Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: Your Account
Enviado por
Priya KotariDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: Your Account
Enviado por
Priya KotariDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Spring Interview Questions FAQs Interview Questions Spring Tutorial JSF...
1 of 4
http://www.developersbook.com/spring/interview-questions/spring-inter...
search
Your Account
Few pages of this site are under construction and we are constantly trying to improve it. If you have any suggestions or ideas about how to imp
Spring Framework Interview Questions
Previous | Go To Page:
Next
1. What is IOC (or Dependency Injection)?
The basic concept of the Inversion of Control pattern (also known as dependency injection) is that you do not
create your objects but describe how they should be created. You don't directly connect your components and
services together in code but describe which services are needed by which components in a configuration file. A
container (in the case of the Spring framework, the IOC container) is then responsible for hooking it all up.
i.e., Applying IoC, objects are given their dependencies at creation time by some external entity that coordinates
each object in the system. That is, dependencies are injected into objects. So, IoC means an inversion of
responsibility with regard to how an object obtains references to collaborating objects.
New to Spring ? Check Spring tutorial
2. What are the different types of IOC (dependency injection) ?
There are three types of dependency injection:
Constructor Injection (e.g. Pico container, Spring etc): Dependencies are provided as constructor
parameters.
Setter Injection (e.g. Spring): Dependencies are assigned through JavaBeans properties (ex: setter methods).
Interface Injection (e.g. Avalon): Injection is done through an interface.
Note: Spring supports only Constructor and Setter Injection
3. What are the benefits of IOC (Dependency Injection)?
Benefits of IOC (Dependency Injection) are as follows:
Minimizes the amount of code in your application. With IOC containers you do not care about how services
are created and how you get references to the ones you need. You can also easily add additional services by
adding a new constructor or a setter method with little or no extra configuration.
Make your application more testable by not requiring any singletons or JNDI lookup mechanisms in your unit
test cases. IOC containers make unit testing and switching implementations very easy by manually allowing
you to inject your own objects into the object under test.
Loose coupling is promoted with minimal effort and least intrusive mechanism. The factory design pattern is
more intrusive because components or services need to be requested explicitly whereas in IOC the
dependency is injected into requesting piece of code. Also some containers promote the design to interfaces
not to implementations design concept by encouraging managed objects to implement a well-defined service
9/3/2015 8:30 PM
Spring Interview Questions FAQs Interview Questions Spring Tutorial JSF...
2 of 4
http://www.developersbook.com/spring/interview-questions/spring-inter...
interface of your own.
IOC containers support eager instantiation and lazy loading of services. Containers also provide support for
instantiation of managed objects, cyclical dependencies, life cycles management, and dependency resolution
between managed objects etc.
4. What is Spring ?
Don't Miss...
Spring is an open source framework created to address the complexity of enterprise Spring Certification article
application development. One of the chief advantages of the Spring framework is its
Spring Basic Tutorial
layered architecture, which allows you to be selective about which of its components
JSF Basic Tutorial
you use while also providing a cohesive framework for J2EE application development.
JSF-Spring2.0 Integration
Spring-iBatis Integration
5. What are the advantages of Spring framework?
The advantages of Spring are as follows:
Spring has layered architecture. Use what you need and leave you don't need now.
Spring Enables POJO Programming. There is no behind the scene magic here. POJO programming enables
continuous integration and testability.
Dependency Injection and Inversion of Control Simplifies JDBC
Open source and no vendor lock-in.
6. What are features of Spring ?
Lightweight:
spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around
1MB. And the processing overhead is also very negligible.
Inversion of control (IOC):
Loose coupling is achieved in spring using the technique Inversion of Control. The objects give their
dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects.
Aspect oriented (AOP):
Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and enables cohesive development by separating application
business logic from system services.
Container:
Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects.
MVC Framework:
Spring comes with MVC web application framework, built on core Spring functionality. This framework is
highly configurable via strategy interfaces, and accommodates multiple view technologies like JSP, Velocity,
Tiles, iText, and POI. But other frameworks can be easily used instead of Spring MVC Framework.
Transaction Management:
Spring framework provides a generic abstraction layer for transaction management. This allowing the
developer to add the pluggable transaction managers, and making it easy to demarcate transactions without
dealing with low-level issues. Spring's transaction support is not tied to J2EE environments and it can be also
used in container less environments.
JDBC Exception Handling:
The JDBC abstraction layer of the Spring offers a meaningful exception hierarchy, which simplifies the error
handling strategy. Integration with Hibernate, JDO, and iBATIS: Spring provides best Integration services with
Hibernate, JDO and iBATIS
7. How many modules are there in Spring? What are they?
(Roll over to view the Image )
Spring comprises of seven modules. They are..
The core container:
The core container provides the essential functionality of the Spring framework. A primary component of the
core container is the BeanFactory, an implementation of the Factory pattern. The BeanFactory applies the
9/3/2015 8:30 PM
Spring Interview Questions FAQs Interview Questions Spring Tutorial JSF...
3 of 4
http://www.developersbook.com/spring/interview-questions/spring-inter...
Inversion of Control (IOC) pattern to separate an application's
configuration and dependency specification from the actual application
code.
Spring context:
The Spring context is a configuration file that provides context
information to the Spring framework. The Spring context includes
enterprise services such as JNDI, EJB, e-mail, internalization,
validation, and scheduling functionality.
Spring AOP:
The Spring AOP module integrates aspect-oriented programming functionality directly into the Spring
framework, through its configuration management feature. As a result you can easily AOP-enable any object
managed by the Spring framework. The Spring AOP module provides transaction management services for
objects in any Spring-based application. With Spring AOP you can incorporate declarative transaction
management into your applications without relying on EJB components.
Spring DAO:
The Spring JDBC DAO abstraction layer offers a meaningful exception hierarchy for managing the exception
handling and error messages thrown by different database vendors. The exception hierarchy simplifies error
handling and greatly reduces the amount of exception code you need to write, such as opening and closing
connections. Spring DAO's JDBC-oriented exceptions comply to its generic DAO exception hierarchy.
Spring ORM:
The Spring framework plugs into several ORM frameworks to provide its Object Relational tool, including
JDO, Hibernate, and iBatis SQL Maps. All of these comply to Spring's generic transaction and DAO exception
hierarchies.
Spring Web module:
The Web context module builds on top of the application context module, providing contexts for Web-based
applications. As a result, the Spring framework supports integration with Jakarta Struts. The Web module
also eases the tasks of handling multi-part requests and binding request parameters to domain objects.
Spring MVC framework:
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework is a full-featured MVC implementation for building Web
applications. The MVC framework is highly configurable via strategy interfaces and accommodates numerous
view technologies including JSP, Velocity, Tiles, iText, and POI.
8. What are the types of Dependency Injection Spring supports?>
Setter Injection:
Setter-based DI is realized by calling setter methods on your beans after invoking a no-argument constructor
or no-argument static factory method to instantiate your bean.
Constructor Injection:
Constructor-based DI is realized by invoking a constructor with a number of arguments, each representing a
collaborator.
Are you a Spring Certified developer ? Spring Certification
9. What is Bean Factory ?
A BeanFactory is like a factory class that contains a collection of People who read this, also read:beans. The BeanFactory holds Bean Definitions of multiple beans
within itself and then instantiates the bean whenever asked for by
AJAX Interview Questions
clients.
XML Questions
SCMAD Certification
BeanFactory is able to create associations between
JSF Integration with Spring Framework
collaborating objects as they are instantiated. This removes
9/3/2015 8:30 PM
Spring Interview Questions FAQs Interview Questions Spring Tutorial JSF...
4 of 4
http://www.developersbook.com/spring/interview-questions/spring-inter...
the burden of configuration from bean itself and the beans
Spring Interview Questions
client.
BeanFactory also takes part in the life cycle of a bean, making calls to custom initialization and destruction
methods.
10. What is Application Context?
A bean factory is fine to simple applications, but to take advantage of the full power of the Spring framework, you
may want to move up to Springs more advanced container, the application context. On the surface, an application
context is same as a bean factory.Both load bean definitions, wire beans together, and dispense beans upon
request. But it also provides:
A means for resolving text messages, including support for internationalization.
A generic way to load file resources.
Events to beans that are registered as listeners.
11. What is the difference between Bean Factory and Application Context ?
On the surface, an application context is same as a bean factory. But application context offers much more..
Application contexts provide a means for resolving text messages, including support for i18n of those
messages.
Application contexts provide a generic way to load file resources, such as images.
Application contexts can publish events to beans that are registered as listeners.
Certain operations on the container or beans in the container, which have to be handled in a programmatic
fashion with a bean factory, can be handled declaratively in an application context.
ResourceLoader support: Springs Resource interface us a flexible generic abstraction for handling low-level
resources. An application context itself is a ResourceLoader, Hence provides an application with access to
deployment-specific Resource instances.
MessageSource support: The application context implements MessageSource, an interface used to obtain
localized messages, with the actual implementation being pluggable
Next : More Spring FAQs >>
Previous | Go To Page:
5 |
Next
9/3/2015 8:30 PM
Você também pode gostar
- Spring and Spring Boot Interview Questions and Answers. Tech interviewer’s notesNo EverandSpring and Spring Boot Interview Questions and Answers. Tech interviewer’s notesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- iOS 5 Programming Pushing the Limits: Developing Extraordinary Mobile Apps for Apple iPhone, iPad, and iPod TouchNo EverandiOS 5 Programming Pushing the Limits: Developing Extraordinary Mobile Apps for Apple iPhone, iPad, and iPod TouchAinda não há avaliações
- What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?Documento12 páginasWhat Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?Krishna Chaitanya GanapaAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview QuestionsDocumento19 páginasSpring Interview Questionssanthu4632100% (1)
- 50 Spring Interview Questions 1Documento18 páginas50 Spring Interview Questions 1sandeepsharma2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions PDFDocumento18 páginasSpring Interview Questions PDFAbhi Roy OviAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview QuestionsDocumento10 páginasSpring Interview Questionsronak_sp100% (1)
- Spring Faq: What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?Documento13 páginasSpring Faq: What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?tmohammedAinda não há avaliações
- What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: Spring TutorialDocumento24 páginasWhat Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: Spring TutorialGeetha RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Framework Questions Part 1 What Is Spring Framework?Documento12 páginasSpring Framework Questions Part 1 What Is Spring Framework?Satish BabuAinda não há avaliações
- What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: LightweightDocumento5 páginasWhat Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?: Lightweightফিউরিয়াস পাবেলAinda não há avaliações
- JavaDocumento5 páginasJavapriyasonawane.elnAinda não há avaliações
- Op 100 Spring Interview Questions and Answers (Part 1)Documento41 páginasOp 100 Spring Interview Questions and Answers (Part 1)PRABHU SORTURAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions - Posted On June 27, 2013 at 17:05 PM by Kshipra SinghDocumento85 páginasSpring Interview Questions - Posted On June 27, 2013 at 17:05 PM by Kshipra Singhvijaykumar015Ainda não há avaliações
- Spring Amp HibernateDocumento32 páginasSpring Amp HibernatePRABHU SORTURAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Based Interview QuestionsDocumento13 páginasSpring Based Interview QuestionsamitAinda não há avaliações
- 69 Spring Interview Questions and Answers - The ULTIMATE List (PDF Download)Documento12 páginas69 Spring Interview Questions and Answers - The ULTIMATE List (PDF Download)Mohan RajAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Question and Answers What Is A Spring Bean?Documento16 páginasSpring Question and Answers What Is A Spring Bean?bimal09Ainda não há avaliações
- Answers:: What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?Documento6 páginasAnswers:: What Is IOC (Or Dependency Injection) ?Anna CarterAinda não há avaliações
- The Spring SeriesDocumento7 páginasThe Spring Seriesapi-3701708Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To MVC Pattern: Model-View-Controller (MVC) Is A Software Architecture or An Architectural PatternDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To MVC Pattern: Model-View-Controller (MVC) Is A Software Architecture or An Architectural PatternmanishsatishAinda não há avaliações
- Old SpringDocumento16 páginasOld SpringSawkat Ali SkAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Hibernate WebservicesDocumento44 páginasSpring Hibernate WebservicesNitesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 2Documento12 páginas2BharatAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions: Q. What Is Spring?Documento20 páginasSpring Interview Questions: Q. What Is Spring?surestceAinda não há avaliações
- Module V (Spring) : 1. Dependency Injection or Inversion of Control (IOC)Documento14 páginasModule V (Spring) : 1. Dependency Injection or Inversion of Control (IOC)Dhruv KakkarAinda não há avaliações
- Springcore 161022154617Documento66 páginasSpringcore 161022154617Piyush MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- What Are The Major Features in Different Versions of Spring Framework?Documento20 páginasWhat Are The Major Features in Different Versions of Spring Framework?Jitendra KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Spring ModuleDocumento56 páginasSpring ModulernpAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview QuestionsDocumento10 páginasSpring Interview QuestionsCvenAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions and Answers (2023) - InterviewBitDocumento44 páginasSpring Interview Questions and Answers (2023) - InterviewBitIkramul HaqueAinda não há avaliações
- Fullstack - Cafe - Tech Interview Plan: Q1: What Is Spring?Documento6 páginasFullstack - Cafe - Tech Interview Plan: Q1: What Is Spring?mukesh singhAinda não há avaliações
- Devjournals - SpringDocumento16 páginasDevjournals - SpringPrasanna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- FullStack QuestionsDocumento6 páginasFullStack QuestionswwAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Spring Framework: by Shailesh PawarDocumento21 páginasIntroduction To Spring Framework: by Shailesh Pawarsanjay joshiAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Questions and Answers 1653726507Documento24 páginasSpring Questions and Answers 1653726507RUCHIR ANAND ARYAAinda não há avaliações
- Preguntas de Entrevista de Trabajo - SpringDocumento12 páginasPreguntas de Entrevista de Trabajo - SpringKapi PorlaAinda não há avaliações
- Spring: A Head Start - Introduction (Part 1) : This Is A Long Series of Tutorials. We Are Going CoverDocumento9 páginasSpring: A Head Start - Introduction (Part 1) : This Is A Long Series of Tutorials. We Are Going CoverLedX19Ainda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions and Answers - Spring Framework Training - EdurekaDocumento21 páginasSpring Interview Questions and Answers - Spring Framework Training - Edurekasatish.sathya.a2012Ainda não há avaliações
- Q1. What Is Spring Framework?Documento12 páginasQ1. What Is Spring Framework?BharatAinda não há avaliações
- Spring PrepDocumento26 páginasSpring PrepHARSHIT TRIPATHIAinda não há avaliações
- General Questions - Spring Interview Questions: 1. What Are The Major Features in Different Versions of Spring Framework?Documento23 páginasGeneral Questions - Spring Interview Questions: 1. What Are The Major Features in Different Versions of Spring Framework?BharatAinda não há avaliações
- Spring in GeneralDocumento12 páginasSpring in GeneralDipen DahalAinda não há avaliações
- Spring NotesDocumento211 páginasSpring NotesrahulAinda não há avaliações
- Spring IntroductionDocumento30 páginasSpring IntroductionM.I.M KRUPHAAinda não há avaliações
- What Does Spring DoDocumento62 páginasWhat Does Spring DobabithAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview Questions and Answers: 1. What Is Spring Framework?Documento25 páginasSpring Interview Questions and Answers: 1. What Is Spring Framework?BharatAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Interview QuestionsDocumento35 páginasSpring Interview QuestionsSenthilAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Application Framework: White Paper OnDocumento44 páginasOracle Application Framework: White Paper OnRabahAinda não há avaliações
- 005 Spring63Documento63 páginas005 Spring63JPAinda não há avaliações
- Spring MVC Interview Questions and Answers: MinutesDocumento13 páginasSpring MVC Interview Questions and Answers: MinutesShailendra SBAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Chapter 3Documento5 páginasSpring Chapter 3vidhyaa1011Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is A Controller?: Oracle OAF TrainingDocumento3 páginasWhat Is A Controller?: Oracle OAF TrainingDjshahzadAinda não há avaliações
- Application Development FrameworkDocumento23 páginasApplication Development FrameworkisaritaAinda não há avaliações
- Spring Assignment JavaDocumento12 páginasSpring Assignment JavaNav SoodAinda não há avaliações
- Spring & Hibernate Interview QuestionsDocumento10 páginasSpring & Hibernate Interview Questionscmehta8286% (7)
- Top Spring Interview Questions and Answers: Question: Please List Down The Various Features of Spring Framework andDocumento14 páginasTop Spring Interview Questions and Answers: Question: Please List Down The Various Features of Spring Framework andBharatAinda não há avaliações
- Spring & Hibernate (Question & Answers)Documento8 páginasSpring & Hibernate (Question & Answers)Anirudha KumbharAinda não há avaliações
- Java/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo EverandJava/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT4Documento16 páginasUNIT4sinibanu369Ainda não há avaliações
- Python Project With SQL - HotelDocumento6 páginasPython Project With SQL - Hotelmonkey wiseAinda não há avaliações
- DBA Lecture 2 ERDocumento48 páginasDBA Lecture 2 ERareanAinda não há avaliações
- SDA-Lecture 4+1 Model ViewDocumento11 páginasSDA-Lecture 4+1 Model ViewMudasser HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Srija Puppala ResumeDocumento11 páginasSrija Puppala ResumeHARSHAAinda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full Database Concepts 7th Edition Kroenke Test Bank PDFDocumento35 páginasDwnload Full Database Concepts 7th Edition Kroenke Test Bank PDFhudsons6opk100% (13)
- Unit V:Normalization: Normalization: Relational Database Design Pitfalls, Denormalized Data, DecompositionDocumento30 páginasUnit V:Normalization: Normalization: Relational Database Design Pitfalls, Denormalized Data, DecompositionArnav ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between Primary Key and Unique KeyDocumento4 páginasDifference Between Primary Key and Unique KeyjosearchingAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation 1Documento10 páginasPresentation 1Gurpal Singh BaathAinda não há avaliações
- TocfDocumento19 páginasTocfvignesh GupthaAinda não há avaliações
- ICT Unit 3 Notes - G12Documento5 páginasICT Unit 3 Notes - G12Dagim YenenehAinda não há avaliações
- Building s2 ApplicationsDocumento62 páginasBuilding s2 Applicationsapi-3698136Ainda não há avaliações
- 12 IpDocumento4 páginas12 IpPreeti JijnodiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Spring MVC FinalDocumento357 páginasSpring MVC FinalJayAinda não há avaliações
- General Micro - Web Services Flashcards QuizletDocumento20 páginasGeneral Micro - Web Services Flashcards QuizletganamAinda não há avaliações
- Project Document TemplateDocumento5 páginasProject Document TemplateMUHAMMAD IRFANAinda não há avaliações
- CST 204 Database Management Systems, June 2023Documento4 páginasCST 204 Database Management Systems, June 2023binnytmzAinda não há avaliações
- Fundametals of Database ModuleDocumento153 páginasFundametals of Database Moduledemissie ejoAinda não há avaliações
- CT075!3!2 DTM Topic2 EntityRelationshipModellingDocumento21 páginasCT075!3!2 DTM Topic2 EntityRelationshipModellingPyo Wai Lian HKAinda não há avaliações
- DBMS Q1Documento4 páginasDBMS Q1prabhudeenAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Notes Relational Database Management SystemDocumento3 páginas05 Notes Relational Database Management SystemSapnaSagar100% (1)
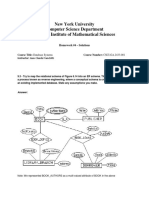
- Homework 4 SolutionsDocumento8 páginasHomework 4 SolutionsBudi Pekerti JayaAinda não há avaliações
- Fullstack 1052111652197347511Documento164 páginasFullstack 1052111652197347511AnuprekshaChowhanAinda não há avaliações
- Client Server Architecture - TutorialDocumento118 páginasClient Server Architecture - TutorialFFAMOC0% (2)
- Homework 1: 1. What Is ? and Be Able To Give Example Diagram. A. Relational Model?Documento5 páginasHomework 1: 1. What Is ? and Be Able To Give Example Diagram. A. Relational Model?dbircs for lifeAinda não há avaliações
- ISDM - Lab Sheet 08Documento4 páginasISDM - Lab Sheet 08it21083396 Galappaththi S DAinda não há avaliações
- U4 Database Management System (DBMS)Documento31 páginasU4 Database Management System (DBMS)Arun MishraAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Struts Framework?: Actionerrors Validate (Actionmapping, Httpservletrequest)Documento7 páginasWhat Is Struts Framework?: Actionerrors Validate (Actionmapping, Httpservletrequest)Saurit KarAinda não há avaliações
- Liberery Management FinalDocumento18 páginasLiberery Management FinalMayur DhawleAinda não há avaliações
- Pvp19 Dbms Unit-4 MaterialDocumento41 páginasPvp19 Dbms Unit-4 MaterialPrakash SinghAinda não há avaliações