Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cell Study Guide Biology I Honors
Enviado por
nomore8910 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
46 visualizações1 páginabio
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentobio
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
46 visualizações1 páginaCell Study Guide Biology I Honors
Enviado por
nomore891bio
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
Study Guide Biology I Honors
1. List the scientists important in discovering cells.
2. Explain the three components of the cell theory and how it came to be.
3. Differentiate between the following microscopes: dissecting, compound light, scanning electron, and transmission
electron. (You should be able to tell how they magnify and by how much.)
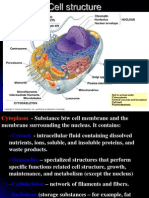
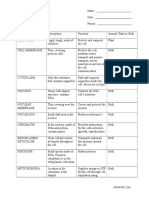
4. What is the function of each of the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, nucleus, nucleolus,
contractile vacuole, mitochondrion, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosome, microfilaments,
microtubules, cytoskeleton, chloroplast, cytoplasm, centrioles, chromosomes.
5. What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote.
6. What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell.
7. Draw a portion of the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. Show the polar and nonpolar regions. Why cant
ions (charged atoms) go directly through the membrane?
8. Explain why the lipid bilayer is considered to be selectively permeable.
9. What is diffusion? Osmosis? Facilitated Diffusion?
10. What is the difference between passive and active transport?
11. Explain the difference between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions. What happens to the cell in each of
those cases?
12. Differentiate between turgor pressure and plasmolysis.
13. Explain the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis.
14. What are the two types of endocytosis? Explain the difference.
15. What is the sodium-potassium pump? Explain its significance.
16. Explain the three components of the cell cycle.
17. Explain the 4 steps of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
18. Explain the difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
19. What are spindles made of? What is their function?
20. Differentiate between a centromere, centriole, chromatid, and chromosome.
21. What does it mean to be a haploid or diploid cell? Which cells in the human body are haploid and which are diploid?
Study Guide Biology I Honors
1. List the scientists important in discovering cells.
2. Explain the three components of the cell theory and how it came to be.
3. Differentiate between the following microscopes: dissecting, compound light, scanning electron, and transmission
electron. (You should be able to tell how they magnify and by how much.)
4. What is the function of each of the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, nucleus, nucleolus,
contractile vacuole, mitochondrion, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosome, microfilaments,
microtubules, cytoskeleton, chloroplast, cytoplasm, centrioles, chromosomes.
5. What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote.
6. What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell.
7. Draw a portion of the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. Show the polar and nonpolar regions. Why cant
ions (charged atoms) go directly through the membrane?
8. Explain why the lipid bilayer is considered to be selectively permeable.
9. What is diffusion? Osmosis? Facilitated Diffusion?
10. What is the difference between passive and active transport?
11. Explain the difference between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions. What happens to the cell in each of
those cases?
12. Differentiate between turgor pressure and plasmolysis.
13. Explain the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis.
14. What are the two types of endocytosis? Explain the difference.
15. What is the sodium-potassium pump? Explain its significance.
16. Explain the three components of the cell cycle.
17. Explain the 4 steps of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
18. Explain the difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
19. What are spindles made of? What is their function?
20. Differentiate between a centromere, centriole, chromatid, and chromosome.
21. What does it mean to be a haploid or diploid cell? Which cells in the human body are haploid and which are diploid?
Você também pode gostar
- Orstway Amegay Everay: OntentscayDocumento2 páginasOrstway Amegay Everay: Ontentscaynomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Social Media Authorization FormDocumento1 páginaSocial Media Authorization Formnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Take Out Menu Chestnut18Documento2 páginasTake Out Menu Chestnut18nomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Kimberly Hetzler WallDocumento3 páginasKimberly Hetzler Wallnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Cullen Performance Hall at The University of Houston Parking InformationDocumento3 páginasCullen Performance Hall at The University of Houston Parking Informationnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Dioxide Sequestration Via Direct Dry Mineral Carbonation Using Ferronickel Slag"Documento1 páginaDioxide Sequestration Via Direct Dry Mineral Carbonation Using Ferronickel Slag"nomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Arrowood CR: Houston, TX 77063Documento3 páginasArrowood CR: Houston, TX 77063nomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Sick and Feverish Glimpse of Cherry Blossoms Still ShiveringDocumento1 páginaSick and Feverish Glimpse of Cherry Blossoms Still Shiveringnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Methodology: Table 3.1. Enthalpy and Entropy of Magnesium, Calcium and Iron (II) CarbonatesDocumento8 páginasMethodology: Table 3.1. Enthalpy and Entropy of Magnesium, Calcium and Iron (II) Carbonatesnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics SyllabusDocumento6 páginasPhysics Syllabusnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- 2.1 Rates of Change and LimitsDocumento23 páginas2.1 Rates of Change and Limitsnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Welcome To Information Storage and Management v2.: 1 Course IntroductionDocumento5 páginasWelcome To Information Storage and Management v2.: 1 Course Introductionnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- An Old Pond! A Frog Jumps in The Sound of WaterDocumento1 páginaAn Old Pond! A Frog Jumps in The Sound of Waternomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Fallen Sick On A Journey, in Dreams I Run Wildly Over A Withered MoorDocumento1 páginaFallen Sick On A Journey, in Dreams I Run Wildly Over A Withered Moornomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Green Frog, Is Your Body Also Freshly Painted?Documento1 páginaGreen Frog, Is Your Body Also Freshly Painted?nomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Without Flowing Wine How To Enjoy Lovely Cherry Blossoms?Documento1 páginaWithout Flowing Wine How To Enjoy Lovely Cherry Blossoms?nomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Over The Wintry Forest, Winds Howl in Rage With No Leaves To BlowDocumento1 páginaOver The Wintry Forest, Winds Howl in Rage With No Leaves To Blownomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Everything I Touch With Tenderness, Alas, Pricks Like A BrambleDocumento1 páginaEverything I Touch With Tenderness, Alas, Pricks Like A Bramblenomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- Trusting The Buddha, Good and Bad, I Bid Farewell To The Departing YearDocumento1 páginaTrusting The Buddha, Good and Bad, I Bid Farewell To The Departing Yearnomore891Ainda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1 Week 1 Module 1Documento4 páginasGeneral Biology 1 Week 1 Module 1Florene Bhon GumapacAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Sorting and Transport:: The Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, and LysosomesDocumento99 páginasProtein Sorting and Transport:: The Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, and LysosomesSrikant SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Cell and Cytology Resonance PDFDocumento79 páginasCell and Cytology Resonance PDFEkta Manglani100% (1)
- Jejas Dan Kematian SelDocumento48 páginasJejas Dan Kematian SelLIEBERKHUNAinda não há avaliações
- Biology FSC Chapter 1Documento8 páginasBiology FSC Chapter 1Diana PriyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Golgi Apparatus: Morphology and Function With Recent FactsDocumento8 páginasThe Golgi Apparatus: Morphology and Function With Recent FactsBlaxez YTAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Nur Haura Zhafirah Lubis Olinda Calista Yetri ClassDocumento8 páginasName: Nur Haura Zhafirah Lubis Olinda Calista Yetri ClassNur HauraAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Sheet Formative AssessmentDocumento4 páginasAnswer Sheet Formative Assessmentapi-328130455Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 TestDocumento8 páginasChapter 7 Testkwilliams1994Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell - Structure and Function: Module - 1Documento35 páginasCell - Structure and Function: Module - 1Manas TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Cell FractionationDocumento3 páginasCell FractionationNg Kei CheongAinda não há avaliações
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocumento8 páginasCell and Molecular BiologySofia Christel JavierAinda não há avaliações
- QuestionsDocumento66 páginasQuestionsfay_ten92Ainda não há avaliações
- Student Slides - Fill in The BlanksDocumento20 páginasStudent Slides - Fill in The Blanksapi-663039855Ainda não há avaliações
- Parts of The Cell and FunctionsDocumento31 páginasParts of The Cell and FunctionsMary Joy Llosa Redulla100% (1)
- Visible Biology Site License Lab Activities Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells StudentDocumento13 páginasVisible Biology Site License Lab Activities Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells StudentALEXANDRE RAFAEL KUREKAinda não há avaliações
- Ribosomes and Golgi ApparatusDocumento31 páginasRibosomes and Golgi ApparatusAabdullah IftikharAinda não há avaliações
- XOXOXDocumento7 páginasXOXOXVazima QtAinda não há avaliações
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8Documento15 páginasImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8lavanya rajaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell CytoplasmDocumento55 páginasCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocumento4 páginasLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Structure and Function: Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen FitzpatrickDocumento115 páginasCell Structure and Function: Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen FitzpatrickAbdelrahman Al SamhouriAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 páginasCell Organelles Worksheet537777333% (3)
- Cytology McqsDocumento8 páginasCytology McqsZiyad AbdallahAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento1 páginaAnimal CellHillary ReedAinda não há avaliações
- Fronda Exam in Adveanced Cell Mol Bio 12072021Documento6 páginasFronda Exam in Adveanced Cell Mol Bio 12072021Jericho D. FrondaAinda não há avaliações
- August 20-24, 2018Documento5 páginasAugust 20-24, 2018Maria Virginia Fernandez100% (1)
- Activity 2 - Making Venn DiagramDocumento3 páginasActivity 2 - Making Venn DiagramVea Ann CantollasAinda não há avaliações
- Cilia and Flagella Rebeca GDocumento18 páginasCilia and Flagella Rebeca GLloquetaAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental Unit of Life 1-25Documento25 páginasFundamental Unit of Life 1-25Anisha PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNo EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)