Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Electrodes
Enviado por
MinMinDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Electrodes
Enviado por
MinMinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Electrode
The choice of electrode for SMAW depends on a number of factors, including the weld
material, welding position and the desired weld properties. The electrode is coated in a metal
mixture called flux, which gives off gases as it decomposes to prevent weld contamination,
introduces deoxidizers to purify the weld, causes weld-protecting slag to form, improves the
arc stability, and provides alloying elements to improve the weld quality.
There are many different types of electrodes used in the shielded metal arc welding, (SMAW)
process.
ELECTRODE IDENTIFICATION
Arc welding electrodes are identified using the A.W.S, (American Welding Society) numbering
system and are made in sizes from 1/16 to 5/16 . An example would be a welding rod identified as
an 1/8" E6011 electrode.
The electrode is 1/8" in diameter
The "E" stands for arc welding electrode.
Next will be either a 4 or 5 digit number stamped on the electrode. The first two numbers of a 4 digit
number and the first 3 digits of a 5 digit number indicate the minimum tensile strength (in thousands
of pounds per square inch) of the weld that the rod will produce, stress relieved. Examples would be
as follows:
E60xx would have a tensile strength of 60,000 psi E110XX would be 110,000 psi
The next to last digit indicates the position the electrode can be used in.
EXX1X is for use in all positions
EXX2X is for use in flat and horizontal positions
EXX3X is for flat welding
The last two digits together, indicate the type of coating on the electrode and the welding current
the electrode can be used with. Such as DC straight, (DC -) DC reverse (DC+) or A.C.
I won't describe the type of coatings of the various electrodes, but will give examples of the type
current each will work with.
ELECTRODES AND CURRENTS USED
EXX10 DC+ (DC reverse or DCRP) electrode positive.
EXX11 AC or DC- (DC straight or DCSP) electrode negative.
EXX12 AC or DCEXX13 AC, DC- or DC+
EXX14 AC, DC- or DC+
EXX15 DC+
EXX16 AC or DC+
EXX18 AC, DC- or DC+
EXX20 AC ,DC- or DC+
EXX24 AC, DC- or DC+
EXX27 AC, DC- or DC+
EXX28 AC or DC+
CURRENT TYPES
SMAW is performed using either AC or DCcurrent. Since DC current flows in one direction, DC
current can be DC straight, (electrode negative) or DC reversed (electrode positive). With DC
reversed,(DC+ OR DCRP) the weld penetration will be deep. DC straight (DC- OR DCSP) the weld will
have a faster melt off and deposit rate. The weld will have medium penetration.
Ac current changes it's polarity 120 times a second by it's self and can not be changed as can DC
current.
SOME ELECTRODE TYPES
This section will briefly describe four electrodes that are commonly used for maintenance and repair
welding of mild steel. There are many other electrodes available for the welding of other kinds of
metals.
Check with your local welding supply dealer for the electrode that should be used for the metal you
want to weld.
E6010 This electrode is used for all position welding using DCRP. It produces a deep penetrating weld
and works well on dirty,rusted, or painted metals
E6011 This electrode has the same characteristics of the E6010, but can be used with AC and DC
currents.
E6013 This electrode can be used with AC and DC currents. It produces a medium penetrating weld
with a superior weld bead appearance.
E7018 This electrode is known as a low hydrogen electrode and can be used with AC or DC. The
coating on the electrode has a low moisture content that reduces the introduction of hydrogen into
the weld. The electrode can produce welds of x-ray quality with medium penetration. (Note, this
electrode must be kept dry. If it gets wet, it must be dried in a rod oven before use.)
E7018-X E Indicates that this is an electrode
70 Indicates how strong this electrode is when welded. Measured in thousands of pounds per square
inch.
1 Indicates in what welding positions it can be used.
8 Indicates the coating, penetration, and current type used. (See Classification Table below)
X Indicates that there are more requirements. (See Additional Requirements below)
WELDING POSITIONS
1 Flat, Horizontal, Vertical (up), Overhead
2 Flat, Horizontal
4 Flat, Horizontal, Overhead, Vertical (down)
Flat Position - usually groove welds, fillet welds only if welded like a V
Horizontal - Fillet welds, welds on walls (travel is from side to side).
Vertical - welds on walls (travel is either up or down).
Overhead - weld that needs to be done upside down.
CLASSIFICATION TABLE
Class Electrode Coating Penetration Current Type
Exxx0 Cellulose, Sodium Deep DCEP
Exxx1 Cellulose, Potassium Deep AC, DCEP
Exxx2 Rutile, Sodium Medium AC, DCEN
Exxx3 Rutile, Potassium Light AC, DCEP, DCEN
Exxx4 Rutile, Iron Powder Medium AC, DCEP, DCEN
Exxx5 Low Hydrogen, Sodium Medium DCEP
Exxx6 Low Hydrogen, Potassium Medium AC, DCEP
Exxx7 Iron Powder, Iron Oxide Medium AC, DCEN
Exxx8 Low Hydrogen, Iron Powder Medium AC, DCEP
Exxx9 Iron Oxide, Rutile, Potassium Medium AC, DCEP, DCEN
Você também pode gostar
- Enough SleepDocumento1 páginaEnough SleepMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Compressive Strength of Concrete at Various Ages PDFDocumento1 páginaCompressive Strength of Concrete at Various Ages PDFMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- BIM DimensionDocumento1 páginaBIM DimensionMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Bored Pile RecordDocumento1 páginaBored Pile RecordMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Schedule of Structural Works For The Next QuarterDocumento1 páginaSchedule of Structural Works For The Next QuarterMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Attendance Record For Site SupervisorDocumento1 páginaAttendance Record For Site SupervisorMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Barg Gauge PressureDocumento1 páginaBarg Gauge PressureMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
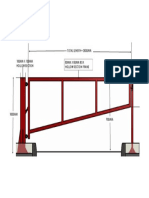
- Manual Car Barrier: Total Length 3500MmDocumento1 páginaManual Car Barrier: Total Length 3500MmMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- GBW RequirementsDocumento40 páginasGBW RequirementsMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Attendance Record For Site Supervisor: Project TitleDocumento1 páginaAttendance Record For Site Supervisor: Project TitleMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- List of Defects: Project: Contract 999A Sewer Diversion Wroks at Tuas BayDocumento1 páginaList of Defects: Project: Contract 999A Sewer Diversion Wroks at Tuas BayMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Tolerance of RC Jacking Pipe PDFDocumento1 páginaTolerance of RC Jacking Pipe PDFMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Abc BQDocumento3 páginasAbc BQMinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- CSC 03Documento1 páginaCSC 03MinMinAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Manager: 28 September 2014Documento1 páginaThe Manager: 28 September 2014MinMinAinda não há avaliações
- Blank Form (Jsea)Documento4 páginasBlank Form (Jsea)MinMin100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- ECU Remapping SolutionDocumento19 páginasECU Remapping SolutionMuhammad Novianto85% (13)
- Pruebas r3925 y Tarjeta Nueva EhwicDocumento74 páginasPruebas r3925 y Tarjeta Nueva EhwicarmanriqueAinda não há avaliações
- Quick Start Guide: HUAWEI Ascend Y210Documento28 páginasQuick Start Guide: HUAWEI Ascend Y210azeem2009Ainda não há avaliações
- Harmonic CSF LW SpecsheetDocumento8 páginasHarmonic CSF LW SpecsheetElectromateAinda não há avaliações
- Des Cote Actuated Globe ValvesDocumento4 páginasDes Cote Actuated Globe ValvesOrueta ClaudioAinda não há avaliações
- Cosasco Side Tee Access Fittings PDFDocumento2 páginasCosasco Side Tee Access Fittings PDFKannan KarunakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Cooperative Clustering Protocol For Saving Energy of Mobile Devices With WLAN and Bluetooth InterfacesDocumento3 páginasCooperative Clustering Protocol For Saving Energy of Mobile Devices With WLAN and Bluetooth InterfacesPriyanka PriyadarsiniAinda não há avaliações
- Using NetshDocumento2 páginasUsing NetshMohcin AllaouiAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Piaggio Beverly 125 (EN)Documento278 páginasPiaggio Beverly 125 (EN)ManuallesAinda não há avaliações
- Air Vee BendingDocumento4 páginasAir Vee BendingMohak Patel100% (1)
- Msi ms-7326 Rev 200 SCHDocumento39 páginasMsi ms-7326 Rev 200 SCHssanti2006Ainda não há avaliações
- AA 3350 Thermal Window: Enhance Your Views With Exceptional Value and PerformanceDocumento2 páginasAA 3350 Thermal Window: Enhance Your Views With Exceptional Value and PerformanceMandi MorrisAinda não há avaliações
- GeepstarDocumento1 páginaGeepstarethanicus0% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Welding Symbol and Its PositionDocumento12 páginasWelding Symbol and Its PositionKrishna PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Bem Webinar 2023 - Introduction of The New Bem Outcome Based Pae (8.3.2023) RestrictedDocumento84 páginasBem Webinar 2023 - Introduction of The New Bem Outcome Based Pae (8.3.2023) RestrictedAzamOthmanAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT I 2 MarksDocumento5 páginasUNIT I 2 MarkscourageouscseAinda não há avaliações
- Combined Structural and Piping Analysis Methodology - ANSYSDocumento45 páginasCombined Structural and Piping Analysis Methodology - ANSYS2challengersAinda não há avaliações
- SR2Documento37 páginasSR2ramitAinda não há avaliações
- Mpeg-Introuduction: MPEG Video Compression Seminar Report 01Documento33 páginasMpeg-Introuduction: MPEG Video Compression Seminar Report 01Santhiraj David JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Global Quality ManualDocumento92 páginasGlobal Quality ManualDuško KovačevićAinda não há avaliações
- BS en 12927-2-2004Documento16 páginasBS en 12927-2-2004widiantoekoAinda não há avaliações
- Ddoocp Ms March2012 FinalDocumento11 páginasDdoocp Ms March2012 FinalSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- Software Testing - Goals, Principles, and LimitationsDocumento4 páginasSoftware Testing - Goals, Principles, and LimitationsTederAinda não há avaliações
- MBDOC48Documento87 páginasMBDOC48Alberto Valero PelaezAinda não há avaliações
- Setan 1Documento2 páginasSetan 1anjingAinda não há avaliações
- AEC (UK) CADStandardsForDrawingManagement v1.0Documento26 páginasAEC (UK) CADStandardsForDrawingManagement v1.0RaffaeleAinda não há avaliações
- IS: 2911 (Part I/Sec 1) - 1979 CODE OF PRACTICE FOR DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF PILE FOUNDATIONSDocumento33 páginasIS: 2911 (Part I/Sec 1) - 1979 CODE OF PRACTICE FOR DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF PILE FOUNDATIONSranjith6688100% (2)
- CCNAquestions Apr 2019 PDFDocumento276 páginasCCNAquestions Apr 2019 PDFdufreine100% (1)
- Boat Trim SystemDocumento4 páginasBoat Trim SystemDino MandicAinda não há avaliações
- Serial Communication: User's Manual QJ71C24N, QJ71C24N-R2 QJ71C24N-R4 QJ71C24, QJ71C24-R2Documento24 páginasSerial Communication: User's Manual QJ71C24N, QJ71C24N-R2 QJ71C24N-R4 QJ71C24, QJ71C24-R2Ing Capriel CaprielAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesNo EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (9)
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsNo EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsAinda não há avaliações