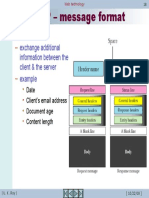
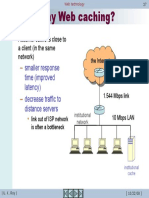
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
How To Set Performance Options in Windows XP
Enviado por
iwc2008007Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
How To Set Performance Options in Windows XP
Enviado por
iwc2008007Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
How to set performance options in Windows XP
Skip Navigation
Support
By product
Downloads
Store
Contact us
How to set performance options in Windows XP
Print
Email
Article translations
Support for Windows XP has ended
Microsoft ended support for Windows XP on April 8, 2014. This change has affected your
software updates and security options.
Learn what this means for you and how to stay protected.
Article ID: 308417 - View products that this article applies to.
System Tip
This article applies to a different version of Windows than the one you are using. Content in this article may not be relevant to you.
Visit the Windows 7 Solution Center
This article was previously published under Q308417
Expand all | Collapse all
On This Page
INTRODUCTION
Windows allocates resources according to its settings and manages devices and programs accordingly. However, you can use the
System item in Control Panel to change these performance options and how Windows manages them.
This article describes how to set the performance options for your computer by downloading and using Guided Help, or by using
manual steps.
Back to the top | Give Feedback
More information
Guided Help to set performance options in Windows XP
Guided Help files are unique programs that help you perform some common tasks in Windows XP. Guided Help is available
to set performance options in Windows XP. Guided Help can guide you through the steps or can automatically perform the
steps for you.
The actions that this Guided Help performs can be undone if it is necessary. To undo the actions that this Guided Help
performs, run this Guided Help again, and then select your previous performance settings.
For more information about Guided Help, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
915092 Description of Guided Help for Microsoft Knowledge Base articles
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/308417[30-Jun-15 8:18:30 AM]
Sign in
How to set performance options in Windows XP
Requirements to install and to use this Guided Help
You must be logged on to Windows by using a computer administrator account to install and to use this Guided Help.
You must be running Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, Windows XP Media Center Edition, or Windows
XP Tablet PC Edition to install and to use this Guided Help.
You must first download the Guided Help file, and then double-click the file to run it. After you start Guided Help, follow the stepby-step instructions. To download this Guided Help, click the following link:
Download Guided Help
If you cannot download or install Guided Help you can follow the manual steps in this article.
Manual steps to set performance options in Windows XP
If you would rather not install and run Guided Help, you can set performance options in Windows XP manually.
This section is intended for advanced computer users. If you are not comfortable with advanced instructions, you might want to
contact Support. For information about how to do this, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus
Note You must be logged on to Windows by using a computer administrator account in order to set many of these performance
options. To verify that you are logged on to Windows with a user account that is a computer administrator, visit the following
Microsoft Web site:
http://support.microsoft.com/gp/admin
To manually set performance options for your computer, follow these steps:
Step 1: Manually manage processor scheduling
There are a finite number of resources that are available for a computer's CPU. Windows manages these resources automatically, and
can allocate tasks between processors or manage multiple processes on a single processor. You can adjust how Windows manages
these resources by prioritizing them between the foreground programs and the background services.
By default, Windows puts a priority on the foreground programs. The added processing resources cause programs to respond more
quickly. However, if you have background services, such as printing or disk backup that run while you work and you want them to
respond faster, you can have Windows share processor resources equally between background and foreground programs.
Note If you are using your Windows XP computer as a server, allocating more resources to background services is recommended.
To manually change the performance of foreground and background programs, complete these steps:
1. Click Start, click Run, type sysdm.cpl in the Open box, and then press ENTER to open the System Properties dialog box.
2. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Performance click Settings.
3. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Processor scheduling use one of the following methods:
Click Programs to assign more processor resources to the foreground programs. This setting is recommended for most
users.
Click Background services to assign equal amounts of processor resources to all running services. This includes print
jobs and applications.
4. Click OK to apply preferences and close the dialog box.
Step 2: Manually manage computer memory
When your computer's physically installed random-access memory (RAM) is running low, Windows adds available memory by using a
paging file, generally known as virtual memory, on the hard disk to simulate physical RAM. By default, the virtual memory paging file
that is created during installation is 1.5 times the physical RAM on your computer. Therefore, a computer that has 1GB of installed
RAM will have 1.5GB of virtual memory.
You can manually change the size of the paging file to make it larger or smaller. You can also optimize virtual memory use by
dividing the file space between multiple drives and by removing allocated space from slow or heavily accessed drives. To optimize
your virtual memory space, divide it among as many physical hard drives as possible. When you select drives, follow these guidelines:
Try to avoid having a paging file on the same drive as the system files, usually drive C.
Avoid putting a paging file on a fault-tolerant drive such as a mirrored volume or a RAID-5 volume. Paging files do not
require fault tolerance, and some fault-tolerant computers experience slow data writes because they write data to multiple
locations.
Do not put multiple paging files on different partitions on the same physical disk drive.
How to manually change the size of the virtual memory paging file
You must be logged on as an administrator or as a member of the administrators group to complete this procedure. If your
computer is connected to a network, network policy settings may prevent you from completing this procedure.
To manually change the size of virtual memory, follow these steps:
1. Click Start, click Run, type sysdm.cpl in the Open box, and then press ENTER.
2. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Performance click Settings.
3. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Virtual memory click Change.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/308417[30-Jun-15 8:18:30 AM]
How to set performance options in Windows XP
4. Under Drive [Volume Label], click the drive that contains the paging file that you want to change.
5. Under Paging file size for selected drive, click Custom size, type a new paging file size in megabytes (MB) in the Initial
size (MB) or Maximum size (MB) box, and then click Set.
6. Click OK to close the dialog box and apply changes.
Note After you change the size of the paging file, you may be prompted to restart Windows. If you are prompted to restart, the
changes will not take effect until Windows is restarted.
Notes
To have Windows select the best paging file size, click System managed size. The recommended minimum size is the same
as 1.5 times the RAM on your computer, and 3 times that figure for the maximum size. For example, if you have 256 MB of
RAM, the minimum size is 384 MB, and the maximum size is 1152 MB.
For best performance, do not set the initial size to less than the minimum recommended size under Total paging file size
for all drives. The recommended size is the same as 1.5 times the RAM on your computer. It is good practice to leave the
paging file at its recommended size as performance can decrease if a paging file is too large. However, you may increase its
size if you frequently use programs that use lots of memory, such as graphics programs or games.
We strongly recommend that you do not disable or delete the paging file because this can lessen the computer's
performance. However, if you decide to delete a paging file, set both the initial size and the maximum size to zero, or click
No paging file.
How to manually optimize the memory usage
You can optimize your computer's memory usage to reflect your specific needs. If your computer is used as a workstation instead of
as a server, you can increase performance by devoting more memory to your programs. Your programs will work faster and the
system cache size will remain the default size that was included with Windows XP. Or, you can set aside more computer memory for
a larger system cache if your computer is used primarily as a server, or if you use programs that require a large system cache.
1. Click Start, click Run, type sysdm.cpl in the Open box, and then press ENTER.
2. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Performance click Settings.
3. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Memory usage use one of the following methods:
Click Programs if you use your computer primarily as a workstation instead of as a server. This option allocates more
memory to your programs.
Click System cache if your computer is used primarily as a server or if you use programs that use a large system
cache.
4. Click OK to save preferences and close the dialog box.
Step 3: Manually change the visual effects
Windows provides several options to set the visual effects of your computer. For example, you can show shadows under menus or
you can configure Windows to display all the contents of a window while you move the window on your screen.
Note Although many of the visual effects can make computer use more enjoyable by offering a more attractive interface, they can
slow down your computer.
Windows provides options to turn on all visual effects options, turn off all options, or automate them. You can also restore the
default settings or set your own custom options by selecting for yourself what visual effects that you want to use.
To change the visual effects, follow these steps:
1. Click Start, click Run, type sysdm.cpl in the Open box, and then press ENTER.
2. Click the Advanced tab, and then under Performance click Settings.
3. Click the Visual Effects tab, and then use one of the following methods:
Click Let Windows choose what's best for my computer to have Windows select the visual effects.
Click Adjust for best appearance to have Windows automatically adjust the settings for best appearance.
Click Adjust for best performance to have Windows automatically adjust the settings for best performance.
Click Custom, and then select the check boxes for those items that you want to turn on. Clear the check boxes for the
items that you want to turn off.
4. Click OK to apply changes and to close the dialog box.
Note Regardless of which visual effects option you select, you can always customize the setting by individually selecting or clearing
items listed. If you change any item, the Custom button will automatically be selected.
Glossary
background program A background program is a program that runs while the user is working on another task. The computer's
microprocessor assigns fewer resources to background programs than to foreground programs.
environment variable An environment variable is a string of environment information such as a drive, path, or file name that is
associated with a symbolic name that Windows can use. You use System in Control Panel or the set command at the command
prompt to define environment variables.
foreground program A foreground program is a program that runs in the active window (the upper-most window with the
highlighted title bar). The foreground program responds to commands that the user issues.
mirrored volume A mirrored volume is a fault-tolerant volume that duplicates data on two physical disks. A mirrored volume
provides data redundancy by using two identical volumes. These volumes are known as mirrors. They duplicate the information that
the volume contains. A mirror is always located on a different disk. If one of the physical disks fails, the data on the failed disk
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/308417[30-Jun-15 8:18:30 AM]
How to set performance options in Windows XP
becomes unavailable, but the system continues to operate in the mirror on the remaining disk. You can create mirrored volumes only
on dynamic disks.
paging file Generally known as "virtual memory", a paging file is a section of a hard disk that is created in order to extend available
memory. When Windows runs low on physical memory (RAM) that is installed, the paging file will be used as "virtual" memory. By
default, Windows transfers data for background services and idle programs to this paging file in order to free more RAM for
programs that are currently being used.
partition A partition is part of a physical disk that functions as if it were a physically separate disk. After you create a partition, you
must format it and assign it a drive letter before you can store data on it. On basic disks, partitions are known as basic volumes. Basic
volumes include primary partitions and logical drives. On dynamic disks, partitions are known as dynamic volumes. Dynamic volumes
include simple, striped, spanned, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
RAID-5 volume A RAID-5 volume is a fault-tolerant volume with data and parity striped intermittently across three or more physical
disks. Parity is a calculated value that is used to reconstruct data after a failure. If a part of a physical disk fails, Windows recreates the
data that was on the failed part from the remaining data and parity. You can create RAID-5 volumes only on dynamic disks, and you
cannot mirror or extend RAID-5 volumes.
Back to the top | Give Feedback
NEXT STEPS
If these methods did not work for you, you can use the Microsoft Customer Support Services Web site to find other solutions to your
problem. Some services that the Microsoft Customer Support Services Web sites provide include the following:
Searchable Knowledge Base: Search technical support information and self-help tools for Microsoft products.
Solution Centers: View product-specific frequently asked questions and support highlights.
Other Support Options: Use the Web to ask a question, contact Microsoft Customer Support Services, or provide feedback.
If you need more help setting performance options in Windows XP, you might want to contact Support:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus
For help with system performance issues in Windows Vista, visit the following Microsoft web page:
Problems with overall system speed and system performance
Back to the top | Give Feedback
References
For more information about how to move the paging file, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft
Knowledge Base:
307886 How to move the paging file in Windows XP
Back to the top | Give Feedback
Properties
Article ID: 308417 - Last Review: June 22, 2013 - Revision: 12.0
Applies to
Microsoft Windows XP Professional
Keywords:kbhowto kbacwsurvey kbvirtualmem kbenv KB308417
Back to the top | Give Feedback
Give Feedback
Was this information helpful?
Yes
No
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/308417[30-Jun-15 8:18:30 AM]
How to set performance options in Windows XP
Somewhat
How much effort did you personally put forth to use this article?
Very low
Low
Moderate
High
Very high
Tell us what we can do to improve this article
Submit
Back to the top
Other Microsoft sites
Windows
Office
Surface
Windows Phone
Mobile devices
Xbox
Skype
MSN
Downloads
Support
Popular resources
Download center
Supported Products list
Windows keyboard shortcuts
Windows downloads
Product support lifecycle
Microsoft Visual C library runtime error
Office downloads
Small and medium business support
Service Pack downloads
IT Pro support
Windows Installer error: service could not be
accessed
Direct X download
Developer support
Security
About Microsoft
Virus and Security solution center
Microsoft
Security home page
Careers
Microsoft Update
Company news
Download Security Essentials
Investor relations
Malware Removal tool
Site map
How to: Windows XP system restore
Windows update error message
Microsoft Security Essentials manual update
download
Inbox Scanpst.exe
Privacy questions
Bing
Microsoft Store
United States
Contact Us
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/308417[30-Jun-15 8:18:30 AM]
Terms of Use
Trademarks
Privacy & Cookies
About our ads
2015 Copyright
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Activation Windows 10 Et Office 2013Documento3 páginasActivation Windows 10 Et Office 2013pol polAinda não há avaliações
- Ms Excel PPT For Sept 18 2023Documento14 páginasMs Excel PPT For Sept 18 2023Leewhy Macatimpag100% (5)
- Install FireWorks v8.1 on Win10Documento2 páginasInstall FireWorks v8.1 on Win10RaviAinda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 6-HyperText Transfer ProtocolDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 6-HyperText Transfer Protocoliwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 5-The Web: Some JargonDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 5-The Web: Some Jargoniwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 7-URLDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 7-URLiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 4-World Wide Web-A Repository of InformationDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 4-World Wide Web-A Repository of Informationiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 9-HTTP - ExampleDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 9-HTTP - Exampleiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 15-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 15-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 11-HTTP Protocol - Message FormatDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 11-HTTP Protocol - Message Formatiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 10-HTTP - Example (CNT'D)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 10-HTTP - Example (CNT'D)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 16-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 16-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 8-URL - ContinuedDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 8-URL - Continuediwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 14-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 14-HTTP - Message Format (Status Code)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 13-HTTP - Message FormatDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 13-HTTP - Message Formatiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 18-HTTP - Message FormatDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 18-HTTP - Message Formatiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 22-HTTP - Message Format (Entity Header)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 22-HTTP - Message Format (Entity Header)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 20-HTTP - Message Format (Request Header)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 20-HTTP - Message Format (Request Header)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 21-HTTP - Message Format (Response Header)Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 21-HTTP - Message Format (Response Header)iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 27 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 27 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 19-HTTP - Message FormatDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 19-HTTP - Message Formatiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 26-Web Caches - ProxyDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 26-Web Caches - Proxyiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 24-HTTP Messages - An ExampleDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 24-HTTP Messages - An Exampleiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 4 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 4 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 26 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 26 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 25-Persistent and Nonpersistent ConnectionsDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 25-Persistent and Nonpersistent Connectionsiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 27 Why Web Caching?Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 27 Why Web Caching?iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 28 Consistency of Web CachingDocumento1 páginaWeb Technology 28 Consistency of Web Cachingiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web Technology 27 Why Web Caching?Documento1 páginaWeb Technology 27 Why Web Caching?iwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 23 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 23 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 22 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 22 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- Web-Technology 24 PDFDocumento1 páginaWeb-Technology 24 PDFiwc2008007Ainda não há avaliações
- EXNO10-Writes Data To The SD CardDocumento7 páginasEXNO10-Writes Data To The SD CardPriyadarshiniAinda não há avaliações
- Mqrzgmvy Solid Works KnjigaDocumento5 páginasMqrzgmvy Solid Works Knjigafiatbrava1551Ainda não há avaliações
- Windows 8 and 8.1 product keysDocumento2 páginasWindows 8 and 8.1 product keysAtnoz Jilid IIAinda não há avaliações
- Genuine Microsoft KeysDocumento5 páginasGenuine Microsoft Keysguttapavan2067100% (1)
- Gshultz DR Robocopy 10-29Documento3 páginasGshultz DR Robocopy 10-29erroneousashesAinda não há avaliações
- How To Check Windows 10 Computer System Specs & Requirements - Microsoft PDFDocumento8 páginasHow To Check Windows 10 Computer System Specs & Requirements - Microsoft PDFBilal AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Remove Win 10 Update IconDocumento19 páginasRemove Win 10 Update Iconvon.nebullaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Install Anbox On Debian: Core InstallationDocumento6 páginasHow To Install Anbox On Debian: Core Installationprasanth c41mAinda não há avaliações
- LS Deploy ADPrepDocumento87 páginasLS Deploy ADPrepShripal JainAinda não há avaliações
- Mainactivity JavaDocumento4 páginasMainactivity JavaAisya ZuhudiAinda não há avaliações
- Net FX Setup EventsDocumento1 páginaNet FX Setup EventsManuel Lorenzo Sarmiento toledoAinda não há avaliações
- Obtain WHQL Driver Package Certification with DUA SubmissionDocumento2 páginasObtain WHQL Driver Package Certification with DUA SubmissionDavid QuelhasAinda não há avaliações
- Maximum Partition Size Using FAT16 File SystemDocumento9 páginasMaximum Partition Size Using FAT16 File SystemShivakumar S KadakalAinda não há avaliações
- CNAV-MAN-013.4 (C-Setup Quick Start Guide)Documento13 páginasCNAV-MAN-013.4 (C-Setup Quick Start Guide)Jose CasasAinda não há avaliações
- Install Windows 10 Apps To An External Hard DiskDocumento8 páginasInstall Windows 10 Apps To An External Hard DiskNimish MadananAinda não há avaliações
- Toolkit ReferenceDocumento465 páginasToolkit ReferencezahirhussianAinda não há avaliações
- Install and Use ERMaster with Eclipse IDEDocumento15 páginasInstall and Use ERMaster with Eclipse IDEYe Yint AungAinda não há avaliações
- Mod Menu Log - Com - Ea.game - nfs14 - RowDocumento22 páginasMod Menu Log - Com - Ea.game - nfs14 - RowMEMES ChwieyaAinda não há avaliações
- EzCoding Manual Rev1.01Documento6 páginasEzCoding Manual Rev1.01Huy DoanAinda não há avaliações
- Install VS Code, Grab The Extensions, Issue A Command. Oh It's On!Documento3 páginasInstall VS Code, Grab The Extensions, Issue A Command. Oh It's On!MarijaAinda não há avaliações
- WPI LogDocumento5 páginasWPI LogMarcos Josef Chuquimia CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- CSC6402CT-Linux Programming HistoryDocumento19 páginasCSC6402CT-Linux Programming HistoryMithu gopiAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento15 páginasUntitledHiuman JuegosAinda não há avaliações
- RuN CMDDocumento3 páginasRuN CMDapi-26257902Ainda não há avaliações
- Windows 10 Update Stuck at Preparing To InstallDocumento3 páginasWindows 10 Update Stuck at Preparing To Installpgpm20 SANCHIT GARGAinda não há avaliações
- XMeye User Manual For IphoneDocumento5 páginasXMeye User Manual For Iphonerosemberg_trujilloAinda não há avaliações
- Release Notes For Acronis True Image WD Edition: System RequirementsDocumento19 páginasRelease Notes For Acronis True Image WD Edition: System RequirementsRpya YarpAinda não há avaliações