Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Exp - 2 Bubble Cap Distillation Column
Enviado por
Adawiyah Al-jufriTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Exp - 2 Bubble Cap Distillation Column
Enviado por
Adawiyah Al-jufriDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
Experiment 2
BUBBLE CAP DISTILLATION PROCESS
1.0
OBJECTIVES
To operate vapor liquid separation process using a Packed Column Distillation
Unit.
2.0
To analyze the effect of reflux ratio on separation of ethanol-water system.
To determine the number of stages by using McCabe Thiele method
OVERVIEW
Distillation is a separation method in which mixture components in a liquid mixture are
separated based on their relative volatilities. The distillation column provides an environment
where the liquid and vapour phases can approach equilibrium within a column. In the packed
column there is high surface area for contact between the vapor and liquid, whereas the plate
column provides distinct stages at which equilibrium can be approached. Separation is achieved
by condensed vapor flowing as a liquid down the column theoretically achieving equilibrium with
the vapor flowing up the column. The distribution of components differs in each phase and results
in the separation. In the case of a binary mixture in batch distillation under total reflux, the vapor
condensing at the top of the distillation column will be rich in one of the components. Liquid
leaving the reboiler at the base of the column rich in the other component. As the system reaches
equilibrium the separation process reaches steady state for that apparatus and set of operating
conditions. This experiment is designed to study the distillation of a binary mixture of Ethanol
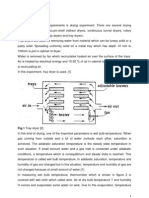
Water in a tray distillation column. Figure 1 is a sketch of a tray with bubble cap and Figure 2
shows the schematic diagram of the apparatus in this experiment.
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
Figure 1: Bubble cap tray
Figure 2 shows the schematic diagram of the apparatus in this experiment.
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
Figure 2: Packed distillation column
3.0
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
3.1
Chemicals and Ancillary Equipments Required:
PART A: Calibration curve of ethanol-water mixtures
Chemicals required:
Ethanol industrial grade.
Deionized-Water.
Ancillary equipments required:
Test Tube( 20 test tube per group)
Beakers (50 ml).
Dropper
Glass rod
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
Refractometer
PART A: Calibration curve of Ethanol-Water mixtures
1. Obtain 21 test tubes; label the test tubes with A1 until A21. Total volume in each test
tube is 20 ml.
2. Prepare the mixture of ethanol and deionized water to each test tube according to
volume indicate by Table 1.
3. Note that, Stir the mixture of solution (A1 until A21) with glass rod.
4. Obtain the refractive index reading for solution in each tube using refractometer.
5. Record the refractive index reading for each tube tests using Table 1.
Table 1: The volume of chemical needed in each test tube
Test tube
A1
Volume of
Ethanol(ml)
0
Volume of DeionizedWater(ml)
20
A2
19
A3
18
A4
17
A5
16
A6
15
Refractive
Index(RI)
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
A7
14
A8
13
A9
12
A10
11
A11
10
10
A12
11
A13
12
A14
13
A15
14
A16
15
A17
16
A18
17
A19
18
A20
19
A21
20
PART B: Operate vapor -liquid separation process using a Packed Column Distillation Unit
under reflux ratio.
Chemicals required:
Ethanol industrial grade.
Deionized-Water.
Ancillary equipments required:
Dropper
Beakers (50 ml)
Tissue
Refractometer
3.2 General start-up procedures.
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
1. Prepare 30 litres mixture of ethanol-deionized water by adding 10 % of ethanol
from total volume of the mixture.
2. Ensure valves V3, V4 and V5 are closed.
3. Ensure valves V2, V8 and V10 are open.
4. Ensure that the Bottom Product sampling valve V5 and Top Product sampling valve
V4 are closed.
5. Slowly turn on the Cooling Water (CW) supply to the Condenser. Make sure water is
indeed flowing through it by makesure water flows to the drain from the Cooling
Water outlets. Do not start the experiment until the Cooling Water flow is visible in
the outlets to the drain.
6. Set water flowrate of Cooling Water (CW) to 6 L/min by adjusting water flow
control FCV2.
7. Open valve V6, fill the reboiler vessel(B1) with the 30 L Ethanol-Water mixtures.
8. Close the valve V6 and open valve V2 after finish fill reboiler vessel with the 30 L
Ethanol-Water mixtures.
9. Check that the liquid level in Reboiler vessel is satisfactory (Refer to instructor /
technician).Otherwise top up with the Ethanol Water mixture through the Charge
Port (Refer to instructor / technician).
10 Turn on the main power control switch.
11 Turn on the power switch of the heater.
12 Switch on electrical supply (green heater on button).
13 Set heater controller HC4 to maximum setting (about 230V@ 30A).
14 Allow a period of 15 minutes for the equipment to maintain thermal equilibrium with
surroundings.
15 The unit is now ready to be used for an experiment.
Experiment: Operation under reflux ratio condition
1. When mixture is start to boil, close valves V2.
2. When distillate liquid is seen to flow through R1.1C, adjust both valve for Reflux
Ratio RCV1 so that both readings on R1 and R2 provide a reflux ratio of 1.0 for the
operation.
3. Ensure that the Reflux Ratio is maintained at 1.0.
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
4. Collect samples for bottom product from valve V5 and the overhead product from
valve V4 for every 5 minutes.
5. Observe the temperature of the reboiler T14.If the temperature is already 90 OC,
reduce the current of the reboiler to between 20A.
6. Concentration of the samples drawn is measure using the refractive index method
7. Repeat step 2-6 ,for reflux ratio of 1.5 and 2.0
3.3
General shut down procedures.
1. Adjust heater controller HC.4 to minimum setting.
2. Switch off electrical supply (red heater off button).
3. Turn off the power switch of the reboiler.
4.
Turn off the Main power control switch.
5. Do not drain the hot liquid from the Reboiler. If necessary, the liquid within the
system could be drained only when the liquid is already cooled.
6. Allow the cooling water to run for some time.
5.0
ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
Discuss all your results. The questions below only serve as a guideline. Your discussion
should not only limit to these questions.
1. Make a calibration graph based on your data obtained from Experiment A by
plotting Refractive index (RI) on the y-axis against mole fraction of ethanol on the xaxis.
2. Determine the mole fraction of ethanol for the top and bottom product for each reflux
by refer to calibration graph.
3. Calculate the complete overall and component mass balance of the process.
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
4. Determine the number of stages that occur in the processes for each reflux by
construct the graph McCabe Thiele Method. Equilibrium data for ethanol-water
system is given in Appendix A.
5. Discuss the results obtained and effect of reflux ratio for ethanol-water mixture
separation
6. Discuss any possible errors in the experiment and state any recommendation to
improve the process.
5.0
REFERENCES
1. Treybal, R.E., Mass Transfer Operations, 3rd ed., Mc-Graw-Hill, 1981
2. McCabe & Smith, Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, 5th ed, Mc-Graw-Hill,
1993
3. Geankoplis,C. J. Z., Mass Transport Phenomena, 4th Ed., Rine Hart Winston, New
York.
4. Coulson & Richardson, Chemical Engineering. Vol. 2 Pergamon Press, Oxford.
APPENDIX A
Table of Results
Reflux ratio
= 1.0
Rotameter reading R1 (L/hr)
= __________________
Rotameter reading R2 (L/hr)
= __________________
Temperature T4 (oC)
= __________________
Temperature T2 (oC)
= __________________
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
Time, t
(min)
CLB 20804
TOP PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
BOTTOM PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Reflux ratio
= 1.5
Rotameter reading R1 (L/hr)
= __________________
Rotameter reading R2 (L/hr)
= __________________
Temperature T4 (oC)
= __________________
Temperature T2 (oC)
= __________________
Time, t
(min)
TOP PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
BOTTOM PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Reflux ratio
= 2.0
Rotameter reading R1 (L/hr)
= __________________
Rotameter reading R2 (L/hr)
= __________________
Temperature T4 (oC)
= __________________
Temperature T2 (oC)
= __________________
Time, t
(min)
TOP PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
BOTTOM PRODUCT
Refractive index
Mole fraction
(RI)
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
APPENDIX B
Equilibrium Data for Ethanol-Water Mixtures
Mole fraction of ethanol in liquid, x
Mole fraction of ethanol in vapor, y
0.00
0.00
0.05
0.38
10
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
0.10
0.53
0.40
0.75
0.60
0.79
0.80
0.86
0.94
0.94
0.90
0.91
0.94
0.94
0.96
0.96
0.98
0.99
STEP BY STEP TO CONSTRUCT GRAPH MCCABE THIELE METHOD
1. Draw the equilibrium curve based on data given in Appendix B, by plotting mole fraction
of ethanol in vapor on the y-axis against mole fraction of ethanol in liquid on the x-axis.
2. Draw the 45-degree line( y =x)
3. Indicate distillate (xD), bottom (xB) and feed (xF) composition on the graph based on
data obtained from experiment.(refer to appendix A).
4. Draw the feed line (q line). For saturated liquid, this is a vertical line running from the
feed composition (xF) through the equilibrium curve.
11
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
5. For a specified reflux ratio, r, draw the 'rectifying' line (ROL). This rectifying line begins
at the point xD on the 45-degree line and has intercept on y-axis.
ROL equation:
6. Draw the 'stripping' line (SOL) by connecting the intersection of the feed line and the
rectifying line and the point xB on the 45-degree line.
7. Beginning at the point xD on the rectifying line, draw a horizontal line to the equilibrium
curve and then a vertical line to the operating (rectifying or stripping) line.
8. Repeat step 7 forming a staircase until you reach or pass the point x B on the 45-degree
line.
9. Each point where the staircase intersects the equilibrium curve denotes one stage in the
column.
12
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Mass Transfer I
CLB 20804
13
NA/Exp1/SEPT 2014
Você também pode gostar
- Quarter 1 - Module 1Documento31 páginasQuarter 1 - Module 1Roger Santos Peña75% (4)
- Sakui, K., & Cowie, N. (2012) - The Dark Side of Motivation - Teachers' Perspectives On 'Unmotivation'. ELTJ, 66 (2), 205-213.Documento9 páginasSakui, K., & Cowie, N. (2012) - The Dark Side of Motivation - Teachers' Perspectives On 'Unmotivation'. ELTJ, 66 (2), 205-213.Robert HutchinsonAinda não há avaliações
- ISO 27001 Introduction Course (05 IT01)Documento56 páginasISO 27001 Introduction Course (05 IT01)Sheik MohaideenAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report (Initial Boiling Point)Documento10 páginasLab Report (Initial Boiling Point)nisasoberiAinda não há avaliações
- Lieh TzuDocumento203 páginasLieh TzuBrent Cullen100% (2)
- Liquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentNo EverandLiquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentAinda não há avaliações
- Rom 2 - 0-11 (En)Documento132 páginasRom 2 - 0-11 (En)Mara HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- High-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationNo EverandHigh-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report Aspen Hysis UiTMDocumento12 páginasLab Report Aspen Hysis UiTMAhmad SiddiqAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Chemical Thermodynamics for GeoscientistsNo EverandPractical Chemical Thermodynamics for GeoscientistsAinda não há avaliações
- ECE Companies ListDocumento9 páginasECE Companies ListPolaiah Geriki100% (1)
- Exp 2 Bubble Cap DistillationDocumento7 páginasExp 2 Bubble Cap DistillationFaris HamirAinda não há avaliações
- Batch Distillation at Total Reflux Using Sieve Tray DistillationDocumento5 páginasBatch Distillation at Total Reflux Using Sieve Tray DistillationNurul Atikah JapryAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report - Distillation of Bubble CapDocumento21 páginasLab Report - Distillation of Bubble Capratish100% (1)
- Suspension Od Solid Particles (Revised Report)Documento7 páginasSuspension Od Solid Particles (Revised Report)michsantosAinda não há avaliações
- Sep Lab Exp 1 LatestDocumento20 páginasSep Lab Exp 1 LatestChan Chun ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment: Batch Reactor Unit Operations Lab I (CHEGR3787L) Fall 2004Documento5 páginasExperiment: Batch Reactor Unit Operations Lab I (CHEGR3787L) Fall 2004Janice YanAinda não há avaliações
- H W5Documento1 páginaH W5Bahadır KayaAinda não há avaliações
- CSTR 40LDocumento17 páginasCSTR 40LMuhammad Affifudin100% (1)
- Series and Parallel PumpsDocumento11 páginasSeries and Parallel PumpsKevin Devastian100% (1)
- PDFDocumento88 páginasPDFMuralidharanAinda não há avaliações
- Apparatus, Procedure, Recommendation Tray DryerDocumento4 páginasApparatus, Procedure, Recommendation Tray DryerillyzlAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 2 - Forced Draft Cooling TowerDocumento14 páginasExperiment 2 - Forced Draft Cooling TowerSonia YuAinda não há avaliações
- Results and Discussion of CSTR in SeriesDocumento3 páginasResults and Discussion of CSTR in SeriesleenzalalAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Operation Laboratory 2 (CCB 3062)Documento7 páginasUnit Operation Laboratory 2 (CCB 3062)Carl Erickson100% (1)
- C4 Lab ReportDocumento11 páginasC4 Lab ReportchaitanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer Lab Manual 2015-16Documento99 páginasHeat Transfer Lab Manual 2015-16Harshit Sinha100% (1)
- IYOHA COLLINS 16CF020531 Batch Reactor ReportDocumento19 páginasIYOHA COLLINS 16CF020531 Batch Reactor ReportDavid OvieAinda não há avaliações
- Boiling ExperimentDocumento7 páginasBoiling ExperimentFareeha SaeedAinda não há avaliações
- 123 Reynolds ApparatusDocumento5 páginas123 Reynolds ApparatusKonem SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1Documento12 páginasLab 1JoeJeanAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No.: 03 Name of The Experiment: Determination of Fluid Flow Condition by Osborne Reynold's Apparatus. ObjectiveDocumento6 páginasExperiment No.: 03 Name of The Experiment: Determination of Fluid Flow Condition by Osborne Reynold's Apparatus. ObjectiveMd Afif AbrarAinda não há avaliações
- Osbourne ReynoldDocumento13 páginasOsbourne ReynoldN Afiqah Razak0% (1)
- Vle UnitDocumento26 páginasVle UnitAhmad Ifwat50% (2)
- Experiment 1 CSTR DynamicsDocumento24 páginasExperiment 1 CSTR DynamicsFarhan Hazeeq50% (2)
- Unsteady Heat ConductionDocumento15 páginasUnsteady Heat ConductionShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- Lab10 CompleteDocumento22 páginasLab10 CompleteMastura Ahmad Termizi100% (1)
- RI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureDocumento12 páginasRI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureAnonymous VeJYFSMWLIAinda não há avaliações
- Bubble Cap Distillation ColumnDocumento3 páginasBubble Cap Distillation Columnnhalieza1067Ainda não há avaliações
- Schx4007 Mass Transfer LabDocumento60 páginasSchx4007 Mass Transfer LabAhmed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Characterization of Solid ParticlesDocumento8 páginasCharacterization of Solid ParticlesShary Mosquera50% (2)
- Experiment 1B - Tubular ReactorDocumento14 páginasExperiment 1B - Tubular ReactorNajmul Puda PappadamAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM3002 Tutorial Sheet 3Documento1 páginaCHEM3002 Tutorial Sheet 3Sunmoon Al-HaddabiAinda não há avaliações
- S-Lab Manual Exp 3 - Air Flow Process ControlDocumento12 páginasS-Lab Manual Exp 3 - Air Flow Process Controlarif arifinAinda não há avaliações
- Cre 1 IntroductionDocumento4 páginasCre 1 IntroductionEvangeline LauAinda não há avaliações
- Bernoullis Equation Lab ReportDocumento12 páginasBernoullis Equation Lab ReportgeduyoxAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 4 Batch Evaporative Crystallization PDFDocumento9 páginasExp 4 Batch Evaporative Crystallization PDFmirza farhanAinda não há avaliações
- Cooling Tower ReportDocumento11 páginasCooling Tower Reportbae zazAinda não há avaliações
- P4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperatureDocumento7 páginasP4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperaturejayaprinaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report TPP Experiment 3Documento10 páginasLab Report TPP Experiment 3Nurul Najwa100% (1)
- Files 2-Experiments Homogenuous Batch ReactorDocumento6 páginasFiles 2-Experiments Homogenuous Batch ReactorS M AseemAinda não há avaliações
- CHE 463 Heat Transfer Assignment 2: Group Member Id NumberDocumento6 páginasCHE 463 Heat Transfer Assignment 2: Group Member Id NumberFakrul HakimiAinda não há avaliações
- g3 Thermodynamics ExperimentsDocumento42 páginasg3 Thermodynamics Experimentsarda Максим50% (2)
- Distillation ColumnDocumento6 páginasDistillation ColumnArif HanafiAinda não há avaliações
- Vapour Liquid Equilibrium ExpDocumento5 páginasVapour Liquid Equilibrium ExpAakash Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 4Documento43 páginasChapter 4aliAinda não há avaliações
- Discussion Tray DryerDocumento3 páginasDiscussion Tray DryerIskandar ZulkarnainAinda não há avaliações
- Isothermal CSTR PDFDocumento9 páginasIsothermal CSTR PDFprashant_cool_4_uAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 1 Tray DrierDocumento7 páginasLab Report 1 Tray Drier_never_mind_100% (1)
- CHE516 - Lab Report On Plug Flow Reactor PDFDocumento25 páginasCHE516 - Lab Report On Plug Flow Reactor PDFCesarah Cabungcal100% (1)
- Absorption in Packed Bed Lab ManualDocumento5 páginasAbsorption in Packed Bed Lab ManualAshish Verma100% (1)
- LleDocumento30 páginasLlefirstlove_492_736373Ainda não há avaliações
- Series and Parallel Pumps Lab ReportDocumento16 páginasSeries and Parallel Pumps Lab ReportHannan AyubAinda não há avaliações
- Insights into Chemical Engineering: Selected Papers of P.V. DanckwertsNo EverandInsights into Chemical Engineering: Selected Papers of P.V. DanckwertsAinda não há avaliações
- 22 Khan S.Documento7 páginas22 Khan S.scholarlyreseachjAinda não há avaliações
- rp10 PDFDocumento77 páginasrp10 PDFRobson DiasAinda não há avaliações
- Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing World, Fourth EditionDocumento41 páginasSystems Analysis and Design in A Changing World, Fourth EditionKoko Dwika PutraAinda não há avaliações
- HatfieldDocumento33 páginasHatfieldAlex ForrestAinda não há avaliações
- Winter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportDocumento6 páginasWinter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportColette AdamsAinda não há avaliações
- QuexBook TutorialDocumento14 páginasQuexBook TutorialJeffrey FarillasAinda não há avaliações
- CV & Surat Lamaran KerjaDocumento2 páginasCV & Surat Lamaran KerjaAci Hiko RickoAinda não há avaliações
- FuzzingBluetooth Paul ShenDocumento8 páginasFuzzingBluetooth Paul Shen许昆Ainda não há avaliações
- The cardioprotective effect of astaxanthin against isoprenaline-induced myocardial injury in rats: involvement of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathwayDocumento7 páginasThe cardioprotective effect of astaxanthin against isoprenaline-induced myocardial injury in rats: involvement of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathwayMennatallah AliAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Documento1 páginaPhysics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Nilima Aparajita SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Bill of Quantities ChurchDocumento52 páginasSummary of Bill of Quantities ChurchBiniamAinda não há avaliações
- CL57T V4.0Documento14 páginasCL57T V4.0dimitriAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocumento7 páginasNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Caspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Documento255 páginasCaspar Hirschi - The Origins of Nationalism - An Alternative History From Ancient Rome To Early Modern Germany-Cambridge University Press (2012)Roc SolàAinda não há avaliações
- Peer PressureDocumento13 páginasPeer PressuremightymarcAinda não há avaliações
- EqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25Documento7 páginasEqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25du2efsAinda não há avaliações
- KsDocumento5 páginasKsnurlatifahAinda não há avaliações
- Review On AlgebraDocumento29 páginasReview On AlgebraGraziela GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 23Documento9 páginasChapter 23Javier Chuchullo TitoAinda não há avaliações
- Antena TelnetDocumento4 páginasAntena TelnetMarco PiambaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6 - Vibration ControlDocumento62 páginasLesson 6 - Vibration ControlIzzat IkramAinda não há avaliações
- MultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFDocumento10 páginasMultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFAndrés ColmenaresAinda não há avaliações
- Where We Are in Place and Time "We Are Part of The Universe and Feel Compelled To Explore It."Documento1 páginaWhere We Are in Place and Time "We Are Part of The Universe and Feel Compelled To Explore It."Safia-umm Suhaim- FareedAinda não há avaliações
- English Homework 10 Grammar Focus 2: Lecturer: Mr. Dr. H. Abdul Hamid, M.SiDocumento4 páginasEnglish Homework 10 Grammar Focus 2: Lecturer: Mr. Dr. H. Abdul Hamid, M.SiMutiara siwa UtamiAinda não há avaliações