Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
3-DC Motor Starting
Enviado por
John-Paul MollineauxDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3-DC Motor Starting
Enviado por
John-Paul MollineauxDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Power Converters and
Drives, PCVD320B
DC MOTORS:
STARTING
StartingofDCMotors
At starting conditions, the motor is not turning ( = 0),
therefore the internal generated voltage EA = K = 0V.
The only component to limit starting current is the
armature resistance, which, in most DC motors is a very
low value (approximately one ohm or less),
Therefore, a very high current flows in the armature
circuit during starting condition.
I a , Starting
ADEL ELGAMMAL
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Starting a dc motor across the line.
If a dc motor is started with full supply voltage across its
terminals, a very high current will flow, which may damage the
motor due to heavy sparking at commutator and heating of the
winding.
Vt Ea Vt
Ra
Ra
Starting of DC motor
At stand-still, ( = 0), EA = K = 0 Volt
Ia
Vt
Ra
I a , Starting
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor problems on
starting
For instance, for a 50 hp, 250 V DC motor with armature
resistance RA of 0.06 and a full-load current about 200
A, the starting current is
IA
VT E A 250 0
4167
A
RA
0.06
This current is over 20 times the motors rated full-load
current and may severely damage the motor.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Vt
Ra
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Starting of DC motor
Therefore, it is necessary to limit the
current to a safe value during starting.
For normally designed machines, twice the
rated current can be allowed to flow and
for specially designed machines it can be
3.5 times.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Starter in DC Motor
StartingofDCmotor
Ia
We can limit Ia at start-up by:
Speed
1) Controlling Vt using variable supply e.g. using
power electronics converter
At Starting, = 0, then Ea = 0
Vt Ea
Ra
I st
o
V Ea
Td K t
Ra
Motor
Operating
Point
V
I st t
Ra
V K
Td K t
Ra
Ia
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Vt
Ra
Current
V
Tst K t
Ra
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
StartingofDCmotor(voltagereduction)
Starter in DC Motor
We can limit Ia at start-up by:
2) Adding external resistor known as starter
V
I st t
Ra
Ia
Ist1
Vt2
Ist2
Ia
When Ea = 0
A solution to the problem of excessive starting
current is to insert a starting resistor in series with
the armature to limit the current until EA can build up
to limit the armature current.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Starting DC Motor
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Vt
R a R st
Rst
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
However, this resistor must be removed from the
circuit as the motor speed is high since otherwise
such resistor would cause losses and would decrease
the motors torque-speed characteristic.
Starting resistors are usually incorporated into the
motor design to limit starting current to 125 to 200
percent of full load current .
As motor accelerates and back emf rises, one section
of the resistor is cut out at a time, either manually or
automatically with the help of contactors, such that
the current is kept within specified maximum and
minimum values.
Ia
+
Ea
Vt
Vt1
Ra
StartingofDCmotor(startingresistance)
Ra
Ra + R
Vt
R I
a a
K
K
Ist1
Ist2
I st
Vt
Ra Rst
V
Rst t Ra
I st
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Ia
Example
Solution
A dc separately excited motor has the following data:
Rated torque = Td K I a 3 (5) 15 NM (Newton Meter)
K = 3.0 Vs (Volt second)
Vt = 600.0 V
Ra = 2.0
Ia = 5.0 A (armature current at full load)
Calculate the rated torque, starting torque and starting
current at full voltage.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Starting torque = Tst Vt
K
600.0 * 3.0 / 2.0 900.0 NM
Ra
V
Starting current = I st t 300.0 A
Ra
starting torque is 60 times the rated torque
starting current is also 60 times the rated current
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Example
Solution
A dc separately excited motor has the following data:
K = 3.0 Vs (Volt second)
Vt = 600.0 V
Ra = 2.0
Ia = 5.0 A (armature current at full load)
How can you reduce the starting current to 6 times
the rated current?
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Method 1: Reduce the starting voltage
Vst I st Ra 6 (5.0) (2.0) 60.0 V
Method 2: Increase the starting resistance
V
R Ra t
I st
V
600.0
R t - Ra
- 2.0 18
I st
30.0
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
A dc shunt motor has the following data: 240 V, 18 A,
1100 r/min, and armature-circuit resistance Ra=0.33 .
The no-load saturation curve for the machine is given
in the following Fig.
The motor is to be started by a manual starter, shown in
next following Fig.; the field current is set at 5.2 A.
If the current during starting varies between 20 and 40
A, determine the starting resistors R1, R2, and R3
needed in the manual starter.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
No-load saturation
curve for a 240-V,
1100-r/min
dc
generator.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Manual starter for a shunt motor
I a (0) I max I a (t1 ) I min
I a (t 2 ) I min
I a (t1 ) I max
I a (t 2 ) I max
t1 t1
t 2 t 2
t3 t3
E (t3 ) E (t3 )
E (t 2 ) E (t 2 )
E (t1 ) E (t1 )
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
1. At t = 0; Ia = Imax , Ea = 0 V
Calculate Armature Current at Standstill
At the first contact on the manual starter, 240 V
dc is applied to the shunt field; the field rheostat
has been set to allow I=5.2 A.
Thus, the armature current Ia=IL-I= 40 A-5.2
A=34.8 A.
The 40 A is the maximum permissible load
current.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
2. At t = t1- , Ia = Imin , Ea = ?? V
Calculate the Induced Armature Voltage, Ea,
when the Machine Accelerates ((R1 + R2 +R3)
still inserted in the armature)
As the machine accelerates, an induced armature
voltage is created, causing the armature current to fall
to Imin.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
Calculate the Value of the Starter
Resistance, (R1 + R2 +R3)
Use the equation:
(R1 + R2 +R3) =(Vt/Ia)-Ra=(240 V)/(34.8 A)0.330 =6.57 .
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
When the armature current drops to the
minimum allowed during starting
Ia=IL- I=20 A-5.2 A=14.8 A,
the induced voltage is obtained from the
equation:
Ea(t1-)=Ea(t1+)=Vt-Ia(Ra+(R1+R2+R3))
=240V-(14.8 A)(0.330 +6.57 )=137.9 V.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
3. At t = t1+, R1 is removed from the
circuit, Ia = Imax, Ea = 137.9 V
Calculate the Starter Resistance, (R2+ R3)
Use the equation:
(R2+ R3) = ((Vt-Ea) / Ia) - Ra=(240 V137.9 V)/34.8 A-0.330 =2.60 .
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
5. At t = t2+, R2 is removed from the
circuit, Ia = Imax, Ea = 196.6 V
Calculate the Starter Resistance, (R3)
Use the equation:
(R3) =(Vt-Ea)/Ia-Ra=(240 V-196.6 V)/34.8
A-0.330 =0.917 .
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor problems on
starting
In practice, a starting resistor is made up of a series of resistors that can be successively
removed from the circuit as the motor speeds up.
A shunt motor with an extra starting
resistor that can be cut out of the
circuit in segments by closing the 1A,
2A, and 3A contacts.
Therefore, two considerations are
needed to be taken into account:
Select the values and the number of
resistor segments needed to limit the
starting current to desired
ranges; Design a control circuit shutting the resistor bypass contacts at the proper time to
remove particular parts of the resistor from the circuit.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
4. At t = t2- , Ia = Imin , Ea = ?? V
Calculate the Induced Armature Voltage, Ea,
when Machine Again Accelerates
Ea(t2-) = Ea(t2+) = Vt-Ia(Ra+(R2+ R3))
=240V- (14.8A)(0.330+2.60)
=196.6 V.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DESIGN OF A MANUAL STARTER
FOR A DC SHUNT MOTOR
6. Calculate the Three Starting
Resistances, R1, R2, and R3
From the preceding steps,
R3= 0.917 ,
R2=1.683 , and
R1=3.97 .
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor problems on
starting: Ex
Example 5.6: A 100 hp, 250 V 350 A shunt DC motor with an armature resistance of 0.05
needs a starter circuit that will limit the max starting current to twice its rated value and
which will switch out sections of resistor once the armature current decreases to its rated
value.
a. How many stages of starting
resistance will be required to limit
the current to the specified range?
b. What must the value of each segment
of the resistor to be? At what voltage
should each stage of the starting
resistance be cut out?
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
I a (0) I max I a (t1 ) I min
I a (t 2 ) I min
I a (t1 ) I max
I a (t 2 ) I max
t1 t1
t 2 t 2
DC motor problems on
starting: Ex
t3 t3
The starting resistor must be selected such that the current flow at the start equals twice the
rated current. As the motor speeds up, an internal voltage EA (which opposes the terminal
voltage of the motor and, therefore, limits the current) is generated. When the current falls
to the rated value, a section of the starting resistor needs to be taken out to increase the
current twice. This process (of taking out sections of the starting resistor) repeats until the
entire starting resistance is removed. At this point, the motors armature resistance will
limit the current to safe values by itself.
The original resistance in the starting circuit is
E (t ) E (t )
Rtot R1 R2 ... RA
VT
I max
E (t 2 ) E (t 2 )
After the stages 1 through i are shorted out, the total resistance left in the starting circuit is
E (t1 ) E (t1 )
Rtot ,i Ri 1 ... RA
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor starting: Ex
I A,min
VT E A,1
Rtot
I
RA Rtot , n min Rtot
I max
I min 350 A
After the resistance R1 is out of the circuit,
the armature current must increase to
VT E A,2
I A,max
Rtot ,1
Solving for n:
I max 700 A
Rtot
I min Rtot VT E A I max Rtot ,1
The resistance left in the circuit is
n
I
I min
Rtot Rtot ,n min Rtot
I max
ADEL
max
IELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor problems on
starting: Ex
b. The armature circuit will contain the armature resistance RA and three starting resistors.
At first, EA = 0, IA = 700 A, and the total resistance is 0.357 . The total resistance will be
in the circuit until the current drops to 350 A. This occurs when
E A,1 VT I A,min Rtot 250 350 0.357 125V
At this time, the starting resistor R1 will be taken out making
Rtot ,1 RA R2 R3
VT E A,1
I max
250 125
0.1786
700
This (new) total resistance will be in the circuit until the current drops again to 350 A. This
occurs when
E A,2 VT I A,min Rtot ,1 250 350 0.1786 187.5V
At this time, the starting resistor R2 will be taken out leaving
Rtot ,2 RA R3
VT E A,2
I
250 187.5
0.0893
700
max
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
log RA Rtot
log I min I max
Notice that the number of stages n must be
rounded up to the next integer.
Since EA = K, the quantity VT EA must
be constant when the resistance is switched
out. Therefore
Rtot ,1
DC motor starting: Ex
The starting process is completed when Rtot,n is not greater than the internal armature
resistance RA. At the boundary:
The resistance R1 must be switched out of the
circuit when the armature current falls to
VT
250
0.357
I max 700
n
log RA Rtot log 0.05 0.357
2.84 3
log I min I max
log 350 700
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor problems on
starting: Ex
This total resistance will be in the circuit until the current drops again to 350 A. This occurs
when
E A,3 VT I A,min Rtot ,2 250 350 0.0893 218.75V
At this time, the starting resistor R3 will be taken out leaving only RA in the circuit. The
motors current at that moment will increase to
I A,3
VT E A,3
RA
250 218.75
625 A
0.05
which is less than the allowed value. Therefore, the resistances are
R3 Rtot ,3 RA 0.0893 0.05 0.0393
R2 Rtot ,2 R3 RA 0.1786 0.0393 0.05 0.0893
R1 Rtot ,1 R2 R3 RA 0.357 0.1786 0.0393 0.05 0.1786
The resistors R1, R2, and R3 are cut out when EA reaches 125 V, 187.5 V, and 218.75 V,
respectively.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
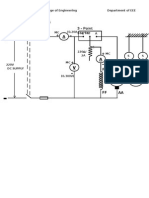
3-POINT STARTER
3-POINT STARTER
A 3-point starter is extensively used to start a D.C
shunt motor.
It provides additional protective features such as over
load protection and no volt protection.
The diagram of a 3-point starter connected to a shunt
motor is shown in figure .
The starter is shown enclosed within the dotted
rectangular box having three terminals marked as A,
L and F for external connections.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
3-POINT STARTER
3-POINT STARTER
Terminal A is connected to one armature terminal Al
of the motor. Terminal F is connected to one field
terminal F1 of the motor and terminal L is connected
to one supply terminal as shown.
F2 terminal of field coil is connected to A2 through
an external variable field resistance and the common
point connected to supply (-ve).
The external armatures resistances consist of several
resistances connected in series and are shown in the
form of an arc.
The junctions of the resistances are brought out as
terminals (called studs) and marked as 1,2,.. .12. Just
beneath the resistances, a continuous copper strip also
in the form of an arc is present.
There is a handle which can be moved in the
clockwise direction against the spring tension. The
spring tension keeps the handle in the OFF position
when no one attempts to move it.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
3-POINT STARTER
3-POINT STARTER
Now let us trace the circuit from terminal L (supply + ve). The
wire from L passes through a small electro magnet called
OLRC, and enters through the handle shown by dashed lines.
Near the end of the handle two copper strips are firmly
connected with the wire. The furthest strip is shown circular
shaped and the other strip is shown to be rectangular.
When the handle is moved to the right, the circular strip of the
handle will make contacts with resistance terminals 1, 2 etc.
progressively.
On the other hand, the rectangular strip will make
contact with the continuous arc copper strip.
The other end of this strip is brought as terminal F
after going through an electromagnet coil (called
NVRC). Terminal F is finally connected to motor
field terminal Fl.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
Initially the handle is in the OFF position. Neither
armature nor the field of the motor gets supply.
Now the handle is moved to stud number 1. In this
position armature and all the resistances in series gets
connected to the supply. Field coil gets full supply as
the rectangular strip makes contact with arc copper
strip.
As the machine picks up speed handle is moved
further r to stud number 2. In this position the
external resistance in the armature circuit is less as
the first resistance is left out.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
The no volt release coil (NVRC) carries same current
as that of the field coil.
In case supply voltage goes off, field coil current will
decrease to zero.
Hence NVRC will be de-energised and will not be
able to exert any force on the soft iron piece of the
handle.
Restoring force of the spring will bring the handle
back in the OFF position.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
Now gap between the electromagnet and the soft iron
piece is so adjusted that for IL<Irated the iron piece will
not be pulled up.
However, if IL > Irated force of attraction will be
sufficient to pull up iron piece.
This upward movement of the iron piece of OLRC is
utilized to de-energize NVRC. To the iron a copper
strip (A shaped in figure) is attached.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
Field however, continues to get full voltage by virtue of
the continuous arc strip.
Continuing in this way, all resistances will be left out
when stud number 12 (ON) is reached. In this position,
the electromagnet (NVRC) will attract the soft iron
piece attached to the handle.
Even if the operator removes his hand from the handle,
it will still remain in the ON position as spring
restoring force will be balanced by the force of
attraction between NVRC and the soft iron piece of the
handle.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
The starter also provides over load protection for the
motor. The other electromagnet, OLRC overload
release coil along with a soft iron piece kept under it,
is used to achieve this.
The current flowing through OLRC is the line current
IL drawn by the motor. As the motor is loaded, Ia
hence IL increases. Therefore, IL is a measure of
loading of the motor.
Suppose we want that the motor should not be over
loaded beyond rated current.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
During over loading condition, this copper strip will
also move up and put a short circuit between two
terminals B and C.
Carefully note that B and C are nothing but the two
ends of the NVRC. In other words, when over load
occurs a short circuit path is created across the NVRC.
Hence NVRC will not carry any current now and gets
de-energised. The moment it gets de-energised, spring
action will bring the handle in the OFF position thereby
disconnecting the motor from the supply.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
THE OPERATION OF THE
STARTER
Three-point starter has one disadvantage. If we want
to run the machine at higher speed (above rated
speed) by field weakening (i.e., by reducing field
current), the strength of NVRC magnet may become
so weak that it will fail to hold the handle in the ON
position and the spring action will bring it back in the
OFF position.
Thus we find that a false disconnection of the motor
takes place even when there is neither over load nor
any sudden disruption of supply.
DC motor starting circuits
Several different schemes can be used to short contacts and cut out the sections of a
starting resistor. Some devices commonly used in motor-control circuits are
Fuses:
protects
against short
circuits
Spring-type push button switches
Time delay
relay similar to
ordinary relay
except for
having
adjustable time
delay.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Overload: a
heater coil
and
normally
closed
contacts
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
DC motor starting circuits
DC motor starting circuits
A common DC motor starting circuit:
Another type of motor starter:
A series of time delay relays shut contacts removing
each section of the starting resistor at approximately
correct times.
A series of relays sense the value of armature voltage
EA and cut out the starting resistors as it riches certain
values.
Notice that the relay 1TD is energized at the same
time as the motor starts contacts of 1TD will shut a
part of the starting resistor after some time. At the
same instance, relay 2TD is energized and so on
Observe also 4 fuses protecting different parts of the
circuit and the overload in series with the armature
winding.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Relay: a
main coil
and a
number of
contacts
This starter type is more robust to different loads.
FL is the field loss relay: if the field is lost for any
reason, power to the M relay will be turned off.
Armature
current in a DC
motor during
starting.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Problem # 1
Chapter's
Assignment
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
A 10 kW , 100 V , 1000 rpm dc machine has Ra=0.1
ohm and is connected to a 100 V dc supply.
a) Determine the starting current if no starting
resistance is used in the armature circuit
b) Determine the value of the starting resistance if the
starting current is limited to twice the rated current
c) This dc machine is to run as a motor, using starter
box. Determine the values of resistance required in
the starter box such that the armature current Ia is
constraint within 100% to 200% of its rated value
during start-up.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Problem # 2
Problem # 3
Calculate the require resistance for a four-step starter
to limit the starting current of a DC shunt motor to
150% 0f rate current. Assume that all four steps have
an equal resistance value. The motor has rating as 25
Hp, 240 Volts, 860 rpm. And armature resistance is
0.08 Ohms, the overall efficiency 90%. Determine at
each speed of the starter resistance must be take into
the starting circuit to maintained the rate value during
start up period. Assume that the field current is
negligible compared to rate armature current.
A 10 hp (7.46kW) 200 V shunt motor has full-load
efficiency of 85%. The armature has a resistance of
0.25. Calculate the value of the starting resistance
necessary to limit the starting current to 1.5 times the
full-load current at the moment of first switching on.
The shunt current may be neglected. Find also the
back emf of the motor, when the current has fallen to
its full load value, assuming that the whole of the
starting resistance is still in circuit.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Problem # 4
A 25-kW, 230-V shunt motor has an armature resistance of 0.064 and a field-circuit
resistance of 95 . The motor delivers rated output power at rated voltage when its
armature current is 122 A. When the motor is operating at rated voltage, the speed is
observed to be 1150 r/min when the machine is loaded such that the armature current is
69.5 A.
a) Calculate the rated-load speed of this motor. In order to protect both the motor and the
dc supply under starting conditions, an external resistance will be connected in series
with the armature winding (with the field winding remaining directly across the 230-V
supply). The resistance will then be automatically adjusted in steps so that the armature
current does not exceed 200 percent of rated current. The step size will be determined
such that, until all the external resistance is switched out, the armature current will not
be permitted to drop below rated value. In other words, the machine is to start with 200
percent of rated armature current and as soon as the current falls to rated value,
sufficient series resistance is to be cut out to restore the current to 200 percent. This
process will be repeated until all of the series resistance has been eliminated.
b) Find the maximum value of the series resistance.
c) How much resistance should be cut out at each step in the starting operation and at
what speed should each step change occur?
Problem # 5
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
10
A dc shunt motor drives a centrifugal pump at
a speed of 1000 rpm when the terminal voltage
and line currents are 200 V and 50 A,
respectively. The armature and field
resistances are 0.1 and 100 , respectively.
Design a starting resistance for a maximum
starting current of 120 A in the armature
circuit.
ADEL ELGAMMAL
THE UNIVERSITY OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO UTT
Você também pode gostar
- Electrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFDocumento83 páginasElectrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFsk ibrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringDocumento21 páginasElectrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringSreerag Kunnathu SugathanAinda não há avaliações
- M.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Documento97 páginasM.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Preethi RanganathanAinda não há avaliações
- EE6365 EE Lab ManualDocumento58 páginasEE6365 EE Lab Manualjk100% (1)
- Parul Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento20 páginasParul Institute of Engineering & Technologyrworld999Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 Machine LabDocumento4 páginas2 Machine LabManoj GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Exp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andDocumento9 páginasExp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andSanjay MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Practice ProblemsDocumento4 páginasPractice Problemsdragon_warrior112456804Ainda não há avaliações
- Analysis of D.C. Electric Motors: EEEE 531 - Mechatronics Experiment #2Documento8 páginasAnalysis of D.C. Electric Motors: EEEE 531 - Mechatronics Experiment #2kay_rolAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento27 páginasChapter 4Selemon AssefaAinda não há avaliações
- Exp MachinesDocumento8 páginasExp MachinesAngelina JolieAinda não há avaliações
- Panasonic OptoTriac FormulaDocumento2 páginasPanasonic OptoTriac Formulaajisetyo1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Induction Motor Lab ManualDocumento11 páginasInduction Motor Lab ManualRabah ZaimeddineAinda não há avaliações
- An 9742Documento12 páginasAn 9742Alejandra SeguraAinda não há avaliações
- DC Motor Part IIIDocumento26 páginasDC Motor Part IIIMohd YasirAinda não há avaliações
- Machines Dcmotors 2 April 14Documento20 páginasMachines Dcmotors 2 April 14Pola RismaAinda não há avaliações
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Documento24 páginasSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshAinda não há avaliações
- 142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolDocumento15 páginas142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolgettinAinda não há avaliações
- EE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsDocumento10 páginasEE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsjegjegtAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocumento6 páginasExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalAinda não há avaliações
- An 9742Documento12 páginasAn 9742EmersonMagnoMoraesAinda não há avaliações
- EXPERIMENT8 IDocumento12 páginasEXPERIMENT8 IAbhay KotnalaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5Documento8 páginasExperiment 5rastgonikoAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of DC Machines PDFDocumento58 páginasTheory of DC Machines PDFGoitom Tadesse100% (2)
- Aula - Ensaio de Vazioem Gerador Síncrono - 230831 - 175852Documento6 páginasAula - Ensaio de Vazioem Gerador Síncrono - 230831 - 175852cristian kelvinAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report: Engineering Analysis and Design (EEN 206)Documento6 páginasLab Report: Engineering Analysis and Design (EEN 206)saksham mahajanAinda não há avaliações
- ELE 2251 11 Mar 2023Documento4 páginasELE 2251 11 Mar 2023Siddhartha MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Induction MatlabDocumento12 páginasInduction Matlabgrido002Ainda não há avaliações
- No Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationDocumento11 páginasNo Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationKsr Akhil100% (1)
- Me 2209 Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocumento45 páginasMe 2209 Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSai Karthi100% (1)
- Techint Trainee Manual Transformer Sizing CalculationsDocumento10 páginasTechint Trainee Manual Transformer Sizing CalculationsYogesh MittalAinda não há avaliações
- EC2259 Electrical Engineering and Control SystemDocumento46 páginasEC2259 Electrical Engineering and Control SystemManoj KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 2CV Series For 230 Vac Capacitor Start Motors and 2VR Series For 230 Vac Capacitor Start/Capacitor Run MotorsDocumento2 páginas2CV Series For 230 Vac Capacitor Start Motors and 2VR Series For 230 Vac Capacitor Start/Capacitor Run MotorsmachevallieAinda não há avaliações
- EV Class NotesDocumento30 páginasEV Class NotesVinod BabaleshwarAinda não há avaliações
- Phenomena: Module 9: Motor StartDocumento12 páginasPhenomena: Module 9: Motor StartalpizraAinda não há avaliações
- Ee311 Test 1Documento1 páginaEe311 Test 1Efron MdindileAinda não há avaliações
- Exp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorDocumento7 páginasExp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorKailash Jagarwal100% (1)
- Busbar Differential Stabllity Test Procedure PDFDocumento8 páginasBusbar Differential Stabllity Test Procedure PDFMoinullah Khan Ateeq100% (1)
- Electrical Machines I Lab ManualDocumento54 páginasElectrical Machines I Lab ManualThangam Mahesh89% (18)
- Assignment (ELE3307)Documento3 páginasAssignment (ELE3307)●●●●●●●1Ainda não há avaliações
- Retardation TestDocumento53 páginasRetardation Testkiran_y2100% (9)
- Definition of A DC MotorDocumento76 páginasDefinition of A DC MotorKiyoshi Jiro MalinaoAinda não há avaliações
- ST SERIES Single-Phase AC Synchronous GeneratorDocumento8 páginasST SERIES Single-Phase AC Synchronous Generatorlonski2k100% (1)
- Saa1042v PDFDocumento7 páginasSaa1042v PDFVinny TukAinda não há avaliações
- Brake Test On DC Shunt MotorDocumento4 páginasBrake Test On DC Shunt Motorkudupudinagesh87% (31)
- Operation: Current Is Applied To The Solenoid by Turning On The Key-Operated Switch. The SolenoidDocumento7 páginasOperation: Current Is Applied To The Solenoid by Turning On The Key-Operated Switch. The SolenoidSyukrirashiduhakim SubandiAinda não há avaliações
- DC MotorDocumento47 páginasDC MotorArun SaraswathyAinda não há avaliações
- Moc3023 PDFDocumento7 páginasMoc3023 PDFEricko JustopoAinda não há avaliações
- 45 - 6575 - EE328 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 328 - Lect - 05Documento7 páginas45 - 6575 - EE328 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 328 - Lect - 05binu_10Ainda não há avaliações
- Lm555 555c TimerDocumento12 páginasLm555 555c TimerAlexis Orellana VediaAinda não há avaliações
- Star Delta Wiring Diagram Motor Start yDocumento16 páginasStar Delta Wiring Diagram Motor Start ydataroma100% (1)
- Motorola Saa1042 0587f49ff7Documento6 páginasMotorola Saa1042 0587f49ff7Kevin StrongAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Ainda não há avaliações
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNo Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlNo EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetAinda não há avaliações
- TST CSECPhysg 01238020 MayJune2019 PDFDocumento28 páginasTST CSECPhysg 01238020 MayJune2019 PDFPhilip MooreAinda não há avaliações
- Urbanization (Envi Sci)Documento21 páginasUrbanization (Envi Sci)John-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Unit 2 P2 RORDocumento5 páginas2008 Unit 2 P2 RORJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Unit 2 P1 TTDocumento16 páginas2008 Unit 2 P1 TTJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Unit 1 P2 RORDocumento6 páginas2008 Unit 1 P2 RORJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- The Demographic Transition ModelDocumento2 páginasThe Demographic Transition ModelJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Unit 2 P1 RORDocumento11 páginas2008 Unit 2 P1 RORJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Unit 1 P2 TTDocumento7 páginas2008 Unit 1 P2 TTJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Commercial Arable Wheat ProductionDocumento14 páginasCommercial Arable Wheat ProductionJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Population Control MeasuresDocumento18 páginasPopulation Control MeasuresJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Science: Population DynamicsDocumento12 páginasEnvironmental Science: Population DynamicsJohn-Paul Mollineaux100% (1)
- Principal Impacts & Mitigation MeasuresDocumento10 páginasPrincipal Impacts & Mitigation MeasuresJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- ClimateDocumento10 páginasClimateJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Bearings and GradientDocumento9 páginasBearings and GradientJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- ComparativeDocumento19 páginasComparativeJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- ClimateDocumento10 páginasClimateJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Location in TrinidadDocumento6 páginasIndustrial Location in TrinidadJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- AgricultureDocumento24 páginasAgricultureJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Mineral ResourcesDocumento7 páginasMineral ResourcesJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Population Resource RelationshipsDocumento5 páginasPopulation Resource RelationshipsJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Population Pyramid Activity0001Documento2 páginasPopulation Pyramid Activity0001John-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- CSEC Geography 2015 PaperDocumento14 páginasCSEC Geography 2015 PaperJohn-Paul Mollineaux67% (3)
- Cloud Identification ChartDocumento1 páginaCloud Identification ChartJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Migration WorksheetDocumento3 páginasMigration WorksheetJohn-Paul Mollineaux100% (1)
- CAPE Geography Unit 1 Paper 3 2 May June 2005Documento7 páginasCAPE Geography Unit 1 Paper 3 2 May June 2005John-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Owlie HurricaneDocumento7 páginasOwlie HurricaneKimberly Winter and SparrowAinda não há avaliações
- CSEC Tourism QuestionDocumento2 páginasCSEC Tourism QuestionJohn-Paul Mollineaux0% (1)
- CXC CAPE 2013 Caribbean Studies Paper 02 PDFDocumento3 páginasCXC CAPE 2013 Caribbean Studies Paper 02 PDFJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Poverty Envi Sci QuestionDocumento1 páginaPoverty Envi Sci QuestionJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Microclimate Question For CAPEDocumento1 páginaMicroclimate Question For CAPEJohn-Paul MollineauxAinda não há avaliações
- Paper:Introduction To Economics and Finance: Functions of Economic SystemDocumento10 páginasPaper:Introduction To Economics and Finance: Functions of Economic SystemQadirAinda não há avaliações
- Deictics and Stylistic Function in J.P. Clark-Bekederemo's PoetryDocumento11 páginasDeictics and Stylistic Function in J.P. Clark-Bekederemo's Poetryym_hAinda não há avaliações
- Service M5X0G SMDocumento98 páginasService M5X0G SMbiancocfAinda não há avaliações
- Buku BaruDocumento51 páginasBuku BaruFirdaus HoAinda não há avaliações
- Policy Implementation NotesDocumento17 páginasPolicy Implementation NoteswubeAinda não há avaliações
- SOLVING THE STEADY STATE SOLVER AND UNSTEADY or TRANSIENT SOLVER 2D HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEM BY USINGDocumento3 páginasSOLVING THE STEADY STATE SOLVER AND UNSTEADY or TRANSIENT SOLVER 2D HEAT CONDUCTION PROBLEM BY USINGGodwin LarryAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Tools PDFDocumento57 páginasMachine Tools PDFnikhil tiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Student Committee Sma Al Abidin Bilingual Boarding School: I. BackgroundDocumento5 páginasStudent Committee Sma Al Abidin Bilingual Boarding School: I. BackgroundAzizah Bilqis ArroyanAinda não há avaliações
- EIL 6-51-0051-Rev 06 - 1.1kv-Xlpe - Dimension Cat - B Armour-BbpDocumento2 páginasEIL 6-51-0051-Rev 06 - 1.1kv-Xlpe - Dimension Cat - B Armour-BbpShubham BaderiyaAinda não há avaliações
- High Intermediate 2 Workbook AnswerDocumento23 páginasHigh Intermediate 2 Workbook AnswernikwAinda não há avaliações
- English 8 q3 w1 6 FinalDocumento48 páginasEnglish 8 q3 w1 6 FinalJedidiah NavarreteAinda não há avaliações
- Management of StutteringDocumento182 páginasManagement of Stutteringpappu713100% (2)
- Life Assessment of High Temperature HeadersDocumento31 páginasLife Assessment of High Temperature HeadersAnonymous UoHUag100% (1)
- Language EducationDocumento33 páginasLanguage EducationLaarni Airalyn CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Data - Tad1342veDocumento9 páginasTechnical Data - Tad1342veRachid SmailiAinda não há avaliações
- MJDF Mcqs - Mixed - PDFDocumento19 páginasMJDF Mcqs - Mixed - PDFAyesha Awan0% (3)
- Mars Atlas MOM 8 13Documento6 páginasMars Atlas MOM 8 13aldert_pathAinda não há avaliações
- Python Programming Laboratory Manual & Record: Assistant Professor Maya Group of Colleges DehradunDocumento32 páginasPython Programming Laboratory Manual & Record: Assistant Professor Maya Group of Colleges DehradunKingsterz gamingAinda não há avaliações
- Research in International Business and Finance: Huizheng Liu, Zhe Zong, Kate Hynes, Karolien de Bruyne TDocumento13 páginasResearch in International Business and Finance: Huizheng Liu, Zhe Zong, Kate Hynes, Karolien de Bruyne TDessy ParamitaAinda não há avaliações
- ZyLAB EDiscovery 3.11 What's New ManualDocumento32 páginasZyLAB EDiscovery 3.11 What's New ManualyawahabAinda não há avaliações
- Mastering American EnglishDocumento120 páginasMastering American Englishmarharnwe80% (10)
- Appsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper III 1fcbb2c9Documento12 páginasAppsc Aee Mains 2019 Electrical Engineering Paper III 1fcbb2c9SURYA PRAKASHAinda não há avaliações
- Application of The Ritz Method To The Analysis of Non-Linear Free Vibrations of BeamsDocumento12 páginasApplication of The Ritz Method To The Analysis of Non-Linear Free Vibrations of BeamsKuldeep BhattacharjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Uxc01387a PDFDocumento16 páginasUxc01387a PDFmahesh123Ainda não há avaliações
- Sip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedDocumento17 páginasSip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedANNALLENE MARIELLE FARISCALAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Management System 2016Documento16 páginasIntegrated Management System 2016Mohamed HamedAinda não há avaliações
- Unix SapDocumento4 páginasUnix SapsatyavaninaiduAinda não há avaliações
- AnkitKumar InternshalaResume PDFDocumento2 páginasAnkitKumar InternshalaResume PDFkusha010Ainda não há avaliações
- 0n9) O6..,w48j-GDocumento14 páginas0n9) O6..,w48j-GMocha FurrerAinda não há avaliações
- DOMESDocumento23 páginasDOMESMukthesh ErukullaAinda não há avaliações