Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
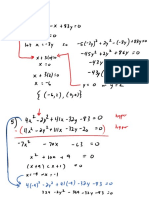
Xy Xy: Factoring
Enviado por
api-168512039Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Xy Xy: Factoring
Enviado por
api-168512039Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
Factoring
Greatest Common Factor
ax k
The monomial
is called the greatest common factor (GCF) of a polynomial in x
with integer coefficients if both of the following are true:
a is the greatest integer factor common to all of the polynomial coefficients
k is the smallest exponent on x found in all of the terms of the polynomial
14 x 2 y 2 10 xy 3
1)
2)
30 x 4 20 x 3 10 x 2
Factoring Formulas: Special Polynomial Forms
a 2 b 2 (a b)(a b)
Difference of Two Squares
a 2 2ab b 2 (a b)2
Perfect Squares
a 2 2ab b 2 (a b) 2
Sum of Two Cubes
a 3 b3 (a b)(a 2 ab b 2 )
Difference of Two Cubes
a 3 b3 (a b)(a 2 ab b 2 )
1)
4)
x2 9
x 2 8 x 16
2)
4x2 9
144 81y 2
3)
y 2 10 y 25
5)
4 x 2 12 xy 9 y 2
6)
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
7)
t 3 27
y 3 64
8)
9)
27 8x 3
Factoring a Trinomial whose leading coefficient is 1
1)
x2 6x 5
y2 2 y 3
2)
y 2 10 y 9
3)
Factoring a Trinomial whose leading coefficient is not 1
2 y2 5 y 3
1)
2)
3t 2 7t 2
3)
4 x 2 2 x 12
Factoring by Grouping
1)
x3 x 2 2 x 2
Rational Expressions
Operation
Multiplying Rational
Expressions
Dividing Rational
Expressions
Example
2
3x
6x
x 1 x 1 ( x 1)( x 1)
2
3x
x 1 x 1
2 x 1
x 1 3x
2( x 1)
3x( x 1)
Note
State domain
restrictions.
When dividing rational
expressions, remember
to check for additional
domain restrictions
once the division is
rewritten as
multiplication by a
reciprocal.
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
Adding/Subtracting
rational expressions
with no common factors
The least common
denominator (LCD) is
the product of the two
denominators.
2
3x
x 1 x 1
2( x 1) 3x( x 1)
( x 1)( x 1)
2 x 2 3 x 2 3x
( x 1)( x 1)
3x 2 5 x 2
( x 1)( x 1)
(3 x 1)( x 2)
( x 1)( x 1)
LCD:(x+1)(x1)
Adding and subtracting
rational expressions
with common factors
3
2
x( x 1) x( x 2)
3( x 2) 2( x 1) 3 x 6 2 x 2
x( x 1)( x 2)
x( x 1)( x 2)
x4
x( x 1)( x 2)
The LCD is the product
of each of the distinct
factors raised to the
highest power that
appears in any of the
denominators.
Reduce the Rational Expression to lowest terms.
( x 3)( x 9)
2( x 3)( x 9)
1)
Multiply the rational expressions and simplify.
2)
(2t 1)(t 2)
4t 8
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
1)
3)
x 2 3x 5
x 1 x 2
t 2 t 6 8t
t 2 4 2t 2
4( x 2)( x 5)
16 x
8x
( x 5)( x 5)
2)
4)
3x 2 15 x 2 x 2 7 x 15
2 x 3 50 x 3x 2 15 x
Divide the rational expressions and simplify.
1)
1
5
2
x 1 x 1
2)
x 2 4 x 21 x 2 2 x 63
x 2 3 x 10 x 2 x 20
Add or subtract the rational expression and simplify.
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
1)
3)
5)
3 2
x 5x
7
5
2x 1 1 2x
x 1 x 6
x 2 x2 4
3
5p
p 2 p 1
2)
3y2 1 2 y
y 1 y 1
4)
7
6)
2x
x 3
Factoring
1)
2x2 9x 5
2)
6 x 2 19 x 7
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
3)
5)
7)
16 x 2 25
x3 125
2 x 2 4 x 2 30 x
Simplify
9)
t2 t 6
t2 t 2
Perform the indicated operation and simplify.
10)
x 2 3x 10 x 2 x 2
x2 2 x 3 x2 x 6
4)
6)
8)
9 x 2 30 x 25
1 8x 3
2 x3 x 2 6 x 3
College Algebra & Trig
Chapter 0 Review Part II
11)
12)
13)
x2 x 2
x 1
2
3
2
x 3x
x 2x
1
x3
x 1 x 4
3 x
x
2x 1 x 1
Você também pode gostar
- Transactional Licensing Comparison ChartDocumento3 páginasTransactional Licensing Comparison Chartjonder2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - PARTIAL FRACTIONSDocumento16 páginasChapter 1 - PARTIAL FRACTIONSkrissypainty33% (3)
- Remainder and Factor Theorems WorksheetDocumento3 páginasRemainder and Factor Theorems WorksheetKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Integration by Partial FractionDocumento26 páginasIntegration by Partial FractionSyarifah Nabila Aulia RantiAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 Differentiation Barely PassedDocumento10 páginas2012 Differentiation Barely PassedcsanjeevanAinda não há avaliações
- Partial fractions techniquesDocumento8 páginasPartial fractions techniquesDaniel ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Model Answer Spring 2016-03-MAT161Documento2 páginasMidterm Model Answer Spring 2016-03-MAT161Abdelrhman HusseinAinda não há avaliações
- Finding Limits AnalyticallyDocumento63 páginasFinding Limits AnalyticallyKaviarasu SubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- Product Rule:: Uv Udv VduDocumento35 páginasProduct Rule:: Uv Udv Vduمحمد شهريل محمد نورAinda não há avaliações
- A1 Phs 27 1Documento3 páginasA1 Phs 27 1api-215160782Ainda não há avaliações
- Integrali i pacaktuarDocumento20 páginasIntegrali i pacaktuartutiAinda não há avaliações
- Math 8 1.4Documento16 páginasMath 8 1.4Via Camille Hermoso JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 7 2Documento10 páginasNotes 7 2api-275303967Ainda não há avaliações
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 4 Addition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsDocumento16 páginasG8 Math Q1 - Week 4 Addition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsWenilyn MananganAinda não há avaliações
- LEsson 8 AddingSubtracting RE With Unike DenominatorsDocumento20 páginasLEsson 8 AddingSubtracting RE With Unike DenominatorsJumedeluna05yahoo.com Jumelynjumelyn199411Ainda não há avaliações
- A2T RationalExpRevDocumento3 páginasA2T RationalExpRevjennyAinda não há avaliações
- 3.3 Special Products and FactoringDocumento37 páginas3.3 Special Products and FactoringLorraine LacuestaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDocumento2 páginas5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDudeAinda não há avaliações
- INTEGRATION RULES AND TECHNIQUESDocumento11 páginasINTEGRATION RULES AND TECHNIQUESahlam_1995Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Math Exam NotesDocumento13 páginasGrade 11 Math Exam Notespkgarg_iitkgpAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Math Polynomials and Partial FractionsDocumento4 páginasBasic Math Polynomials and Partial FractionsSyazwan KusrinAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Quadratic Equations by FactorisingDocumento1 páginaSolving Quadratic Equations by FactorisingRoberto CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus NoteDocumento95 páginasCalculus NoteAfeef Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- Math Review Material #5: Division of IntegersDocumento3 páginasMath Review Material #5: Division of IntegersKeith Kevin Dave DandanAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ RevisionDocumento133 páginasMCQ RevisionTibem soAinda não há avaliações
- SEKOLAH MENENGAH DATUK PETER MOJUNTIN EXAMDocumento9 páginasSEKOLAH MENENGAH DATUK PETER MOJUNTIN EXAMAileen Beh Chik HeangAinda não há avaliações
- MAT1581 Tutorial SolutionsDocumento20 páginasMAT1581 Tutorial SolutionsmatshonaAinda não há avaliações
- Practive AP Calculus Test 1 Oct 2020 CHPT 2Documento5 páginasPractive AP Calculus Test 1 Oct 2020 CHPT 2MAinda não há avaliações
- Express fraction with quadratic and linear factors as partial fractionsDocumento12 páginasExpress fraction with quadratic and linear factors as partial fractionsCY100% (1)
- MalloDocumento34 páginasMalloBea DatayAinda não há avaliações
- ODD01Documento21 páginasODD01ilovedamonsalvatore3Ainda não há avaliações
- Please Note: This A Revision Not A Practice Test. Actual Test May Have Lesser/ More Number of QuestionsDocumento5 páginasPlease Note: This A Revision Not A Practice Test. Actual Test May Have Lesser/ More Number of QuestionsJames LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Formulasheetalgebra 2 TrigDocumento4 páginasFormulasheetalgebra 2 Trigapi-265200443Ainda não há avaliações
- Quiz Ch81234Documento5 páginasQuiz Ch81234ZaidBAinda não há avaliações
- PP Limits 1516Documento13 páginasPP Limits 1516Amirul FadlinAinda não há avaliações
- Math 0362 Unit 2 Chapter 7 - Rationals: Updated: Summer 2015Documento9 páginasMath 0362 Unit 2 Chapter 7 - Rationals: Updated: Summer 2015Afsana MohammadAinda não há avaliações
- College Algebra Final Exam Review Rational Expressions and FunctionsDocumento4 páginasCollege Algebra Final Exam Review Rational Expressions and Functionszahed83Ainda não há avaliações
- No. Solutions: Tanjong Katong Secondary School A Maths Sec 4 Prelims 2010 Paper 1 Solution 1Documento6 páginasNo. Solutions: Tanjong Katong Secondary School A Maths Sec 4 Prelims 2010 Paper 1 Solution 1Francis Ho HoAinda não há avaliações
- Deriving Using Product and Quotient Rules: Michael Turner Alex BarboloviciDocumento31 páginasDeriving Using Product and Quotient Rules: Michael Turner Alex BarboloviciAlex BarboloviciAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Mathematics CXC 2014 SolvedDocumento5 páginasAdditional Mathematics CXC 2014 SolvedAbigail Johnson67% (24)
- Indices IxDocumento5 páginasIndices IxAgung JatiariskaAinda não há avaliações
- Factor Polynomials and Solve Problems Involving FactorsDocumento4 páginasFactor Polynomials and Solve Problems Involving FactorsJa NeenAinda não há avaliações
- Calcprobonly PDFDocumento71 páginasCalcprobonly PDFSLKAinda não há avaliações
- Outline (Week 3) 3.1 Partial Fractions (8.6) 3.2 Numerical Integration (8.7)Documento10 páginasOutline (Week 3) 3.1 Partial Fractions (8.6) 3.2 Numerical Integration (8.7)Yifei ChengAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 7 Test Review Fall 2021Documento2 páginasUnit 7 Test Review Fall 2021BobAinda não há avaliações
- Techniques of Integrating Rational and Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento8 páginasTechniques of Integrating Rational and Trigonometric FunctionsS M AkashAinda não há avaliações
- Partial FractionsDocumento10 páginasPartial FractionsSsentongo NazilAinda não há avaliações
- FKB20203-Tutorial (Limits and Continuity)Documento12 páginasFKB20203-Tutorial (Limits and Continuity)Shafinaz ChachaAinda não há avaliações
- Polynomial Long Division and Factorization ReviewDocumento16 páginasPolynomial Long Division and Factorization ReviewAngel PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- LastDocumento107 páginasLastAnonymous XC6BngAinda não há avaliações
- Remainder and Factor TheoremDocumento19 páginasRemainder and Factor Theorem4121370% (1)
- Factorisation: Synopsis - 1Documento6 páginasFactorisation: Synopsis - 1Snigdharani SahooAinda não há avaliações
- Latihan integral parsial teknik tanzalinDocumento9 páginasLatihan integral parsial teknik tanzalinValen FransAinda não há avaliações
- Guia2 LimitesDocumento5 páginasGuia2 LimitescarlaleivaAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Calculus Quiz 2C: LimitsDocumento9 páginasAp Calculus Quiz 2C: LimitsteachopensourceAinda não há avaliações
- DLM 1 - Unit 4 Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocumento32 páginasDLM 1 - Unit 4 Rational Algebraic ExpressionsvicAinda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 4/6/16Documento5 páginasAAA Notes 4/6/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 4/11/16Documento2 páginasAAA Notes 4/11/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
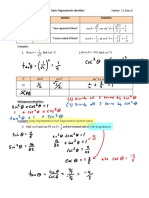
- REVIEW - 7.1 Basic Trigonometric Identities: Sin Cos 1 Tan 1 Sec 1 Cot CSCDocumento2 páginasREVIEW - 7.1 Basic Trigonometric Identities: Sin Cos 1 Tan 1 Sec 1 Cot CSCapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Sin 1 Sin: CAT 7.1 (Day 3)Documento2 páginas1 Sin 1 Sin: CAT 7.1 (Day 3)api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
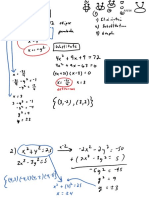
- Xy X y Xy y X X Y: Section 7.1 Try These Problems Now. Simplify Each Expression, Find A Common Denominator FirstDocumento1 páginaXy X y Xy y X X Y: Section 7.1 Try These Problems Now. Simplify Each Expression, Find A Common Denominator Firstapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 4/4/16Documento5 páginasAAA Notes 4/4/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Algebra A 2015-2016 Prystalski: Date Section Topic HomeworkDocumento1 páginaAdvanced Algebra A 2015-2016 Prystalski: Date Section Topic Homeworkapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- (Sin) 3 3 Sin 2 4: Sin 3 Sin 2 (Cos) Cos 1 Cos 2 1 1 Cos 2 8Documento2 páginas(Sin) 3 3 Sin 2 4: Sin 3 Sin 2 (Cos) Cos 1 Cos 2 1 1 Cos 2 8api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- College Algebra and Trig (CAT) Prystalski Chapter 7 - Analytic Trigonometry Number Date Due Read Section Topic AssignmentDocumento2 páginasCollege Algebra and Trig (CAT) Prystalski Chapter 7 - Analytic Trigonometry Number Date Due Read Section Topic Assignmentapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 3/1/16Documento5 páginasAAA Notes 3/1/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 4/6/16Documento5 páginasAAA Notes 4/6/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- CAT Pi Notes 3.14Documento3 páginasCAT Pi Notes 3.14api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Law of Sines Law of Cosines NeitherDocumento3 páginasLaw of Sines Law of Cosines Neitherapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
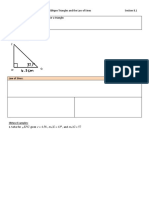
- Review: What Does It Mean To Solve For A Triangle:: CAT Oblique Triangles and The Law of Sines Section 8.1Documento3 páginasReview: What Does It Mean To Solve For A Triangle:: CAT Oblique Triangles and The Law of Sines Section 8.1api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Section 8-6 PracticeDocumento2 páginasAAA Section 8-6 Practiceapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Notes 3/15/16Documento3 páginasAAA Notes 3/15/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- AAA Section 8-6 PracticeDocumento2 páginasAAA Section 8-6 Practiceapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 6.5 Trig Functions of Nonacute Angles: Mathematician: - PeriodDocumento2 páginas6.5 Trig Functions of Nonacute Angles: Mathematician: - Periodapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- CAT Transformations: NameDocumento3 páginasCAT Transformations: Nameapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning Goals: I Can Convert Between Degrees and Radians. I Can Calculate The Length of An Arc Along A CircleDocumento2 páginasLearning Goals: I Can Convert Between Degrees and Radians. I Can Calculate The Length of An Arc Along A Circleapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento4 páginasUntitledapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Aaa Notes 2/22/16Documento5 páginasAaa Notes 2/22/16api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Aaa NotesDocumento5 páginasAaa Notesapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Full Rotation 360 2 (Degrees) (Radians)Documento3 páginas1 Full Rotation 360 2 (Degrees) (Radians)api-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento2 páginasUntitledapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 6.5 - PART 3: Mathematician: - PeriodDocumento1 página6.5 - PART 3: Mathematician: - Periodapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Angular/Linear Velocity ProblemsDocumento3 páginasAngular/Linear Velocity Problemsapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 6.5 - PART 2: 1. Find All Possible Values of Between, Where CotDocumento1 página6.5 - PART 2: 1. Find All Possible Values of Between, Where Cotapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning Goals: I Can Determine What Angles Result in A Given Trigonometric FunctionDocumento1 páginaLearning Goals: I Can Determine What Angles Result in A Given Trigonometric Functionapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- 6.5 - PART 1: 1. Indicate The Quadrant in Which The Terminal Side of Be True: TanDocumento1 página6.5 - PART 1: 1. Indicate The Quadrant in Which The Terminal Side of Be True: Tanapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Java Chegg HistogramDocumento3 páginasJava Chegg Histogramashit kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 01 Automation ToolsDocumento46 páginasLesson 01 Automation ToolsKrish LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Tn179 05 PDFDocumento517 páginasTn179 05 PDFchimbwaAinda não há avaliações
- CRM Total Cost of Ownership Analysis1Documento11 páginasCRM Total Cost of Ownership Analysis1RobinvarshneyAinda não há avaliações
- PhonologicalDocumento363 páginasPhonologicalakbar mekka hamiduAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Module 5 PDFDocumento5 páginasRevision Module 5 PDFavineshAinda não há avaliações
- Commentz-Walter: Any Better Than Aho-Corasick For Peptide Identification?Documento5 páginasCommentz-Walter: Any Better Than Aho-Corasick For Peptide Identification?White Globe Publications (IJORCS)Ainda não há avaliações
- Application Form Submitted Successfully ConfirmationDocumento2 páginasApplication Form Submitted Successfully Confirmationchemistry WorldAinda não há avaliações
- Excel Programming Tutorial 1: Macros and FunctionsDocumento13 páginasExcel Programming Tutorial 1: Macros and FunctionsSk AkashAinda não há avaliações
- Operational GuideDocumento55 páginasOperational GuidehossainmzAinda não há avaliações
- InstnwndDocumento284 páginasInstnwndjwooAinda não há avaliações
- Tobias LevkovichDocumento21 páginasTobias Levkovichapi-8861784Ainda não há avaliações
- Casio Standard/Desktop/Scientific CalculatorsDocumento2 páginasCasio Standard/Desktop/Scientific CalculatorsNathaniel Lumpas EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Make A Simple Computer Virus - Code in Code - BlocksDocumento3 páginasHow To Make A Simple Computer Virus - Code in Code - BlocksasmaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)Documento7 páginasUnderstanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)api-26860950100% (2)
- Mom PDFDocumento8 páginasMom PDFThug LifeAinda não há avaliações
- Object Oriented SAD-2 Part IDocumento80 páginasObject Oriented SAD-2 Part IbtittyAinda não há avaliações
- L6 Systems of InequalitiesDocumento25 páginasL6 Systems of InequalitiesFlorence FlorendoAinda não há avaliações
- Solver Out PutDocumento26 páginasSolver Out PutRogerIvan GaristoAinda não há avaliações
- Multi-region computational framework for gas-solid catalytic reactorsDocumento30 páginasMulti-region computational framework for gas-solid catalytic reactorsMatteo CalonaciAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Review on FunctionsDocumento50 páginasModule 1 Review on FunctionsRonald DalidaAinda não há avaliações
- Matrices DeterminantsDocumento3 páginasMatrices DeterminantsSUDHANSHU PANWARAinda não há avaliações
- BTU To Watts (W) Conversion CalculatorDocumento2 páginasBTU To Watts (W) Conversion Calculatorbudi_alamsyahAinda não há avaliações
- Logistics ManagementDocumento4 páginasLogistics Managementeduard john antiqueraAinda não há avaliações
- Ready Key Pro Soft Ware Users GuideDocumento16 páginasReady Key Pro Soft Ware Users Guidejroute101Ainda não há avaliações
- Logic in Computer Science: BITS PilaniDocumento11 páginasLogic in Computer Science: BITS PilaniPranjal GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet BFH - SolutionDocumento7 páginasWorksheet BFH - SolutionAmogh D GAinda não há avaliações
- Mathcad's Programming Language: The for LoopDocumento13 páginasMathcad's Programming Language: The for LoopJéssica GonçalvesAinda não há avaliações