Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
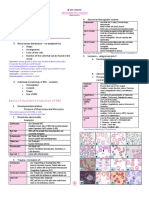
Blood Volume1
Enviado por
Dee GeeDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Blood Volume1
Enviado por
Dee GeeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
BLOOD VOLUME
}
Total amount of blood in the circulation
}
Normal blood volume
Male: approx. 5.8 L
Female: approx. 4.5 L
}
Definition of terms:
Normovolemia
Normal volume of blood in the body
Hypovolemia
Decrease in the volume of the blood
Hypervolimia
Excessive volume of blood in the body
Oligemia
Total reduction of blood volume
A condition in which the total volume of
the blood is reduced
NORMAL MATURATION OF CELLS
3 Principles:
1) Cytoplasmic Differentiation
}
Several Factors:
Loss of Basophilia
Associated with color blue
Nucleus
Acidic part of the cell
Methylene Blue
Cytoplasm
Basophilic part of the
cell
Eosin
Cytoplasmic Granules
Increase in granules, the
more mature
Elaboration of hemoglobin
Increase in hemoglobin, the
more mature
FACTORS RELATED TO DECREASE () BLOOD VOLUME
}
Loss of whole blood
Hemorrhage
}
Loss of RBC
Spherocytosis
An auto-hemolytic anemia
}
Loss of plasma
Burned patients, Dehydration
}
Loss of body water
Decrease consumption of water
2)
Nuclear Maturation
}
Subdivisions:
a) Structure & Cytochemistry
Presence of round/oval
nucleus
Young cell-compact
Large nucleus to cytoplasm
ratio
The larger the
nucleus, the more
immature
The larger the
cytoplasm, the more
mature
Nuclear chromatin
Rich in RNA
The more nuclear
chromatin, the
younger the cell
Decrease in the number of
Normal neutrophil
nucleoli
2-5 lobes
Found on the most
Hypersegmented neutrophil
immature stage
More than 5 lobes
The more lobulated,
Pernicious Anemia
the more mature
b) Changes in the shape of nucleus
Lobulation of nucleus
The more lobulated,
the more mature
FACTORS RELATED TO INCREASE () BLOOD VOLUME
}
During blood transfusion
}
Intravenous fluid
}
Due to increase fluid intake
FORMULA:
Plasma Volume + Packed Cell Volume = Total Blood Volume
Blood = 45% Formed Elements (Cells) + 55% Liquid Elements (Plasma)
}
}
}
Plasma volume should comprise 55% of the total blood
volume
Packed cell volume should be round 45% of the total blood
volume
Total reduction of blood volume
Packed Cell Volume
Measured by counting with use of radioactive
materials
Radioisotopes for the determination
of Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
Examples:
Cr-51, P-32, Radio Iron
Inject Radioisotopes: attach to
RBC
Plasma Volume
Measured by intravenous injection of foreign
substances of known amount and concentration
that will allow the measurement of the body fluid
Could be radio active material (radioisotope iodine
131 and with the use of dyes)
Examples of Dyes:
Evans Blue
Congo Red
Labeled Human Serum Albumin
3)
Reduction of cell size
}
The smaller the cell, the more mature
}
The larger the cell, the more immature
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
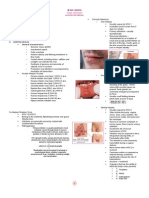
HEME SYNTHESIS
}
FACTORS AFFECTING THE HEMOGLOBIN AFFINITY (ATTACHMENT)
WITH OXYGEN
First Step
Condensation of succinyl co-enzyme A + glycine in
the presence of pyroxidal phosphate and delta
aminolevulinic acid synthesis will react to co-enzyme A
and glycine to produce delta aminolevulinic acid
dehydrogenase
I.
Body Temperature
}
An increase in the body temperature causes the
hemoglobin to release oxygen more readily
}
* In Body temperature = in Oxygen released
Shift to the right
In the release of Oxygen &
release of uptake in Carbon
dioxide
II.
Blood pH/Bohr Effect
}
The relationship of the blood pH and oxygen affinity
is what we call the Bohr effect which tells us an
increase in pH favors the uptake of Oxygen
}
* pH = Alkaline
}
* Blood pH = uptake of Oxygen
Shift to the left
in the uptake of Oxygen &
release of Carbon dioxide
III.
2,3 Diphosphoglycerate (DPG)
}
An increase amount of DPG level will cause a
diminish oxygen affinity
Shift to the right
DPG = Oxygen (release)
affinity
IV.
Carbon Dioxide
}
An increase of Carbon dioxide will diminish the
affinity of Oxygen
Shift to the right
V.
Presence of HbF (Fetal Hemoglobin)
}
An increase of HbF in the fetus will cause increase
oxygenation of the fetal blood
Shift to the left
*For adults: Shift to the right (Not Normal)
VI.
Presence of Hemoglobin Variance
}
The number of normal hemoglobin balance will show
either shift to the left or right
}
Different types of Hemoglobin
HbM & HbO Right
HbA2 & HbA Left
VII.
Decrease affinity of oxygen and increase carbon dioxide
}
Haldane Effect
Affinity = Right
Synthesis of nucleus
Spleen graveyard of RBC
RBC (120 days)
Hemoglobin
heme globin (reabsorbed protein)
Iron (Fe) Porphyrin
HEMOGLOBIN
}
Red coloring pigment of the blood
}
Main component of RBC
35% of the total RBC
Sometimes called respiratory pigment because of its capacity to
transport O2 and CO2
A gram of hemoglobin can carry approximately 1.34mL of
Oxygen and 3.47mg of Iron
The adult RBC mass of 600grams hemoglobin can carry
approximately 800mL of Oxygen
Women need 400-800g of iron supplement
Conjugated CHON (Protein) that is made up of 1 globin molecule of
heme groups and the globin is divided into 4 polypeptide chains
Each chain is attached to 1 heme group
Heme
Heme
1 Globin Molecule
Heme
Heme
Polypeptide chain
Made up of amino acid
In normal adult hemoglobin, it is made up of
2 alpha and 2 beta chain
Alpha chain
Made up of 141 amino acid
First Amino Acid Valine
Last Amino Acid Arginine
Beta chain
Made up of 146 amino acid
First Amino Acid Valine
Last Amino Acid Histidine
Body Temperature shift to the LEFT
HbF adult shift to the RIGHT
Haldane Effect shift to the RIGHT
Oxygen uptake shift to the LEFT
2, 3 DPG shift to the LEFT
The rest of the globin chain contains 146 amino acids
2
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
CLASSIFICATION OF HEMOGLOBIN
A.
Normal Hemoglobin
}
Capable of transporting blood gases particularly
Oxygen & Carbon dioxide
According to Function
Oxyhemoglobin
Arterial blood
Bright red
Oxygen
Reduced Hemoglobin
Venous blood
Dark red
Carbon dioxide
}
Hemoglobin in Adult (post-neonatal)
HbA
Constitutes majority of adult Hg
96-98% Hg
2 & 2 chains
HbA2
Normal adult Hg
1.5 3% total types of Hg
2 & 2 (delta) chains
HbF
Major hg in fetus (90-95% hg)
0.5 1% hg
2 & 2 (gamma) chains
}
B.
Abnormal/Non-functional Hemoglobin
}
Formed due primarily to a defect in the
polypeptide chain of hemoglobin molecule
}
Category:
Carboxyl Hemoglobin (HbCO)
Reacts with Carbon monoxide in
which the affinity of CO 218x
greater than Oxygen at 37C
Do not transport oxygen that may
lead to hypoxia & finally death of
the patient
Produces cherry red blood color
Concentration to non-smokers:
0 2.3%
Smokers: 2.1 4.2%
Test for HbCO
Katayamas Test
a. 10 mL Distilled H2O
b. + 5 drops of blood
from patients/ control
blood
c. + 5 drops of
Ammonium sulfide
d. + Acidify with acetic
acid
3.
Met Hemoglobin
A.k.a.
Hemiglobin
Oxidized Hemoglobin
Ferri Hemoglobin
Reversible reaction
Normal individual
approximately 1% of
methylene blue
Characteristic color:
Chocolate brown
Hemoglobin C
Found also among blacks, rare in whites
Appears also in homozygous & heterozygous
state
If present, it demonstrate target cell
Target cell
Condensation of Hg at the
center/periphery
A.k.a.
Bulls eye cell
Codocyte
Leptocyte
Mexican hat cell
Happy Hormones:
{
Serotonin
{
Adrenaline
{
Epinephrine
if NORMAL BLOOD : Dirty greenish, Brown
if HbCO (+): Rose red color
Other Test for HbCO:
r
Sanderman Dethionite Test
r
Palmers Test
Yersinia enterocolitica
Hemoglobin D
Most common for HbD Purijab & HbD Los Angeles
Both alpha & beta chain abnormally have been
reported
Shows no sickling of RBC
Blood pH becomes basic
Humble yourselves, therefore, under Gods mighty hand, that he may lift you
up in due time. Cast all your anxiety on him because he cares for you.
- 1 Peter 5:6,7
Sulfhemoglobin
Blood with combined sulfide
Benign condition
With significant effect of
cyanosis
Cause & effect of drug
Mauve lavender color
VARIANCE OF HEMOGLOBIN
}
Hemoglobin S
Causes sickling of RBC
Confined to blacks
Homozygous state causes sickle cell anemia
Heterozygous state causes/shows sickle cell
fomite
Heterozygous carrier parents
If both parents HbS(+) = Sickle Cell Anemia
HbS + HbA = Sickle cell Trait
HgS + HgS = Sickle cell Anemia
HgS + HgA = Sincle cell shape (carrier)
Embryonic Hemoglobin (Pregnant)
Gower 1
2 (epsilon) & 2 (zeta) chains
Gower 2
2 & 2 chains
Hemoglobin Portland
2 (zeta) & 2 gamma chains
1.
2.
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
HEMOGLOBINOMETRY
}
Screening test associated with anemia
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED OF HEMOGLOBIN
}
Hyperchromia
Increase intensity in the color of hemoglobin
}
Polycythemia
Increase in RBC
}
High altitude
Depletion of oxygen
Hypoxia will trigger the release of erythropoietin
in kidney Bone marrow RBC
}
Dehydration
Loss of fluid within the body
}
Heart disease
Patient with heart problem will have
hemoglobin pigmentation because of the
compensation of erythropoietin
FACTORS IN DECREASE HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION
}
Pregnancy
Competition for hemoglobin with the fetus
Ferric sulfide/iron supplements needed ^
}
Anemia
}
Women
Females naturally have low hemoglobin
because of menstruation
Males naturally have high hemoglobin because
of testosterone (which is associated with
maturation/production of RBCs)
Normal low hemoglobin counts
It is quite common for women to experience low
hemoglobin counts during pregnancy.
Some people might also experience this as a
natural way of life it is simply how their body
works.
Low counts in these cases shouldnt be alarming.
Conditions and diseases that cause fewer than normal
red blood cells
Some conditions can cause lower numbers of red
blood cells which can lead to a low hemoglobin
count
Anemia, cancer, cirrhosis (scarring/ tumor in the liver |
Kirros means yellow), kidney disease and lead
poisoning are just a few reasons.
Conditions and diseases that destroy red blood cells
Sometimes your body cant produce red blood cells
fast enough.
Conditions like Sickle cell anemia,
vasculitis(Inflammation of blood vessels) and an enlarged
spleen can all destroy red blood cells quickly
which leads to low hemoglobin.
Blood loss
Losing large amounts of blood can easily lead to
low hemoglobin.
This can also be a warning sign of internal blood
loss.
Vitamin deficiency
Vitamins such as B12 or foliate help your body
create red blood cells. If you arent getting enough,
your hemoglobin levels can drop
Blood disorders
Some conditions, such as some cancers, can lead
to low hemoglobin. These blood disorders mean
that your bone marrow isnt producing red blood
cells fast enough.
Aplastic anemia
Bone marrow disorder
Incapable of releasing RBC
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
This is a vitamin that helps your body absorb iron,
which is essential to hemoglobin production.
Eat foods that contain Vitamin C and take a
supplement that helps your body get even more of
it.
Other foods
The staples of a healthy diet can keep your
hemoglobin high.
Nuts of all kinds, fish and lean meats, poultry,
eggs, organ meats and even fortified cereals can
help.
Herbs
Iron deficiency
Iron is required to create hemoglobin, so if your
body needs more iron, your hemoglobin counts
are probably low.
In fact, this is the most common cause of
anemia
HOW TO INCREASE HEMOGLOBIN COUNTS
}
Fruits and vegetables
Look for fruits of all kinds and vegetables that are
bursting with leafy green color.
Cabbage, peas, beans, lettuce, broccoli and
tomatoes are good places to start.
You can opt for all kinds of fruits, such as
grapefruits, oranges, bananas, raspberries, kiwi
and mango
CAUSES OF LOW HEMOGLOBIN COUNTS
}
There are many herbs that up your hemoglobin
counts,
Including fenugreek seeds, rosemary, basil,
thyme, sage, nettle leaf and yellow dock root,
among others.
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
METHODS OF HEMOGLOBIN DETERMINATION
I.
Colorimetry
II.
Specific gravity method
III.
Gasometric
IV.
Chemical method
THINGS TO AVOID
}
Iron blockers
Anything that blocks iron absorption is bad.
Avoid things like coffee, foods with high levels of
fiber, tea, and some antacids and medications
}
I.
Foods with oxalic acid
This can prevent absorption, and should be
avoided.
Spinach is the biggest culprit among foods with
oxalic acid
Dont combine leafy green with fruits because it causes
very high oxalic acid
Foods with gluten
Wheat products, such as breads or pasta can
cause trouble for those who have gluten allergies.
But they can also lead to problems with iron, and
they can lead to low hemoglobin.
Reduce your intake of foods that contain gluten
Dares method
The blood is drawn through capillary
action between 2 glass plates
c)
Acid hematin
Hemoglobin in a known quantity of
blood in the presence of acid such as
0.1 N HCl is converted to acid
hematin. Which is brown colored
solution diluted with distilled water
drop by drop until it matches the
standard solution
d)
Sahli hellige method
Sahli hayden method
Sahli adam s method
Osgood-haskin method
New comer
Alkaline hematin
Same principle except we use an
alkaline solution produces alkaline
hematin
D.1 Wu method
D.2 Clegg and king method
Equivalent hemoglobin
Symptoms in children
The symptoms in children can be more severe, as
low hemoglobin can lead to long-term
consequences. Look for paleness, a rapid heart
beat, a lowered ability to concentrate, poor
neurological development and disturbed
behavior patterns
High hemoglobin in children are NORMAL
b)
C.1
C.2
C.3
C.4
C.5
Rare symptoms
Other symptoms that might occur but are relatively
rare include excessive sweating, vomiting and
persistent heartburn(because of too much acidity or very
low/decrease of hemoglobin).
You might experience swelling in your arms or
legs, and could even notice bloody stool when you
go to the bathroom
2 types
1) Direct visual colorimetry
a) A tallguist method
Measures hemoglobin using an
absorbent pad.
The color is match using a standard
White pasta/white bread inhibit proper absorption
SYMPTOMS OF LOW HEMOGLOBIN COUNTS
}
General symptoms
In general, the signs of low hemoglobin include
dizziness, headache, fatigue and a general
feeling or tiredness. It might be tough to
concentrate. You can experience an irregular
heartbeat or notice the skin, gums or nail beds
are very pale in color.
In addition, you might experience shortness of
breath, palpitations and chest pain with more
severe cases of low hemoglobin.
}
COLORIMETRY
14-18
gms
/dL
Male
12-16
gms
/dL
Female
14-26
gms
/dL
Children
GEN CAMATO
BLOOD
VOLUME
2)
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
Photoelectric colorimetry
a) Oxyhemoglobin method
Measures only normal hemoglobin
Reagent:
0.007N NH4OH or 0.1%
NaCo3 solution
Wavelength: 540nm
III.
GASOMETRIC METHOD
}
}
}
b)
Cyanment hemoglobin
Also known as ferriHbCN
Considered as the most accurate
method of hemoglobin determination
since It measures all Hb except the
Sulfhemoglobin
Reagents:
Drabkins reagent
KCN2 (Potassium cyanide)
K3Fe(CN)6 (potassium ferricyanide)
NaHCO3 (Sodium bicarbonate)
Distilled water
Principle: blood is diluted in a solution K3Fe(CN)6, KCN,
K3Fe(CN)6 oxidizes hemoglobin to hemoglobin. The
gemiglobin will further oxidize the KCN to form
cyanmethemoglobin and that cyanmethemoglobin has a
borad absorption max 540.
II.
IV.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY = DENSITY OF SUBSTANCE
DENSITY OF WATER
CuSO4 (Copper sulfate) METHOD
Commonly used in blood banks
Easily acquire fast
May start 1.055 in counting
Approximation of donors
Heavy CUSO4, the blood will sink & vice versa
Sink if:
>12.5 g/dL (can donate blood)
Suspended blood if:
<12.5 g/dL (rejected)
Another indirect method based on the principle that gram
of hemoglobin can carry 3.47 mg of Fe (Iron)
Ex.
Wongs
kennedys method
ABNORMAL HEMOGLOBIN
1) Several test for abnormal hb pigments:
a. Naked eye test
b. Dilution test
c. Alkali spot plate test
d. Katayamas test (Important, nakakalason sa dugo)
e. Hand spectroscopic test
f.
Spectrophotometric method
Ratio of the weight of a volume of the blood to the
ratio of the weight to the same volume of water at
room temperature.
CHEMICAL METHOD
}
SPECIFIC GRAVITY METHOD
}
Base on ability of hemoglobin to carry 1.34mL of
oxygen/gram of hemoglobin.
Also called indirect method
Disadvantage:
Abnormal hemoglobin may not be measure
Ex.
vanSlyke,
Haldane
smith
Be strong and of a good courage, fear not, nor be afraid of them:
for the LORD thy God, he it is that doth go with thee; he will not
fail thee, nor forsake thee.
- Deuteronomy 31:6
6
Você também pode gostar
- II. Renal FunctionDocumento3 páginasII. Renal FunctionDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- QA MonitoringDocumento3 páginasQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocumento7 páginasAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- QA MonitoringDocumento3 páginasQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- II. Renal FunctionDocumento3 páginasII. Renal FunctionDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- II. Renal FunctionDocumento3 páginasII. Renal FunctionDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- QA MonitoringDocumento3 páginasQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocumento3 páginasIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocumento7 páginasAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocumento3 páginasIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocumento7 páginasAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocumento3 páginasIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocumento7 páginasAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- I. Safety in The Clinical LabDocumento3 páginasI. Safety in The Clinical LabDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Scripture Songs: 1 Corinthians, 1 John, 1 PeterDocumento2 páginasScripture Songs: 1 Corinthians, 1 John, 1 PeterDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocumento3 páginasIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- GENDocumento2 páginasGENDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- QA MonitoringDocumento3 páginasQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- 4 HDocumento10 páginas4 HDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- 5 HDocumento4 páginas5 HDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- God's Love LetterDocumento1 páginaGod's Love LetterDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- 2HDocumento6 páginas2HDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Haemoglobin Opa ThiesDocumento4 páginasHaemoglobin Opa ThiesDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- ABBDocumento16 páginasABBDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Dna VirusesDocumento3 páginasDna VirusesDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Hematology LaboratoryDocumento3 páginasHematology LaboratoryDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Test CCDocumento3 páginasPractice Test CCDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- CC2 ChartDocumento2 páginasCC2 ChartDee Gee100% (1)
- PH Le BotomyDocumento4 páginasPH Le BotomyDee Gee100% (1)
- RBC Studies MidtermDocumento3 páginasRBC Studies MidtermDee GeeAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Pharmacology Lab (1) : Routes of Drug AdministrationDocumento14 páginasPharmacology Lab (1) : Routes of Drug AdministrationBotan AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical InfectionsDocumento310 páginasSurgical InfectionsOmar Ed ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- CH 142: Sepsis and Septic Shock ANSWERSDocumento2 páginasCH 142: Sepsis and Septic Shock ANSWERSTop VidsAinda não há avaliações
- Denial Codes 05aug2020Documento9 páginasDenial Codes 05aug2020naharmampillyAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive CocciDocumento11 páginasGram Positive CocciUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Complete Genetics Disease ChartDocumento14 páginasComplete Genetics Disease ChartJames FlanneryAinda não há avaliações
- Malaria effects and causesDocumento17 páginasMalaria effects and causesAnonymous XByxyTAinda não há avaliações
- Antimicrobial Activity of Disinfectants Commonly Used in The Food Industry in MexicoDocumento6 páginasAntimicrobial Activity of Disinfectants Commonly Used in The Food Industry in MexicoJoel CarinoAinda não há avaliações
- Autophagy and CancerDocumento349 páginasAutophagy and CancerSohibun21Ainda não há avaliações
- HESI Study Guide Psychiatric NursingDocumento26 páginasHESI Study Guide Psychiatric NursingDean Winchester100% (4)
- Winkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefDocumento4 páginasWinkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefKhalid Bin FaisalAinda não há avaliações
- The Privacy Isuues of AppleDocumento7 páginasThe Privacy Isuues of Applephysicser15Ainda não há avaliações
- Seizures in The Preterm NeonateDocumento10 páginasSeizures in The Preterm NeonateRoosevelt Santibañez Dla TorreAinda não há avaliações
- Vaccine Research StatusDocumento112 páginasVaccine Research StatusJunko Tsukuda100% (1)
- Intubasi Sulit: Nur Hajriya BrahmiDocumento26 páginasIntubasi Sulit: Nur Hajriya BrahmiFathiah HusainAinda não há avaliações
- Staph Lecture MicrococcusDocumento30 páginasStaph Lecture Micrococcussophia salibaAinda não há avaliações
- FNDRC Vol 2 AppendicesDocumento43 páginasFNDRC Vol 2 AppendicesJohn Michael Macabenta100% (1)
- WEEK 1 Lecture - Introduction - Student'sDocumento54 páginasWEEK 1 Lecture - Introduction - Student'smike angelo albacieteAinda não há avaliações
- Group 3 Team 1 - Case AnalysisDocumento14 páginasGroup 3 Team 1 - Case AnalysisLaureen CordovaAinda não há avaliações
- Expanding Consensus in Portal HypertensionDocumento29 páginasExpanding Consensus in Portal HypertensionJosé Pepo Apey Reinoso100% (1)
- Fetal Assessment DRDocumento1 páginaFetal Assessment DRMicah Lou CalambaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Save Your TeethDocumento193 páginasHow To Save Your TeethTanon Jaturonnatee100% (2)
- The Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocumento11 páginasThe Male and Female Reproductive SystemKelli McDaniel Marchbanks0% (1)
- Annex A. ChecklistDocumento2 páginasAnnex A. ChecklistroseannurakAinda não há avaliações
- Nice Neotech - Accessories - 20Documento1 páginaNice Neotech - Accessories - 20David Gnana DuraiAinda não há avaliações
- List of Consultants at KEM Hospital PuneDocumento8 páginasList of Consultants at KEM Hospital PuneRitesh AkhandeAinda não há avaliações
- The Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareDocumento3 páginasThe Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareScott PuckettAinda não há avaliações
- Substance AbuseDocumento16 páginasSubstance AbuseAkansha JohnAinda não há avaliações
- (Hema Manucript) Myelophthisic Anemia FINALCMPDocumento6 páginas(Hema Manucript) Myelophthisic Anemia FINALCMPJohney Doe100% (1)
- Toacs 5Documento244 páginasToacs 5Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)