Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Notes On Static and Dynamic Friction
Enviado por
drhillDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes On Static and Dynamic Friction
Enviado por
drhillDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes on Static and Dynamic Friction
Friction is a force between two surfaces that resists motion and the
force that creates motion
Friction is caused by mechanical contact between rough surfaces, the
surfaces locking together requiring the side force to lift the surfaces
apart. It is also caused by temporary chemical bonds.
In a situation of sliding, or skidding these bonds do not get a chance to
form and the surfaces are springing apart. This Dynamic friction is
lower and less powerful than the static.
A cars antilock braking system detects when the wheel has stopped
rolling and the wheels are using dynamic friction. The force is lower, so
the car looses it energy over a greater distance. To avoid this the cars
computer actually overrides the drive releasing the brake and
increasing the stopping force.
Wheels are machines that overcome the friction between surfaces.
The understanding of the wheel is only taught indirectly in the HSC
course, in the form of pulleys and cars that move around corners.
The wheels rotate with respect to the vehicle so that the point of
contact with the road is stationary, the axle is moving at the speed of
the car but the top is moving at twice the velocity. Friction is basically
eliminated by ball bearings that roll rather than slip. If they slipped they
would use energy
Energy = F x d
The ball bearings roll and have their surface stationary on the inner
and outer "race". Thus the modern wheel is infact a circular railway
track with the ball bearings acting at the train.
When a car comes to rest using its brakes it is applying a force over a
distance (doing work) to lower its Kinetic Energy. Newton developed both
these ideas from his second law.
Newton second law states that "a body that has an unbalanced external
force acting on it will accelerate in the direction of that force, and
accelerate inversely proportional to the mass"
A rigid body is a mathematical idea of an object that can not deform. It is
drawn in outline with a central point marked at its COM.
Mathematically N2 is
Unfiled Notes Page 1
Mathematically N2 is
(The net force is found by adding vectors the tail of the next vector is
placed at the head of the vector before )
If you multiply both sides of N2 by d you get
Fxd=mxaxd
Now F x d is defined by Newton as energy (10 N x 2 m = 20 J or 20 Nm)
Now this equals m x a x d
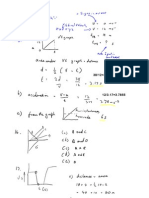
From velocity verses time diagrams a = (v-u) / t
Also vaverage = (v+u)/2 and therefore d = (v+u)/2xt
Therefore
M x a x d = m x (v-u)/t x (v+u)/2 x t The time cancels to give
= 1/2 m (v-u)x (v+u)
Newton then defined moving Energy or kinetic energy Ek = 1/2mv 2
Prac
You can measure friction force by working out the resultant force on an
Inclined plane
Friction = W sin (theta)
Friction is always parallel to the surface 90 deg
to N
Unfiled Notes Page 2
Você também pode gostar
- Rough - The Stress Material and Physical Properties of Car Bodies in Engineering With Analysis of Crumple Zones Isolated Systems Safety Mechanisms Photo-Elasticity Collisions and Drag ForceDocumento34 páginasRough - The Stress Material and Physical Properties of Car Bodies in Engineering With Analysis of Crumple Zones Isolated Systems Safety Mechanisms Photo-Elasticity Collisions and Drag Forceapi-244817040Ainda não há avaliações
- 5.laws of MotionDocumento16 páginas5.laws of Motionmonu991Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is Friction?Documento5 páginasWhat Is Friction?Hallette TampocAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionDocumento19 páginasLinear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionrezaewewqewqeAinda não há avaliações
- Motion and Dynamics: 3.1 Making Sense of Dynamic EquilibriumDocumento6 páginasMotion and Dynamics: 3.1 Making Sense of Dynamic EquilibriumnasirfahimAinda não há avaliações
- Jca DynamicsDocumento16 páginasJca DynamicsDanica DevezaAinda não há avaliações
- Robot Drivetrain Design PrinciplesDocumento22 páginasRobot Drivetrain Design PrinciplesTaufik RhomeAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetics of Particles: Forces, Motion and EquationsDocumento29 páginasKinetics of Particles: Forces, Motion and EquationsIjal Haizal100% (1)
- Frictional Forces..or Lack ThereofDocumento43 páginasFrictional Forces..or Lack ThereofNuri GracioAinda não há avaliações
- FrictionDocumento43 páginasFrictionEduardo BasonAinda não há avaliações
- Static & Kinetic FrictionDocumento4 páginasStatic & Kinetic FrictionLogesh BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Work Done by A Frictional Force: Name(s)Documento7 páginasWork Done by A Frictional Force: Name(s)Estefania Delgado ArdilaAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Forces Worksheet 1 PhysicsDocumento11 páginasSolutions To Forces Worksheet 1 PhysicsLixAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws ApplicationsDocumento44 páginasNewton's Laws ApplicationssamAinda não há avaliações
- Useful Tables Fatigue Mechanics ImpactDocumento9 páginasUseful Tables Fatigue Mechanics ImpactroladinAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 1Documento10 páginasPhysics 1SIBTE 999 [Legit Slayer FF]Ainda não há avaliações
- Sdof VibrationDocumento59 páginasSdof Vibrationevo2005_2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Car PhysicsDocumento27 páginasCar PhysicsHarikrishnan Rajendran0% (1)
- Impulse and MomentumDocumento31 páginasImpulse and MomentumFrancisQuiwaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Compute Impact ForceDocumento15 páginasHow To Compute Impact ForceMary Antoinette C. MadoloraAinda não há avaliações
- Roll Number 124Documento6 páginasRoll Number 124ahmadrafaqat351Ainda não há avaliações
- Static and Kinetic FrictionDocumento20 páginasStatic and Kinetic FrictionIan Gabriel Gatdula MoraAinda não há avaliações
- Sdoc 02 09 SiDocumento6 páginasSdoc 02 09 Siahmadrafaqat351Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine Elements: Friction and ClutchesDocumento19 páginasMachine Elements: Friction and ClutchesRamanathan DuraiAinda não há avaliações
- Crammer Powerpoint p2Documento43 páginasCrammer Powerpoint p2Mrs S BakerAinda não há avaliações
- Physics CompilationsDocumento117 páginasPhysics CompilationsRenard Vince MalunesAinda não há avaliações
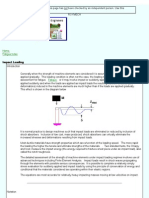
- Impact of Load on StructuresDocumento11 páginasImpact of Load on StructuresMamoon RashidAinda não há avaliações
- Find Coefficient of Kinetic Friction for Metallic WheelsDocumento6 páginasFind Coefficient of Kinetic Friction for Metallic WheelsUsamaIjazAinda não há avaliações
- 123Documento16 páginas123Jj MontillaAinda não há avaliações
- Car PhysicsDocumento24 páginasCar PhysicsVipulAinda não há avaliações
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocumento55 páginasRigid Body DynamicsKenn ConsueloAinda não há avaliações
- EUI - Static and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction ExperimentDocumento22 páginasEUI - Static and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction ExperimentMohammed ZaitounAinda não há avaliações
- Newton S Laws Force Friction 291Documento20 páginasNewton S Laws Force Friction 291Shorya KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Force and Motion IIDocumento10 páginasForce and Motion IIShubham ParabAinda não há avaliações
- Last Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014Documento13 páginasLast Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014YuChenQianAinda não há avaliações
- Friction Problems PDFDocumento21 páginasFriction Problems PDFMaicol Nelson Polo MauricioAinda não há avaliações
- CLUTCHDocumento48 páginasCLUTCHhaymanotAinda não há avaliações
- Mech 351 Fnal LectureDocumento17 páginasMech 351 Fnal LectureNoel Christian FabregarAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 15Documento6 páginasNotes 15BoyntonhighAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Unit 2 AssignmentDocumento11 páginasPhysics Unit 2 AssignmentJadeAinda não há avaliações
- CH 10Documento29 páginasCH 10Ardian20Ainda não há avaliações
- BS Physics 1 Fundamentals of Mechanics: The Banked CurveDocumento1 páginaBS Physics 1 Fundamentals of Mechanics: The Banked CurveRana SamiAinda não há avaliações
- Spring 2001 Physics 2048 Test 3 Solutions: Problem 1. (Short Answer: 15 Points)Documento5 páginasSpring 2001 Physics 2048 Test 3 Solutions: Problem 1. (Short Answer: 15 Points)yanzcomey comeyAinda não há avaliações
- 3 FrictionDocumento8 páginas3 Frictionthinkiit100% (2)
- Additional Applications of Newton's Laws ChapterDocumento152 páginasAdditional Applications of Newton's Laws ChaptergeovanniAinda não há avaliações
- 362145ijsetr1436 385Documento4 páginas362145ijsetr1436 385EuniceEspinosaAinda não há avaliações
- Accident Studies: Partha Partim Dey IIT BhubaneswarDocumento33 páginasAccident Studies: Partha Partim Dey IIT Bhubaneswarsandeep kumarAinda não há avaliações
- VCEPhysics 2000 Unit 4 SolutionsDocumento3 páginasVCEPhysics 2000 Unit 4 Solutionsthe_perfectionistAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Test-3-Laws of Motion-Circular MotionDocumento14 páginasPractice Test-3-Laws of Motion-Circular MotionLynn Hollenbeck BreindelAinda não há avaliações
- How To Calculate The Force of A Falling ObjectDocumento8 páginasHow To Calculate The Force of A Falling ObjectbootkuAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugal ForceDocumento9 páginasCentrifugal ForcecataiceAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS 201 - Impulse and MomentumDocumento14 páginasPHYS 201 - Impulse and MomentumSamuel CaoAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics of Machinery 2 Marks PDFDocumento14 páginasDynamics of Machinery 2 Marks PDFThilli KaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter ThreeDocumento40 páginasChapter ThreehaymanotAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Notes - Section 11 Engineering Physics - AQA Physics A-Level56758747Documento23 páginasDetailed Notes - Section 11 Engineering Physics - AQA Physics A-Level56758747Marcos MansoAinda não há avaliações
- Vehicle Dynamics For Racing GamesDocumento18 páginasVehicle Dynamics For Racing GameskrishnasrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Ideas To ImplementationDocumento44 páginasIdeas To ImplementationdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- HSC Knowledge QuizDocumento2 páginasHSC Knowledge QuizdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- Faraday ScenarioesDocumento3 páginasFaraday ScenarioesdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- HSC Homework: Sunday, 7 February 2010 10:22 PMDocumento7 páginasHSC Homework: Sunday, 7 February 2010 10:22 PMdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- Eddy C LQ 2001Documento1 páginaEddy C LQ 2001drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Motor Prac + HomeworkDocumento29 páginasMotor Prac + HomeworkdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- Eddy Current Question 2001Documento1 páginaEddy Current Question 2001drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Notes For 2008Documento5 páginasRevision Notes For 2008drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Jacaranda Q22Documento3 páginasJacaranda Q22drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Guide For EnergyDocumento1 páginaGuide For EnergydrhillAinda não há avaliações
- Year 11 HomeworkDocumento3 páginasYear 11 HomeworkdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- Jacaranda Homework: Unfiled Notes Page 1Documento4 páginasJacaranda Homework: Unfiled Notes Page 1drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Year 11 Prac 3 +Documento27 páginasYear 11 Prac 3 +drhillAinda não há avaliações
- HSC Homework: Sunday, 7 February 2010 10:22 PMDocumento7 páginasHSC Homework: Sunday, 7 February 2010 10:22 PMdrhillAinda não há avaliações
- HSC Homework Wrap Up Jacaranda Q8: Unfiled Notes Page 1Documento4 páginasHSC Homework Wrap Up Jacaranda Q8: Unfiled Notes Page 1drhillAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Inverse Proportion Worksheet G8Documento2 páginasDirect and Inverse Proportion Worksheet G8Simrah shaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two Class 9thDocumento18 páginasChapter Two Class 9thAliAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Units and MeasurementDocumento9 páginasMCQ Units and MeasurementShreya Chakroverty ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- PSGDocumento6 páginasPSGsenthilkumarAinda não há avaliações
- EE340 IITK Assignments 2012Documento2 páginasEE340 IITK Assignments 2012Debdeep SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Definition by Vasumitra GajbhiyeDocumento3 páginasPhysics Definition by Vasumitra GajbhiyeHuzaifa ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Documento69 páginasPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
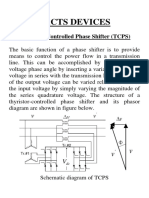
- Control Power Flow Using FACTS DevicesDocumento8 páginasControl Power Flow Using FACTS DeviceskhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Low Voltage-380vacDocumento1 páginaLow Voltage-380vacTantely RazafimahatratraAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogue Samwha CapacitorDocumento68 páginasCatalogue Samwha CapacitorAnu MaliAinda não há avaliações
- White Paper: Lightning and Surge Protection For Wind TurbinesDocumento0 páginaWhite Paper: Lightning and Surge Protection For Wind TurbineslmagasAinda não há avaliações
- MOCK-CET PHYSICS PAPER-1 REVIEWDocumento10 páginasMOCK-CET PHYSICS PAPER-1 REVIEWRohan G (Simplinovus)Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 The Classroom Learning AcademyDocumento6 páginas1 The Classroom Learning AcademyJR3A Grace Low Shing WeiAinda não há avaliações
- LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer ExplainedDocumento8 páginasLVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer ExplainedRakesh MahajanAinda não há avaliações
- Code MATH Course Details PDFDocumento80 páginasCode MATH Course Details PDFAnees RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Aug.27, 146 I A 2. F 2,212,845: ... Cross Reference Search RgoDocumento5 páginasAug.27, 146 I A 2. F 2,212,845: ... Cross Reference Search RgoJorton Moreira de OliveriaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch23 (Young-Freedman) Parte 2Documento19 páginasCh23 (Young-Freedman) Parte 2JorgeCortezAinda não há avaliações
- Universal Current SensorDocumento12 páginasUniversal Current SensorBhargav MushiniAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Study On Progressive Collapse-Resistant Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Frame StructuresDocumento7 páginasExperimental Study On Progressive Collapse-Resistant Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structureshector rodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- 5th Classes - English For Electrical EngineeringDocumento36 páginas5th Classes - English For Electrical Engineeringduc_khanh_89100% (2)
- Fluke 5500a-Coil Inst SheetDocumento2 páginasFluke 5500a-Coil Inst SheetasAinda não há avaliações
- A Tentative Design Guideline For A New Steel Beam Connection Detail To Composite Tube ColumnsDocumento8 páginasA Tentative Design Guideline For A New Steel Beam Connection Detail To Composite Tube ColumnsRMKD PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Distribution SystemDocumento27 páginas12 Distribution SystemPao Castillon100% (1)
- Kinematic Standing CyclingDocumento15 páginasKinematic Standing Cyclingb.avilla9408Ainda não há avaliações
- Mock Test 5 Paper 1 Q. PaperDocumento16 páginasMock Test 5 Paper 1 Q. PaperRare RootAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Bearings PDFDocumento50 páginasChapter 4 Bearings PDFAnonymous 7aN0oYUm7vAinda não há avaliações
- Stress and Integral Formulations of General PrinciplesDocumento44 páginasStress and Integral Formulations of General PrinciplesVíctor Manuel Osorio RestrepoAinda não há avaliações
- BioMechanics of Canine RetractionDocumento113 páginasBioMechanics of Canine Retractionarshabharata100% (5)
- Lecture 2 StaticsDocumento41 páginasLecture 2 StaticsMaro IdehAinda não há avaliações
- The Design Process of A Self-Propelled Oor CraneDocumento12 páginasThe Design Process of A Self-Propelled Oor CraneVijay MylswamyAinda não há avaliações