Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Skema - Program Inap Ilmu Ibnu Khaldun 2016 Biologi SPM
Enviado por
Mazura AhmadDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Skema - Program Inap Ilmu Ibnu Khaldun 2016 Biologi SPM
Enviado por
Mazura AhmadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
APPLICATION LEVEL
1. Diagram 2.2 and 2.3 show the condition of two plants which are added with fertilizer. The
plant in Diagram 2.3 is added with excess fertilizer. Explain the condition of the plant in
Diagram 2.3.
Rajah 2.2 dan 2.3 menunjukkan keadaa dua batang pokok yang disiram dengan baja.
Pokok dalam Rajah 2.3 disiram dengan baja yang berlebihan. Terangkan keadaan pokok
dalam Rajah 2.3.
Diagram 2.2
Diagram 2.3
Excess fertilizer dissolves in the soil water is hypertonic to the cell sap of plant
roots.
Water diffuses from the cell sap into soil by osmosis.
The cells are plasmolysed and the plant wilts.
[3 marks]
2.
A dog suddenly barks and chases you. Your heartbeat increases and your palms
become sweaty. You feel so scared and run away.
Seekor anjing tiba-tiba menyalak dan mengejar anda. Degupan jantung anda
meningkat dan tapak tangan anda berpeluh. Anda merasa amat takut dan terus
melarikan diri.
Based on the above statement describe how endocrine system is involved in the fight
and flight situation.
Berdasarkan penyataan di atas, huraikan bagaimana sistem endokrin terlibat dalam
situasi lawan dan lari.
F adrenaline is secreted by adrenal gland
P1 (adrenaline) cause the heartbeat / breathing rate increase
P2 more oxygen and glucose are sent/ transported to the tissues
P3 metabolic rate / cellular respiration increases
P4 - more energy is produced (to run away)
[4 marks]
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
3. Diagram 3 shows an experiment to determine the energy values of a peanut and a dried
prawn.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu eksperimen untuk menentukan nilai tenaga satu biji kacang
tanah dan seekor udang kering
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
In this experiment, 20 cm3 of distilled water is used and 2.0 g of peanut and 1.8 g of
dried prawn is burnt. The initial and final temperature of water is shown in Table 1
below.
Dalam eksperimen ini ,20 cm3 air suling digunakan dan 2.0 g kacang tanah dan 1.8
g
udang kering dibakar. Suhu awal dan suhu akhir air ditunjukkan dalam Jadual 1 di
bawah.
Food sample
Sampel
makanan
Peanut
Kacang tanah
Dried prawn
Udang kering
Mass
Jisim
(g)
Initial
temperature of
water
Suhu awal air
(C)
Final
temperature of
water
Suhu akhir air
(C)
Rise in
temperature
of the water
Kenaikan
suhu air
(C)
2.0
29
45
16
1.8
30
34
(b) Record the rise in temperature of the water in the spaces provided in Table 1.
Rekod kenaikan suhu air dalam ruang yang disediakan pada Jadual 1.
[1 mark ]
(c) The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 Jg-1 oC -1. Use the following formula to calculate
the energy values of the peanut and the dried prawn.
2
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
Muatan haba tentu air ialah 4.2 Jg-1 oC -1.Gunakan rumusan berikut untuk mengira nilai
tenaga untuk kacang tanah dan udang kering
Energy value = ( mass of water X 4.2 X rise in temperature of water ) Jg-1
mass of food
Nilai tenaga = (jisim air X 4.2 X kenaikan suhu air ) Jg-1
jisim makanan
Energy value of the peanut = 20 X 4.2 X 16 Jg-1
2.0
= 672.0 Jg-1
Energy value of the dried prawn = 20 X 4.2 X 4 Jg-1
1.8
= 186.7 Jg-1
[ 4 marks ]
4. A mango farmer picked ten baskets of immature mangoes for sale. Give one
suggestion to make all the mangoes ripen on the same time.
Seorang pekebun mangga telah memetik sepuluh bakul buah mangga untuk dijual.
Berikan satu cadangan untuk membolehkan semua buah mangga tersebut masak
serentak.
The farmer can use ethylene.
[1 mark]
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
ANALYSIS LEVEL
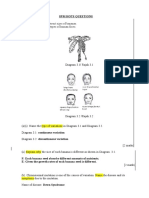
1. Diagram 4.1 shows the blood circulatory system in organism P and Q.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan sistem peredaran darah bagi organism P dan organism Q.
(a) Explain one difference in the structure of the heart between organism P and organism.
Terangkan satu perbezaan antara struktur jantung organisma P dan organisma Q.
F : heart of organism P has 4 chamber but organism Q has two chamber
P1: organism P has right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle but
organism Q has ventricle and an atrium // organism P has two atriums and
two ventricles but organism Q has one ventricle and one atrium
P2: in organism P, the heart receives both oxygenated blood and deoxygenated
blood while in organism Q, the heart only receives deoxygenated blood.
F + Any P
[2 marks]
2. (c ) Diagram 7. 3 shows two activities of movement in an earthworm and a grasshopper.
Rajah 7.3 menunjukkan dua aktiviti pergerakan bagi seekor cacing tanah dan
belalang.
Diagram7.3 (i)
Rajah 7.3(i)
4
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
Diagram7.3 (ii)
Rajah 7.3(ii)
Explain one similarity and four differences between skeletal systems in both
organisms.
Terangkan satu persamaaan dan empat perbezaan antara sistem rangka bagi keduadua organisma.
[10 marks]
Similarity:
F1 : Both organism has antagonistic muscles
E1 : to allow coordinate movements of the body
Differences :
F2 : Earthworm has hydrostatic skeleton but grasshopper has exoskeleton
E2 : Earthworm the force of contraction is applied to a fluid-filled
cavity (coelom)//
Grasshopper muscles attached to the interior surface of exoskeleton
F3 : Earthworm has longitudinal and muscular muscle but grasshopper has
flexor and extensor muscles
E3 : for muscle contraction and relaxation
F4 : Earthworm muscle produce peristaltic waves along the body but for
grasshopper this will cause bending and straightening of the legs
E4 : in order to produce locomotion
F5 : Earthworm has bristles (chaetae) but grasshopper has a pair of long and
strong hind legs.
E5 : Chaetae is used to anchor the ground for earthworm but hind legs are
adapted for hopping for grasshopper.
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
3.
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
SYNTHESIS LEVEL
1. Farmers add chemical fertilisers and spray insecticides on their crops. Discuss the good
and bad effects of both activities and their impact on agriculture and the environment.
Para petani menambahkan baja kimia dan menyembur racun serangga kepada tanaman.
Bincangkan kesan baik dan buruk kedua-dua aktiviti tersebut terhadap pertanian dan
persekitaran.
[10 marks]
Add chemical fertilisers
Good Effects
G1 : Supplying required minerals/ions/nitrates/ammonia
G2 : Increase yield of crop
Any 1
Bad Effects
B1 : Excess fertilizers may be washed away
B2 : causing enrichment of water
B3 : Results in rapid growth of algae / algae bloom
B4 : Increased in BOD of water // decrease of oxygen content in river
B5 : Causes death of fish/aquatic animals in the river
Any 4
Spray chemical insecticides
Good Effects
G3 : An effective way to kill/destroy/ insects /weeds
G4 : Population of insects / weeds reduce
Any 1
Bad Effects
B6 : Hazardous to farmers if inhaled
B7 : Contaminate the underground water / rivers
B8 : Causes the death of aquatic animals
B9 : In the long term, the insects / weeds may develops into mutant strain which
is resistance to the chemicals
B10 : Chemical insecticide no longer effective for the pest/weeds control
Any 4
2. Diagram 9.2 and 9.3 show a few examples of fresh food and processed food.
Rajah 9.2 dan 9.3 menunjukkan beberapa contoh makanan segar dan makanan diproses.
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
Diagram 9.2
Rajah 9.2
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
Discuss the good effects and bad effects of processed food in our daily life.
Bincangkan kesan-kesan baik dan buruk makanan diproses dalam kehidupan harian
kita.
[10 marks]
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
Contoh Soalan Biologi Kertas 2 SPM
NO
MARK SCHEME
(a)
(i)
1
1
1
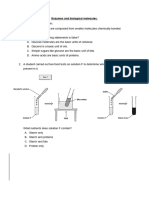
Able to state two characteristics of enzyme L based on Diagram 3
Sample answer:
F1 - Enzyme L is ( highly ) specific // Enzyme L can only catalyse one
kind of substrate
F2 - Enzyme L is not destroyed by the reaction //Enzyme L remain
unchanged at the end of the reactions
(c)
1
1
Able to Name molecule K, molecule M and enzyme L.
Sample answer:
Molecule K : maltose
Molecule M : glucose
Enzyme L : maltase
(b)
TOTAL
MARK
Able to name organ X and organ Y.
Sample answer:
Organ X : small intestine // ileum
Organ Y : liver
(ii)
SUB
MARK
1
1
Able to explain the importance of forming glycogen in organ Y
Sample answer:
E1 as ( carbohydrate ) storage
E2 - excess blood sugar / glucose will be converted into glycogen
E3 glycogen will be converted to glucose when the blood sugar /
glucose level fall / when body needs energy
1
1
1
Max 2
2
9
SKEMA PROGRAM INAP ILMU IBNU KHALDUN 2016 BIOLOGI
SPM
(d)
Able to explain why molecules M are transported from organ Y to
muscle cells..
Sample answer:
F - muscle cells need (to produce a lot of )energy to carry out body
activities / movement.
E1 - muscle cells used ( molecule )M to carry out cellular respiration (to
produce energy) // (Molecule) M will be oxidised
E2 - molecule M produce energy
1
1
1
12
10
Você também pode gostar
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesNo EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- EBEA Training PDFDocumento100 páginasEBEA Training PDFAnonymous SQ5kprsQnAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822Documento76 páginasNatural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822SAMANTHA SMITHAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Essay CollectionDocumento67 páginasBiology Essay Collectionyeelin96Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocumento15 páginasBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzAinda não há avaliações
- Kibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 FinalDocumento15 páginasKibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 Finalmins.succesorAinda não há avaliações
- 11biology S6 Theory - 202305110900131Documento7 páginas11biology S6 Theory - 202305110900131Mutaganda Ami fideleAinda não há avaliações
- Perfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Documento15 páginasPerfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Farhanah AlawdeenAinda não há avaliações
- Set Soalan PT3Documento35 páginasSet Soalan PT3Anthony Hunt100% (1)
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocumento10 páginasNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiAinda não há avaliações
- 0610 s13 QP 31Documento20 páginas0610 s13 QP 31Choudhry WalidAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Paper 2Documento13 páginasBiology Paper 2Aniel DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 BioDocumento9 páginasSkema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 Biogomathi24Ainda não há avaliações
- Australian Biology Olympiad 2008Documento31 páginasAustralian Biology Olympiad 2008Science Olympiad BlogAinda não há avaliações
- Biology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Documento9 páginasBiology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Sushi Emilia100% (1)
- Q Bio 2012Documento24 páginasQ Bio 2012Visva VisvamAinda não há avaliações
- 0610 s11 QP 31Documento20 páginas0610 s11 QP 31karan79Ainda não há avaliações
- (198 Marks) : The Following Diagram Shows The Synthesis and Regulation of Some Amino AcidsDocumento37 páginas(198 Marks) : The Following Diagram Shows The Synthesis and Regulation of Some Amino AcidsEmAinda não há avaliações
- Topical Test Chapter 9 EssayDocumento4 páginasTopical Test Chapter 9 Essaylimsi74Ainda não há avaliações
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support Document (3 - 231031 - 124406Documento37 páginasLife Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support Document (3 - 231031 - 124406Anesu MachowaniAinda não há avaliações
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocumento10 páginasNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiAinda não há avaliações
- Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyDocumento102 páginasModule SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyKen Yew PiongAinda não há avaliações
- 2021-2022 S3 AE AnswersDocumento12 páginas2021-2022 S3 AE AnswersEndi WongAinda não há avaliações
- Jawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section ADocumento34 páginasJawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section AArleenaAmnaAinda não há avaliações
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support DocumentDocumento36 páginasLife Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support DocumentLiezel100% (1)
- Ujian Tengah Semester: Gambar 1Documento3 páginasUjian Tengah Semester: Gambar 1Riza McShaneAinda não há avaliações
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 8Documento37 páginasBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 8Shephard Png100% (8)
- 2022 FA DBQ Topic 4Documento11 páginas2022 FA DBQ Topic 4Zulkarnyne RezaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 RespirationDocumento13 páginasPaper 2 RespirationRetaj KhassawnehAinda não há avaliações
- GE-ES Module3Documento11 páginasGE-ES Module3EnzuAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)Documento9 páginasTopic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)한서현Ainda não há avaliações
- 2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQDocumento180 páginas2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQArthur ChoiAinda não há avaliações
- BIO121 - Experiment 4Documento7 páginasBIO121 - Experiment 4Tan Ri ShenAinda não há avaliações
- Ecology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsDocumento6 páginasEcology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsJoeAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeDocumento283 páginasModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeCikgu Faizal87% (15)
- MCQ Theory Revision Enzymes and Biological MoleculesDocumento8 páginasMCQ Theory Revision Enzymes and Biological Moleculesnflbubba468Ainda não há avaliações
- 4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestDocumento15 páginas4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestMia Isabella San InocencioAinda não há avaliações
- Bio S2 Exercises NewDocumento7 páginasBio S2 Exercises NewNSABIMANA JANVIERAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1 Bio 2011Documento30 páginasPaper 1 Bio 2011Hafiq IkhwanAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsDocumento10 páginasSkema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsFidaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Maranda End Term 2 Form 2 - FREE KCSE PAST PAPERSDocumento6 páginasBiology Maranda End Term 2 Form 2 - FREE KCSE PAST PAPERSclinAinda não há avaliações
- KS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test SQ AnswersDocumento8 páginasKS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test SQ AnswersPaul Burgess0% (1)
- Peperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/SjDocumento8 páginasPeperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/SjDavid SwanggerboyAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedDocumento4 páginasSample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedCarl Agape DavisAinda não há avaliações
- 0610 w11 QP 32Documento20 páginas0610 w11 QP 32Seif HatemAinda não há avaliações
- M.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)Documento11 páginasM.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)sumizulfi786Ainda não há avaliações
- Dissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Productivity LabDocumento6 páginasDissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Productivity Labapi-235548856Ainda não há avaliações
- SP Dse Bio 1 1Documento31 páginasSP Dse Bio 1 1ddd dddAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel TzulDocumento7 páginasPrimary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel Tzulapi-323831182Ainda não há avaliações
- Biologi Kertas 1Documento29 páginasBiologi Kertas 1ain_senseiAinda não há avaliações
- 9.2.1.a Most Organisms Are Active in A Limited Temperature RangeDocumento10 páginas9.2.1.a Most Organisms Are Active in A Limited Temperature RangeTroy SouthwellAinda não há avaliações
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionNo EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Biology and Troubleshooting of Facultative LagoonsNo EverandThe Biology and Troubleshooting of Facultative LagoonsAinda não há avaliações
- Freshwater Algae: Identification, Enumeration and Use as BioindicatorsNo EverandFreshwater Algae: Identification, Enumeration and Use as BioindicatorsAinda não há avaliações
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemAinda não há avaliações
- Aquaculture Ecosystems: Adaptability and SustainabilityNo EverandAquaculture Ecosystems: Adaptability and SustainabilitySaleem MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Atlantic Cod: A Bio-EcologyNo EverandAtlantic Cod: A Bio-EcologyGeorge A. RoseAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Ecology of the OceansNo EverandMicrobial Ecology of the OceansJosep M. GasolAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Writing Research AnjaliDocumento7 páginasAcademic Writing Research AnjaliAnjali RamnaniAinda não há avaliações
- Illocutionary Acts Expressed Through Sign Language in "Silence Movie"Documento74 páginasIllocutionary Acts Expressed Through Sign Language in "Silence Movie"vivianAinda não há avaliações
- Danik Bhaskar Jaipur 04-30-2014Documento24 páginasDanik Bhaskar Jaipur 04-30-2014bhaskar_newsAinda não há avaliações
- Chaos Theory and The Lorenz EquationDocumento15 páginasChaos Theory and The Lorenz EquationloslogosehAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle r2rDocumento12 páginasOracle r2rMichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Cathodic Protection For New Fixed Offshore Steel Structures (AmendmentsSupplements To DNVGL-RP-B401)Documento22 páginasCathodic Protection For New Fixed Offshore Steel Structures (AmendmentsSupplements To DNVGL-RP-B401)Abd.Buhari Abd.GalimAinda não há avaliações
- Inthanon Phase1 Report-BlockchainDocumento48 páginasInthanon Phase1 Report-BlockchainHimanshu DavadaAinda não há avaliações
- 22nd Session of The IPCCDocumento43 páginas22nd Session of The IPCCIntergovernmental Panel on Climate ChangeAinda não há avaliações
- Attitude Change Social PsychologyDocumento16 páginasAttitude Change Social PsychologyJaebeom's Best FriendAinda não há avaliações
- Arl TR 3567Documento72 páginasArl TR 3567AndrewScotsonAinda não há avaliações
- Address: 140-P, SECTOR-1, Extension Trikuta Nagar, Jammu, P/O-180012 Mobile:+919622235979,+917006398105Documento2 páginasAddress: 140-P, SECTOR-1, Extension Trikuta Nagar, Jammu, P/O-180012 Mobile:+919622235979,+917006398105shubham guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Raz lm27 Voyagersinspace CLR PDFDocumento9 páginasRaz lm27 Voyagersinspace CLR PDFRachelle Ann MarianoAinda não há avaliações
- Using Bapi in LSMWDocumento17 páginasUsing Bapi in LSMWapi-3731371100% (2)
- Henry Corbin and The Archetypal RealmDocumento2 páginasHenry Corbin and The Archetypal RealmZeteticus100% (2)
- Solar Pavement - A New Emerging TechnologyDocumento13 páginasSolar Pavement - A New Emerging TechnologyMauricio Pertuz ParraAinda não há avaliações
- Transferring A 38DLP - FTP Format File Using 2GB MicroSD CardDocumento5 páginasTransferring A 38DLP - FTP Format File Using 2GB MicroSD CardBoulHich BoulHichAinda não há avaliações
- Human Resource DepartmentDocumento6 páginasHuman Resource DepartmentHardik BabelAinda não há avaliações
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8857 FSB - 0510Documento6 páginasChemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8857 FSB - 0510PromagEnviro.comAinda não há avaliações
- EURASIA v8n4 OzgelenDocumento10 páginasEURASIA v8n4 OzgelenSeptiana SariAinda não há avaliações
- Kiran S (1) - Kedlaya - The William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition 1985-2000Documento351 páginasKiran S (1) - Kedlaya - The William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition 1985-2000ellioatAinda não há avaliações
- BIC3313-Internet Payment Systems-Assignment 1Documento2 páginasBIC3313-Internet Payment Systems-Assignment 1Borotho MolemoAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Test For Pec 5Documento10 páginasPractice Test For Pec 5Thuỳ Linh Đinh TháiAinda não há avaliações
- GMO's and LabelingDocumento30 páginasGMO's and LabelingNational Press FoundationAinda não há avaliações
- Catatan Statisktik FIXDocumento59 páginasCatatan Statisktik FIXAndrian WicaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Asclepius, Commentary On Nicomachus PDFDocumento90 páginasAsclepius, Commentary On Nicomachus PDFSpyros MarkouAinda não há avaliações
- Astm d2624Documento8 páginasAstm d2624mehrez100% (1)
- Transcribed Speech Roberto Mangabeira Unger at Social FrontiersDocumento4 páginasTranscribed Speech Roberto Mangabeira Unger at Social Frontiersmarli_kaboomAinda não há avaliações
- Placas Estructurales PrefabricadasDocumento12 páginasPlacas Estructurales PrefabricadasDaniela VMAinda não há avaliações
- Pledge Parent DeclarationDocumento2 páginasPledge Parent Declarationabc xyz100% (3)