Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Embedded Sytem Routroy
Enviado por
Kaustuv MishraTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Embedded Sytem Routroy
Enviado por
Kaustuv MishraDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Real
Time Embedded Systems
Module1 . Architecture of Embedded Systems
Unit 1 Concepts and Examples
Unit 2 Reverse Engineering of a Cell Phone
Unit 3 Reverse Engineering of a Digital Camera
Unit 4 Generic Architecture of an Embedded System
Unit 5 Components of Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Concepts and Examples
What makes a Real Time Embedded System ?
What made it possible ?
VLSI
Sensor and Actuator Technology
BaBery Technology
Microwave Devices
What is the future ?
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Embedded Systems at Work
http://www.redsalt.com/service/automotive-systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
A short list of embedded systems
Anti-lock brakes
Auto-focus cameras
Automatic teller machines
Automatic toll systems
Automatic transmission
Avionic systems
Battery chargers
Camcorders
Cell phones
Cell-phone base stations
Cordless phones
Cruise control
Curbside check-in systems
Digital cameras
Disk drives
Electronic card readers
Electronic instruments
Electronic toys/games
Factory control
Fax machines
Fingerprint identifiers
Home security systems
Life-support systems
Medical testing systems
Modems
MPEG decoders
Network cards
Network switches/routers
On-board navigation
Pagers
Photocopiers
Point-of-sale systems
Portable video games
Printers
Satellite phones
Scanners
Smart ovens/dishwashers
Speech recognizers
Stereo systems
Teleconferencing systems
Televisions
Temperature controllers
Theft tracking systems
TV set-top boxes
VCRs, DVD players
Video game consoles
Video phones
Washers and dryers
Real Time Embedded Systems
What is an embedded system and why at all we should
make a disJncJon and hence need a deniJon
A general deniJon of embedded systems is:
embedded systems are compuJng systems
with Jghtly coupled hardware and soMware
integraJon, that are designed to perform a
dedicated funcJon. The word embedded
reects the fact that these systems are usually
an integral part of a larger system, known as
the embedding system. MulJple embedded
systems can coexist in an embedding system.
Real Time Embedded Systems
common characterisJcs of embedded systems
Single-funcJoned
Executes a single program, repeatedly
Tightly-constrained
Low
cost,
low
power,
small,
fast,
etc.
ReacJve and real-Jme
ConJnually reacts to changes in the systems
environment
Must compute certain results in real-Jme without
delay
Real Time Embedded Systems
CharacterisJcs
Dependable
Reliability:
the
probability
that
the
system
would
not
fail
Maintainability:
Probability
that
the
failed
system
can
be
repaired
Availability:
Probability
that
the
system
is
available
Safety:
The
failing
system
will
not
cause
any
harm
Security:
the
property
that
the
condenJal
data
remains
condenJal
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
Real Time Embedded Systems
CharacterisJcs
Ecient
Energy
Code-Size
Run-Time
eciency
Weight
Cost
Dedicated User Interfaces
Ubiquitous CompuJng
Ambient Intelligence
Disappearing Computer
Example ABS systems in automobiles
Real Time Constraints
A guaranteed system response has to be explained without staJsJcal
arguments
Hybrid
Both
Analog
and
Digital
Both
Low
and
High
Frequency
Both
Sensors
and
actuators
Real Time Embedded Systems
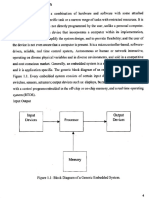
Simplied Design Flow
Real Time Embedded Systems
Design
Technology
The
manner
in
which
we
convert
our
concept
of
desired
system
funcJonality
into
an
implementaJon
Você também pode gostar
- Introduction To Embedded SystemDocumento42 páginasIntroduction To Embedded SystemMohd FahmiAinda não há avaliações
- Presented By: - Tanaya Das - Mca 5 Sem - Roll No - 46Documento15 páginasPresented By: - Tanaya Das - Mca 5 Sem - Roll No - 46Tanaya DasAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded System - Sec1320Documento106 páginasEmbedded System - Sec1320Sharmila chowdary tellaAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems - MSC Sem III (Final)Documento162 páginasEmbedded Systems - MSC Sem III (Final)nAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Emb SystemDocumento95 páginasIntroduction To Emb SystemAyan AcharyaAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 1 Real Tima Embeded System at MwuDocumento23 páginasUNIT 1 Real Tima Embeded System at Mwudine62611Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction Embedded System by Surendra Shrestha Ioenotes PDFDocumento31 páginasChapter 1 Introduction Embedded System by Surendra Shrestha Ioenotes PDFSuman PoudelAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems - MSC Sem IIIDocumento75 páginasEmbedded Systems - MSC Sem IIInAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento16 páginasIntroduction To Embedded SystemsMalieka MuzaffarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Embedded Systems: ObjectivesDocumento39 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Embedded Systems: Objectivessreen67Ainda não há avaliações
- Embedded System Lecture Notes by Prof. Dr. Surendra Shrestha SirDocumento698 páginasEmbedded System Lecture Notes by Prof. Dr. Surendra Shrestha SirAakura Pyakura50% (2)
- 1.embedded Systems Chapter-1Documento29 páginas1.embedded Systems Chapter-1Goitom HaileAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1Documento6 páginasLesson 1OCTAL, Krisia Helena May C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Esd NotesDocumento135 páginasEsd NotesDr D S Naga Malleswara RaoAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Unit-I Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento29 páginas1-Unit-I Introduction To Embedded SystemsNallappan Rajj AAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded SystemDocumento25 páginasEmbedded Systemvidhya seemanAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded System Design: Pavitra Y JDocumento11 páginasEmbedded System Design: Pavitra Y JPranav Sankar MAinda não há avaliações
- Es - Unit 1Documento55 páginasEs - Unit 1Manish SinghalAinda não há avaliações
- System Integration and Hardware Architecture: Dr. Ahmed AL-JanadDocumento17 páginasSystem Integration and Hardware Architecture: Dr. Ahmed AL-JanadSabawoonz fkzAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento9 páginasIntroduction To Embedded SystemsElearning AdminAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems: by Jagadeesh.KDocumento40 páginasEmbedded Systems: by Jagadeesh.Kjagadeeshjack100% (1)
- Embedded Systems: An IntroductionDocumento36 páginasEmbedded Systems: An IntroductionReetika GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Notes Related To CIE-1Documento16 páginasEmbedded Systems Notes Related To CIE-130035ravi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- What's An Embedded System?Documento14 páginasWhat's An Embedded System?Khánh QuốcAinda não há avaliações
- IntroductionDocumento56 páginasIntroductionbrightchanda2002Ainda não há avaliações
- OS Session 4 Embedded OS SlidesDocumento45 páginasOS Session 4 Embedded OS SlidesSHAME BOPEAinda não há avaliações
- ESD-Ch1 2016 PDFDocumento55 páginasESD-Ch1 2016 PDFngoc an nguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 1 IntroductionDocumento67 páginasUnit - 1 IntroductionMurali Dhara Sesha Giri Rao GoddantiAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Design 1Documento50 páginasEmbedded Systems Design 1Asante WilliamAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems - Note - 1Documento29 páginasEmbedded Systems - Note - 1HermanAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems IareDocumento137 páginasEmbedded Systems Iarerocky dAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocumento35 páginas1 Chapter 1 - IntroductionLord JackAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded System Life Cycle, GPIO and Intro To ArduinoDocumento108 páginasEmbedded System Life Cycle, GPIO and Intro To ArduinoavogadroangsterAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento29 páginasChapter 1አምላኬ አባቴAinda não há avaliações
- Embeded Systems: No Name Team: Mai Khắc Nguyên Lê Thị Huyền Nguyễn Văn Nam Cao Anh Dũng Hoàng Thị PhươngDocumento26 páginasEmbeded Systems: No Name Team: Mai Khắc Nguyên Lê Thị Huyền Nguyễn Văn Nam Cao Anh Dũng Hoàng Thị PhươngLê HuyềnAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Embedded Systems ObjectivesDocumento45 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Embedded Systems ObjectivesGurvinder SinghAinda não há avaliações
- ES Unit-1Documento28 páginasES Unit-1palaji pradeepAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems 2023Documento64 páginasEmbedded Systems 2023خالد الغامديAinda não há avaliações
- EE512 EmbeddedSystemAutumn2022Documento53 páginasEE512 EmbeddedSystemAutumn2022DaanyalAinda não há avaliações
- To Embedded Systems Date-10/10/2009: Ravi Kumar A.V Lecturer Electronics and CommunicationDocumento19 páginasTo Embedded Systems Date-10/10/2009: Ravi Kumar A.V Lecturer Electronics and CommunicationDr Ravi Kumar A.VAinda não há avaliações
- New Trends in Embedded SystemsDocumento62 páginasNew Trends in Embedded Systemssheimy20004240Ainda não há avaliações
- Embedded SystemDocumento19 páginasEmbedded SystemMohd SohailAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Overview of Embedded Systems-05!01!2024Documento107 páginas3-Overview of Embedded Systems-05!01!2024kx.graphyAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Notes Parrt 1Documento22 páginasUnit 1 Notes Parrt 1shAinda não há avaliações
- MICROCONTROLLERDocumento141 páginasMICROCONTROLLERKhayrinNajmi100% (3)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Embedded SystemDocumento9 páginasChapter 1 - Introduction To Embedded SystemStephanie CalabungAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Communication Engineering Focus Area Course Code-Eceg4202Documento20 páginasEmbedded Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Communication Engineering Focus Area Course Code-Eceg4202yacob JacobAinda não há avaliações
- Prof. Santanu Chaudhury Prof. Wajeb GharibiDocumento39 páginasProf. Santanu Chaudhury Prof. Wajeb GharibiRajeev RawalAinda não há avaliações
- Topic: Course Name: Embedded System Design With ARMDocumento12 páginasTopic: Course Name: Embedded System Design With ARMArun AvAinda não há avaliações
- Typical Embedded SystemDocumento18 páginasTypical Embedded SystemMohanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3Documento48 páginasUnit 3Sultan BepariAinda não há avaliações
- Designed To Perform A Specific FunctionDocumento18 páginasDesigned To Perform A Specific FunctionSayeda Asma NoorAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded 1Documento109 páginasEmbedded 1SHUBHANKAR SONIAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded SystemsDocumento65 páginasEmbedded SystemsDebesh ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento27 páginas01 Introduction To Embedded SystemsPriscillaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1Documento20 páginasModule 1pranavAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Lecture 1Documento23 páginasEmbedded Systems Lecture 1Nebiyu TakeleAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento6 páginasIntroduction To Embedded Systemsరమణ రాజుAinda não há avaliações
- BEE 027 Microcontroller Based System DesignDocumento83 páginasBEE 027 Microcontroller Based System DesignBen StarkAinda não há avaliações
- Open-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsNo EverandOpen-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Tool Video 04Documento20 páginasTool Video 04Kaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Ad 5933Documento2 páginasAd 5933Kaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- MakingDocumento1 páginaMakingKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Tool Video 02 AnnotationDocumento33 páginasTool Video 02 AnnotationKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- How To Make A Powerpoint Presentation and How Not To: Amit Patra Department of Electrical Engineering IIT KharagpurDocumento4 páginasHow To Make A Powerpoint Presentation and How Not To: Amit Patra Department of Electrical Engineering IIT KharagpurKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- How To Make A Powerpoint Presentation and How Not To: Amit Patra Department of Electrical Engineering IIT KharagpurDocumento4 páginasHow To Make A Powerpoint Presentation and How Not To: Amit Patra Department of Electrical Engineering IIT KharagpurKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- HM6264Documento10 páginasHM6264Kaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Traction TransformersDocumento4 páginasTraction TransformersKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Digital CameraDocumento23 páginasDigital CameraKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- BARC 2010 ElectronicsDocumento3 páginasBARC 2010 ElectronicsKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Optimal Reception of Digital SignalsDocumento40 páginasOptimal Reception of Digital SignalsKaustuv Mishra100% (1)
- BARC 2010 ElectronicsDocumento3 páginasBARC 2010 ElectronicsKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- AntennaDocumento4 páginasAntennaKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Sun TrackerDocumento6 páginasSun TrackerKaustuv MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear AlgebraDocumento3 páginasSyllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebraapi-273759951Ainda não há avaliações
- Best Energy Management: For HVACDocumento10 páginasBest Energy Management: For HVACMarc Emil CasilaoAinda não há avaliações
- A 71 Samsung Electrical Part ListDocumento12 páginasA 71 Samsung Electrical Part ListIsabel GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- LSQ5 Man-0964 V3.1.0 enDocumento48 páginasLSQ5 Man-0964 V3.1.0 enDiego Mondragon100% (1)
- Saep 350 PDFDocumento15 páginasSaep 350 PDFRami Elloumi100% (1)
- Handouts EIM. SS1 Week 2Documento4 páginasHandouts EIM. SS1 Week 2myco sauraAinda não há avaliações
- Siemens: Programming GuideDocumento459 páginasSiemens: Programming Guideplantaolaminado07Ainda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting StabilityDocumento8 páginasFactors Affecting StabilitySteve MusarurwaAinda não há avaliações
- Input Impedance Modeling and Analysis of Line-Commutated RectifiersDocumento9 páginasInput Impedance Modeling and Analysis of Line-Commutated RectifiersWaqar QuredhiAinda não há avaliações
- Stealth Antennas PDFDocumento18 páginasStealth Antennas PDFJesus M. Espinosa Echavarria100% (1)
- On Line Ups 6-10kva User ManualDocumento32 páginasOn Line Ups 6-10kva User ManualADY Resources100% (1)
- Modi Con 512Documento60 páginasModi Con 512Time To Use BrainAinda não há avaliações
- 10 - Operating Instruction - DSC... - CAN Bus, Serial Bus - BEA - 209283-En-03Documento8 páginas10 - Operating Instruction - DSC... - CAN Bus, Serial Bus - BEA - 209283-En-03jose mondacaAinda não há avaliações
- Slva 714 DDocumento24 páginasSlva 714 DMarcio WjbAinda não há avaliações
- TPG 3 (Stringset)Documento4 páginasTPG 3 (Stringset)rostyo tioAinda não há avaliações
- 09072310301310Documento18 páginas09072310301310Walker BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Building A Phase ConverterDocumento11 páginasBuilding A Phase ConverterAlvaro Del Cid100% (1)
- Single-Chip IC: For Home Stereo IC With Electronic Tuning SupportDocumento9 páginasSingle-Chip IC: For Home Stereo IC With Electronic Tuning SupportVicenteAlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Iec 62109-2Documento16 páginasIec 62109-2Rohit Mittal33% (6)
- HT 306PD (sm-AFN75354522)Documento65 páginasHT 306PD (sm-AFN75354522)Roberd MihailovAinda não há avaliações
- Logic Circuit & Switching Theory Pre - Final Quiz 1Documento14 páginasLogic Circuit & Switching Theory Pre - Final Quiz 1Russel Mendoza100% (1)
- Sound Into ElctricityDocumento12 páginasSound Into ElctricityRitam ChandAinda não há avaliações
- Cylon KNX GatewayDocumento4 páginasCylon KNX GatewayJulián HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Shake Table II User ManualDocumento36 páginasShake Table II User ManualMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Selection Guide CamarasDocumento12 páginasSelection Guide CamarasServando Roman EstradeAinda não há avaliações
- OTDR TRAINING 83 SlideDocumento83 páginasOTDR TRAINING 83 SlideFerry Kurniawan80% (5)
- Fusibles HH de ETIDocumento9 páginasFusibles HH de ETIYben ZutaAinda não há avaliações
- SAGEM Link F User GuideDocumento123 páginasSAGEM Link F User Guidemsplm28100% (2)
- Basic Electrical Characteristics and Application Designs of Low-I PhotocouplersDocumento31 páginasBasic Electrical Characteristics and Application Designs of Low-I PhotocouplersWagner MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Ee321 ObjectivesDocumento3 páginasEe321 ObjectivesJomar DadorAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Metal DetectionDocumento36 páginasBasic Metal DetectionAnthony ProdeniantaAinda não há avaliações