking Realitiestorquewip100% (1)
- Racial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceDocumento2 páginasRacial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceYony Gutierrez100% (1)
- GTA Max Profit Bunker Locations Update v1.4Documento1 páginaGTA Max Profit Bunker Locations Update v1.4Sam FarrelAinda não há avaliações
- DMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFDocumento305 páginasDMGT403 Accounting For Managers PDFpooja100% (1)
- MCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutDocumento3 páginasMCS Adopts Milyli Software Redaction Tool BlackoutPR.comAinda não há avaliações
- Bron 2017Documento73 páginasBron 2017Anggia BungaAinda não há avaliações
- BA50BCODocumento6 páginasBA50BCOpedroarlindo-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Supply Chain Management of VodafoneDocumento8 páginasSupply Chain Management of VodafoneAnamika MisraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5Documento11 páginasChapter 5XDXDXDAinda não há avaliações
- BS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsDocumento26 páginasBS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsBorn ToSinAinda não há avaliações
- Airbus Reference Language AbbreviationsDocumento66 páginasAirbus Reference Language Abbreviations862405Ainda não há avaliações
- Schedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Documento7 páginasSchedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Jay PatelAinda não há avaliações
- 2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Documento65 páginas2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Hoang ThanhhAinda não há avaliações
- Eladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel VaultsDocumento18 páginasEladio Dieste's Free-Standing Barrel Vaultssoniamoise100% (1)
- Gild PitchDocumento19 páginasGild PitchtejabharathAinda não há avaliações
- Present Perfect.Documento1 páginaPresent Perfect.Leidy DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Chiller Carrier - 30gn-9siDocumento28 páginasChiller Carrier - 30gn-9siZJ Limited (ZJLimited)Ainda não há avaliações
- Rieka Fitri Sutrisno-CGK-SXBHSY-BTH-FLIGHT - ORIGINATINGDocumento2 páginasRieka Fitri Sutrisno-CGK-SXBHSY-BTH-FLIGHT - ORIGINATINGfairuz fanaAinda não há avaliações
- TD EGGER Eurospan E1E05 TSCA Hydro P3 (Rec 224) enDocumento2 páginasTD EGGER Eurospan E1E05 TSCA Hydro P3 (Rec 224) enClarencegiAinda não há avaliações
- UEME 1143 - Dynamics: AssignmentDocumento4 páginasUEME 1143 - Dynamics: Assignmentshikai towAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 Nutrition Diagnosis Terminologi 2015Documento9 páginas2015 Nutrition Diagnosis Terminologi 2015Vivin Syamsul ArifinAinda não há avaliações
- CONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESDocumento4 páginasCONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESSHIVAM BHATTACHARYAAinda não há avaliações
- COP Grease BrochureDocumento4 páginasCOP Grease Brochured86299878Ainda não há avaliações
- Pirates and Privateers of the Caribbean: A Guide to the GameDocumento25 páginasPirates and Privateers of the Caribbean: A Guide to the GameLunargypsyAinda não há avaliações
- Certification of Psychology Specialists Application Form: Cover PageDocumento3 páginasCertification of Psychology Specialists Application Form: Cover PageJona Mae MetroAinda não há avaliações
- LinkedIn Learning - Workplace Learning Report 2021 EN 1Documento65 páginasLinkedIn Learning - Workplace Learning Report 2021 EN 1Ronald FriasAinda não há avaliações