Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Belle-Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Enviado por
Rashed ShatnawiDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Belle-Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Enviado por
Rashed ShatnawiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
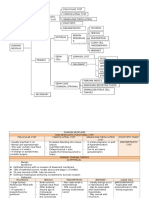
GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM)
Classification
Whites Classification
Diabetes mellitus DM= Fasting venous glucose
type I --- insulin
concentration > 8.0 mmol/l and 2
dependent
hrs (75 gm load ) > 11.0 mmol/l
(Ketosis-prone)
(or) one of the above + Symptoms
Diabetes mellitus IGT = Fasting < 8.00 mmol/l, but 2
type II--- nonhr (75 gm load) = (9.0-10.9)
How
do diabetic pt present
insulin
Symptoms
dependent
Risk factors ( history &
(Ketosisexamination)
resistant)
Impaired Glucose Blood tests--screening
Tolerance and
Screening
Gestational
30% have none of the Above risk
Diabetes (IGT)
factors
Diabetogenic
Effects of
Not all DM, IGT, have persistent
Pregnancy
glucosuria
Insulin resistance 50% of pregnant women have
Increased
glucosuria at some time
lipolysis
Altered maternal
gluconeogenesis
Risk Factors
DM, IGT, must be suspected
4. Obesity
in Pregnant women with
5. Hypertension in multipara
1. Age > 30
6. Polyhydramnios
2. Family history of DM
7. Recurrent
WHO recommended modified GTT ( 75 gm load)
Normal
Fasting
Impaired glucose tolerance
6.0 >
Hours 2
6.0-7.9
Or
And
9.0>
9.0-10.9
3. Past history of:
- Diabetes in a previous
pregnancy
- Unexplained I.U.F.D.,
Neonatal death
- Congenital abnormalities
- Recurrent abortions
- Large babies > 90th centile
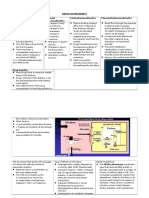
Risk factors
Complications
Maternal
Obstetric
- Polyhydramnios
infections:Urinary, Fungal
8. Significant Glycosuria
Complications
Neurol
ogic
Fetal
(1) Macrosomia &
Traumatic delivery
Central Nervous
system
** Note: when a two-vessel
cord is found, suspect a high
- pre-eclampsia (10- Peripheral
(30% in seemingly
15%)
neuropathy
controlled)
(2) Delayed organ
Diabetic
Gastrointestinal
maturity (RDS) 6x
Emergencies
disturbance
(3) Congenital
- Hypoglycaemia
malformations:
- Ketoacidosis
Infecti
Cardiovascular :
- Diabetic coma
ons
Vascular &
- Urinary
Transposition of great
End-Organs
vessels
-Renal
Ventricular septal defect
- Ophthalmic
Aortic coarctation
Artial septal defect
- Peripheral vascular
Complications
Principles of management:
(Neonatal)
Start in preconception time
Hypoglycaemia
Specific during pregnancy
RDS
Specific
- Anencephaly
Holoprosencephaly
- Encephalocele
Skeletal & spinal
-Caudal regression
Genitourinary
- Renal agenesis
- ureteral dupliction
Gastrointestinal
- anal atresia
Control
incidence of congenital
anomalies
(4) Intrauterine fetal
Death
(5) Growth restriction (in
advanced DM)
Hypocalcaemia
Polycythaemia
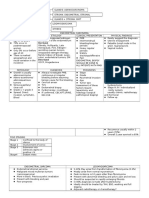
Diet:
16 x Wt. (pounds ) + 300 = CALORIES
Carbohydrates
60%
Fat
20%
Protein
20%
Insulin:
Regiment A
* 3 times sol.-with meals
+ lnt. Evening
Or
- Regiment B
* 2 types (short &
intermediate)
Twice Daily
Dose (daily) = wt. (kg) x 0.6 first
x 0.7 second
x 0.8 third
2/3 in A.M.
2/3 1nt + 1/3 short
1/3 in P.M.
1/2 1nt + short.
Control :
Fasting < 5.0 mmol/1
2 hrs P.P. < 7.0 mmol/1
Adjustment when necessary
Glycosylated Hb A1c (retrospective) < 6
Fetal well being:
AFP 16-18 wks
Detailed scan 19-20 wks
Biophysical assay from 28 wks
Fetal wt. & growth two weekly (3rd)
Delivery:
- Timing depends on: (Around 38 wks)
Maternal factors
Biochemical control
Fetal status
- Method --- LSCS in any medical or obstetric
complication.
**Insulin dose adjusted on hourly basis with caloric
requirements intravenously.
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Obsandgyne Tables 200pagesDocumento221 páginasObsandgyne Tables 200pagesRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle-Premature Rupture of MembraneDocumento5 páginasBelle-Premature Rupture of MembraneRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Vaginal DischargeDocumento12 páginasBelle Vaginal DischargeRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle RH IsoimmunizationDocumento3 páginasBelle RH IsoimmunizationRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle-Fetal Growth AssessmentDocumento10 páginasBelle-Fetal Growth AssessmentRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- IM NotesDocumento74 páginasIM NotesRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle STDDocumento8 páginasBelle STDRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Sga IugrDocumento6 páginasBelle Sga IugrRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle PuerperiumDocumento11 páginasBelle PuerperiumRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle PreTerm Labor PROMDocumento3 páginasBelle PreTerm Labor PROMRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Shoulder DystociaDocumento2 páginasBelle Shoulder DystociaRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Prolonged PregnancyDocumento2 páginasBelle Prolonged PregnancyRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle PuerperiumDocumento10 páginasBelle PuerperiumRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Infertility Management ARTDocumento6 páginasBelle Infertility Management ARTRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Multiple GestationsDocumento2 páginasBelle Multiple GestationsRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle-Preterm Labour ManagementDocumento4 páginasBelle-Preterm Labour ManagementRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Preterm BirthDocumento9 páginasBelle Preterm BirthRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle PPHDocumento4 páginasBelle PPHRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle MenopauseDocumento7 páginasBelle MenopauseRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Preinvasive Invasive Cervical DiseaseDocumento5 páginasBelle Preinvasive Invasive Cervical DiseaseRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Ovarian NeoplasmDocumento6 páginasBelle Ovarian NeoplasmRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- (Belle) MalpresentationDocumento4 páginas(Belle) MalpresentationAray Al-AfiqahAinda não há avaliações
- Belle PIDDocumento2 páginasBelle PIDRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Medical Disorders in PregnancyDocumento4 páginasBelle Medical Disorders in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Induction of LaborDocumento5 páginasBelle Induction of LaborRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle-Drugs in PregnancyDocumento17 páginasBelle-Drugs in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Instruments For OGDocumento1 páginaBelle Instruments For OGRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Malignant Lesions of The Body of UterusDocumento2 páginasBelle Malignant Lesions of The Body of UterusRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- Belle Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocumento6 páginasBelle Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Moraxela CatarhalisDocumento20 páginasMoraxela Catarhalisshinwar benyamenAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Humairah Sari Putri NIM: 1711110475 Class: A 2017 1Documento1 páginaName: Humairah Sari Putri NIM: 1711110475 Class: A 2017 1humairah sari putriAinda não há avaliações
- Serous Fluids AnalysisDocumento15 páginasSerous Fluids AnalysisMustafa Khandgawi100% (1)
- Nursing Careplan Inadequate Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasNursing Careplan Inadequate Tissue PerfusionAudrey LewisAinda não há avaliações
- Ds OresolDocumento1 páginaDs OresolShannie Padilla100% (1)
- Lupus NephritisDocumento15 páginasLupus NephritisVilza maharaniAinda não há avaliações
- Check List of Claim DocumentsDocumento2 páginasCheck List of Claim Documentsmohammed hussainAinda não há avaliações
- The Galeniko-Noone MethodDocumento82 páginasThe Galeniko-Noone MethodLouFerrignoAinda não há avaliações
- Reiki Plain and SimpleDocumento76 páginasReiki Plain and Simpleshaileshkaran100% (4)
- PDRI TablesDocumento7 páginasPDRI TablesCamille Chen100% (1)
- EBOT. Columna DegenerativaDocumento43 páginasEBOT. Columna DegenerativaAna GarridoAinda não há avaliações
- Kantar Article (2012) PsychopathologyDocumento3 páginasKantar Article (2012) PsychopathologyShelby Jones-StachnikAinda não há avaliações
- Getting Past Your BreakupDocumento4 páginasGetting Past Your BreakupKrish Malhotra0% (1)
- OsteoarthritisDocumento10 páginasOsteoarthritisRehanAinda não há avaliações
- Norton Mental Health Annual Catalog 2016Documento84 páginasNorton Mental Health Annual Catalog 2016NortonMentalHealthAinda não há avaliações
- Ucrete MFDocumento3 páginasUcrete MFMohiuddin MuhinAinda não há avaliações
- WebberDocumento8 páginasWebberHusainiAinda não há avaliações
- Sprint-8 Intervals: Turn On Your Afterburners!: Directions: For "Optimal" Results, Follow These Simple GuidelinesDocumento1 páginaSprint-8 Intervals: Turn On Your Afterburners!: Directions: For "Optimal" Results, Follow These Simple Guidelinesknowman1Ainda não há avaliações
- The Opioid Epidemic - Medical, Nursing and Counseling Behavioral Treatment-NovaDocumento269 páginasThe Opioid Epidemic - Medical, Nursing and Counseling Behavioral Treatment-NovaClinica MonserratAinda não há avaliações
- LOG BOOK FOR Objective Assessment C P I II KMU 1Documento13 páginasLOG BOOK FOR Objective Assessment C P I II KMU 1sayed imadAinda não há avaliações
- Product CatalogueDocumento27 páginasProduct CatalogueHemang M. GajjarAinda não há avaliações
- Pub105961487 PDFDocumento164 páginasPub105961487 PDFTriandini SanusiAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin A DeficiencyDocumento14 páginasVitamin A DeficiencyelitaAinda não há avaliações
- Primal Kitchen Cookbook ReviewDocumento338 páginasPrimal Kitchen Cookbook ReviewPrimalBlueprint100% (21)
- Oral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IIDocumento5 páginasOral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IItaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- The Grief Recovery Method Guide For LossDocumento14 páginasThe Grief Recovery Method Guide For LossRiyan Portuguez100% (2)
- Expressing EmpathyDocumento2 páginasExpressing EmpathyAlexandra DumitruAinda não há avaliações
- Journal of Food Composition and AnalysisDocumento11 páginasJournal of Food Composition and AnalysisJessica WeaverAinda não há avaliações
- Homoeopathy Shoots The Shooting Pain (A Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated at Ber Sarai Dispensary)Documento14 páginasHomoeopathy Shoots The Shooting Pain (A Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated at Ber Sarai Dispensary)Homoeopathic Pulse100% (1)
- Occipitocervical Instability & DislocationDocumento205 páginasOccipitocervical Instability & DislocationM Ivan Pratama ZebuaAinda não há avaliações