Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CRT Monitor Student Information Sheet
Enviado por
AbdullionDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CRT Monitor Student Information Sheet
Enviado por
AbdullionDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CRT Monitor Student Information Sheet (Abdul.
)
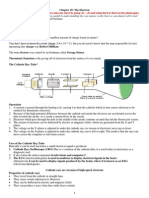
Structure of a Cathode Ray Tube Monitor:
Figure 1 Retrieved from Physics Principles with application, written by Douglas C.
Giancoli
Figure 1 illustrates some of the key components of a CRT.
Function and physics principles involved in the CRT monitor:
1. A transfer of electric potential energy to the cathode transforms into heat
energy causing vibrations in the cathode which then again transforms into
electrical potential energy via the emitted electrons from the cathode.
2. The anode attracts the electrons, as it is positive. (Remember that,
opposite charges attract.)
3. Electrons pass through a hole in the anode and reach the deflection plates.
The deflection plates can be surrounded by an electric field or a magnetic
field produced by an electromagnet.
4. A varying voltage supply to the deflection plates causes the electrons to
deflect to a particular part of the screen. The varying voltage supply
creates fields of different strengths, directing the electrons. Upon impact
with the phosphoric screen, it emits light as phosphoric substances do
when hit with electrons and hence an image is displayed on the monitor.
- It should be noted that an electron experiences a force in both an
electric and a magnetic field. This is an important physics
principle which allowed for the development of the CRT monitor.
This relationship between electricity and magnetism is an
important feature in many physics development over the course
of history, and is a key focus in our current module.
- It should also be noted that cathode rays were not established to be
electrons until later, hence their name. They were originally thought to be
waves by renowned scientist Heinrich Hertz.
- A Cathode is a negative electrode, an anode is a positive electrode and a
cathode ray is a beam of electrons. (An electrode is a conductor of
electricity.)
There always needs to be a power source for the
cathode.
Figure 2 on the right is an illustration of an ordinary CRT
monitor that students may have encountered before.
Some impacts on understanding in physics
because of the invention of CRT monitors.
Invention of the
Cathode Ray Tube
Invention of television
Discovery of XDiscovery of
Rays
electrons.
X-Ray
Image
crystallography
monitors
& machine.
The invention of theDiscovery
CRT led toofmany developments in understanding
physics. Although it atomic
should be understood that the CRT wasnt the
nucleus.
direct basis for these further developments, however invention of the
CRT lead to greater understanding of physics which in turn lead to
greater advance with physics.
X-Ray crystallography was extremely vital to uncover DNA.
Brief historical outline:
-
Julius Plucker is the first person credited for noticing behaviour of cathode
rays in a magnetic field. (He wasnt fully aware of the significance at the
time.
A physicist by the name of Karl Ferdinand Braun was the first however to
utilise this observation and construct the first known model of a CRT which
is the basis for current day CRT monitors.
It was not until J.J. Thompson that cathode rays were identified as particles
with a negative charge, which further developed understanding of major
principles, concepts and ideas in physics.
Impact of invention of the CRT monitor on society:
A more united society in that, invention of the television and monitor
which utilised Cathode Ray Tubes allowed for a quicker and more efficient
transfer of information over long distances.
Connected society with current affairs and offered a new source of
entertainment.
However it was also the reason for more isolation in physical interaction
between people.
Further development of technology due to greater understanding of
physics as a ripple effect of CRT invention had a vital impact on society in
terms of medicine, entertainment and so forth.
Você também pode gostar
- Siemens CT - Low - Dose - GuideDocumento66 páginasSiemens CT - Low - Dose - GuideSyazwanee Nasir100% (1)
- The ElectronDocumento16 páginasThe ElectronAyan SantraAinda não há avaliações
- Apparatus To Rectify Ether EnergyDocumento12 páginasApparatus To Rectify Ether EnergyV-Knows100% (1)
- Physical Science Week4 Additional ActivitiesDocumento14 páginasPhysical Science Week4 Additional ActivitiesquincyAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics 3 PDFDocumento38 páginasModern Physics 3 PDFDodi SaputraAinda não há avaliações
- The Tiger and The Shark Empirical Roots of Wave-Particle DualismDocumento380 páginasThe Tiger and The Shark Empirical Roots of Wave-Particle DualismClaudia Abreu100% (1)
- CG Presentation Srishti DasguptaDocumento8 páginasCG Presentation Srishti DasguptaSrishti DasguptaAinda não há avaliações
- Oatley1982 PDFDocumento14 páginasOatley1982 PDFLiviu BadeaAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- EShop - Exp 1 - Cathode Ray Tube Technology and AppliancesDocumento16 páginasEShop - Exp 1 - Cathode Ray Tube Technology and AppliancesfarukAinda não há avaliações
- Waves and PhasorsDocumento106 páginasWaves and Phasorsalenagroup100% (1)
- 01 Optical FibersDocumento72 páginas01 Optical FibersBereket TarikuAinda não há avaliações
- Name-Arpit Goyal REG. NO.-20BIT0054 Course Code-Phy1701: TOPIC: Importance of Quantum Mechanics in The Modern WorldDocumento5 páginasName-Arpit Goyal REG. NO.-20BIT0054 Course Code-Phy1701: TOPIC: Importance of Quantum Mechanics in The Modern WorldarpitAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Quantum Tunneling SensorsDocumento22 páginasElectron Quantum Tunneling Sensorsmariamargareth168Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics: FiitjeeDocumento1.319 páginasPhysics: FiitjeeBISWAJEET100% (2)
- Modern PhysicsDocumento86 páginasModern Physicstapas kundu100% (1)
- Particle Accelerator TorDocumento12 páginasParticle Accelerator Tormonica pradhanAinda não há avaliações
- AC TheoryDocumento108 páginasAC TheorySwapnil JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Electrons and Holes Put to Work in the Semiconductor ChipNo EverandElectrons and Holes Put to Work in the Semiconductor ChipNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Wave Properties of ParticleDocumento35 páginasWave Properties of ParticleAnnida ChairatunisaAinda não há avaliações
- The Photoelectric EffectDocumento6 páginasThe Photoelectric Effectapi-644343097Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorial TWTDocumento19 páginasTutorial TWTjk556Ainda não há avaliações
- From Ideas To Implementation: Study Notes: (From Syllabus Dot Points)Documento19 páginasFrom Ideas To Implementation: Study Notes: (From Syllabus Dot Points)Belinda ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Unit 3 AyangDocumento28 páginasLaporan Unit 3 AyangMurphy LinxAinda não há avaliações
- Moderm PhysicsDocumento39 páginasModerm Physicsgul zarrinAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Positron and Other AntiparticlesDocumento18 páginas1-Positron and Other AntiparticlesAbdulrhman fAinda não há avaliações
- Classical Physcisvs Quantum PhysicsDocumento8 páginasClassical Physcisvs Quantum PhysicsIchlasulAinda não há avaliações
- Phys:1200 Lecture 33 - Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocumento8 páginasPhys:1200 Lecture 33 - Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsbalkyderAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Particle Duality and Heisenberg Principle, Schrodinger Wave Equation, Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein DistributionsDocumento17 páginasWave Particle Duality and Heisenberg Principle, Schrodinger Wave Equation, Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein DistributionsmaniAinda não há avaliações
- Rider 267 Fundamentals of Transistor Physics Irving GottliebDocumento152 páginasRider 267 Fundamentals of Transistor Physics Irving GottliebJean-Luc Tambasco100% (2)
- History of Transmission Electron MicrosDocumento14 páginasHistory of Transmission Electron MicrosSiti FatimahAinda não há avaliações
- Physics T SafdarDocumento17 páginasPhysics T SafdarSAFDAR HafizAinda não há avaliações
- Cern 94 01 V1Documento523 páginasCern 94 01 V1mertsekerciAinda não há avaliações
- A Brief History and Review of AcceleratorsDocumento17 páginasA Brief History and Review of AcceleratorsNikolina ŠarčevićAinda não há avaliações
- FALLSEMFY2023-24 PHY1701 ETH CH2023241700859 Reference Material I 18-08-2023 Module 1 Introduction To Modern PhysicsDocumento55 páginasFALLSEMFY2023-24 PHY1701 ETH CH2023241700859 Reference Material I 18-08-2023 Module 1 Introduction To Modern PhysicsTannya PasrichaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Particle AcceleratorDocumento14 páginasWhat Is A Particle AcceleratormeerAAinda não há avaliações
- Class11 Chemistry 1 Unit02 NCERT TextBook English EditionDocumento44 páginasClass11 Chemistry 1 Unit02 NCERT TextBook English EditionAkash SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Kech102 PDFDocumento45 páginasKech102 PDFAlex RiderAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Puc Physics Chapter1-Physical World Notes by U N SwamyDocumento6 páginas1st Puc Physics Chapter1-Physical World Notes by U N Swamyashwinikumari bAinda não há avaliações
- BBC Documentary Shock and AweDocumento3 páginasBBC Documentary Shock and AweDuran, Wilhem John S.Ainda não há avaliações
- The Standard Model of Particle Physics: European Review December 2014Documento8 páginasThe Standard Model of Particle Physics: European Review December 2014Maria ArteagaAinda não há avaliações
- Electron Emission From Solids (I) : History & TheoryDocumento6 páginasElectron Emission From Solids (I) : History & Theorydei_sandeep7994Ainda não há avaliações
- Structure of Atom: Unit 2Documento45 páginasStructure of Atom: Unit 2Akshay NarayanAinda não há avaliações
- 5) Quantum Mechanics - UpdatedDocumento86 páginas5) Quantum Mechanics - UpdatedGame 1Ainda não há avaliações
- Semiconductors - NotesDocumento106 páginasSemiconductors - NotesAmit ShanuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1: Physical World: 10+1 Physics Study Material-Chapter 1 WWW - Rsnotes.InDocumento4 páginasChapter 1: Physical World: 10+1 Physics Study Material-Chapter 1 WWW - Rsnotes.InAnkit SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 2021 - Week 2Documento29 páginasLecture 2 2021 - Week 2Lenny NdlovuAinda não há avaliações
- HSC Physics Topic 3 From Ideas To ImplementationDocumento38 páginasHSC Physics Topic 3 From Ideas To ImplementationGary ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- Phy Topic 5 F4Documento9 páginasPhy Topic 5 F4Kandrossy GlassAinda não há avaliações
- Electrodynamic Waves: Wireless Transmission Through Air, Metals, Water and the Human BodyNo EverandElectrodynamic Waves: Wireless Transmission Through Air, Metals, Water and the Human BodyAinda não há avaliações
- CT scanImageProductionProcedures StatPearls NCBIBookshelfDocumento11 páginasCT scanImageProductionProcedures StatPearls NCBIBookshelfBipun patelAinda não há avaliações
- History: Vitaly KhlopinDocumento7 páginasHistory: Vitaly KhlopinramAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Mechanics Notes-Part 1Documento15 páginasQuantum Mechanics Notes-Part 1aman bhatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3 Elements of Quantum MechanicsDocumento65 páginasModule 3 Elements of Quantum MechanicsArnav AryaAinda não há avaliações
- Electron TheoryDocumento13 páginasElectron TheoryAilene Tsui Alferez PaciaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes - Quantum Theory of Light and Matter WavesDocumento34 páginasNotes - Quantum Theory of Light and Matter Wavesphysics olympiad100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanical Model of The Atom C12-2-04Documento11 páginasQuantum Mechanical Model of The Atom C12-2-04Lisabel FactorAinda não há avaliações
- Structure of Atoms (Class-11) - CompressPdf - PdfToPowerPointDocumento45 páginasStructure of Atoms (Class-11) - CompressPdf - PdfToPowerPointFlowring PetalsAinda não há avaliações
- 5 CH24 Acid-Base Balance 2015Documento22 páginas5 CH24 Acid-Base Balance 2015AbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015Documento29 páginas10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015AbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 6 CH25 General Anatomy & Digestive Processes & Mouth To Esophagus 2015Documento32 páginas6 CH25 General Anatomy & Digestive Processes & Mouth To Esophagus 2015AbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 4 CH24 Water and Electrolyte Balance 2015aDocumento25 páginas4 CH24 Water and Electrolyte Balance 2015aAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 2011 Chemistry NotesDocumento70 páginas2011 Chemistry NotesAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Year 11 CAFS Assessment Task 1Documento11 páginasYear 11 CAFS Assessment Task 1AbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 9.2 - Production of MaterialsDocumento52 páginas9.2 - Production of MaterialsMeena LochniAinda não há avaliações
- Elijah's Math NotesDocumento58 páginasElijah's Math NotesAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Physics NotesDocumento12 páginas2008 Physics NotesAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Hpat Ireland Additional Practice Questions PDFDocumento33 páginasHpat Ireland Additional Practice Questions PDFAbdullion50% (2)
- 2008 Physics NotesDocumento1 página2008 Physics NotesAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Writing FormulaDocumento2 páginasCreative Writing FormulaAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Motors and Generators: First Hand Investigations From The SyllabusDocumento26 páginasMotors and Generators: First Hand Investigations From The SyllabusAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- By Abdul Bhatti, Dean Lipowicz and Elijah Mercado.: Risk Assessment For Open-Ended Investigation: SpaceDocumento4 páginasBy Abdul Bhatti, Dean Lipowicz and Elijah Mercado.: Risk Assessment For Open-Ended Investigation: SpaceAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Assessment Task MetalsDocumento11 páginasChemistry Assessment Task MetalsAbdullionAinda não há avaliações
- Astm D1405 - 08Documento7 páginasAstm D1405 - 08mancjaAinda não há avaliações
- TLE7 AFA AGRICROP - Q1 - M3 - v2Documento37 páginasTLE7 AFA AGRICROP - Q1 - M3 - v2Alan Banluta100% (1)
- Gas Market ReportQ2 2023-IEADocumento52 páginasGas Market ReportQ2 2023-IEAhirobeAinda não há avaliações
- The Problem and Its ScopeDocumento44 páginasThe Problem and Its ScopeRosenia BaliAinda não há avaliações
- 01 TL Design AspectsDocumento4 páginas01 TL Design AspectschandrakantnuAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Test Method For Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (And Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)Documento18 páginasStandard Test Method For Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (And Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)LuisEduardoRomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Flow Measurement by Orifice Meter and by Ventury Meter BOMBAYDocumento7 páginasFlow Measurement by Orifice Meter and by Ventury Meter BOMBAYCedric GallusAinda não há avaliações
- Aits 2021 FT II Jeea Paper 2Documento11 páginasAits 2021 FT II Jeea Paper 2Manideep ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Everyday Forces ACTIVITYDocumento9 páginasEveryday Forces ACTIVITYirene manigbasAinda não há avaliações
- IECDocumento8 páginasIECShrikant KajaleAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21Documento16 páginasCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21shabanaAinda não há avaliações
- Mipower PDFDocumento11 páginasMipower PDFM.KAinda não há avaliações
- Distance Learning Programme: Pre-Medical: Rank Booster Test SeriesDocumento56 páginasDistance Learning Programme: Pre-Medical: Rank Booster Test SeriesAnanya SamantaAinda não há avaliações
- Varistor Productcatalog Sep07Documento41 páginasVaristor Productcatalog Sep07rushbrAinda não há avaliações
- Automatic Plant Watering SystemDocumento5 páginasAutomatic Plant Watering Systemsmartxdigital marketAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 3 Electric Fields and Electric PotentialDocumento5 páginasLab Report 3 Electric Fields and Electric PotentialsamiAinda não há avaliações
- Richard Becker (Auth.) - Theory of Heat-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1967) PDFDocumento393 páginasRichard Becker (Auth.) - Theory of Heat-Springer Berlin Heidelberg (1967) PDFJulian SierraAinda não há avaliações
- Ck-12 Physical Science For Middle School Flexbook® 2.0 Answer KeyDocumento5 páginasCk-12 Physical Science For Middle School Flexbook® 2.0 Answer KeyDa'Mya GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- WAZ5 PRO RTD enDocumento4 páginasWAZ5 PRO RTD enjack2012scribdAinda não há avaliações
- Weight Estimation of Vessels AppsDocumento28 páginasWeight Estimation of Vessels AppsAlvin Smith60% (5)
- downloadpdfD2K M PDFDocumento3 páginasdownloadpdfD2K M PDFNisha MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Lincoln 1100 Series Manual ServicioDocumento72 páginasLincoln 1100 Series Manual ServicioIsidro Ramos MermaAinda não há avaliações
- Crystal Reports - Complete SC1 Bus 4Documento9 páginasCrystal Reports - Complete SC1 Bus 4Hilda Mega MarcellaAinda não há avaliações
- Instructions: High Pressure Float Valve Régulateur Modulant de Niveau Haute Pression HFIDocumento4 páginasInstructions: High Pressure Float Valve Régulateur Modulant de Niveau Haute Pression HFIcaovadio88Ainda não há avaliações
- General Physics 2module 5 and 6Documento17 páginasGeneral Physics 2module 5 and 6RENDIE C. BEDOLIDOAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics Codes in Aerodynamic Analysis of Transonic Flows Over Wings and AirfoilsDocumento120 páginasEvaluation of Commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics Codes in Aerodynamic Analysis of Transonic Flows Over Wings and AirfoilsДмитрий СеменовAinda não há avaliações
- MCC 1Documento14 páginasMCC 1Arif SugestyanAinda não há avaliações
- How To Select A Peltier Module PDFDocumento11 páginasHow To Select A Peltier Module PDFdaAinda não há avaliações
- De-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDocumento2 páginasDe-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDahanyakage WickramathungaAinda não há avaliações
- Lamis Theorem 6Documento13 páginasLamis Theorem 6Sudhanshu SharmaAinda não há avaliações