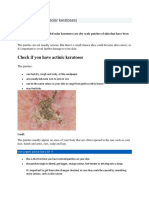
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Asdasdasd
Enviado por
Jayjay AgustinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Asdasdasd
Enviado por
Jayjay AgustinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The integumentary system [is the organ system that protects the body from various kinds of
damage, such as loss of water or abrasion from outside. The system comprises the skin and its
appendages (including hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails).
Epidermis
The epidermis is the relatively thin, tough, outer layer of the skin. Most of the cells in the epidermis
are keratinocytes. They originate from cells in the deepest layer of the epidermis called the basal
layer. New keratinocytes slowly migrate up toward the surface of the epidermis. Once the
keratinocytes reach the skin surface, they are gradually shed and are replaced by newer cells pushed
up from below.
I. EPIDERMIS
A. Cells of the Epidermis
Cells: consists of keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkel cells and Langerhans cells.
Keratinocytes: tightly packed and connected to desmosomes; originate from stratum
basale; produce keratin
Melanocytes: spider-like cells that produce melanin (forms a pigment shield that
protects the nucleus from the UV rays).
Langerhans cells: star-shaped cells from bone marrow. Function to activate the
immune system as macrophages.
Merkel cells: function as sensory receptors
B. Layers of the Epidermis
Stratum basale: consist of predominantly single row of keratinocytes; some
melanocytes (10-25%) and Merkel cells;
Stratum spinosum: several layers thick; Contains flattened irregularly-shaped
keratinocytes, pre-keratin intermediate filaments.
Stratum granulasum: consist of flattened keratinocytes which accumulate
keratohyaline granules (granules form keratin) and lamellated granules (produce
water-resistant chemical).
Stratum lucidum: present only in thick skin and made up
of a few rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes.
Stratum corneum: outermost layer, conts many layers of cells (cornified or horny
cells). Dead skins slough off.
II.
DERMIS
Richly supplied with nerves (sensory receptors), blood vessels,
lymphatic vessels, sweat and sebaceous glands derived from the
epidermis. Contains two layers: papillary and reticular
Papillary layer: Consists of areolar connective tissue made up of
loose collagen and elastic fibers, projections called papillae which
contain touch and pain receptors (Messsners
corpusles). The papillae also form epidermal ridges found on the
surfaces of palms, fingers and feet. On the palm and fingers they
form the fingerprints (genetic markers of individualilty).
Reticular layer: account for about 80% of thickness of dermis;
consist of dense irregular connective tissue. The ECM of this layer
consist of bundles of collagenous fibers which run in parallel and
opposite directions. The fibers give strength and resilience
(toughness) and recoil, while collagen absorbs water and keep the
skin hydrated. Stretch marks found on the buttocks, thighs,
abdomen and breast are due to these fibers.
Disturbances of the skin
Stretch and tear; blisters
Skin Coloration
Skin color is due to a combination of three
pigments: melanin, carotene and hemoglobin.
Melanin is a brown-black pigmentation formed in cells called
melanocytes. Cells are found in the stratum basale and spinosum.
The amount of melanin produced by an individuals is based on
inheritance. Freckles are small patches of Melanin on the skin due
to uneven distribution.
Hemoglobin is the molecules found in RBC that gives blood its red
coloration. It is made of non-protein (heme which contains iron)
and the protein (globin).
Carotene is the yellowish pigment found in the corneum and the
dermis.
Skin color of human races occur as a result of the relative
abundance of melanin and carotene. Dark-skin coloration is due to
melanin. Caucacians produce more carotene than melanin.
III.
Melanin protects the skin and cells of the skin by shielding the UV
light of the sun against the nucleus.
ACCESSORY STRUCTURES
Accessory structures include hair, nail, and glands.
Hair: formed of keratinized cells and consist of two parts: a shaft
and root. The shaft is above the skin and root embedded in the
dermis, in a hair follicle connected to blood supplies and arrector
muscle.
Nail: they are formed of keratinized epidermal cells and occur on
the finger and toes. Consist of a visible area (body) and the root
(embedded in the dermis).
Glands: There are there exocrine (conts ducts)
glands: sebaceous, sudoriferous and ceruminous glands. These
glands secrete their contents to the exterior unlike endocrine which
secrete their contents directly into blood.
a.
Sebaceous glands: produce oil (sebaum) which keeps the
skin oily. The glands are branched and attached to the hair
follicle. Blockage of the gland causes acne.
b.
Sudoriferous(sweat) gland: produce sweat or perspiration
composed of water, salt, urea and uric acid. They are coiled and
tubular shaped and of two types: Eccrine (found on forehead,
back of palm and soles), and Apocrine (larger that eccrine,
found in pubic regions and secrete into hair
follicles). Mammary glands: are specialized form of
sudoriferous gland secrete milk.
c.
Ceruminous glands: found only in the external auditory canal
where they secrete cerumen (earwax). Cerumen is an insect
repellant and also keep the eardrum (tympanic membrane) from
drying out. Excess amount may block.
Skin Cancers
Basal cell carcinoma: originate from the stratum basel (about
70% of skin cancers). Treated by excision.
Squamous carcinoma: originate from cells immediately above
the basale layer. Treatment consist of X-ray and excision.
Malignant melanoma: most life-threatening arises from
melanocytes in the basale. Most often begins as a mole-like
growth and enlarges. May change and metastatize. Often
removed by excision, x-ray.
Temperature Regulation
The regulation of body temperature is carried out by
the hypothalamus in conjunction with the skeletal muscle. The
system works similar to the thermostat in buildings.
Normal body temperature is 37 C(98.6F). This temperature is
produced as a result of metabolic activities which produce heat in
the body.
During the cold when heat loss is excessive, the blood vessel
constrict (therefore less blood to the surface) the muscle contract
frequently (shivering) to produce heat.
In the summer, the vessels dilate (more blood to the skin surface,
more heat loss), sweat pores open and produce perspiration that
cool the surface as heat is lost.
Skin Aging
After 50 years, wrinkles and sagging of the skin become more
noticeable.
Effects of aging are a result of deterioration of collagen, elastic
fibers; decrease in sebaum production, decrease in melanin
production, decrease in content and decomposition of cutaneous
fat.
Disorders of the skin
There are several types of skin disorders associated with the skin.
Some of them are infectious (contagious) or non-infectious.
These disorders include acne, athletes foot, boils, fever blisters,
impetigo, warts, alopecia, burns, calluses (corns), cancers,
dandruff, eczema, moles psoriasis and others.
Contagious skin disorders
A.
Contagious disorders are caused by bacteria or virus or fungus
Acne: characterized by plugged hair follicles that form pimples.
Caused by bacteria, prevalent in teenage years.
Boils: painful infection of hair follicles and sebaceous glands by
Staphylococcus bacteria.
Fever blisters: cold soresfluid filled blisters on the lips or oral
membrane caused by Herpes simplex virus and transmitted by
oral and respiratory exposure. Genital Herpes are painful blisters
on the genitals and transmitted by sexual contact.
Impetigo: highly contagious skin infection caused by bacteria,
occurs in children and characterized by fluid-filled pustules
forming yellow crust over infected area.
Warts: small skin tumors caused by viral infection that stimulate
excessive growth of epithelial cells
B. Non-contagious skin disorders
Alopecia: loss of hair (pattern baldness) is most prevalent in
males and inherited. May also be caused by factors such as poor
nutrition, sensitivity to drugs, and eczema.
Eczema: inflammation producing redness, itching, scalding and
cracking of skin. Seborrheic eczema is produced by hyperactivity of
the sebaceous glands.
Psoriasis: a chronic dermatitis characterized by reddish raised
patches of skin covered with whitish scales. Result from excessive
cell production caused by emotional stress or poor health. Occurs
often on the buttocks, elbows, scalp and knees. Others conditions
are: dandruff, cancers, calluses, hives, burnes.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Bilateral Multiple Apocrine Hidrocystoma of The Eyelids: K E Y WordsDocumento3 páginasBilateral Multiple Apocrine Hidrocystoma of The Eyelids: K E Y WordsAde HaslindaAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Introduction To Sculpting: FlippednormalsDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Sculpting: FlippednormalsAbiyu05Ainda não há avaliações
- Potts R. O. (Ed.), Guy R. A. (Ed.) - Mechanisms of Transdermal Drug Delivery (1997) (357s)Documento368 páginasPotts R. O. (Ed.), Guy R. A. (Ed.) - Mechanisms of Transdermal Drug Delivery (1997) (357s)楊宗棠Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Q2 Second Periodical Test 2023 2024Documento12 páginasQ2 Second Periodical Test 2023 2024ALMA BANIELAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Manoliu Ana - AMG 1 - Grupa 104 - Tema Engleza - BurnsDocumento22 páginasManoliu Ana - AMG 1 - Grupa 104 - Tema Engleza - BurnsAna ManoliuAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Principle of Wound ClosureDocumento39 páginasPrinciple of Wound Closureanon_41679241950% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Triplebottom Hides and Skins Quality Requirements.2Documento77 páginasTriplebottom Hides and Skins Quality Requirements.2John WaweruAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Forensic FingerprintingDocumento11 páginasForensic FingerprintingDioner Ray80% (5)
- Rehabilitation Methods For The Burn Injured Individual PDFDocumento25 páginasRehabilitation Methods For The Burn Injured Individual PDFNestor BalboaAinda não há avaliações
- DA99 Mechanism enDocumento27 páginasDA99 Mechanism enDana DaniatiAinda não há avaliações
- Lession Plan of DermatitisDocumento5 páginasLession Plan of Dermatitismanish dafdaAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Ophthalmology - Wills Eye Institute Oculoplastics 2 PDFDocumento303 páginasColor Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Ophthalmology - Wills Eye Institute Oculoplastics 2 PDFdinul21Ainda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Chapter 18 - SkinDocumento29 páginasChapter 18 - SkinMohammad Riovaldo Radja NugrohoAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Miliaria-An Update: August 2017Documento9 páginasMiliaria-An Update: August 2017Shafira TamaraAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 12 The Skin That Protects You Problem: How Does The Skin Protect You?Documento5 páginasActivity 12 The Skin That Protects You Problem: How Does The Skin Protect You?Roi Vincent VillaraizAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Baumann Skin Type QuestionnaireDocumento19 páginasThe Baumann Skin Type QuestionnaireVigi PrastyanAinda não há avaliações
- Harper S Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology Wiley Blackwell 2020 PDFDocumento2.511 páginasHarper S Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology Wiley Blackwell 2020 PDFAlinaAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Derm CatalogDocumento20 páginasDr. Derm CatalogCosmetics Bulgaria100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Obagi Price ListDocumento3 páginasObagi Price ListANDELYNAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Quiz #1 Questions A&P 1Documento14 páginasQuiz #1 Questions A&P 1trick49Ainda não há avaliações
- Forensic Medicine: It Is The Sum Total of All Reaction of Tissue or Organ To TraumaDocumento2 páginasForensic Medicine: It Is The Sum Total of All Reaction of Tissue or Organ To TraumaLex Tamen CoercitorAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Actinic KeratosesDocumento2 páginasActinic KeratosesًAinda não há avaliações
- Jock ItchDocumento9 páginasJock ItchJo CanensAinda não há avaliações
- Form Sales DailyDocumento1 páginaForm Sales DailyHeru PratamaAinda não há avaliações
- Derma NotesDocumento36 páginasDerma NotesMaya TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- The Seven Dhatus (Tissues) in Ayurvedic MedicineDocumento20 páginasThe Seven Dhatus (Tissues) in Ayurvedic MedicineMicael MendesAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Ujian Sekolah B.Inggris 12Documento8 páginasSoal Ujian Sekolah B.Inggris 12luthfi nabilAinda não há avaliações
- A&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideDocumento2 páginasA&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideJoe ChounramanyAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Ultherapy Patient BrochureDocumento2 páginasUltherapy Patient BrochureSusantiAinda não há avaliações
- Peelings PDFDocumento222 páginasPeelings PDFEdy Estévez100% (3)