Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Internal Analysis
Enviado por
leo_monty007Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Internal Analysis
Enviado por
leo_monty007Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
INTERNAL ANALYSIS
Three ingredients are critical to the success of a strategy:
First, the strategy must be consistent with conditions in the competitive
environment. Specifically it must take advantage of existing or projected
opportunities and minimize the impact of major threats.
Second, the strategy must place realistic requirements on the firms' internal
capabilities. In other words, the firms pursuit of market opportunities must
be based not only on the existence of such opportunities but also on the
firms key internal strengths.
Finally, the strategy must be carefully executed.
Techniques of Internal Analysis
Managers have historically relied on two approaches to structure their analysis of
internal capabilities so that they introduce greater objectivity into their firms
strategic decision-making process:
Value Chain Analysis
SOWT Analysis
Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is based on the assumption that a businesss basic
purpose is to create value for users of its products or services.
In value chain analysis, mangers divide the activities of their firm into sets of
separate activities that add value.
Each of these activities can add value and each can be a source of
competitive advantage.
By identifying and examining these activities, mangers often acquire an indepth understanding of their firms capabilities, its cost structure, and how
these create competitive advantage or disadvantage.
Value chain analysis divides a firms activities into two major categories,
primary activities and support activities.
Primary activities are those involved in the physical creation of the product,
marketing and transfer to the buyer, and after-sales support.
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
Support activities assist the primary activities by providing infrastructure or
inputs that allow them to take place on an ongoing basis. The value chain
includes a profit margin since a markup above the cost of providing a firms
value-adding activities is normally part of the price paid by buyer creating
value that exceeds cost so as to generate a return for the effort.
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
The most important application of Value Chain Analysis is to expose how a
particular companys cost position compares with the cost positions of its
rivals. What are needed are competitor-versus-competitor estimates for
supplying a product /service to a well-defined customer group or market
segment.
A companys cost competitiveness depends not only on the costs of internally
performed activities (own value chain) but also on cost in the value chains of
its supplies and forward channel allies.
A companys relative cost position and overall competitiveness is linked with
the entire industry value chain system.
Conducting a Value Chain Analysis
The initial step in value chain analysis is to divide a companys operations into
specific activities or business processes, usually grouping them similarly to the
primary and support activities category.
Within each category, a firm typically performs a number of discrete activities that
may represent key strengths or weaknesses. Service activities for example, may
include such discrete activities as installation, repair, parts distribution, and
upgrading any of which could be a major source of competitive advantage or
disadvantage.
The next step is to attempt to attach costs to each discrete activity.
Value chain analysis requires managers to assign costs and assets to each
activity, thereby providing the basis to estimate costs of each activity. The
result provides mangers with a very different way of viewing costs than
traditional cost accounting procedures would produce. Many mangers find the
value activity cost more useful in drawing conclusions about and managing
internal strengths and weakness.
Once the company's value chain has been documented and costs
determined, mangers need to identify the activities that are critical to buyer
satisfaction and market success. It is those that are deserving major scrutiny
in an internal analysis.
Three conditions are essential at this stage in the value chain analysis.
First, the companys basic mission needs to influence mangers choice of activities
they examine in detail. If the company is focused on being a low-cost provider, then
management attention to lower costs should be very visible.
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
Second, the nature of value chains and the relative importance of the activities
within them vary by industry.
Third, the relative importance of value activities can vary by a companys position in
a broader value system that includes the value chains of its upstream suppliers and
downstream customers or partners involved in providing products or services to end
users.
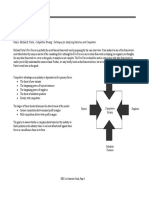
SWOT Analysis
SWOT is an acronym for the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of a firm and
the environmental Opportunities and Threats facing that firm.
Strength is a resource, skill, or other advantage relative to competitors and
the needs of the markets a firm serves or expects to serve.
Weakness is a limitation or deficiency in resource, skills or capabilities that
seriously impedes a firms effective performance.
An opportunity is something that a company may grab for growth and
profitability.
A threat is something a company may be exposed to in the external
environment that may cause suffering in growth or profitability.
SWOT analysis is a useful tool for analyzing an organizations overall
situation.
This approach attempts to balance the internal strengths and weaknesses of
the organization with the external opportunities and threats.
It helps to draw conclusions about (a) how strategy can be matched to both
its resources and market opportunities; and (b) how weaknesses can be
corrected and threats can be guarded against.
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
Steps in SWOT Analysis
While undertaking SWOT analysis of your company you can follow the following four
major steps:
Identification of opportunities and threats posed by external environment.
Identification of opportunities and threats posed by competitors.
Identification of the internal strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
Assessing the attractiveness of the organizations situations and draw conclusions
regarding the need for strategic action.
External Environmental Analysis
Identify the key political, economic, social-cultural, demographic, natural/ecological
and technological forces that are most likely to affect the organization.
Monitor information on the environmental forces.
Select the method to be used in forecasting these forces.
Forecast the trends in these forces.
Identify the market opportunities on the basis of the forecasts of these forces.
Identifying the threats to a companys future profitability.
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
Competitive Analysis
Analyze the industry structure.
Analyze the nature of competition.
Identify and analyze individual competitors.
Identify key strengths and weaknesses of the company as compared to those of
competitors.
Identifying companys market opportunities
Identify threats and opportunities based on industry competitiveness.
Internal Environmental Analysis
Identify the areas for analysis (such as financial position, product position, etc.)
Analyze each of the selected areas.
Identifying companys internal strengths and resource capabilities.
Identifying companys internal weaknesses and resource deficiencies.
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses for their strategy-making implications.
Concluding SWOT Analysis
Khondokar Shah Md Shohidullah
Senior Lecturer
Dania University College
Assess the attractiveness of organizations situation on the basis of identified
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Draw conclusions regarding the need for strategic action.
Managers need to (a) undertake actions to protect/improve the companys
strengths, (b) initiate efforts to overcome the weaknesses, (c) pursue market
opportunities well-suited to the companys resource capabilities, and (d) take
actions to defend against external threats to the companys business.
Você também pode gostar
- Mcqs ST MGTDocumento51 páginasMcqs ST MGTWasama WaqarAinda não há avaliações
- Product Line Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo EverandProduct Line Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- The BCG MatrixDocumento7 páginasThe BCG Matrixkiran808Ainda não há avaliações
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Documento40 páginasSupply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Abdur RajakAinda não há avaliações
- The Mckinsey and Company Case StudyDocumento2 páginasThe Mckinsey and Company Case StudyDoreenAinda não há avaliações
- Organization Development & Change: by Santro Sophia JepilDocumento17 páginasOrganization Development & Change: by Santro Sophia JepilJepil M Philip100% (1)
- Porter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4Documento28 páginasPorter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4mariaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Distribution ManagementDocumento42 páginasIntroduction To Distribution ManagementMANIKANTH TALAKOKKULAAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook DevOps For CIOs PDFDocumento8 páginasEbook DevOps For CIOs PDFDiego Marin MAinda não há avaliações
- Looking Over My ShoulderDocumento53 páginasLooking Over My ShouldertemplercAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing OverviewDocumento9 páginasMarketing OverviewGourav SihariyaAinda não há avaliações
- Developing A Customer Value-Based Theory of The Firm: Marketing in The 21St CenturyDocumento6 páginasDeveloping A Customer Value-Based Theory of The Firm: Marketing in The 21St CenturyAlesa A To ZAinda não há avaliações
- QVARTZ Case Interview Handbook FINAL WebDocumento56 páginasQVARTZ Case Interview Handbook FINAL WebEmmaAinda não há avaliações
- FitzsimmonsMKT382Documento27 páginasFitzsimmonsMKT382Carlos Delgado Nieto100% (1)
- BCG MatrixDocumento4 páginasBCG MatrixDigvijay PatilAinda não há avaliações
- INBO Outline EMBADocumento2 páginasINBO Outline EMBAkaran_girotra_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Professional Ethics PDFDocumento4 páginasProfessional Ethics PDFSanskruti KhuneAinda não há avaliações
- Ch4 PowerpointDocumento20 páginasCh4 Powerpointjaya2504Ainda não há avaliações
- UT Dallas Syllabus For mkt6380.501.11f Taught by Joseph Picken (jcp016300)Documento12 páginasUT Dallas Syllabus For mkt6380.501.11f Taught by Joseph Picken (jcp016300)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupAinda não há avaliações
- IIT BHU Casebook 23Documento182 páginasIIT BHU Casebook 23jai deepakAinda não há avaliações
- Employment Report of WHU MBA 2018 ClassDocumento10 páginasEmployment Report of WHU MBA 2018 ClassSameer Gupta100% (1)
- Supply Chain As A Service1Documento10 páginasSupply Chain As A Service1Shivshankar HondeAinda não há avaliações
- Economies of Scale & Diseconomies of ScaleDocumento17 páginasEconomies of Scale & Diseconomies of ScaleHafizul RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Report FinalDocumento36 páginasBrand Report Finalfahadsiddiqui123Ainda não há avaliações
- BUS416Week5PricingTaxonomy 11466Documento12 páginasBUS416Week5PricingTaxonomy 11466diana.yantiAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Perspectives On The Organizational BuyerDocumento25 páginas2 - Perspectives On The Organizational BuyerRonak ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Case Interview Preparation: Practice Session 2Documento22 páginasCase Interview Preparation: Practice Session 2danielAinda não há avaliações
- Effective Category ManagementDocumento20 páginasEffective Category Managementharjyot cheemaAinda não há avaliações
- BCG Classics TheoriesDocumento18 páginasBCG Classics TheoriesSHALINI ARYA-IBAinda não há avaliações
- The CIO S Guide To ITIL in The MidmarketDocumento13 páginasThe CIO S Guide To ITIL in The MidmarketHasti YektaAinda não há avaliações
- Project - Digital Business StrategyDocumento25 páginasProject - Digital Business Strategydhruvslg86Ainda não há avaliações
- Harvard - CV Packet 2014Documento83 páginasHarvard - CV Packet 2014my009.tkAinda não há avaliações
- Paul Pignataro Leveraged BuyoutsDocumento11 páginasPaul Pignataro Leveraged Buyoutspriyanshu14Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice Online Case Answer GuideDocumento18 páginasPractice Online Case Answer GuideMai TaAinda não há avaliações
- How To Think Like A Strategy Consultant A Primer For General Managers1Documento3 páginasHow To Think Like A Strategy Consultant A Primer For General Managers1jexxicuhAinda não há avaliações
- Competitive AnalysisDocumento38 páginasCompetitive AnalysisGravin LeoAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write A Case AnalysisDocumento18 páginasHow To Write A Case AnalysisLes CanoAinda não há avaliações
- INSEAD 2011 BrochureDocumento32 páginasINSEAD 2011 Brochuretheseus1422Ainda não há avaliações
- Strategy Frameworks: MBA299 - SPRING 2005Documento27 páginasStrategy Frameworks: MBA299 - SPRING 2005Sergio ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy in PracticeDocumento26 páginasStrategy in PracticeVivek KotakAinda não há avaliações
- Case Interview Questions F8Documento2 páginasCase Interview Questions F8Wasif KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Book Presentation of Marketing of High-Tech Products and ServicesDocumento23 páginasBook Presentation of Marketing of High-Tech Products and Servicesankushrasam700Ainda não há avaliações
- Greater China Smartphone Sector 130904Documento52 páginasGreater China Smartphone Sector 130904BLBVORTEXAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures EDocumento89 páginasLectures EEmadRaAinda não há avaliações
- B01.2301.01 MarcianoDocumento12 páginasB01.2301.01 Marcianoprashantrai1Ainda não há avaliações
- Societatea Junimea: Bura GabrielaDocumento27 páginasSocietatea Junimea: Bura GabrielaGabriela BuraAinda não há avaliações
- Empp: Ethics AssignmentDocumento2 páginasEmpp: Ethics AssignmentMason SaidAinda não há avaliações
- Caselet IITBDocumento60 páginasCaselet IITBHarshit SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 5C's and 4 P'S: Customers Company Competitors Collaborators ContextDocumento26 páginas5C's and 4 P'S: Customers Company Competitors Collaborators ContextRohit ChourasiaAinda não há avaliações
- Promotions in The Retail Industry - ConsumerDocumento13 páginasPromotions in The Retail Industry - ConsumerSoumit GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide To Case AnalysisDocumento3 páginasA Guide To Case Analysishegdemahesh1Ainda não há avaliações
- Case FrameworksDocumento14 páginasCase FrameworksVaishnaviAinda não há avaliações
- BPCC CasebookDocumento78 páginasBPCC CasebookAnonymous GehpCj25sAinda não há avaliações
- CCI Yale ConsultingIndustryDocumento20 páginasCCI Yale ConsultingIndustrynparlanceAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 Duke Fuqua MBA CC CasesDocumento50 páginas2008 Duke Fuqua MBA CC Casesr_okoAinda não há avaliações
- Intra Industry AnalysisDocumento9 páginasIntra Industry AnalysisManzzieAinda não há avaliações
- (191018) Aerospace Co. - BainDocumento12 páginas(191018) Aerospace Co. - BainRossieDameLasriaAinda não há avaliações
- IMC PromotionDocumento6 páginasIMC Promotionleo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- Advertising and Promotion: An Integrated Marketing Communications PerspectiveDocumento12 páginasAdvertising and Promotion: An Integrated Marketing Communications Perspectivedawgshit100% (1)
- Anisur RahmanDocumento291 páginasAnisur Rahmanleo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- Typing Exercise PDFDocumento8 páginasTyping Exercise PDFleo_monty00775% (4)
- Service Marketing (Pubali Bank)Documento12 páginasService Marketing (Pubali Bank)leo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- OM Question - Mid 1Documento1 páginaOM Question - Mid 1leo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap009 (Sarwar Pulak's Conflicted Copy 2015-12-21)Documento21 páginasChap009 (Sarwar Pulak's Conflicted Copy 2015-12-21)leo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- Bangladesh University of Professionals: Course Title: Consumer BehaviorDocumento1 páginaBangladesh University of Professionals: Course Title: Consumer Behaviorleo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- Dania University College: Bba 4 & 6 Semester-2015 1 Midterm RoutineDocumento1 páginaDania University College: Bba 4 & 6 Semester-2015 1 Midterm Routineleo_monty007Ainda não há avaliações
- CABE Space - A Guide To Producing Park and Green Space Management PlansDocumento48 páginasCABE Space - A Guide To Producing Park and Green Space Management PlansbenconnolleyAinda não há avaliações
- Out To Lunch: © This Worksheet Is FromDocumento1 páginaOut To Lunch: © This Worksheet Is FromResian Garalde BiscoAinda não há avaliações
- ADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFDocumento30 páginasADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFAnonymous n7rLIWi7100% (2)
- Carim JR Et Al (2016) - Using Procedures Doens't Mean Follow It - A Cognitive Approach To How A Cockpit Manages EmergenciesDocumento11 páginasCarim JR Et Al (2016) - Using Procedures Doens't Mean Follow It - A Cognitive Approach To How A Cockpit Manages EmergenciesFrancisco SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Masters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Documento238 páginasMasters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Bruce SpielbauerAinda não há avaliações
- Business Management Business ManagementDocumento31 páginasBusiness Management Business ManagementDoyieAinda não há avaliações
- The Mystery of The Secret RoomDocumento3 páginasThe Mystery of The Secret RoomNur Farhana100% (2)
- A Proposed Approach To Handling Unbounded Dependencies in Automatic ParsersDocumento149 páginasA Proposed Approach To Handling Unbounded Dependencies in Automatic ParsersRamy Al-GamalAinda não há avaliações
- WK5 SR MOD001074 Grundy 2006 PDFDocumento18 páginasWK5 SR MOD001074 Grundy 2006 PDFadwiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Savage Cyberpunk 2020Documento14 páginasSavage Cyberpunk 2020dmage_uAinda não há avaliações
- Bhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1Documento212 páginasBhrighu Saral Paddhati - 1ErrovioAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Knowledge Syllabus PDFDocumento3 páginasEngineering Knowledge Syllabus PDFsumitAinda não há avaliações
- Annual 2005Documento128 páginasAnnual 2005KarredeLeonAinda não há avaliações
- Mind Map PredictionsDocumento3 páginasMind Map PredictionsIvonne HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- 555LDocumento8 páginas555LVictor Mamani VargasAinda não há avaliações
- Registrable and Non-Registrable Adverse ClaimsDocumento18 páginasRegistrable and Non-Registrable Adverse ClaimsJacob Castro100% (1)
- Vdocuments - MX - Sri Thiruppugal Vidhana Shodasa Upachara Puja PDFDocumento73 páginasVdocuments - MX - Sri Thiruppugal Vidhana Shodasa Upachara Puja PDFDomnick WilkinsAinda não há avaliações
- TDS 39987 Easycoat Profile Decor 3MM Euk GBDocumento3 páginasTDS 39987 Easycoat Profile Decor 3MM Euk GBp4pubgwalyAinda não há avaliações
- Swot Analysis of PiramalDocumento5 páginasSwot Analysis of PiramalPalak NarangAinda não há avaliações
- Formalities in Land LawDocumento4 páginasFormalities in Land LawCalum Parfitt100% (1)
- Las Math 2 Q3 Week 1Documento6 páginasLas Math 2 Q3 Week 1Honeyjo Nette100% (7)
- Homeless Class ActionDocumento36 páginasHomeless Class ActionMichael_Lee_RobertsAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestDocumento12 páginasUnderstanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaAinda não há avaliações
- Permanently End Premature EjaculationDocumento198 páginasPermanently End Premature EjaculationZachary Leow100% (5)
- Lesson 20 PerdevDocumento7 páginasLesson 20 PerdevIvan Joshua RemosAinda não há avaliações
- Friday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksDocumento3 páginasFriday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksCristina Stoian100% (1)
- Audit QuestionnaireDocumento7 páginasAudit QuestionnaireEmz Pleños ValerosoAinda não há avaliações
- DS ClozapineDocumento3 páginasDS ClozapineMiggsAinda não há avaliações
- Bernard New PersDocumento12 páginasBernard New PersChandra SekarAinda não há avaliações
- Kebutuhan Modal Kerja Pada Cv. Cipta Karya Mandiri Di SamarindaDocumento7 páginasKebutuhan Modal Kerja Pada Cv. Cipta Karya Mandiri Di SamarindaHerdi VhantAinda não há avaliações
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistNo EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Summary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (6)
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoNo Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (26)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0No EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffNo Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (19)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNo EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeNo EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (88)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveNo EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (154)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItNo EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (152)
- Summary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsNo EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (48)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleNo EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (48)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)No EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (11)
- Storytelling: A Guide on How to Tell a Story with Storytelling Techniques and Storytelling SecretsNo EverandStorytelling: A Guide on How to Tell a Story with Storytelling Techniques and Storytelling SecretsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (72)
- Understanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationNo EverandUnderstanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (22)
- Visibility Marketing: The No-Holds-Barred Truth About What It Takes to Grab Attention, Build Your Brand, and Win New BusinessNo EverandVisibility Marketing: The No-Holds-Barred Truth About What It Takes to Grab Attention, Build Your Brand, and Win New BusinessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (7)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerNo EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (121)
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"No EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (164)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldNo EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (18)
- Summary: The Intelligent Investor: The Definitive Book on Value Investing by Benjamin Graham: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: The Intelligent Investor: The Definitive Book on Value Investing by Benjamin Graham: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (10)
- Invisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorNo EverandInvisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (131)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeNo EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (278)
- How To Start A Cult: Be bold, build belonging and attract a band of devoted followers to your brandNo EverandHow To Start A Cult: Be bold, build belonging and attract a band of devoted followers to your brandNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- How to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorNo EverandHow to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (33)