Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Enviado por
Lindsay Mills0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
78 visualizações2 páginasThis document summarizes acute glomerulonephritis, which sometimes develops 3 weeks after streptococcal infection, particularly from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria of certain M types. The infection may cause antigen-antibody complexes to form on the glomerular basement membrane of the kidneys. A kidney biopsy can confirm the diagnosis by showing the immune complexes deposited in the glomeruli. Symptoms include pink or cola-colored urine, foamy urine, high blood pressure, and swelling. The M protein of certain S. pyogenes serotypes is associated with acute glomerulonephritis.
Descrição original:
Med
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document summarizes acute glomerulonephritis, which sometimes develops 3 weeks after streptococcal infection, particularly from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria of certain M types. The infection may cause antigen-antibody complexes to form on the glomerular basement membrane of the kidneys. A kidney biopsy can confirm the diagnosis by showing the immune complexes deposited in the glomeruli. Symptoms include pink or cola-colored urine, foamy urine, high blood pressure, and swelling. The M protein of certain S. pyogenes serotypes is associated with acute glomerulonephritis.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
78 visualizações2 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis
Enviado por
Lindsay MillsThis document summarizes acute glomerulonephritis, which sometimes develops 3 weeks after streptococcal infection, particularly from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria of certain M types. The infection may cause antigen-antibody complexes to form on the glomerular basement membrane of the kidneys. A kidney biopsy can confirm the diagnosis by showing the immune complexes deposited in the glomeruli. Symptoms include pink or cola-colored urine, foamy urine, high blood pressure, and swelling. The M protein of certain S. pyogenes serotypes is associated with acute glomerulonephritis.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
I.
ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
This sometimes develops 3 weeks after streptococcal infection,
particularly with M types 12, 4, 2, and 49. Glomerulonephritis may be
initiated by antigen-antibody complexes on the glomerular basement
membrane. The most important antigen is probably in the
streptococcal protoplast membrane.
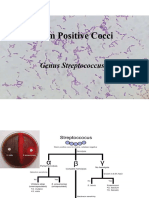
II. CAUSATIVE ORGANISM
STREPTOCOCCUS
PYOGENES
(GABS):
-hemolytic
colonies,
Bacitracin sensitive, PYR (+) hydrolysis of L-pyrrolidonyl-2naphthylamide) and contain the group A antigen
-
Serotype 12 - Poststreptococcal nephritis due to an upper
respiratory infection, occurring primarily in the winter months
Serotype 49 - Poststreptococcal nephritis due to a skin infection,
usually observed in the summer and fall
III. MANNER OF TRANSMISSION
It spread by respiratory droplets or by direct contact.
IV. PROMINENT AND IMPORTANT CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
Acute glomerulonephritis may include pink or cola-colored urine
from red blood cells in your urine (hematuria), foamy urine due to
excess protein (proteinuria), high blood pressure (hypertension), fluid
retention (edema) with swelling evident in your face, hands, feet and
abdomen, fatigue from anemia or kidney failure
V. PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOLOGY
Hyaluronic acid capsule (a polysaccharide) is non-immunogenic;
inhibits phagocytic uptake and the the M-protein which is a virulence
factor, antiphagocytic, used to type group A strep; M12 strains
associated with acute glomerulonephritis. Its spreading factors include
the Streptokinase that breaks down fibrin clot, the Streptococcal DNAse
which liquefies pus and extension of lesion and hyaluronidase that
hydrolyzes the ground substances of connective tissues which is also
important to spread in cellulitis.
VI. PROCEDURE NEEDED FOR DIAGNOSIS
a. SPECIMEN NEEDED
- throat swab, pus, or blood is obtained for culture
- Serum is obtained for antibody determinations
b. LABORATORY TECHNIQUES OR METHODS NEEDED FOR DIAGNOSIS
1. Smears from pus often show single cocci or pairs rather than
definite chains.
2. Culture on blood agar
3. Antigen Detection Tests
4. Kidney Biopsy
c. EXPECTED POSITIVE RESULTS
1. If smears of pus show streptococci but cultures fail to grow,
anaerobic organisms must be suspected
2. Oxygen inactivates streptolysin O. Blood cultures will grow
hemolytic group A streptococci. Group A streptococci can be
rapidly identified by a fluorescent antibody test, the PYR test, and
by rapid tests specific for the presence of the group A-specific
antigen. Streptococci belonging to group A may be presumptively
identified by inhibition of growth by bacitracin
3. Antigen Detection Tests use enzymatic or chemical methods to
extract the antigen from the swab, then use EIA or agglutination
tests to demonstrate the presence of the antigen
d. LIMITATION OF THE PROCEDURE
The resistance to streptococcal diseases is type specific. M
protein interferes with phagocytosis, but in the presence of typespecific antibody to M protein, streptococci are killed by human
leukocytes.
Você também pode gostar
- Streptococcus SPPDocumento52 páginasStreptococcus SPPdrnuaman5Ainda não há avaliações
- True Bacteria - Cocci-Gram Positive Cocci Streptococci: Classification of StreptoccociDocumento11 páginasTrue Bacteria - Cocci-Gram Positive Cocci Streptococci: Classification of StreptoccociSalimAinda não há avaliações
- BacteriologyDocumento36 páginasBacteriologyMuhammad Furqaan Bari100% (1)
- 1 - Systemic BacteriologyDocumento316 páginas1 - Systemic BacteriologyAlsirAinda não há avaliações
- Agent: 1. Haemophilu S InfluenzaDocumento11 páginasAgent: 1. Haemophilu S InfluenzaEd Daniel DavisAinda não há avaliações
- ID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Documento20 páginasID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Oraco1Ainda não há avaliações
- Ultra Structure and DifferenceDocumento6 páginasUltra Structure and DifferenceSteven PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Strep LectDocumento35 páginasStrep LectAnne CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Micro PSGNDocumento32 páginasMicro PSGNMahmoud hilmyAinda não há avaliações
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsDocumento53 páginasStreptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsShyam MishraAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Streptococcus: 3.2.1 The Direct Bacteriological Diagnosis in Streptococcal PharyngitisDocumento5 páginas3 Streptococcus: 3.2.1 The Direct Bacteriological Diagnosis in Streptococcal PharyngitisMahmoud IdlbiAinda não há avaliações
- Module 5Documento15 páginasModule 5MAZIMA FRANKAinda não há avaliações
- Strepto Cocci PDFDocumento34 páginasStrepto Cocci PDFMustafa SaßerAinda não há avaliações
- SGL 11Documento29 páginasSGL 11fasdfAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive Cocci StaphylococciDocumento41 páginasGram Positive Cocci StaphylococciZainab ElgehaniAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive Cocci: Two GeneraDocumento31 páginasGram Positive Cocci: Two GeneraGeorgeNecoară100% (1)
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Smallpox VirusDocumento25 páginasLaboratory Diagnosis of Smallpox Virusማላያላም ማላያላምAinda não há avaliações
- The Genus Streptococcus.: 2.1. Definition. ClassificationDocumento10 páginasThe Genus Streptococcus.: 2.1. Definition. ClassificationMahmoud IdlbiAinda não há avaliações
- GRAM Positive CocciDocumento67 páginasGRAM Positive CocciNoraine Princess TabangcoraAinda não há avaliações
- Hemolysis, Lancefield, DXDocumento1 páginaHemolysis, Lancefield, DXAlyssa Camille PachecoAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Documento45 páginasGram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Charmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- Neisseriaceae FamilyDocumento15 páginasNeisseriaceae FamilyHamidreza RahmaniAinda não há avaliações
- Haemophilus Influenzae: Occasional SitesDocumento7 páginasHaemophilus Influenzae: Occasional SitesJireh LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Neisseria, Diph, AnthraxDocumento53 páginasNeisseria, Diph, AnthraxAyat MostafaAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive Cocci - Sem 1Documento45 páginasGram Positive Cocci - Sem 1Charmaine Corpuz GranilAinda não há avaliações
- Pyogenic Cocci Pyogenic Means " Pus Forming" Cocci Means "Spherical Bacteria"Documento14 páginasPyogenic Cocci Pyogenic Means " Pus Forming" Cocci Means "Spherical Bacteria"Ab AbAinda não há avaliações
- Bacte NoodsDocumento9 páginasBacte NoodsJeanly DoctorAinda não há avaliações
- Nocardia, Bordetella, HaemophilusDocumento31 páginasNocardia, Bordetella, HaemophilusLourdes Cumagon BasiuangAinda não há avaliações
- A. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Streptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae Moraxella CatarrhalisDocumento26 páginasA. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Streptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae Moraxella CatarrhalisMoh EidAinda não há avaliações
- Systemic Bacriology 1Documento87 páginasSystemic Bacriology 1samar yousif mohamedAinda não há avaliações
- 5.0orthomyxoviruses 3.1Documento41 páginas5.0orthomyxoviruses 3.1Jiya MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- STREPTOCOCCUSDocumento24 páginasSTREPTOCOCCUSTUSHAR MORESHWARAinda não há avaliações
- MycoplasmaDocumento2 páginasMycoplasmaHisham ChomanyAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Chapter 17Documento8 páginasMicro Chapter 17Ana AbuladzeAinda não há avaliações
- Msa ComputerDocumento19 páginasMsa ComputerNoor AL Deen SabahAinda não há avaliações
- Pleuropulmonary InfectionsDocumento40 páginasPleuropulmonary InfectionsRahmidatul AftikaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Last Moment RevisionDocumento16 páginasMicrobiology Last Moment RevisionDeepak MainiAinda não há avaliações
- Crypto Cocco SisDocumento32 páginasCrypto Cocco SisLincy JohnyAinda não há avaliações
- Chlamydia SPPDocumento22 páginasChlamydia SPPemmarie gwen tanAinda não há avaliações
- Micro 2 Lec1Documento23 páginasMicro 2 Lec1amerayman2019Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample MCQ's of Bacteriology (M PDFDocumento2 páginasSample MCQ's of Bacteriology (M PDFMohsen Haleem73% (22)
- MCQ MicrobDocumento9 páginasMCQ Microbstationsectiontiga80% (5)
- Gram Positive CocciDocumento55 páginasGram Positive CocciAyat MostafaAinda não há avaliações
- A. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Staphylococcus Epidermidis C. Staphylococcus SaprophyticusDocumento8 páginasA. Staphylococcus Aureus B. Staphylococcus Epidermidis C. Staphylococcus SaprophyticusRuel MaddawinAinda não há avaliações
- Unknown 9Documento3 páginasUnknown 9Adam Ayman MukahalAinda não há avaliações
- Streptococcus PyogenesDocumento40 páginasStreptococcus Pyogenesnshree155Ainda não há avaliações
- Streptocococci enDocumento50 páginasStreptocococci enAndreea Ofelia RusAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumococcus PneumoniaDocumento20 páginasPneumococcus PneumoniaIseoghenaAinda não há avaliações
- CB Part 3Documento76 páginasCB Part 3Mohammad MambuayAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 13Documento8 páginasChapter 13Marah MazahrehAinda não há avaliações
- KROK 1 EXPLANATIONS MicrobiologyDocumento18 páginasKROK 1 EXPLANATIONS MicrobiologyAkpene Racheal100% (1)
- Neisseria: DR John EgbagbaDocumento36 páginasNeisseria: DR John EgbagbaPrincewill SeiyefaAinda não há avaliações
- Streptococcus PyogenesDocumento21 páginasStreptococcus PyogenesSakil MunnaAinda não há avaliações
- Prepared By: Ken Robin A. Canada, RMT, Mls AscpiDocumento35 páginasPrepared By: Ken Robin A. Canada, RMT, Mls AscpiKen Robin CanadaAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran Pernafasan Bawah (MIKRO)Documento36 páginasInfeksi Saluran Pernafasan Bawah (MIKRO)Fawzia Devi FitrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Bacte P3Documento8 páginasBacte P3Reizel GaasAinda não há avaliações
- Pasteurella MultocidaDocumento9 páginasPasteurella MultocidaFatima AbasovaAinda não há avaliações
- Group A Β-Hemolytic Streptococcus: - Tutorial B-1 RSDocumento2 páginasGroup A Β-Hemolytic Streptococcus: - Tutorial B-1 RSGabriella ChafrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Common Micro - Final ExamDocumento43 páginasCommon Micro - Final ExamAbdallah HoussienAinda não há avaliações
- Hontiveros Vs RTCDocumento4 páginasHontiveros Vs RTCLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Rights To Filiation - CivRev1Documento82 páginasRights To Filiation - CivRev1Lindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Zafra Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginasZafra Vs PeopleLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Certification ElectionDocumento4 páginasCertification ElectionLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- PhyllotaxyDocumento11 páginasPhyllotaxyLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Poseidon Fishing Vs NLRCDocumento2 páginasPoseidon Fishing Vs NLRCLindsay Mills100% (2)
- Canon 1-6Documento6 páginasCanon 1-6Lindsay Mills100% (1)
- PNB Vs CA 2009Documento2 páginasPNB Vs CA 2009Lindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Perla Palma Vs CADocumento8 páginasPerla Palma Vs CALindsay Mills100% (1)
- Eagle Star Security Services Vs MirandoDocumento1 páginaEagle Star Security Services Vs MirandoLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Home PlantsDocumento1 páginaHome PlantsLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Quimen Vs CaDocumento4 páginasQuimen Vs CaLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Suntay Vs Cojuanco-SuntayDocumento2 páginasSuntay Vs Cojuanco-SuntayLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Miriam Defensor Santiago Vs COMELECDocumento3 páginasMiriam Defensor Santiago Vs COMELECLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Gatbonton Vs NLRC MapuaDocumento2 páginas2 Gatbonton Vs NLRC MapuaLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Antenatal SteroidsDocumento30 páginasAntenatal Steroidskhadzx100% (2)
- ST Jude at Work Pledge CardsDocumento1 páginaST Jude at Work Pledge CardsJamieAinda não há avaliações
- WICK Digital TWICK Digital TermometarermometarDocumento2 páginasWICK Digital TWICK Digital TermometarermometarRadmila PerovskaAinda não há avaliações
- Declaration of Original WorkDocumento7 páginasDeclaration of Original WorkmoinulmithuAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Health ServicesDocumento2 páginasBasic Health ServicesSam Raven AndresAinda não há avaliações
- Research Article - Burnout Among Nurses in A Nigerian General HospitalDocumento7 páginasResearch Article - Burnout Among Nurses in A Nigerian General HospitalAndrei AlexandruAinda não há avaliações
- VISION 2020 Priority Eye DiseasesDocumento7 páginasVISION 2020 Priority Eye DiseaseschandradwtrAinda não há avaliações
- Therapeutic ExercisesDocumento50 páginasTherapeutic ExercisesBalram Jha100% (3)
- NCP MastectomyDocumento2 páginasNCP MastectomyDoc Duday100% (2)
- MAJ OR PRS - Per CaseDocumento4 páginasMAJ OR PRS - Per CaseAbbie Gail BorromeoAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Health Care PDFDocumento8 páginasPrimary Health Care PDFNindita SariAinda não há avaliações
- ThrombophiliaDocumento37 páginasThrombophiliaapi-272740672Ainda não há avaliações
- Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita of The Upper Limb: Linical RticleDocumento6 páginasArthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita of The Upper Limb: Linical RticleBlajiu BeatriceAinda não há avaliações
- PemphigusDocumento15 páginasPemphigusMelly Narzabal100% (1)
- Rat Anesthesia AnalgesiaDocumento3 páginasRat Anesthesia AnalgesiaAndreea DobrotaAinda não há avaliações
- Methamphetamine 10Documento4 páginasMethamphetamine 10Teodora NeshovaAinda não há avaliações
- Unilateral Greater Occipital Nerve Compression Causing Scalp NumbnessDocumento2 páginasUnilateral Greater Occipital Nerve Compression Causing Scalp NumbnessIzzati N. SariAinda não há avaliações
- Hair Loss Treatment - PRP Hair Fall Treatment E-BookDocumento26 páginasHair Loss Treatment - PRP Hair Fall Treatment E-BookolivaclinicAinda não há avaliações
- Medication Administration Sheet SampleDocumento2 páginasMedication Administration Sheet SampleAmeliaM100% (2)
- Final Exam Questions Module 4 UPLOADEDDocumento4 páginasFinal Exam Questions Module 4 UPLOADEDKane Wang0% (1)
- Bioethics Unit IiiDocumento4 páginasBioethics Unit IiiShannel J. DabalosAinda não há avaliações
- Ham D PDFDocumento1 páginaHam D PDFRabiatul AdawiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Nursiing Management WR. Whole PackageDocumento24 páginasNursiing Management WR. Whole Packageeyna30Ainda não há avaliações
- Inlays and Onlays ReportDocumento32 páginasInlays and Onlays ReportAlnielJoManlapigAinda não há avaliações
- The Basis, Cause, Treatment and Current Research On Cystic FibrosisDocumento10 páginasThe Basis, Cause, Treatment and Current Research On Cystic FibrosiskirkywirkyAinda não há avaliações
- Arrangement of File For Medical PatientDocumento3 páginasArrangement of File For Medical PatientIamnurse NylejAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Disaster Management Guidelines: Directorate of Health Services, KeralaDocumento56 páginasHospital Disaster Management Guidelines: Directorate of Health Services, KeralaPrasetya PerwiraAinda não há avaliações
- About Critical Care NursingDocumento7 páginasAbout Critical Care NursingaivynAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue FeverDocumento7 páginasDengue FeverDrAbhilash RMAinda não há avaliações
- EHOPE GuidelinesDocumento5 páginasEHOPE GuidelinesranAinda não há avaliações
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNo EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNo EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNo EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsNo EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNo EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNo EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)