Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Standardcsa Fallprotect z259!16!2004
Enviado por
Mark SpitzDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Standardcsa Fallprotect z259!16!2004
Enviado por
Mark SpitzDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CSA Standard Z259.
16-2004
Design of Active Fall Protection Systems
Scope and Application:
The standard is intended for professional engineers designing fall protection systems.
The standard shall be used as a design guideline. It specifies requirements for the
design and performance of complete fall protection systems including:
vertical and horizontal fall-arrest systems,
travel restraint systems.
Definition:
Active fall-protection systems a means of providing fall protection that requires
workers to take specific actions, including wearing (and otherwise using) personal
fall protection equipment and following prescribed procedures.
These systems are custom-designed for the intended purpose, but can be relocated if
needed. The standard does not specify design and performance for fall arrest
equipment or systems that have been manufactured and successfully tested in
accordance with the requirements of another standard CSA Z 259 (i.e. pre-engineered
systems).
Requirements:
Drawings and specifications are prepared under the direction of the professional
engineer and shall be signed , sealed, and shall include the following information:
Type of system, layout including details on specifications if applicable;
Number, location, and qualification of workers,
Specifications for all components including the standards that have to be met,
size and minimum breaking strength along with the method of proof testing
required before the system is put into place,
Environmental limitations (i.e. chemical, temperature, radiation, weather factors,
that may temporary of permanently render the system unsafe),
Information of the expected performance, including max. arrest load, sags,
deflection , maximum arrest force, and any other information that would impact
on the system performance and shall be indicated on the drawings,
Instructions for the assembly and installation, including: minimum required
strength of the anchors, clearance requirements ( including special situations),
and any safety precautions that shall be followed during the erection and/or
dismantling of the system,
Instruction for inspection, maintenance and retirement, including description on
how the inspection is conducted and description of the qualifications for the
person undertaking the inspection,
Instruction in safe access to and egress from the system,
A rescue plan for the fall arrest system, or requirement for the employer of the
workers using the system to develop and implement a rescue plan before the
system is used,
A statement of specifications that shall include special notation that
modifications shall not be allowed unless specified by a professional engineer,
A permanent system shall be inspected and certified by a professional engineer
to ensure that the system is installed in accordance with the drawings and
specifications.
Material, equipment and other design requirements outlined in the standard include:
Specific requirements for system components, compatibility
Energy absorber requirements and calculations (not to exceed 6kN impact
acceleration force on the worker, factoring in the free fall distance),
Self-retracting lanyards with limited use in the case of travel restraint systems,
Requirement for lanyards and full body harnesses,
(Over)
Fall arrest system, span length calculation,
Rescue requirements (if the rescue operation will impact the system
performance).
The safety criteria section refers to specific loads to be used in the design of active fallprotection systems, and gives direction on the determination of the components
strength and the structure to which it is attached. Sytems designed under this standard
are based on the following criteria:
R= F* where: R = the factored resistance of the component or the subsystem,
F*= the worst case factored effect of the applied loads on the
component or the subsystem.
Determination of the factored resistance and the factored loads is detailed in the
standards.
Maximum acceleration force or the peak acceleration force experienced by a worker
shall be less than 8 kN. Free standing systems ( systems that are not permanently
attached to a structure) have separate requirements for overturning and sliding,
depending on the type of system.
The fall protection system, loads and forces section, details design consideration for
assumptions calculation of the system along with set-up direction ( i.e clearance
calculations, free fall distance, deceleration distance, stretch out swing fall distance, etc.
) and explicit drawings and scenarios of arresting multiple workers falls.
Design assumptions and analytical methods of calculating the system are also outlined.
Methods of calculation that are acceptable are: dynamic analysis, energy analysis or
static analysis or testing. Other analytical methods may be considered if they can
accurately predict the performance of active fall protection systems.
The standard does not cover determination of the structural strength and behaviour of
components or anchorages of active fall protection systems. It does, however, establish
the safety criteria once the strength and behaviour are known.
This bulletin contains a summary of excerpts taken from the Standard, for general
information purposes only. This bulletin is not reflective of the complete
requirements that the Standard prescribes.
Note: Manitoba Regulation M.R. 217/2006 Section 1.4 inconsistency:
If there is an inconsistency between this regulation and a requirement contained
in a publication, code or standard referenced in this regulation, the provisions in
this regulation prevail.
Você também pode gostar
- Horizontal Life Line CalculationDocumento1 páginaHorizontal Life Line CalculationAlden Cayaga100% (4)
- Calculation of Vertical Fall Arrest ForcesDocumento4 páginasCalculation of Vertical Fall Arrest ForcesCesar100% (4)
- BS en 131-1-2015+a1-2019Documento32 páginasBS en 131-1-2015+a1-2019Elif Öztürk71% (7)
- Horizontal Life Line CalculationDocumento1 páginaHorizontal Life Line Calculationhasan_676489616100% (1)
- BS 7883-2019Documento140 páginasBS 7883-2019yamen sayedAinda não há avaliações
- Fall Protection PDFDocumento91 páginasFall Protection PDFRaphael Pontes100% (1)
- Horizontal Life Line CalculationDocumento1 páginaHorizontal Life Line CalculationgalangAinda não há avaliações
- BSI Standards Publication: Temporary Edge Protection Systems - Product Specification - Test MethodsDocumento40 páginasBSI Standards Publication: Temporary Edge Protection Systems - Product Specification - Test Methodsfmfsantos100% (1)
- Strength Calculation of Lifting EyeDocumento2 páginasStrength Calculation of Lifting EyeJacky Tam50% (2)
- Go Betweens For HitlerDocumento402 páginasGo Betweens For HitlerSagyan Regmi Regmi100% (1)
- HLL Basic CalculationDocumento10 páginasHLL Basic Calculationsebastian9033100% (2)
- ABNT NBR 13541-2 EnglishDocumento10 páginasABNT NBR 13541-2 EnglishCinthia BazethAinda não há avaliações
- Section 2: Procedural Control of Temporary Works: 6 ProceduresDocumento38 páginasSection 2: Procedural Control of Temporary Works: 6 Proceduresezzularab100% (3)
- Improving Fall Protection Design (DR Goh Yang Miang)Documento20 páginasImproving Fall Protection Design (DR Goh Yang Miang)Adam FredrikssonAinda não há avaliações
- NBR 11900-4 EnglishDocumento20 páginasNBR 11900-4 EnglishCinthia BazethAinda não há avaliações
- Din 15019-2Documento7 páginasDin 15019-2Reda El-AwadyAinda não há avaliações
- AISC Crane Runway TipsDocumento25 páginasAISC Crane Runway Tipstpaterno77100% (10)
- Iso 16024-2005Documento22 páginasIso 16024-2005phamngochaocd09aAinda não há avaliações
- Aise - No 11 Standards - Pr-tr011-007Documento11 páginasAise - No 11 Standards - Pr-tr011-007Tango Beltza100% (3)
- Layher Allround Industri Stillas 2015 - Engelsk - Utskrift.2Documento68 páginasLayher Allround Industri Stillas 2015 - Engelsk - Utskrift.2cosmin todoran100% (1)
- BS EN 360 (2002) - Retractable Type Fall ArrestorDocumento14 páginasBS EN 360 (2002) - Retractable Type Fall ArrestorGistek MarcoAinda não há avaliações
- EN 12841 enDocumento2 páginasEN 12841 enMauricio GaviriaAinda não há avaliações
- As 2359.15-2005 Powered Industrial Trucks Fork-Arm Extensions and Telescopic Fork Arms - Technical CharacteriDocumento8 páginasAs 2359.15-2005 Powered Industrial Trucks Fork-Arm Extensions and Telescopic Fork Arms - Technical CharacteriSAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- 500 Volts E1316 Versus 4187Documento43 páginas500 Volts E1316 Versus 4187gattiantonioAinda não há avaliações
- Why There Has Been No Brandies Brief in India? Challenges To Socio-Legal Research in IndiaDocumento2 páginasWhy There Has Been No Brandies Brief in India? Challenges To Socio-Legal Research in IndiaSubhaprad MohantyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Emergency Medical CareDocumento19 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Emergency Medical Carejmmos207064100% (1)
- Precast Beam HLLDocumento16 páginasPrecast Beam HLLVenkatesan VaradhanAinda não há avaliações
- BS en 7883 - Traduzido o Trecho ImportanteDocumento2 páginasBS en 7883 - Traduzido o Trecho ImportanteGustavo Carnevali MendesAinda não há avaliações
- Life Line Calculation PDFDocumento3 páginasLife Line Calculation PDFEri Febrianto100% (1)
- Intro To Z25.16 & Z59.6Documento10 páginasIntro To Z25.16 & Z59.6treyAinda não há avaliações
- Fall ProtectionDocumento93 páginasFall ProtectionMaicon Vinicius SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Iso 9927-3 - 2019Documento11 páginasIso 9927-3 - 2019Federico Sanguineti100% (1)
- NBR 13541-2 EnglishDocumento10 páginasNBR 13541-2 EnglishCinthia BazethAinda não há avaliações
- How To INSTALL Anchors in Accordance With BS 8539Documento4 páginasHow To INSTALL Anchors in Accordance With BS 8539hanyaAinda não há avaliações
- ABNT NBR 11900-5 EnglishDocumento14 páginasABNT NBR 11900-5 EnglishCinthia BazethAinda não há avaliações
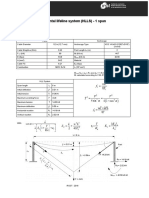
- Horizontal Lifeline System (HLLS) - 1 Span: A Rupt R FmaxDocumento1 páginaHorizontal Lifeline System (HLLS) - 1 Span: A Rupt R FmaxEko Gede Septan DhoAinda não há avaliações
- Results PDFDocumento1 páginaResults PDFRajAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation For Wall Anchor Bracket Project Phase 1A &1B: Data - 08 11 2020 REV 00Documento9 páginasCalculation For Wall Anchor Bracket Project Phase 1A &1B: Data - 08 11 2020 REV 00Antonysamy SanthanamAinda não há avaliações
- Padeye Design & Load Test - DNVDocumento1 páginaPadeye Design & Load Test - DNVjohnAinda não há avaliações
- En Iso 14122-1 (2001)Documento14 páginasEn Iso 14122-1 (2001)Generosa Ferreira100% (1)
- Man Basket Profile and Specification Details: Schedules of Man BasketsDocumento8 páginasMan Basket Profile and Specification Details: Schedules of Man Basketssandip khardeAinda não há avaliações
- Base PlateDocumento4 páginasBase Platejatin kalraAinda não há avaliações
- Horizon Horizontal Lifeline Instruction Manual - enDocumento68 páginasHorizon Horizontal Lifeline Instruction Manual - enrm_037Ainda não há avaliações
- Fall Protection Systems Guidelines Part 1 - Anchorages Lifelines and Temporary Edge Protection Systems - Public ConsultDocumento40 páginasFall Protection Systems Guidelines Part 1 - Anchorages Lifelines and Temporary Edge Protection Systems - Public Consultlwin_oo2435100% (4)
- Terminations For Steel Wireropes-Safety - Splicing of Eyes For Wire Rope Slings BS EN 13411-2Documento12 páginasTerminations For Steel Wireropes-Safety - Splicing of Eyes For Wire Rope Slings BS EN 13411-2PmohamedFazil100% (1)
- As 2317-1998 Collared EyeboltsDocumento8 páginasAs 2317-1998 Collared EyeboltsSAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- CG6 - 09 Scaffold DesignDocumento4 páginasCG6 - 09 Scaffold DesignArdamitAinda não há avaliações
- En 795Documento3 páginasEn 795Sayed Abbas0% (1)
- Asme-B30.22 - 02Documento41 páginasAsme-B30.22 - 02Brayan Montalban GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- WKS 4 Working at Height Safety NetsDocumento36 páginasWKS 4 Working at Height Safety Netsyousuf79Ainda não há avaliações
- Catálogo Guindaste de Coluna DemagDocumento72 páginasCatálogo Guindaste de Coluna Demag0842500% (1)
- KBK Brochure PDFDocumento12 páginasKBK Brochure PDFMahendran KuppusamyAinda não há avaliações
- Horizontal Life Line CalculationDocumento1 páginaHorizontal Life Line Calculationmincho4104Ainda não há avaliações
- Femap v103 Nxnastran AeroelasticityDocumento3 páginasFemap v103 Nxnastran AeroelasticityAlan DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- Slip, Trips Personal - Fall - Arrest - SystemsDocumento7 páginasSlip, Trips Personal - Fall - Arrest - SystemsRëy PañaresAinda não há avaliações
- Control Systems EngineerDocumento11 páginasControl Systems Engineerali18abidAinda não há avaliações
- Sizing Procedures Chapter 2 - Airframe Stress Analysis and Sizing (Niu)Documento9 páginasSizing Procedures Chapter 2 - Airframe Stress Analysis and Sizing (Niu)sqaiba_gAinda não há avaliações
- NRAG Guidance Temporary Aerial Fibre Wire Rope Camera SystemsDocumento2 páginasNRAG Guidance Temporary Aerial Fibre Wire Rope Camera SystemsSophie-Louise MercedesAinda não há avaliações
- Safe Operating Procedure: (Revised 4/19) Personal Fall Arrest SystemsDocumento7 páginasSafe Operating Procedure: (Revised 4/19) Personal Fall Arrest SystemsUlviyye ElesgerovaAinda não há avaliações
- GAPS Guidelines: Special Extinguishing System ReviewDocumento2 páginasGAPS Guidelines: Special Extinguishing System Reviewasad khanAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Switchgear and SafetyDocumento16 páginasElectrical Switchgear and SafetyAli Khamis100% (1)
- Seminar & PPT ON Cad Cam & Applicaations IN Mechanical EngineeringDocumento13 páginasSeminar & PPT ON Cad Cam & Applicaations IN Mechanical EngineeringSumit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Raylı Sistemler - Stinger SystemDocumento24 páginasRaylı Sistemler - Stinger SystemIsmet HizyoluAinda não há avaliações
- Flat Glass-Pilkington-2009finalDocumento74 páginasFlat Glass-Pilkington-2009finalKancharla AnandAinda não há avaliações
- BTS Lesson Preparation FormDocumento1 páginaBTS Lesson Preparation FormTsz Shing WONGAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Hydraulics Trainer's Project Manual PDFDocumento57 páginasIndustrial Hydraulics Trainer's Project Manual PDFrichardppz124100% (2)
- Polynomial Functions 1Documento19 páginasPolynomial Functions 1Arafath Basheer100% (1)
- CDP MCQs - Child Development & Pedagogy (CDP) MCQ Questions With AnswerDocumento4 páginasCDP MCQs - Child Development & Pedagogy (CDP) MCQ Questions With AnswerPallav JainAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration MeasurementDocumento20 páginasVibration MeasurementDae A VeritasAinda não há avaliações
- Vxworks Kernel Programmers Guide 6.8Documento802 páginasVxworks Kernel Programmers Guide 6.8hisahinAinda não há avaliações
- Evacuated Flat Plate Collector PDFDocumento2 páginasEvacuated Flat Plate Collector PDFMattAinda não há avaliações
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento10 páginasAnnotated Bibliographyapi-457225775Ainda não há avaliações
- Stress in CompoundsDocumento3 páginasStress in CompoundsEmma PeelAinda não há avaliações
- TR 4015Documento62 páginasTR 4015Matias AndréAinda não há avaliações
- Strut & Tie ModelDocumento67 páginasStrut & Tie Modelahmed adel100% (9)
- Chapter 1 A CULINARY HISTORYDocumento10 páginasChapter 1 A CULINARY HISTORYMrinalini KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Report FormatDocumento21 páginasThesis Report Formatsebsibe birhanuAinda não há avaliações
- Information On Resource Allocation Within NetbackupDocumento17 páginasInformation On Resource Allocation Within NetbackupAbhishek PondicherryAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview On Co-Operative Societies in BangladeshDocumento11 páginasAn Overview On Co-Operative Societies in BangladeshAlexander DeckerAinda não há avaliações
- MAT565 - Tutorial - Inverse LaplaceDocumento2 páginasMAT565 - Tutorial - Inverse LaplacefaqhrulAinda não há avaliações
- Đề 5Documento4 páginasĐề 5Nga NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Oil Corporation LTD Guwahati RefineryDocumento27 páginasIndian Oil Corporation LTD Guwahati Refineryelectram67% (6)
- Ex 5308-Alexandra Thedeby-Heating and Cooling With Solar Powered Peltier ElementsDocumento93 páginasEx 5308-Alexandra Thedeby-Heating and Cooling With Solar Powered Peltier ElementsMohammad NaufalAinda não há avaliações
- Goodrich 6e Ch03 Arrays PDFDocumento12 páginasGoodrich 6e Ch03 Arrays PDFArjun SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Weather Phenomena MatrixDocumento4 páginasWeather Phenomena MatrixsetolazarAinda não há avaliações
- Central Limit TheoremDocumento46 páginasCentral Limit TheoremAneesh Gopinath 2027914Ainda não há avaliações
- 4.NBT.1 Task 2Documento2 páginas4.NBT.1 Task 2Nur NadzirahAinda não há avaliações
- Samakande A UnprotectedDocumento190 páginasSamakande A Unprotectedathilla27Ainda não há avaliações
- Resarch Paper - Google SearchDocumento2 páginasResarch Paper - Google SearchhudAinda não há avaliações
- MIT 6.00 Notes From Lessons 1,2 and 3.Documento8 páginasMIT 6.00 Notes From Lessons 1,2 and 3.Nikola Nino IvankovićAinda não há avaliações