Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Accounting:: Capital Assets - Liabilities
Enviado por
ashTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Accounting:: Capital Assets - Liabilities
Enviado por
ashDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
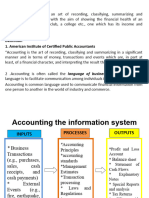
Accounting: Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving,
summarizing, and presenting the information in various reports and analyses. Accounting is also a
profession consisting of individuals having the formal education to carry out these tasks.
Transaction: A business transaction is an economic activity of the business that changes its
financial position.
Transaction may be classified into two types:
External: External transactions are those which involve economic activities between two
independent business entities such as purchase or sale of goods.
Internal: Internal transactions are those economic activities that take place entirely within
one business entity such as depreciation charged on fixed assets.
Account: An account is a record of all business transactions relating to a particular person or item.
In accounting we keep a separate record of each individual, asset, liability, expense or income. The
place where such a record is maintained is termed as an Account.
Capital: It refers to the amount invested by the proprietor in a business enterprise.
Capital = Assets Liabilities
Drawings: Any cash or value of goods withdrawn by the owner for personal use or any private
payments made out of business funds are called drawings.
Liability: It refers to the amount which the firm owes to outsiders.
Liabilities = Assets Capital
Types of liabilities:
Internal liabilities: All amounts which a business entity has to pay to the proprietor or owner.
External liabilities: All amounts which a business entity has to pay to outsiders.
Long term liabilities or fixed liabilities: Liabilities which fall due for payment in a relatively
long period (normally after more than one year).
Short term liabilities or current liabilities: Liabilities which are to be paid in near future
(normally within one year).
Assets: Anything which is in the possession or is the property of a business enterprise including the
amounts due to it from others is called an asset.
Types of assets:
Fixed assets: Assets which are held for: continued use in the business for the purpose of
producing goods or services and are not meant for resale. Examples of fixed assets are Land
and Building, Plant and Machinery, motor Vehicles. Furniture etc.
1. Tangible and Intangible Assets:
i. Tangible assets are those assets which can be seen and touched.
Ex.: Building, Plant, Furniture, Cash etc.
ii.
Intangible Assets are those assets which do not have a physical existence
and which cannot be seen or felt. Ex. Goodwill, Patents, Trade marks
Current Assets: Current assets are those assets which are meant for sale or which the
management would want to convert in to cash within one year.
Examples: Cash in Hand, Cash At Bank, Bills Receivable, Short Term Investments, Debtors,
Stock and Prepaid Expenses.
Revenue: Revenue is the income of a recurring (regular) nature such as receipts from of goods,
rent, commission etc.
Expenditure: Any disbursement of cash or transfer of property or incurring a liability for the
purpose of acquiring assets, goods or services is called expenditure.
Capital expenditure: Any expenditure which is incurred in acquiring or increasing the value
of a fixed asset is termed as capital expenditure.
Revenue expenditure: Any expenditure, the full benefit of which is received during one
accounting period is termed as revenue expenditure.
Expense: Expense is the cost incurred in producing and selling the goods and services.
Income: Excess of revenue over expenses is called income.
Income = Revenue expense
Stock or Inventory: the term stock includes the value of those goods which are lying unsold
at the end of accounting period The Stock may be of two types :1) Opening Stock
2) Closing Stock
Sundry Debtor: Debtors represents those persons or firms to whom goods have been sold
or services rendered on credit and payment has not been received from them.
Sundry creditor: Creditors represents those persons or firms from whom goods have been
purchased or services procured on credit and payment has not been made to them.
Voucher: A voucher is a certificate or document that either allows you to purchase something
or proves that you paid for something. A voucher is sometimes valuable.
Discount: It is a rebate or an allowance given by the seller to the buyer. It is of two types:
1) Trade Discount: When discount is allowed by a seller to its customers at a fixed
percentage on the list or catalogue price of the goods it is called trade discount. It is
not recorded in the books of accounts.
2) Cash Discount: When Discount is allowed to the customers for making prompt
payment it is called cash discount. It is always recorded in the books of accounts.
All accounting transactions are recorded through journal entries that show account
names, amounts, and whether those accounts are recorded in debit or credit side
of accounts.
Methods of Accounting:
Single entry system maintains only personal accounts of debtors and creditors and cash
book.
Double entry system all personal, real and nominal accounts.
Classification of Accounts
Personal Accounts
Impersonal Accounts
Real Accounts
Nominal Accounts
PERSONAL ACCOUNT - These are accounts of parties with whom the business is a carried on.
Personal accounts may be:
Accounts of natural or physical persons. Ex: Rama Account, Krishna Account
Accounts of artificial or legal persons. Ex: ABC & Co.
Representative personal account. Ex: O/S Expenses Account, O/S income Account, Prepaid
Expenses Account, Income Received in Advance.
Rules of Accounting:
Debit the Receiver
Credit the Giver
Real Account - These are asset accounts that appear in the Balance Sheet. They are referred to as
Real Account (or Permanent Accounts) as these are owned by businesses and the balances in these
accounts at the end of an accounting period will be carried over to the next period.
Ex: Cash Account, Land Account, Building Account etc.
Rules of Accounting:
Debit what comes in
Credit what goes out
Nominal Account - These are accounts of expenses and losses which a business incurs and income &
gains which a business earn in the course of business.
Ex: Rent Account, Interest Account.
Rules of Accounting:
Debit all expenses and losses
Credit all income and gains
Você também pode gostar
- The Original Attachment: BasicsDocumento32 páginasThe Original Attachment: BasicsvijayAinda não há avaliações
- Accountancy:: Accounting Concepts Accounting ConventionsDocumento25 páginasAccountancy:: Accounting Concepts Accounting ConventionsVen KatAinda não há avaliações
- Book-Keeping:-: Chapter # 01 AccountingDocumento7 páginasBook-Keeping:-: Chapter # 01 AccountingJehangir AfridiAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting and Financial MangementDocumento25 páginasAccounting and Financial MangementSHASHIAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Term NoteDocumento8 páginasAccounting Term Notemanimeraj506iAinda não há avaliações
- Tally ERP9Documento68 páginasTally ERP9sah100% (10)
- An Introduction To AccountingDocumento20 páginasAn Introduction To AccountingRocket SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Self Complied Book Keeping & AccountancyDocumento14 páginasSelf Complied Book Keeping & AccountancyM AliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter # 1 Business TransactionDocumento22 páginasChapter # 1 Business TransactionWaleed NasirAinda não há avaliações
- BFM Numericals UnformattedDocumento78 páginasBFM Numericals UnformattedAksAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Acc Terms HandoutDocumento3 páginasBasic Acc Terms HandoutpranjalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento23 páginasChapter 1mahiramazoon mazoonAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction AccountsDocumento78 páginasIntroduction AccountsSandya SlideshareAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiDocumento15 páginasBasics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiMukesh DroliaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is AccountingDocumento13 páginasWhat Is AccountingFaridullah MohammadiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 AccountingDocumento12 páginasLesson 3 AccountingDrin BaliteAinda não há avaliações
- Session 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlDocumento10 páginasSession 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlYamu HiadeenAinda não há avaliações
- Tally ERP9Documento68 páginasTally ERP9Jinesh100% (1)
- CH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountsDocumento53 páginasCH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountssagarnarayanmundadaAinda não há avaliações
- The Original Attachment: BasicsDocumento32 páginasThe Original Attachment: BasicsVijayGogulaAinda não há avaliações
- Faa IDocumento18 páginasFaa Iabhiseknanda82495Ainda não há avaliações
- Accounting - : Basic Terms in Accounting - 1. TransactionDocumento14 páginasAccounting - : Basic Terms in Accounting - 1. TransactionKaran Singh RathoreAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 2 Book Keeping and Accounting and Basic TerminologiesDocumento4 páginasChap 2 Book Keeping and Accounting and Basic Terminologiesyousaf.mast777Ainda não há avaliações
- Tally Day 1Documento3 páginasTally Day 1enakta13Ainda não há avaliações
- Accounting Training: Confidential PresentationDocumento74 páginasAccounting Training: Confidential Presentationzee_iitAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Equation: Ads by GoogleDocumento9 páginasAccounting Equation: Ads by GoogleOliver HarmonAinda não há avaliações
- Finance and AccountsDocumento10 páginasFinance and AccountsvijayAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Marks QuestionsDocumento44 páginas2 Marks Questionsvicky241989Ainda não há avaliações
- Basics of Financial Accounting - 1Documento40 páginasBasics of Financial Accounting - 1Dr.Ashok Kumar PanigrahiAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of AccountsDocumento7 páginasPrinciples of AccountsJadeja ChatrieAinda não há avaliações
- Balance SheetDocumento5 páginasBalance Sheet114-CHE-TANMOY PATRAAinda não há avaliações
- ACCOUNTDocumento7 páginasACCOUNTGovind SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Accounting Terms NotesDocumento5 páginasBasic Accounting Terms NotesNathan DavidAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Accountancy Keynotes Ch02 Theory Base of Accounting VKDocumento9 páginas11 Accountancy Keynotes Ch02 Theory Base of Accounting VKAnonymous 1Zepq14UarAinda não há avaliações
- 1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Documento17 páginas1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Shoryamann SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- FIA-FA1 NotesDocumento37 páginasFIA-FA1 NotesAbdul Rehman QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- AccountDocumento37 páginasAccountGaurang MakwanaAinda não há avaliações
- 8011 Topper 21 101 503 550 10598 Basic Accounting Terms Up201904301415 1556613905 1714Documento7 páginas8011 Topper 21 101 503 550 10598 Basic Accounting Terms Up201904301415 1556613905 1714Madhu SAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting - DefinitionsDocumento4 páginasAccounting - DefinitionsYashi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Account Titles T Account Rules of Debit and CreditDocumento9 páginasAccount Titles T Account Rules of Debit and Creditignacio.dant3Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Accounting, Journal, Ledger, Trial BalanceDocumento74 páginasIntroduction To Accounting, Journal, Ledger, Trial Balanceagustinn agustinAinda não há avaliações
- 11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDocumento6 páginas11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDeveshi TewariAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 TAPDocumento19 páginasUnit 1 TAPchethanraaz_66574068Ainda não há avaliações
- Accounting Principles & ProcedureDocumento38 páginasAccounting Principles & ProcedureMuhammad KashifAinda não há avaliações
- Basic NoteDocumento8 páginasBasic Noteworld2learnAinda não há avaliações
- MC1404 - Unit 2Documento111 páginasMC1404 - Unit 2Senthil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- F & A - Basic Accounting TermsDocumento3 páginasF & A - Basic Accounting TermsAbdul Azeez 312Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit I & IIDocumento27 páginasUnit I & IIKapilAinda não há avaliações
- All Basic Terms of AccountingDocumento20 páginasAll Basic Terms of AccountingpoornapavanAinda não há avaliações
- Break-Even Point:c: CC CC CCCCCCCCC CCC CCCCCCCCC C C CCC C CCCC CCCCC C CCCCC CCCCCCCCC C CCCDocumento8 páginasBreak-Even Point:c: CC CC CCCCCCCCC CCC CCCCCCCCC C C CCC C CCCC CCCCC C CCCCC CCCCCCCCC C CCCchanduanu2007Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Accounting Introduction To Accounting Introduction To AccountingDocumento23 páginasIntroduction To Accounting Introduction To Accounting Introduction To AccountingAsitha AjayanAinda não há avaliações
- FA 2 Post-Reading MaterialDocumento7 páginasFA 2 Post-Reading MaterialgggAinda não há avaliações
- Tally Notes Computer Training - Sscstudy PDFDocumento49 páginasTally Notes Computer Training - Sscstudy PDFfreelancertech Nepal100% (1)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes and Chapter Summary: Class-11 Accountancy Chapter 2 - Theory Base of AccountingDocumento9 páginasCBSE Quick Revision Notes and Chapter Summary: Class-11 Accountancy Chapter 2 - Theory Base of AccountingPrashant JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- CLASS XI ACCOUNTANCY NOTES Chapter 2 - Theory Base of AccountingDocumento26 páginasCLASS XI ACCOUNTANCY NOTES Chapter 2 - Theory Base of AccountingPradyumna ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting PDFDocumento10 páginasAccounting PDFRI AZAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of AccountsDocumento4 páginasClassification of AccountsManan MunshiAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Terminology: By: Dr. Deepika Saxena Associate Professor, JIMSDocumento20 páginasAccounting Terminology: By: Dr. Deepika Saxena Associate Professor, JIMSumangAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting NotesDocumento3 páginasAccounting NotesVanya AvramovaAinda não há avaliações
- Cfas Quiz 1 2 3 4Documento47 páginasCfas Quiz 1 2 3 4JONATHAN LANCE JOBLEAinda não há avaliações
- StudentDocumento21 páginasStudentasem shabanAinda não há avaliações
- PAS19 RDocumento1 páginaPAS19 RRarajAinda não há avaliações
- Systems Understanding AidDocumento12 páginasSystems Understanding AidPayton CraigAinda não há avaliações
- Bora AmusementDocumento69 páginasBora Amusementabere100% (2)
- Ink BUSINESS PLAN finalESTDocumento15 páginasInk BUSINESS PLAN finalESTLKMs HUBAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14Documento16 páginasChapter 14Kristian Romeo NapiñasAinda não há avaliações
- Acctg 10 - Final LessonDocumento32 páginasAcctg 10 - Final LessonNANAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer For AccountingDocumento5 páginasReviewer For AccountingAnnie RapanutAinda não há avaliações
- Translation of Foreign Currency StatementDocumento5 páginasTranslation of Foreign Currency StatementPea Del Monte AñanaAinda não há avaliações
- Government Accounting and AuditingDocumento190 páginasGovernment Accounting and AuditingCharles John Palabrica CubarAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting An Introduction To Concepts Methods and Uses 13th Edition by StickneyDocumento32 páginasSolution Manual For Financial Accounting An Introduction To Concepts Methods and Uses 13th Edition by Stickneya540142314Ainda não há avaliações
- R12 Period-End Procedures For Oracle Financials E-Business Suite Document 961285Documento3 páginasR12 Period-End Procedures For Oracle Financials E-Business Suite Document 961285Ravi BirhmanAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Commerce & Management: Semester Subject: Management Accounting Subject Code: BCH 302 Dr. R. S. BisariyaDocumento29 páginasFaculty of Commerce & Management: Semester Subject: Management Accounting Subject Code: BCH 302 Dr. R. S. BisariyaMd Imran Hossain KhanAinda não há avaliações
- National Hydro Power Corporation LTDDocumento4 páginasNational Hydro Power Corporation LTDKeerthi PurushothamanAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Labor: LM-3 Instructions ARDocumento15 páginasDepartment of Labor: LM-3 Instructions ARUSA_DepartmentOfLaborAinda não há avaliações
- Net Plant and EquipmentDocumento3 páginasNet Plant and EquipmentAryo Prastyo AjiAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - CH 4 Accounting Analysis II-w (Color)Documento37 páginas5 - CH 4 Accounting Analysis II-w (Color)Samantha LaiAinda não há avaliações
- REN AND SHINO PartnershipDocumento23 páginasREN AND SHINO PartnershipDaneca Gallardo100% (1)
- (Solution Answers) Advanced Accounting by Dayag, Version 2017 - Chapter 1 (Partnership) - Solution To Problem IDocumento2 páginas(Solution Answers) Advanced Accounting by Dayag, Version 2017 - Chapter 1 (Partnership) - Solution To Problem IJohn Carlos DoringoAinda não há avaliações
- FM09-CH 25Documento9 páginasFM09-CH 25Mukul KadyanAinda não há avaliações
- FAC - Course OutlineDocumento6 páginasFAC - Course OutlineJohn DoeAinda não há avaliações
- BUSCOMDocumento5 páginasBUSCOMGeoreyGAinda não há avaliações
- Fsa 2010 14 PDFDocumento257 páginasFsa 2010 14 PDFsarapariAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Accounting IIDocumento10 páginasPrinciples of Accounting IIEnusah AbdulaiAinda não há avaliações
- Mergers and Acquisitions ValuationDocumento10 páginasMergers and Acquisitions ValuationJack JacintoAinda não há avaliações
- Fas95 PDFDocumento66 páginasFas95 PDFNaamir Wahiyd BeyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3. The Accounting EquationDocumento2 páginasChapter 3. The Accounting EquationKarysse Arielle Noel JalaoAinda não há avaliações
- ValueChain Capstone CaseStudy FinalDocumento28 páginasValueChain Capstone CaseStudy FinalLuisSalvadorPacherresVargasAinda não há avaliações
- ACBS Chapter ManualDocumento12 páginasACBS Chapter ManualJon100% (2)