Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Minerals - Silicates
Enviado por
hDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Minerals - Silicates
Enviado por
hDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
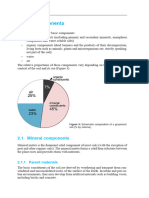
Silicate subgroups are all based on the structural arrangement of the silica tetrahedra in the crystal lattice.
The
importance of most silicate minerals is in their abundance: silicates comprise >95% of the total mass of the Earth's
crust. (Minerals in bold face are those we will study in the laboratory.)
Subgroup
General structure
Examples
Occurrence & uses
Framework
complex 3-dimensional
quartz (SiO2)
occurs in many rocks, very common
silicates
framework
many industrial uses; base for glass
manufacturing
feldspars:
over 50% of entire crust !!!!
orthoclase (KAlSi3O8)
plutonic and metamorphic rocks
microcline (KAlSi3O8)
plutonic igneous rocks
sanidine (KAlSi3O8)
silica-rich volcanic rocks
plagioclase
albite (NaAlSi3O8)
silica-rich igneous & metamorphic
rocks
anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8)
silica-poor igneous &
metamorphic rocks
oligoclase is 70-90% albite; 10-30% anorthite
labradorite is 30-50% albite; 50-70% anorthite
Sheet
silicates
strong sheet structures,
bonds between sheets
weak
micas
muscovite (K-mica)
biotite (K-Fe-Mg-mica)
chlorite (Fe-Mg-mica)
clay minerals
igneous and metamorphic rocks
plutonic and metamorphic rocks
plutonic and metamorphic rocks;
rare in volcanics
metamorphic rocks, soils on
ultramafic intrusives
form by weathering of other
silicates; critical in soils;
used in ceramics, paper, and
many other industrial uses
Major silicate subgroups and minerals
Subgroup
General structure
Chain
tetrahedra in chains
silicates
single chains: pyroxenes
double chains: amphiboles
... Page 2 ...
Examples
Occurrence & uses
augite (complex iron
silicate)
hornblende (complex
iron silicate)
actinolite (complex
Ca-Fe silicate)
silica-poor igneous & metamorphic
rocks
silica-rich igneous and high-grade
metamorphic rocks
metamorphic rocks
Sorosilicates
tetrahedra in pairs
epidote (complex
calcium silicate)
common alteration product in
rocks, esp. igneous rocks
Ring silicates
tetrahedra arranged
in rings
beryl (a beryllium
silicate)
tourmaline (very
complex formula)
beryllium ore; gems (aquamarine,
true emerald)
minor industrial use; mostly
gemstones (Maine state mineral)
Island silicates
tetrahedra unattached to
each other directly;
linked by metallic cations
between tetrahedra
Olivine (Mg,Fe)2SiO4
Staurolite (complex
Ca-Al silicate)
Garnet [M3M2(SiO4)3]
silica-poor igneous rocks
Al-rich metamorphic rocks
Zircon (ZrSiO4)
{ Kyanite (Al2SiO5) }
{ Andalusite (Al2SiO5) }
{ Sillimanite (Al2SiO5) }
(M=Fe,Mg,Al,Ca,Mn,Cr) variable
composition; found in
metamorphic rocks; used for
abrasives and gemstones
usually some U replaces Zr; source
for radon gas in environment;
occurs in granitic and silica-rich
volcanic rocks; zirconium ore &
"cubic zirconia" gemstone
{These three minerals, all with the
same chemical formula, are found
in metamorphic rocks, and are
extremely useful for determining
the pressure and temperature of
recrystallization.}
Você também pode gostar
- Ullman SilicatesDocumento66 páginasUllman SilicatesfxdevuystAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 Guided Exercise: Analysing Network Traffic: ResourcesDocumento5 páginas1.2 Guided Exercise: Analysing Network Traffic: Resourcesh0% (1)
- Minerals SilicatesDocumento2 páginasMinerals SilicatesKareemAmenAinda não há avaliações
- Minerals - SilicatesDocumento2 páginasMinerals - SilicatesER NurAinda não há avaliações
- List of The Rock-Forming MineralsDocumento20 páginasList of The Rock-Forming Mineralsroshan_geo07889667% (3)
- Silicate Minerals Notes 1Documento5 páginasSilicate Minerals Notes 13mmaAinda não há avaliações
- Kristal Dan Mineral - Asrim - 13 - Mineral SilikatDocumento19 páginasKristal Dan Mineral - Asrim - 13 - Mineral SilikatEigerAinda não há avaliações
- Sistematika SilicateDocumento29 páginasSistematika SilicateRAFIAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Silicates (GL 204 My Lecture) - HandoutDocumento19 páginas9 Silicates (GL 204 My Lecture) - HandoutStanliAinda não há avaliações
- EG Unit IIDocumento53 páginasEG Unit IISEKARAinda não há avaliações
- What Are They? Its Uses? How Are They Formed? How Are They Important?Documento53 páginasWhat Are They? Its Uses? How Are They Formed? How Are They Important?IvyAinda não há avaliações
- SilicatesDocumento35 páginasSilicatesCHLORINE SHAKEAinda não há avaliações
- SPLM #2 (Copy 1)Documento12 páginasSPLM #2 (Copy 1)adel antegraAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 5a - Minerals, Definition & ClassesDocumento33 páginasModul 5a - Minerals, Definition & Classesalbert pontusAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3: Rock Forming Minerals: Ardhi UniversityDocumento61 páginasLecture 3: Rock Forming Minerals: Ardhi UniversityInnocent RevocatusAinda não há avaliações
- Silicates: John Kevin D. Villar Bs emDocumento4 páginasSilicates: John Kevin D. Villar Bs emJohnKevinVillarAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 5a - Minerals, Definition & ClassesDocumento33 páginasModul 5a - Minerals, Definition & ClassesSigit HimawanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 MineralogyDocumento53 páginasUnit 2 MineralogyEashan Adil100% (1)
- Minerals Associated With LateritesDocumento14 páginasMinerals Associated With LateritesD'leh EvoletAinda não há avaliações
- Shale: Devanarayanan EM I.Msc Applied GeologyDocumento20 páginasShale: Devanarayanan EM I.Msc Applied GeologyDq DevanAinda não há avaliações
- Silica SandDocumento7 páginasSilica SandHuru HaraAinda não há avaliações
- Rock Forming Minerals: RocksDocumento3 páginasRock Forming Minerals: RocksUche S OsigweAinda não há avaliações
- Nanzyo-Kanno2018 Chapter PrimaryMineralsDocumento25 páginasNanzyo-Kanno2018 Chapter PrimaryMineralsGunasekarAinda não há avaliações
- Clay MineralsDocumento47 páginasClay MineralsLuckyGuptaAinda não há avaliações
- GLY 206 NOTE 6 - NesosilicatesDocumento5 páginasGLY 206 NOTE 6 - NesosilicatesOdebunmi PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Mineralogy: Unit - IIDocumento48 páginasMineralogy: Unit - IIannal100% (1)
- Module 5A - Minerals, Definition & ClassesDocumento32 páginasModule 5A - Minerals, Definition & ClassesZaky FRAinda não há avaliações
- Earth ScienceDocumento11 páginasEarth Sciencesalabsabhga0529Ainda não há avaliações
- Rock Forming MineralsDocumento14 páginasRock Forming MineralsRense Jun PunsalanAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3A - Minerals, Definition ClassesDocumento58 páginasTopic 3A - Minerals, Definition ClassesDessy Indah Intan Christy RoriwoAinda não há avaliações
- Pràctica 9 - EnglishDocumento15 páginasPràctica 9 - EnglishGhislainarrowAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Polymers, Ceramics, Composites-2Documento44 páginasChapter 5 Polymers, Ceramics, Composites-2Mojery MohauAinda não há avaliações
- Teknik PerminyakanDocumento37 páginasTeknik PerminyakanTuti HariyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4.1 Mineral ResourcesDocumento64 páginasChapter 4.1 Mineral ResourcesJeanette FormenteraAinda não há avaliações
- The Second LectureDocumento2 páginasThe Second LectureAliAlMaestroAinda não há avaliações
- Brief Idea of Silicate Structure of Rock Forming MineralsDocumento28 páginasBrief Idea of Silicate Structure of Rock Forming MineralsMounika NallaAinda não há avaliações
- Atlas MineragrafiaDocumento232 páginasAtlas MineragrafiaLaura RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6 F 2014 - SilicatesDocumento45 páginasLecture 6 F 2014 - SilicatesBobby PatelAinda não há avaliações
- 5-1. Extraction of Metals 1Documento40 páginas5-1. Extraction of Metals 1teenoe21Ainda não há avaliações
- Mineral Abrasives 2005Documento56 páginasMineral Abrasives 2005Eduardo QuiteteAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Mineral?: MineralogyDocumento44 páginasWhat Is A Mineral?: MineralogyHemant DhakedAinda não há avaliações
- Minerals 4Documento48 páginasMinerals 4java arunAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah (2) - Earth MaterialsDocumento83 páginasKuliah (2) - Earth Materialsilham nasrunAinda não há avaliações
- Mineral GroupsDocumento14 páginasMineral GroupsSreekanth PadmanAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture No. 1 Fundamentals of GeologyDocumento28 páginasLecture No. 1 Fundamentals of GeologyJovin ManarinAinda não há avaliações
- Cve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsDocumento7 páginasCve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsUduebor MichealAinda não há avaliações
- Silicates The Silicates Are The Largest, The Most Interesting, and The MostDocumento13 páginasSilicates The Silicates Are The Largest, The Most Interesting, and The MostInam Ul HaqAinda não há avaliações
- MineralsDocumento41 páginasMineralsalbert pontusAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Silica MineralDocumento14 páginas10 Silica MineralRadhitya Adzan HidayahAinda não há avaliações
- MineralsDocumento55 páginasMineralsniaz ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Ores and GanguesDocumento16 páginasOres and GanguesRananjay SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Soil ScienceDocumento155 páginasChapter 2 Soil ScienceJulieto ZubradoAinda não há avaliações
- Mineral Silikat: Mineralogi - 8Documento21 páginasMineral Silikat: Mineralogi - 8RosellaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Silicate MineralogyDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Silicate MineralogyMasunji EmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Extrait - Essentiels of Soil SciencesDocumento20 páginasExtrait - Essentiels of Soil SciencesMohamed EL BAGHDADIAinda não há avaliações
- Earth Science Lesson 2.1 - Earth Materials - Minerals2Documento41 páginasEarth Science Lesson 2.1 - Earth Materials - Minerals2MARIEL GRACE JAMEROAinda não há avaliações
- Ecgd2207.102 T032 24112008Documento34 páginasEcgd2207.102 T032 24112008DjayusmannugrahantoAinda não há avaliações
- Materi 05 Endapan Magmatik CairDocumento55 páginasMateri 05 Endapan Magmatik CairNandika Reza Faisal100% (2)
- Geologi Dasar 5Documento53 páginasGeologi Dasar 5Cleryn yolanda aomeAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory 2Documento2 páginasLaboratory 2Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Guide On IT Migration AuditDocumento15 páginasTechnical Guide On IT Migration AudithAinda não há avaliações
- Compliance Audit of CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) Control Room Operations at Eastleigh Borough CouncilDocumento6 páginasCompliance Audit of CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) Control Room Operations at Eastleigh Borough CouncilhAinda não há avaliações
- Ire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test ChecklistDocumento2 páginasIre Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test ChecklisthAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic Locks Checklist: Requirements For All InstallationsDocumento2 páginasElectromagnetic Locks Checklist: Requirements For All InstallationshAinda não há avaliações
- Reference: IA 2016-01: Internal Oversight DivisionDocumento11 páginasReference: IA 2016-01: Internal Oversight DivisionhAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Green Journal: TitleDocumento18 páginasElectronic Green Journal: TitlehAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Safety Maintenance Checklist: Daily Checks (Not Normally Recorded) Yes No N/A CommentsDocumento3 páginasFire Safety Maintenance Checklist: Daily Checks (Not Normally Recorded) Yes No N/A CommentshAinda não há avaliações
- Course: Information Security Management in E-GovernanceDocumento53 páginasCourse: Information Security Management in E-GovernancehAinda não há avaliações
- PIRAPDocumento28 páginasPIRAPhAinda não há avaliações
- M1Approaches of Network SecurityDocumento2 páginasM1Approaches of Network SecurityhAinda não há avaliações
- Icq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapersDocumento1 páginaIcq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapershAinda não há avaliações
- The Fundraising Database Audit: FebruaryDocumento10 páginasThe Fundraising Database Audit: FebruaryhAinda não há avaliações
- Icq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapersDocumento1 páginaIcq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapershAinda não há avaliações
- Network Controls: Internal Control Questionnaire: Control Answer Comments CT Risk Id CTL ICQ REF Y NDocumento1 páginaNetwork Controls: Internal Control Questionnaire: Control Answer Comments CT Risk Id CTL ICQ REF Y NhAinda não há avaliações
- Control Answer Comments CT Risk Id CTL ICQ REF Y NDocumento1 páginaControl Answer Comments CT Risk Id CTL ICQ REF Y NhAinda não há avaliações
- Network Controls: Compliance Tests: Icq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapersDocumento1 páginaNetwork Controls: Compliance Tests: Icq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapershAinda não há avaliações
- Icq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapersDocumento1 páginaIcq Ref CT Ref Compliance Test Working PapershAinda não há avaliações
- AFROSAI-E Regularity Audit Manual 2013Documento471 páginasAFROSAI-E Regularity Audit Manual 2013h100% (3)
- Schedule of Audit Findings and Responses: Franklin County March 4, 2014Documento4 páginasSchedule of Audit Findings and Responses: Franklin County March 4, 2014hAinda não há avaliações
- ConclusionDocumento1 páginaConclusionhAinda não há avaliações
- Report To Congressional Requesters: United States Government Accountability OfficeDocumento64 páginasReport To Congressional Requesters: United States Government Accountability OfficehAinda não há avaliações
- Acknowledgement of The Department of Civil Engineering MR Ravish Chandra Would Like To Exprees Our Feeling On The National Data Ceneter BuildingDocumento1 páginaAcknowledgement of The Department of Civil Engineering MR Ravish Chandra Would Like To Exprees Our Feeling On The National Data Ceneter BuildinghAinda não há avaliações
- Information Systems Audit Review Manual: Leslie D Ball Richard M Housman Arthur V SaraziniDocumento2 páginasInformation Systems Audit Review Manual: Leslie D Ball Richard M Housman Arthur V SarazinihAinda não há avaliações
- Use of Drilling Parameters To Predict In-Situ Stress BoundsDocumento15 páginasUse of Drilling Parameters To Predict In-Situ Stress BoundsCarlos Mario Jimenez RamosAinda não há avaliações
- BBC Horizon - Popis EpizodaDocumento14 páginasBBC Horizon - Popis Epizodatomtom1010Ainda não há avaliações
- MDM-Sagay College, Inc.: Course Syllabus First Semester, School Year 2019-2020Documento3 páginasMDM-Sagay College, Inc.: Course Syllabus First Semester, School Year 2019-2020Remil CastañedaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Reservoir EngineeringDocumento17 páginasChapter 1 - Introduction To Reservoir Engineeringmdkhan1100% (1)
- Compton Field GeologyDocumento115 páginasCompton Field GeologyMattina ContrerasAinda não há avaliações
- Ashtakavarga AnalysisDocumento2 páginasAshtakavarga AnalysisShashikant Madkaiker0% (1)
- Bajuri & Tara - Lab Report - 6Documento7 páginasBajuri & Tara - Lab Report - 6M. Alfin PrayogoAinda não há avaliações
- 60 Year Intervals and October PanicsDocumento3 páginas60 Year Intervals and October Panicstrb301Ainda não há avaliações
- ConvexDocumento3 páginasConvexJayden CalpitoAinda não há avaliações
- Aenigmatite - Aenigmatite Mineral Information and DataDocumento14 páginasAenigmatite - Aenigmatite Mineral Information and DataBlacksacerdoteAinda não há avaliações
- VedicReport11 4 20135 03 22PMDocumento32 páginasVedicReport11 4 20135 03 22PMshubham_mondal9744Ainda não há avaliações
- Sordaria Lab ReportDocumento9 páginasSordaria Lab Reportapi-217409009Ainda não há avaliações
- Coastal ProcessesDocumento15 páginasCoastal Processesapi-258813608Ainda não há avaliações
- Renu Addlakha Scientific Method and Its CritiqueDocumento14 páginasRenu Addlakha Scientific Method and Its CritiquesavitaAinda não há avaliações
- Eyes On The SkyDocumento26 páginasEyes On The SkyaonesimeAinda não há avaliações
- Appc Soil Properties 718Documento5 páginasAppc Soil Properties 718pinkuru100% (1)
- Physical and Cultural Environment - Purba MedinipurDocumento34 páginasPhysical and Cultural Environment - Purba MedinipurashisbhuniyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Alaska Pipeline Starts at The Frozen Edge of TheDocumento4 páginasThe Alaska Pipeline Starts at The Frozen Edge of Thehec120% (1)
- Bcra 14-3-1987Documento52 páginasBcra 14-3-1987Cae MartinsAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced GeomorphologyDocumento30 páginasAdvanced GeomorphologyCarlos Letras100% (3)
- Timing and Formation of Porphyry Cu-Mo Mineralization in The Chuquicamata DistrictDocumento24 páginasTiming and Formation of Porphyry Cu-Mo Mineralization in The Chuquicamata Districtj ZamudioAinda não há avaliações
- Room-And-pillar Method of Open Stope MiningDocumento6 páginasRoom-And-pillar Method of Open Stope MiningIsmaelAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Natural Sciences PDFDocumento13 páginas01 Natural Sciences PDFJennifer PesikAinda não há avaliações
- Astronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFDocumento80 páginasAstronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFKelum BuddhikaAinda não há avaliações
- Schlumberger Anadrill ChartDocumento180 páginasSchlumberger Anadrill ChartTim Hill100% (2)
- A New Chronology of The Old Babylonian Kingdom and Ur I-IIIDocumento10 páginasA New Chronology of The Old Babylonian Kingdom and Ur I-IIIborimoriAinda não há avaliações
- Greg Lynn SimetrieDocumento5 páginasGreg Lynn SimetrieElena MureșanuAinda não há avaliações
- Å. Hjalmarson Et Al - Highlights From The First Year of Odin ObservationsDocumento8 páginasÅ. Hjalmarson Et Al - Highlights From The First Year of Odin ObservationsLupaessAinda não há avaliações
- TPQ - January 2010 QP - Unit 4 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocumento3 páginasTPQ - January 2010 QP - Unit 4 Edexcel Physics A-LevelSamuel Muabia PlanetAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - Plant Diversity PDFDocumento160 páginasModule 1 - Plant Diversity PDFDasari krishna chanduAinda não há avaliações