Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
751-vdg ch05 Ques
Enviado por
Jaica Mangurali TumulakDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
751-vdg ch05 Ques
Enviado por
Jaica Mangurali TumulakDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
5
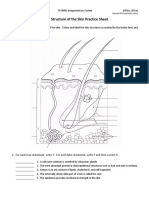
Integumentary System
I.
The Integument as an Organ
Concept: The integument (skin) is the largest organ of the body, and together with its accessory organs (hair,
glands, and nails), it constitutes the integumentary system. In certain areas of the body, it has adaptive
modifications that accommodate protective or metabolic functions. In its role as a dynamic interface between the
continually changing external environment, the skin helps to maintain homeostasis.
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1.
____
2. Which are accessory structures of the integument?
(a) sweat glands
(c) sebaceous glands
(b) fingernails
(d) all of the above
____
3.
Which statement concerning the integument is incorrect?
(a) It is the largest organ of the body.
(b) Its appearance and condition are clinically important.
(c) It protects the body and helps to regulate its function.
(d) It is of uniform thickness.
The skin is thinnest on
(a) the back of the hand.
(b) the tympanum.
(c)
(d)
the ankle.
the scalp.
____
4.
Which skin property is generally not of clinical importance?
(a) color
(c) temperature
(b) texture
(d) distribution of melanin
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
The integument is the largest organ of the body.
____
2.
Fingernails are not considered part of the integumentary system.
____
3.
The integument is of uniform thickness over the entire body.
II. Layers of the Integument
Concept: The integument consists of two principal layers. The outer epidermis is stratified into four or five
structural layers, and the thick and deeper dermis consists of two layers. The hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
connects the skin to underlying organs.
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1. The epidermal layer associated with cellular death and the initiation of keratinization is
(a) the stratum spinosum.
(c) the stratum lucidum.
(b) the stratum granulosum.
(d) the stratum corneum.
____
2.
The epidermal layer that is found only in the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet is
(a) the stratum granulosum.
(c) the stratum corneum.
(b) the stratum spinosum.
(d) the stratum lucidum.
____
3.
A needle would pierce the epidermal layers of the forearm in which order?
(a) basale, spinosum, granulosum, corneum
(b) basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum, corneum
(c) granulosum, basale, spinosum, corneum
(d) corneum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
____
4.
Which substance is not responsible for skin color?
(a) carotene
(c) keratin
(b) melanin
(d) hemoglobin
____
5.
Linea albicantes, or stretch marks, are due to tearing of
(a) the reticular layer.
(c) the papillary layer.
(b) the elastic layer.
(d) the hypodermal layer.
____
6.
Adipose cells are found in
(a) the papillary layer.
(b) the hypodermis.
(c)
(d)
the reticular layer.
the adipal layer.
____
7.
Which of the following is a false statement concerning the hypodermis?
(a) It is thicker in males than in females.
(b) It has abundant loose connective tissue.
(c) It stores lipids.
(d) It binds the dermis to underlying structures.
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
All races have virtually the same number of melanocytes.
____
2.
All races have virtually the same amount of melanin.
____
3.
Friction ridges are caused by the pull of elastic fibers within the dermis.
____
4.
Flexion lines are inherited.
____
5.
There are many more elastic fibers in the dermis of an elderly person than in the dermis of a young person.
____
6.
Vasodilation and vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the dermis regulate body temperature.
III. Functions of the Integument
Concept: The integument not only protects the body from pathogens and external injury, it is a highly dynamic
organ that plays a key role in maintaining body homeostasis.
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1.
Dehydration of terrestrial animals is prevented in part by
(a) vasoconstriction of blood vessels.
(b) keratinization of epidermal cells.
(c) cornification of epidermal cells.
(d) both b and c.
____
2.
Heat loss is associated with
(a) secretion of sweat.
(b) conduction of heat directly through the skin.
(c) radiation from dilated blood vessels.
(d) all of the above.
____
3.
Which muscles are attached to the hair follicles and cause goose bumps?
(a) arrectores integumentum
(c) levatores folliculum
(b) arrectores pilorum
(d) arrectores folliculum
____
4.
Which vitamin is synthesized in the skin in the presence of ultraviolet light?
(a) vitamin D
(c) vitamin A
(b) vitamin E
(d) vitamin K
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
The oily secretions of the skin form a protective alkaline film.
____
2.
The integument plays an important role in communication.
IV. Epidermal Derivatives
Concept: Hair, nails, and integumentary glands form from the epidermal layer, and are therefore of ectodermal
derivation. Hair and nails are structural features of the integument and have a limited functional role. By contrast,
integumentary glands are extremely important in body defense and maintenance of homeostasis.
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1.
Which is not part of a hair?
(a) shaft
(b) root
(c)
(d)
follicle
bulb
____
2.
____
3. Arrector pili muscles are
(a) skeletal muscles.
(b) follicle glands.
(c)
(d)
involuntary smooth muscles.
voluntary smooth muscles.
4. Fetal hair is referred to as
(a) definitive.
(b) angora.
(c)
(d)
nondefinitive.
lanugo.
____
Hair color is determined by
(a) the type of pigment produced in the stratum basale.
(b) the amount of pigment produced in the stratum basale.
(c) air spaces in the hair shaft.
(d) all of the above.
____
5.
A mans beard consists of which type of hair?
(a) definitive
(c) nondefinitive
(b) angora
(d) lanugo
____
6. Sebaceous glands secrete
(a) oil.
(b) sweat.
(c)
(d)
wax.
melanin.
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
Men and women have about the same density of hair on their bodies.
____
2.
Hair texture is determined by its cross-sectional shape.
____
3.
Lanugo is the soft, smooth hair on an infant.
____
4.
Apocrine glands are found in the palms of the hands.
____
5.
Mammary glands are specialized sudoriferous glands.
V. Developmental Exposition of the Integumentary System
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1.
____
2. The dermis is derived from
(a) mesoderm.
(b) endoderm.
During prenatal development, hair, glands, and nails form from
(a) mesoderm.
(c) endoderm.
(b) mesenchyme.
(d) ectoderm.
(c)
(d)
ectoderm.
periderm.
____
3.
At 6 weeks, the ectodermal layer differentiates into
(a) the periderm and vernix caseosa.
(b) the germinal layer and vernix caseosa.
(c) the periderm and germinal layers.
(d) the basal and germinal layers.
____
4.
Which gives rise to the entire epidermis and associated structures?
(a) the periderm
(c) the mesenchyme
(b) the germinal layer
(d) the vernix caseosa
____
5.
Which of the following structures is (are) associated with the development of hair follicles?
(a) hair papilla
(c) mesenchyme and epithelial cells
(b) germinal matrix
(d) all of the above
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
The epidermis, hair, glands, and nails all develop from the ectodermal germ layer.
____
2.
The periderm eventually becomes the vernix caseosa in prenatal development.
____
3.
Melanoblasts produce the dark pigment melanin.
____
4.
Sebaceous glands are actually oil glands.
____
5.
Mammary glands are modified sebaceous glands.
VI. Clinical Considerations
A.
Multiple Choice Questions
____
1.
Which skin disease is potentially life threatening?
(a) psoriasis
(c) erythema
(b) melanoma
(d) dermatitis
____
2.
What is the deepest layer affected by a second-degree burn?
(a) stratum basale
(c) dermis
(b) epidermis
(d) hypodermis
____
3.
Blisters followed by complete recovery are characteristic of
(a) first-degree burns.
(c) third-degree burns.
(b) second-degree burns.
(d) both a and b.
B.
TrueFalse Questions
____
1.
A successful skin transplant is rare because blood flow in the new tissue never becomes well established.
____
2.
Inflammation in an injured area confines the injury and promotes healing.
____
3.
Granulation tissue is formed from fibroblasts.
C.
Completion Questions
1.
In a severe wound, granulation tissue develops into ______________________ tissue.
2.
Brown, plaquelike patches called ______________________ ______________________ are typical on the exposed
portions of the skin of elderly people.
3.
Baldness, or ______________________, is due to genetic factors.
4.
______________________ is a type of skin cancer involving melanocytes.
D.
Matching Questions
Match the clinical term or condition on the left with its description on the right.
____
1. frostbite
(a) mole
____
2. acne
(b) benign epithelial neoplasm
____
3. nevus
(c) baldness
____
4. carbuncle
(d) bacterial infection
____
5. furuncle
(e) itching
____
6. comedo
(f) frozen skin
____
7. albinism
(g) plug of sebum in hair follicle
____
8. cold sore
(h) no melanin synthesis
____
9. alopecia
(i) boil
____ 10. pruritis
(j) herpes simplex virus
____ 11. papilloma
(k) inflammatory sebaceous glands
VII. Chapter Review
A.
1.
Completion Questions
The epidermis of the skin derives from the embryonic ______________________, whereas the dermis derives from
the ______________________.
2.
The integument (skin) is considered an ______________________ and accounts for approximately
______________________ % of a persons weight.
3.
The epidermis of the skin is protective because of the process of ______________________, which occurs in the
stratum granulosum, and the process of ______________________, which occurs in the stratum corneum.
4.
Pigment cells, called ______________________, occur in the stratum basale, where they produce dark coloration in
response to ultraviolet rays.
5.
A ______________________ ______________________, or bedsore, is an open lesion on the skin.
6.
When the bodys heat-producing mechanism cannot keep pace with heat loss, ______________________ results.
7.
After it is activated by ultraviolet light, the compound dehydrocholesterol found in the skin forms
______________________.
8 . The ______________________ ______________________ muscles attached to the hair follicles respond
involuntarily to thermal or psychological stimuli.
9 . Blocked ______________________ glands may become infected, resulting in acne.
10. ______________________ burns involve both the epidermis and dermis, causing blisters to appear. Recovery is
usually complete, but slow.
11. The skin of a fetus is covered by the ______________________ ______________________, which provides a
protective cheeselike coat.
12. Normal skin color results from a combination of melanin, ______________________, and ___________________.
13. ______________________ is a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from cardiovascular or respiratory
problems.
14. Stretch marks, or ______________________ ______________________, are white streaks on the skin resulting
from a tearing of the dermis.
15. ______________________ is a condition characterized by excessive body and facial hair, especially in women.
16. The three layers of hair are the inner medulla, the middle ______________________, and the outer
______________________.
B.
Matching Questions
Match the technical term on the left with its description on the right
____ 1 . keratin
(a) secretes earwax
____ 2 . lunula
(b) bluish discoloration
____ 3 . carotene
(c) fetal hair
____ 4 . sebum
(d) quick, or undersurface, of nail
____ 5 . hyponchium
(e) lipid secretion
____ 6 . lanugo
(f) yellowish pigment
____ 7 . sudoriferous
(g) crescent-shaped area of nail
____ 8 . cyanosis
(h) produced from tyrosine
____ 9 . ceruminous
(i) waterproofing protein
____ 10. melanin
(j) secretes perspiration
Você também pode gostar
- Effective Suction-Imporession For Retentive Mand Dentture PDFDocumento24 páginasEffective Suction-Imporession For Retentive Mand Dentture PDFFaheemuddin MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aDocumento5 páginasHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aKat Jornadal100% (1)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5No EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Catholic Social Teaching2Documento16 páginasCatholic Social Teaching2Jaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Group Case Study Obstetrics Group 5 From SMUDocumento84 páginasGroup Case Study Obstetrics Group 5 From SMUJosephine Mae TumanutAinda não há avaliações
- Newport, D.J. and Nemeroff, C.B. Neurobiology of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Cognitive Neuroscience JAARTALDocumento8 páginasNewport, D.J. and Nemeroff, C.B. Neurobiology of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Cognitive Neuroscience JAARTALg10564433Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Test Structure and Function of Skin: 2. The Blood CapillariesDocumento4 páginasBiology Test Structure and Function of Skin: 2. The Blood CapillariesAnanya ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- CH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemDocumento5 páginasCH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemKatieAinda não há avaliações
- Exam A - PDocumento10 páginasExam A - PAdvaith NairAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System WorksheetDocumento4 páginasIntegumentary System WorksheetLAQUESHA MAJORS0% (1)
- Chapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestDocumento18 páginasChapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestOregon190100% (6)
- Chapter 5 The Integumentary SystemDocumento25 páginasChapter 5 The Integumentary Systemlolasparkle100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 6th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento46 páginasAnatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 6th Edition Saladin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFhuonghuyen2cp9ez100% (13)
- Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 6th Edition Saladin Test BankDocumento25 páginasAnatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 6th Edition Saladin Test Bankcinderyburhcfc03100% (29)
- Week 6 Integumentary WorksheetDocumento2 páginasWeek 6 Integumentary WorksheetAthia ZamanAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System Lab ExerciseDocumento12 páginasIntegumentary System Lab Exercisekams sardinesAinda não há avaliações
- 8Documento11 páginas8caripe22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary SystemDocumento5 páginasThe Integumentary SystemLeona Marie Doctor100% (1)
- Seatwork # 10 Grade 7 - Haniel A.Y 18-19 Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocumento2 páginasSeatwork # 10 Grade 7 - Haniel A.Y 18-19 Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerNicole Daphne AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual Cat Version 2Nd Edition Sarikas Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento28 páginasVisual Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual Cat Version 2Nd Edition Sarikas Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrappelpotherueo100% (7)
- Anaphy IntegumentaryDocumento3 páginasAnaphy IntegumentaryArcher RiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System General Directions: Answer The Following Questions Intelligently and Supply AllDocumento4 páginasIntegumentary System General Directions: Answer The Following Questions Intelligently and Supply AllDANIEL LANCE NEVADOAinda não há avaliações
- Ehap 12e Chapter 04 (Skin and Body Membranes) Test With Answers - Human Anatomy Test BankDocumento25 páginasEhap 12e Chapter 04 (Skin and Body Membranes) Test With Answers - Human Anatomy Test Bankpeter domasAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm ReviewerDocumento17 páginasMidterm ReviewerMa Anna Cris LumongsudAinda não há avaliações
- Full Download Test Bank For Human Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13Th Edition Elaine N Marieb Lori A Smith PDFDocumento26 páginasFull Download Test Bank For Human Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13Th Edition Elaine N Marieb Lori A Smith PDFalice.maxam777100% (11)
- Skin WorksheetDocumento2 páginasSkin WorksheetUZ - 11VT 686029 Lincoln Alexander SSAinda não há avaliações
- Campus Collusio N: Review Questions For Test PreparationDocumento3 páginasCampus Collusio N: Review Questions For Test PreparationGenna LedesmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Integumentary Answer KeyDocumento10 páginasThe Integumentary Answer KeyLeona Marie DoctorAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemDocumento9 páginasBiology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemNicole Athena CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Science6 ST1 Q2Documento2 páginasScience6 ST1 Q2GRACE GLORIANEAinda não há avaliações
- Science6 ST1 Q2Documento2 páginasScience6 ST1 Q2Dave Banay Yabo, LPTAinda não há avaliações
- Science6 ST1 Q2Documento2 páginasScience6 ST1 Q2Cecilia TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Anaphy IntegumentaryDocumento3 páginasAnaphy IntegumentaryArcher RiegoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - Assessing Skin, Hair & NailsDocumento8 páginas1 - Assessing Skin, Hair & NailsFrancine Julia MorilloAinda não há avaliações
- Analec ExamDocumento5 páginasAnalec ExamVin BaniquedAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Study Question Chp3Documento10 páginasAnatomy Study Question Chp3Hema JothyAinda não há avaliações
- English For MedicineDocumento52 páginasEnglish For MedicineRoya NaderiAinda não há avaliações
- Ch. 5 Student Packet (ANP 1)Documento8 páginasCh. 5 Student Packet (ANP 1)Alex ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Year BiologyDocumento3 páginas2nd Year BiologyAbbas KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank 1Documento33 páginasIntroduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank 1dorothy100% (37)
- Introduction To The Human Body 10Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasIntroduction To The Human Body 10Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrichard.nichols145100% (13)
- Pretest-Skin, Nail, HeadDocumento1 páginaPretest-Skin, Nail, HeadJohnard B. RebatoAinda não há avaliações
- BIO201L Lab 5 TissuesDocumento12 páginasBIO201L Lab 5 Tissuesmyra Thiong'oAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test Bank 1Documento31 páginasPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test Bank 1lucile100% (49)
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmary.bethea195100% (11)
- General Biology I QuizDocumento2 páginasGeneral Biology I QuizBenedicto IluminAinda não há avaliações
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test BankDocumento39 páginasHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test Bankscarletdrusillaplwrd100% (29)
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento60 páginasHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 15Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJakeOwensbnpm100% (10)
- Technology and Livelihood Education 9Documento2 páginasTechnology and Livelihood Education 9May S. VelezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 05 - The Integumentary SystemDocumento14 páginasChapter 05 - The Integumentary SystemTran Mong HangAinda não há avaliações
- Genral Path MCQDocumento171 páginasGenral Path MCQAbir AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Bio 104 Final Exam Spring 2013 AnsDocumento5 páginasBio 104 Final Exam Spring 2013 AnsjaderainbowAinda não há avaliações
- Human Body Test: Multiple ChoiceDocumento10 páginasHuman Body Test: Multiple ChoiceClifford FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 12th Edition David ShierDocumento51 páginasTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 12th Edition David ShierAlexaGreenmdyor100% (34)
- Integumentary System Test-GeneralDocumento5 páginasIntegumentary System Test-GeneralZhedriex EspirituAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System - WatermarkedDocumento12 páginasIntegumentary System - WatermarkedMufeeda PkAinda não há avaliações
- 165 Assignment 2Documento3 páginas165 Assignment 2anon-796869Ainda não há avaliações
- IX Biology Pre Exam PaperDocumento3 páginasIX Biology Pre Exam PaperSania JavedAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary System NotesDocumento5 páginasIntegumentary System NotesLeasxz ZxsaelAinda não há avaliações
- Review Assessment: Chapter 005: Reviewing Facts & Terms: Multiple-ChoiceDocumento10 páginasReview Assessment: Chapter 005: Reviewing Facts & Terms: Multiple-ChoicebethsaidajynAinda não há avaliações
- Biology How Life Works 2Nd Edition Morris Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento54 páginasBiology How Life Works 2Nd Edition Morris Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbierbalkgeorge3f17100% (12)
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 13Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFelizabeth.hayes136100% (15)
- Molecular Biology: Y19E - Group 25Documento18 páginasMolecular Biology: Y19E - Group 25Lương Tuấn KiệtAinda não há avaliações
- Checklist of Requirements For SPPDocumento1 páginaChecklist of Requirements For SPPJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- NOTES On CDRRHRDocumento8 páginasNOTES On CDRRHRJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Generic NameDocumento1 páginaGeneric NameJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin A FunctionsDocumento2 páginasVitamin A FunctionsJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Problems in Quality Control 1Documento17 páginasSample Problems in Quality Control 1Jaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 Loose Tabelets and Capsules IdentifierDocumento5 páginas2015 Loose Tabelets and Capsules IdentifierJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Salicylates: Common Name: Acetylsalicylic Acid IUPAC Name: 2-Acetoxybenzoic Acid Molecular Formula: C H ODocumento3 páginasSalicylates: Common Name: Acetylsalicylic Acid IUPAC Name: 2-Acetoxybenzoic Acid Molecular Formula: C H OJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Rev. Fr. Rolando M. Castro: Vice Rector For FinanceDocumento1 páginaRev. Fr. Rolando M. Castro: Vice Rector For FinanceJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Administrative Order No. 55, SDocumento4 páginasAdministrative Order No. 55, SJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Exp4 SeriesParallelDocumento6 páginasExp4 SeriesParallelJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- To Be A "Makabayan": The Essence of NSTP For MeDocumento2 páginasTo Be A "Makabayan": The Essence of NSTP For MeJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- General Characteristics: NematodesDocumento27 páginasGeneral Characteristics: NematodesJaica Mangurali Tumulak100% (1)
- Bataan Nuclear Power Plant Impossible To ReviveDocumento5 páginasBataan Nuclear Power Plant Impossible To ReviveJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento1 páginaPhysicsJaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Variation: Physics 201 Laboratory Experiment 0Documento15 páginasVariation: Physics 201 Laboratory Experiment 0Jaica Mangurali TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders PDFDocumento31 páginasEndocrine and Metabolic Disorders PDFAna-Maria50% (2)
- 11 Ch1208 5127 PDFDocumento25 páginas11 Ch1208 5127 PDFThamarai ElanthirayanAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3 & 4 (Module 3)Documento4 páginasActivity 3 & 4 (Module 3)Marvin GasparAinda não há avaliações
- Bche 4090 1155168548Documento7 páginasBche 4090 1155168548Yenny TsaiAinda não há avaliações
- Ophthalmology PDFDocumento92 páginasOphthalmology PDFMarwa AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Extended SexDocumento18 páginasExtended SexMaría Alejandra MartínezAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocumento8 páginasWorksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsCarlos GuardadoAinda não há avaliações
- Weeks 3 - 8Documento32 páginasWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonAinda não há avaliações
- Form 86 - Health FormDocumento1 páginaForm 86 - Health Formbogtik100% (1)
- Funda 7Documento19 páginasFunda 7Akia Cayasan BayaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyStephannie MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular and Cell Biology of CementumDocumento26 páginasMolecular and Cell Biology of CementumSaul TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Oriflamebeautyacademy SkincareDocumento173 páginasOriflamebeautyacademy Skincareapi-37629474750% (2)
- A Study On Employee MotivationDocumento113 páginasA Study On Employee Motivationk eswari100% (2)
- Psych Motivation & EmotionsDocumento13 páginasPsych Motivation & EmotionsnasibdinAinda não há avaliações
- STGT-16, Biological ScienceDocumento44 páginasSTGT-16, Biological ScienceagnibeshAinda não há avaliações
- Metabolic Fingerprinting of Cannabis Sativa L., Cannabinoids and Terpenoids PDFDocumento16 páginasMetabolic Fingerprinting of Cannabis Sativa L., Cannabinoids and Terpenoids PDFciborg1978100% (1)
- 22 Stretches To Improve Your Flexibility For PoleDocumento10 páginas22 Stretches To Improve Your Flexibility For PoleSarah86% (7)
- Human Body EssayDocumento1 páginaHuman Body EssayAtlas CruxAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 20 - Embryology of The Genitourinary Tract - Campbell - Walsh-Wein UROLOGY 12thDocumento40 páginasChapter 20 - Embryology of The Genitourinary Tract - Campbell - Walsh-Wein UROLOGY 12thkrisnaAinda não há avaliações
- Early Complications of MIDocumento11 páginasEarly Complications of MIjen262004Ainda não há avaliações
- Shoku AnafilaktikDocumento16 páginasShoku AnafilaktikindeenikeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual DownloadDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual DownloadMark Prindle100% (20)
- An Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate SynthesisDocumento13 páginasAn Essential Role of The Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is To Enable Aspartate Synthesisyylf2016Ainda não há avaliações
- II. Blood Vessels Physiology By: Dr. Abdulrahman Aqra MD MSCDocumento12 páginasII. Blood Vessels Physiology By: Dr. Abdulrahman Aqra MD MSCapi-290338101Ainda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Tests InterpretationDocumento12 páginasLaboratory Tests InterpretationKaloy Kamao100% (1)
- Updates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCDocumento7 páginasUpdates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCLenin Zavaleta RodriguezAinda não há avaliações