Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2013 Chemistry
Enviado por
Ganeshwaran KumaresenDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
2013 Chemistry
Enviado por
Ganeshwaran KumaresenDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
SMK TINGGI MELAKA
Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan
PROGRAM GOLDEN HOLIDAY
(PGH)
Siri 1/2013
Modul Latihan Topikal
KIMIA
(Kimia Itu Mudah, Insyaallah A)
Panitia Sains
(Kimia)
MELIORA HIC SEQUAMUR
KE ARAH KECEMERLANGAN PENDIDIKAN
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
PAPER 2: STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
SECTION A
1
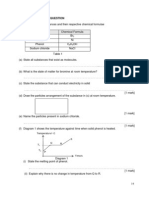
The table 1 below shows the description and observation for two experiments involving two solutions:
Hydrogen chloride in solvent X
Hydrogen chloride in solvent Y
Experiment
Observation
Description
HCl in solvent X
HCl in solvent Y
Reaction of hydrogen chloride in
solvent X and solvent Y with
calcium carbonate lumps.
Effervescence occurs. A
colourless gas is
liberated.
No change occur
II
Electrolysis of hydrogen chloride in
solvent X and solvent Y
Reading of the ammeter
is 1 A
Reading of the
ammeter is 0 A.
Table 1
(a)
Name a suitable compound for
Solvent X : ..................................................................................................................................
Solvent Y: ....................................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
(b)
(i)
Which of the solution shows acidic properties?
.........................................................................................................................................
(ii)
What is the role of solvent in (b) (i) that enables the solution to show acidic properties?
..........................................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
(c)
(i)
Effervescence occurs when hydrogen chloride in solvent X react with calcium
carbonate. Name the gas liberated.
......................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(ii)
Describe a chemical test to identify the gas liberated in (c) (i)
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
[ 2 marks]
(iii)
Write ionic equation for the reaction in (c) (i).
......................................................................................................................... [4 marks]
(d)
Hydrogen chloride in solvent X can conduct electricity but hydrogen chloride in solvent Y cannot
conduct electricity. Explain why.
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
(e)
-3
Calculate the mass of hydrogen chloride gas, HCl to prepare 100 cm of 0.5 mol dm HCl acid.
[Given that the relative atomic mass of H = 1, Cl = 35.5 , C = 12, O = 16 , Ca = 40 ]
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
[3 marks]
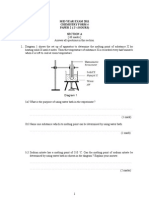
2
Diagram 2 shows series of reactions for the preparation of copper(II) chloride from copper(II)
carbonate.
Step I
Copper(II) carbonate
Solid X
Carbon dioxide gas
Step II
Excess solid X is added to dilute hydrochloric
acid
Solution R
Step III
Copper(II) chloride
Diagram 2
Based on the diagram,
(a) (i) name the solid X
[1 mark]
(ii) suggest how to change copper(II) carbonate to solid X in step I.
[1 mark]
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to show the apparatus set-up that can be used to produce solid X and
identify gas Y in step I.
[2 marks]
(b) (i) Why is excess of solid X added to the heated dilute hydrochloric acid in step II?
[1 mark]
(ii)Write the chemical equation for the reaction in step II.
[1 mark]
(c) Describe how copper(II) chloride crystals are obtained from solution R in step III.
[3 marks]
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
The diagram 3 shows the formation of lead(II) nitrate and its changes to other compounds.
Lead(II) oxide
+ compound J
Lead(II) nitrate
Brown gas
+ copper(II) chloride solution
Compound Z + copper(II) nitrate
Diagram 3
(a)
(i)
Lead(II) oxide has reacted with compound J to form lead(II) nitrate. Name compound J
(ii)
..............................................................................................................................[1 mark]
Write the chemical equation for the reaction in (a) (i)
...........................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(b)
(i)
Name the brown gas.
............................................................................................................................[1 mark]
(ii)
(c)
Write the chemical equation for the reaction in (b) (i)
..........................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
When copper(II) chloride solution is added to lead(II) nitrate solution, a precipitate Z and
copper(II) nitrate are produced.
(i)
Name the type of reaction that occurs.
(ii)
.............................................................................................................................[1 mark]
Write the ionic equation for the formation of compound Z.
...........................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(iii)
State how compound Z is separated from copper(II) nitrate.
...........................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(d)
Sodium hydroxide solution is added a little at a time to lead(II) nitrate solution until in excess.
What is the observation?
........................................................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
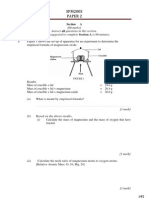
10.0 cm of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium iodide is poured to 8 different test tubes. Different volume of 1.0
mol dm-3 lead(II) nitrate are added to each test tube. The height of precipitate formed in each test
tube is measured.
The graph 4 below is obtained when the height of precipitate is plotted against the volume of lead(II)
nitrate solution.
Height of
precipitate/
cm
Volume of lead(II)nitrate / cm3
1 2
(a)
8
Graph 4
Name the precipitate formed.
.......................................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(b)
3
3
10 cm of 1.0 mol dm-3 lead(II) nitrate is added to 10 cm of 1.0 mol dm-3
solution. Estimate the height of the precipitate formed.
sodium iodide
......................................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(c)
(d)
Based on the above graph, what is the volume of lead(II) nitrate needed to completely react
with sodium iodide solution?
.....................................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
Calculate
(i) the number of moles of sodium iodide in the reaction.
[1 mark]
(ii) the number of moles of lead(II) nitrate that has completely reacted with sodium iodide
solution
[1 mark]
(e)
Write the ionic equation for the formation of the precipitate.
......................................................................................................................................................
[ 1 mark ]
(f)
The concentration of lead(II) nitrate is changed from 1.0 mol dm -3 to 2.0 mol dm-3 . Sketch the
graph obtained on the above graph.
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
[ 1 mark]
PAPER 2 ESSAY
5
(a) Name a soluble salt and an insoluble salt.
Write a chemical equation for the preparation of each type of salt given by you.
[4 marks]
(b) You are given zinc nitrate crystals. Describe how you can perform a chemical test to confirm the
presence of zinc ions and nitrate ions in the zinc nitrate crystals.
[6 marks]
(c) You are required to prepare magnesium nitrate salt from the chemical substances provided below.
Magnesium sulphate solution
Dilute nitric acid
Sodium carbonat solution
Your answer should include all the chemical equations involved in the reactions.
[10 marks]
6 (a)
11.2 g of solid potassium hydroxide, KOH, is dissolved in distilled water to produce a solution of
1000 cm3. The solution produced has the concentration of 11.2 g dm -3 and molarity of x mol dm-3.
(i)
State the meaning of the molarity for the solution produced.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Write the formula that represents the relationship between the number of mole (n), molarity (M)
and volume (V) for the solution.
[1 mark]
(iii)
Find the value of x.
[Relative atomic mass of H=1, O=16, K=39]
[3 marks]
(b) Table 12 shows the results of an experiment to compare the strength of acids.
Acid
Hydrochloric acid of 0.1 mol dm-3
pH value
1
Ethanoic acid of 0.1 mol dm-3
4
Table 12
Explain why the pH values of hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid in Table 12 are different.
[ 5 marks]
(c)
(i)
(ii)
State two preparation method of soluble salts.
Silver chloride is an insoluble salt. With the aid of labelled diagrams, describe how to
prepare silver chloride from silver nitrate.
[10 marks]
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
PAPER 3
7
A student carried out a titration process using hydrochloric acid solution to determine the unknown
concentration of a sodium hydroxide solution. 25 cm 3
of sodium hydroxide solution is poured into a
conical flask. Three drops of phenolphtalein is added to the sodium hydroxide solution. The solution is then
titrated with 0.1 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid from a burette. The titration process is carried out until the end
point is obtained. Initial and final burette reading for the three titrations carried out are shown in Diagram 7
below.
Initial
reading
Final reading
Initial
reading
Titration 1
Final reading
Initial
reading
Final reading
Titration 3
Titration 2
Diagram 7
State the colour change in the conical flask at the end point.
(a)
[3 marks]
Based on the Diagram 16 above, complete the table below.
(b)
Number of titrations
Final reading/cm3
Initial reading/cm3
Volume of hydrochloric
acid solution used/cm3
[3 marks]
(c)
What is the average volume of the hydrochloric acid used to neutralise exactly
25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution?
Titration
[3 marks]
(d)
Based on your answer in (c), determine the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution.
[3 marks]
(e) Predict the volume of the acid used that can neutralise 25 cm 3 of the same sodium
hydroxide solution if the hydrochloric acid solution is being replaced by:
(i)
ethanoic acid 0.1 mol dm-3
(ii)
sulphuric acid 0.1 mol dm-3
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
[3 marks]
Table 8 below shows the data obtained by a student to investigate the relationship between the
concentration of acid with the pH value of hydrochloric acid. The standard concentration of
each solution is 0.1 mol dm3. The solution is then diluted to give solutions with different concentrations.
pH value for each solution is determined with a pH meter and the value recorded.
Concentration / mol dm-3
pH value
0.1
1.0
0.01
0.001
0.0001
0.00001
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
Table 8
(a) Based on the information above, complete the table below.
Name of variables
Action to be taken
(i) Manipulated variable:
(i) The way to manipulate variable:
..
....
................
(ii) Responding variable:
(ii) What to observe in the responding variable:
..
..
(iii) Controlled variable:
(iii) The way to maintain the controlled variable:
....
[6 marks]
(b) State the hypothesis of the experiment.
.........................................................................................................................................................
..
.........................................................................................................................................................
.
[3 marks]
(c) Why does the pH value of hydrochloric acid increase when the concentration decreases?
.
[3 marks]
(d) Why hydrochloric acid solution with the same concentration with ethanoic acid solution has a
lower pH value?
...
..
[3 marks]
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
Sample answer
1
(a) X
Y
water
[organic solvent], example : benzene/ toluene / tetrachloromethane
1
1
(b) (i)
(ii)
HCl in solvent X / water
HCl molecules ionize to produce hydrogen ion / H+
(c) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
Carbon dioxide
Passed the gas through the lime water, the lime water turn chalky
2H+ + CO32- CO2 +
H2O
1
1
1
1
(a) In solvent X / water, hydrogen chloride molecules ionize to produce free moving ions /
H+ and ClIn solvent Y / [organic solvent] hydrogen chloride remains in the form of molecules
/ do not ionize
(e) Number of mol of HCl
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
= MV/1000
= 0.5 x 100
= 0.05
1000
= number of mol x molar mass of HCl
= 0.05 x 36.5
= 1.825 g
Mass of HCl
2 (a)
1
1
1
Copper(II) oxide
Heat strongly // heat
1
1
Copper(II) carbonate
Lime water
Heat
(b)(i)
(ii)
(c)
3(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
All hydrochloric acid has reacted
CuO + 2HCl CuCl2 + H2O
Heat the solution until saturated, cool the solution , filter and dry with filter paper
(i)
(ii)
Nitric acid (dilute)
PbO + 2HNO3
(i)
(ii)
Nitrogen dioxide
2Pb(NO3)2
Pb(NO3)2
H 2O
2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
1+1
1
1
1+1+1
1
1
1
1
(i)
Precipitation reaction /Double decomposition
(ii)
Pb2+
(ii)
Filter, rinse with distill water
2Cl-
White precipitate
Dissolve in excess of sodium hydroxide
PbCl2
solution
1
1
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
4.(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Lead(II) iodide
5 cm
5 cm3
(i)
(ii)
(e)
(f)
Pb2+
1
1
1
the number of mole of sodium iodide
= 1 x 10.0 // 0.01 mol
1000
the number of mole of lead(II) nitrate
= 1 x 5 // 0.005 mol
1000
+ 2I- PbI2
1
1
1
5
1
2.5
5 (a)
(b)
Soluble salt: copper(II) sulphate
Insoluble salt: barium sulphate
H2SO4
H2SO4
+
+
CuO
CuCO3
BaCl2
Na2SO4
1
2
3
4
5
6
(c)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
1
CuSO4 + H2O //
CuSO4 + H2O
BaSO4
CO2
2NaCl
1..4
Zinc nitrate crystals are dissolved in distilled water and the solution is divided into two
portions in two test tubes.
1
For the first portion, ammonia solution is added drop by drop untill in excess.
1
A white precipitate is formed and insoluble in excess ammonia solution.
1
For the second portion, dilute sulphuric acid is added follow by iron(II) sulphate solution.
The mixture is shaken well.
1
Then, concentrated sulphuric acid is added carefully down the side of the test tube. 1
A brown ring is formed.
1..6
Magnesium sulphate solution is added to sodium carbonate solution in a beaker.
The mixture is shaken well/ stirred and a white solid, MgCO 3 is formed.
The white precipitate is filtered out and rinsed with distilled water.
The white precipitate is added to the nitric acid in a beaker until in excess/
some of it no longer dissolve
The excess white precipitate is filter out.
The filtrate is poured into an evaporating dish.
The salt solution is gently heated until saturated.
The hot saturated salt solution is allowed to cool for crystals to form.
The crystals formed are filtered out, washed with a little cold distilled water.
and dried between sheets of filter paper.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 8
10 Chemical equations:
MgSO4
MgCO3
+
+
Na2CO3
2HNO3
MgCO3
+
Na2SO4
Mg(NO3)2 +
H2O
10
+ CO2
1
1..10
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
6(a)
(b)
(i) Number of moles of solute//potassium hydroxide that are present in 1 dm 3 of solution
(ii) n= MV // MV/1000
1
(iii) Relative molecular mass of KOH = 39 + 16 + 1 = 56
Molarity of KOH = 11.2/56
= 0.2 mol dm-3
- Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid whereas ethanoic acid is a weak acid
- Ethanoic acid ionise partially in water to produce a low concentration of hydrogen ions.
- Hydrochloric acid ionise completely in water to produce a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
- The concentration of hydrogen ions in hydrochloric acid is higher than that in ethanoic acid.
- Thus, hydrochloric acid has lower value of pH compared to ethanoic acid
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(c) (i) - Reaction between acid and alkali
- Reaction between acid and metal oxide
- Reaction between acid and reactive metal
- Reaction between acid and metal carbonate
( Any 2 from above)
1
1
1
(ii) - 50 cm3 of 1 mol/dm-3 silver nitrate is measured using a measuring cylinder and poured into a
beaker
- 50 cm3 of 1 mol/dm-3 sodium chloride [any chloride solution] is measured using a measuring
and poured into silver nitrate solution
- The mixture is stirred.
- The mixture is filtered.
- The residue/silver chloride is washed with a little cold distilled water
- and dried between sheets of filter paper.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1+1
11
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
Paper 3
Question
7(a)
Rubric
Pink to colourless
Titration Number
Final reading
Initial reading
Volume of hydrochloric acid used
(b)
(c)
[Steps for calculation]
24.70 cm3
(d)
[Steps for calculation]
0.0988 mol/dm3
(e) (i)
Volume is bigger than 24.70 cm3
(e) (ii)
12.35 cm3
Question
8 (a) (i)
1
24.90
0.10
24.80
2
49.50
24.90
24.60
3
25.70
1.00
24.70
Rubric
Manipulated variable:
Way to manipulate:
Concentration of hydrochloric
acid
Dilute the acid to different concentrations: 0.1
mol dm-3, 0.01 mol dm-3, 0.001 mol dm-3, 0.0001
mol dm-3, dan 0.00001 mol dm-3
What to observe:
The lower the concentration of hydrochloric acid,
the bigger the pH value.
Way to fix the variable
Use the same type of acid in each experiment
Responding variable
pH value
Fixed variable:
Type of acid
8(a) (ii)
The higher the concentration of acid, the lower the pH value.
(b)
The concentration of the hydrogen ions, H+ in the acid decreases
(c)
Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, that will ionise completely in water to give high concentration
of H+ ions.
Ethanoic acid is a weak acid, ionise partially in water to low concentration of H + ions.
12
Modul Latihan KIMIA (Kimia Itu Mudah, Inshaalah A)
13
Você também pode gostar
- CHEM 1110 Practice FinalDocumento14 páginasCHEM 1110 Practice FinalEric CabarloAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 4 Quiz AnswerDocumento8 páginasChemistry Form 4 Quiz Answerkhangsiean89Ainda não há avaliações
- pg10 12Documento3 páginaspg10 12Melor DihatiAinda não há avaliações
- Bengkel Ambang SPM 2009 Kertas 2Documento31 páginasBengkel Ambang SPM 2009 Kertas 2azharsarahAinda não há avaliações
- 2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Documento15 páginas2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Nicholson NicholsonAinda não há avaliações
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Documento15 páginasLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Farah Aisyah AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Irp Set 2Documento22 páginasIrp Set 2rajaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocumento12 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiEmily VinciAinda não há avaliações
- Projek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Documento9 páginasProjek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Zul BaidiAinda não há avaliações
- SOALANnnDocumento13 páginasSOALANnnKeertanaAinda não há avaliações
- Section B: Structured Questions (65 Marks) : F.4 Chemistry Final Exam (2010-2011)Documento8 páginasSection B: Structured Questions (65 Marks) : F.4 Chemistry Final Exam (2010-2011)harrynghomanAinda não há avaliações
- Panduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaDocumento12 páginasPanduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaChew Boon WeiAinda não há avaliações
- Form Four Revision On ChemistryDocumento17 páginasForm Four Revision On Chemistrypatkhsheng@hotmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Trial 2012Documento14 páginasChem Trial 2012Han LingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Documento13 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgAinda não há avaliações
- Diagram 1.1: Revision For Year End ExaminationDocumento16 páginasDiagram 1.1: Revision For Year End ExaminationsookchinAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 5070 End of YearDocumento7 páginasChemistry 5070 End of Yearsamuelbandamiracle20Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocumento12 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiSakinah Saad100% (3)
- PPC SPM 2023 k2 BHGN A No 5-7Documento6 páginasPPC SPM 2023 k2 BHGN A No 5-7NORHEDAYAH BINTI MOHD JANI KPM-GuruAinda não há avaliações
- ExercisesDocumento4 páginasExercisesAini MunirahAinda não há avaliações
- Lira Town College: End of Term Iii Examinations 2018 P525 / 1 Chemistry Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinsDocumento11 páginasLira Town College: End of Term Iii Examinations 2018 P525 / 1 Chemistry Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinsSamuel TusubiraAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper Jan 2003 Unit-3BDocumento8 páginasQuestion Paper Jan 2003 Unit-3BJavaria JavaidAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry (233) Mind JogDocumento23 páginasChemistry (233) Mind JogNishad EsdorAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 Section A: Temperatur E/ C S Q RDocumento5 páginasPaper 2 Section A: Temperatur E/ C S Q RNor Azrul IkwanAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Documento19 páginasSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongAinda não há avaliações
- Form 4 Acids Bases and Salts Questions Teacher - Co .KeDocumento9 páginasForm 4 Acids Bases and Salts Questions Teacher - Co .KeMikeAinda não há avaliações
- STPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2Documento13 páginasSTPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (1)
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Documento16 páginasSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 11 PDFDocumento25 páginasChemistry 11 PDFChanda S MwambaAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Chemistry QuestionDocumento6 páginasSPM Chemistry QuestionSaya MenangAinda não há avaliações
- Ionic Equations & Redox ReactionsDocumento6 páginasIonic Equations & Redox ReactionsAyaanNashidAinda não há avaliações
- Chem pp4Documento8 páginasChem pp4antonettemosweu211Ainda não há avaliações
- Diagram 1: Black CoffeeDocumento9 páginasDiagram 1: Black CoffeeNoorisha MusaAinda não há avaliações
- Strode's College 1Documento132 páginasStrode's College 1Jann ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- 8 SaltsDocumento13 páginas8 SaltswanyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 2Documento5 páginasChemistry 2Rak boyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7: Acid and Bases: Name: .. Class: DateDocumento8 páginasChapter 7: Acid and Bases: Name: .. Class: DateAzie Nurul AkhtarAinda não há avaliações
- Exam Chapter 1 and 2 Model ADocumento10 páginasExam Chapter 1 and 2 Model AMuhamed MahmoudAinda não há avaliações
- Bengkel Ambang SPM 2009paper 2Documento31 páginasBengkel Ambang SPM 2009paper 2Mimi MaliniAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Two Questions From Section A, One Question From Section B, Two Questions From Section C and One Other Question. Section ADocumento6 páginasAnswer Two Questions From Section A, One Question From Section B, Two Questions From Section C and One Other Question. Section AKarren MakamureAinda não há avaliações
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM AnswerDocumento15 páginasLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM AnswerSabrina BanksAinda não há avaliações
- LS Exam PT 2018Documento17 páginasLS Exam PT 2018NIRVAN RAMESHAinda não há avaliações
- spm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Documento14 páginasspm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Suriati Bt A RashidAinda não há avaliações
- Maple Leaf International School: Half Yearly Examination 2021 Subject: CHEMISTRY Class: IX Total Marks: 60Documento13 páginasMaple Leaf International School: Half Yearly Examination 2021 Subject: CHEMISTRY Class: IX Total Marks: 60SN EDUCATIONAinda não há avaliações
- Kerja Cuti TerancangDocumento4 páginasKerja Cuti TerancangEman AllyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Chemical in IndustryDocumento8 páginasChapter 8 Chemical in IndustryADY2022Ainda não há avaliações
- Test On Group II ElementsDocumento5 páginasTest On Group II ElementsKoo Keung EngAinda não há avaliações
- Stoichiometry 5 QPDocumento5 páginasStoichiometry 5 QPCHANDREN ARUMUGAM0% (1)
- Chemistry 11Documento5 páginasChemistry 11Jucken MulengaAinda não há avaliações
- Balanced Equations & Associated Calc's 13 QPDocumento9 páginasBalanced Equations & Associated Calc's 13 QPjade.davis0019Ainda não há avaliações
- Jan 2019Documento27 páginasJan 2019Mariyam ManaarathAinda não há avaliações
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocumento6 páginasAnswer All Questions in This SectionAri AdiantariAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Documento12 páginas1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMISTRY-P2-Teacher Co KeDocumento8 páginasCHEMISTRY-P2-Teacher Co KeASSIGNMENTS PRIORITYAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsNo EverandIndustrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Novel Carbon Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties and ApplicationsNo EverandNovel Carbon Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties and ApplicationsXin JiangAinda não há avaliações
- Pcculiarities Bdelloida) Growth and Reproduction Under Various Temperature ConditionsDocumento17 páginasPcculiarities Bdelloida) Growth and Reproduction Under Various Temperature ConditionsArmando Chiclla SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 16 Gen Chem 1Documento47 páginasChem 16 Gen Chem 1Rovie Del RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Solubilidad ParacetamolDocumento11 páginasSolubilidad ParacetamolYoselin Jazmin Azabache AbdhalaAinda não há avaliações
- Ionic EquilibriaDocumento2 páginasIonic EquilibriaAnonymous ZVYEN6rBNAinda não há avaliações
- Boiler Operator Handbook (CHEMIC)Documento44 páginasBoiler Operator Handbook (CHEMIC)SynesiusAinda não há avaliações
- Fentons ReagentDocumento5 páginasFentons ReagentAhmet FerdiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Tesda-Fruit GrowerDocumento81 páginasTesda-Fruit Growersend notesAinda não há avaliações
- Hanna Instruments General CatalogDocumento980 páginasHanna Instruments General CatalogdenAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Practical Manual BBT1Documento33 páginasChemistry Practical Manual BBT1ishitaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts: Class - X ScienceDocumento14 páginasChapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts: Class - X ScienceDhruv AsodariaAinda não há avaliações
- 2412 Iit JM Nurture (P#1&2) MT-8 PaperDocumento15 páginas2412 Iit JM Nurture (P#1&2) MT-8 PaperPratham MittalAinda não há avaliações
- CBE658 - Lab Report On Food PreservationDocumento23 páginasCBE658 - Lab Report On Food PreservationGua HantuAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Growth PDFDocumento65 páginasMicrobial Growth PDFkingshuk dasAinda não há avaliações
- 9701 w18 QP 41 PDFDocumento20 páginas9701 w18 QP 41 PDFSuhail Alam KhanAinda não há avaliações
- ACJC H2 Chem 2021 P2 SolutionsDocumento20 páginasACJC H2 Chem 2021 P2 Solutionsantesipation ฅ'ω'ฅAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling-Water-Basics NalcoDocumento163 páginasCooling-Water-Basics NalcoAhmed Ansari100% (5)
- Risk Assessment On Water Quality of Calinog CreekDocumento9 páginasRisk Assessment On Water Quality of Calinog CreekHoney Grace Lumahang PalasanAinda não há avaliações
- Suthar2010-Simulation of The Effect of Different Parameters On The Swelling Characteristics of A Ph-Sensitive HydrogelDocumento10 páginasSuthar2010-Simulation of The Effect of Different Parameters On The Swelling Characteristics of A Ph-Sensitive HydrogelLuis Enrique Flores ValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 17 Lab Manual 2Documento28 páginasChem 17 Lab Manual 2Chrizamae BarlasAinda não há avaliações
- Ionic Liquid Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocumento322 páginasIonic Liquid Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems Fundamentals and ApplicationsDaniela AchimAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Metal Complex EquilibriaDocumento12 páginas03 Metal Complex EquilibriaAndrew James ViernesAinda não há avaliações
- Langelier Saturation IndexDocumento2 páginasLangelier Saturation IndexNur HidayahAinda não há avaliações
- Lca Operations Manual 170501Documento28 páginasLca Operations Manual 170501camaleonAinda não há avaliações
- Cider MakingDocumento44 páginasCider Makingmacaco logo100% (1)
- AP Lab #6 Cellular RespirationDocumento7 páginasAP Lab #6 Cellular RespirationAnya KureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Acids and Bases Unit Test 2011Documento8 páginasAcids and Bases Unit Test 2011jkdfal1Ainda não há avaliações
- 2012 June ISA CHEM6TP Question PaperDocumento9 páginas2012 June ISA CHEM6TP Question PaperjamesAinda não há avaliações
- GCE in Chemistry Course PlannerDocumento35 páginasGCE in Chemistry Course PlannerShammahAinda não há avaliações
- Development and Evaluation of Novel DDS For Topical Delivery of Quercetin For Treatment of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento16 páginasDevelopment and Evaluation of Novel DDS For Topical Delivery of Quercetin For Treatment of Rheumatoid ArthritisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações