Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Gastroenteritis and Enterocolitis PBL Objectives
Enviado por
Paul A IBattledaily ScavellaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Gastroenteritis and Enterocolitis PBL Objectives
Enviado por
Paul A IBattledaily ScavellaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Paul Scavella
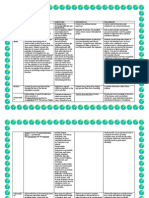
Objective Number 10 concerning Enterocolitis and Gastroenteritis
Enterocoliti
s
Gastroenter
itis
Symptoms
Fever, Abdominal
Swelling, Nausea,
Vomiting, Diarrhea,
Rectal bleeding,
Sluggishness
Fever, Nausea, Mildto-moderate diarrhea,
Crampy painful
bloating, Vomiting,
blood in vomit or
stool, Dehydration
Types
Bacterial,
Viral,
Fungal,
Parasitic
Bacterial,
Viral,
Parasitic,
food
allergies
or food
poisoning
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the lining of the intestines caused
by a virus, bacteria or parasites. Viral gastroenteritis is the second
most common illness in the U.S. It spreads through contaminated food
or water, and contact with an infected person. The best prevention is
frequent hand washing.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis include diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, fever
and chills. Most people recover with no treatment.
The most common problem with gastroenteritis is dehydration. This happens if you do
not drink enough fluids to replace what you lose through vomiting and diarrhea.
Dehydration is most common in babies, young children, the elderly and people with weak
immune systems.
Gastroenteritis has many causes. Viruses and bacteria are the most common.
The infectious agents can come from outside your body or internally from some
abnormal condition. For example, both normal and disease-causing intestinal bacteria
may grow when antacids or other medication alter the stomach acidity.
Viruses and bacteria are very contagious and can spread through contaminated food or
water. In up to 50% of diarrheal outbreaks, no specific agent is found. Improper hand
washing following a bowel movement or handling a diaper can spread the disease from
person to person.
Gastroenteritis caused by viruses may last 1-2 days. On the other hand, bacterial cases
can last a week or more.
Bacteria: These are the most common bacterial causes:
o
Escherichia coli - Travelers diarrhea, food poisoning, dysentery, colitis,
or uremic syndrome
Salmonella Typhoid fever; handling poultry or reptiles such as turtles
that carry the germs
Campylobacter - Undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk
Shigella - Dysentery
Viruses: Viral outbreaks (30-40% of cases in children) can spread rapidly through
close contact among children in day care and schools. Poor handwashing habits
can spread viruses. Common viral causes include the following:
o
Adenoviruses
Rotaviruses
Caliciviruses
Astroviruses
Norovirus (formerly called Norwalk-like virus or NLV) and Norwalk virus
Norovirus was attributed to 9 out of the 21 outbreaks of acute
gastroenteritis on cruise ships reported to the CDCs Vessel
Sanitation Program from January 1, 2002, to December 2, 2002.
Noroviruses cause about 23 million cases of acute gastroenteritis
each year and are the leading cause of outbreaks.
Parasites and protozoans: These tiny organisms are less frequently responsible for
intestinal irritation. You may pick up one of these by drinking contaminated water.
Swimming pools are common places to come in contact with these parasites.
Common parasites include these:
o
Giardia - The most frequent cause of waterborne diarrhea causing
giardiasis
Cryptosporidium - Affects mostly people with weakened immune systems,
causes watery diarrhea
Other common causes: Chemical toxins most often found in seafood, food
allergies, heavy metals, antibiotics, and other medications also may be responsible
for bouts of gastroenteritis that are not infectious to others.
o
Medications
Aspirin
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (such as Motrin or
Advil)
Antibiotics
Caffeine
Steroids - Excessive use or a sudden change in frequency or
dosage
Laxatives
Inability to tolerate the sugar lactose in milk and milk products such as
cheese and ice cream
Exposure to heavy metals sometimes present in drinking water
Arsenic
Lead
Mercury
Gastroenteritis may affect both the stomach and the intestines, resulting in one or more of
the following symptoms:
Common symptoms
o
Low grade fever (99F)
Nausea with or without vomiting
Mild-to-moderate diarrhea: May range from 2-4 loose stools per day for
adolescents and adults to stools that run out of the diaper in infants.
Crampy, painful bloating
Vomiting: May or may not accompany diarrhea. If you do vomit, your
dehydration rate will increase. Either together or alone, diarrhea and
vomiting result not only in loss of significant amounts of fluid, leading to
dehydration and possibly shock, but also loss of potassium, sodium, and
bicarbonate.
More serious symptoms
o
Blood in vomit or stool
Vomiting more than 48 hours
Fever higher than 101F
Swollen abdomen or abdominal pain coming from the right lower side
Dehydration - Little to no urination, extreme thirst, lack of tears, and dry
mouth (dry diapers in infants)
Enterocolitis
Inflammation of the large and small intestines. Enteritis specifically
refers to an inflammation of the small intestine and colitis specifically
refers to inflammation of the large intestine. One of the possible
causes of the inflammation is antibiotic use.
The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Enterocolitis includes
the 7 symptoms listed below:
Fever
Abdominal swelling
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Rectal bleeding
Sluggishness
Note that Enterocolitis symptoms usually refers to various symptoms known to a patient,
but the phrase Enterocolitis signs may refer to those signs only noticeable by a doctor.
Mediation/Drugs
o Sulfasalazine
Is a pain killer which works mainly by stopping prostaglandin
synthesis.
o Antibiotics
Tylosin
o Glucocorticoids
Efficacy of these drugs are related to their anti-inflammatory and
immunosuppressive
Electrolyte solution
Replaces electrolytes and fluids that may have been lost during
vomiting and diarrhea.
Você também pode gostar
- DiarrheaDocumento19 páginasDiarrheaShaffy UngaAinda não há avaliações
- Cholera: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Prevention, Self-Care, Diet Plans, Herbal and Homeopathic Remedies: Homeopathy, #2No EverandCholera: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Prevention, Self-Care, Diet Plans, Herbal and Homeopathic Remedies: Homeopathy, #2Ainda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis Bronchopneumonia Ear InfectionDocumento34 páginasGastroenteritis Bronchopneumonia Ear InfectionAnn Michelle TarrobagoAinda não há avaliações
- Intestinal Parasitic Diseases, A Simple Guide to These ConditionsNo EverandIntestinal Parasitic Diseases, A Simple Guide to These ConditionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- gastroenteritisDocumento14 páginasgastroenteritisJils SureshAinda não há avaliações
- Peptic Ulcer Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandPeptic Ulcer Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (10)
- GastroenteritisDocumento9 páginasGastroenteritisCheyenne TorioAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis in Adults and Older Children: EpidemiologyDocumento4 páginasGastroenteritis in Adults and Older Children: Epidemiologyjotq19Ainda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis - Is A General Term For Inflammation and Infection of The DigestiveDocumento3 páginasGastroenteritis - Is A General Term For Inflammation and Infection of The DigestiveLev MeisterAinda não há avaliações
- Food Poisoning OverviewDocumento28 páginasFood Poisoning Overviewfdudz06Ainda não há avaliações
- Causes: GastroenteritisDocumento5 páginasCauses: Gastroenteritispragna novaAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis: Saima Alam AfridiDocumento23 páginasGastroenteritis: Saima Alam AfridiMahnoor ParvezAinda não há avaliações
- FWBD - Major Health ProblemDocumento3 páginasFWBD - Major Health ProblemDez TabiosAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Diarrheal Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocumento33 páginasAcute Diarrheal Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentZaryab Umar100% (1)
- The Signs and Symptoms of Typhoid FeverDocumento6 páginasThe Signs and Symptoms of Typhoid FeverwahyuAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Stomach FluDocumento49 páginasGastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Stomach Flukinasal21Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute: Gastroenterit ISDocumento25 páginasAcute: Gastroenterit ISFrancoise Nicolette PesebreAinda não há avaliações
- GastroenteritisDocumento27 páginasGastroenteritisJhoanna Jhoi Alves VarillaAinda não há avaliações
- Food Borne DiseasesDocumento9 páginasFood Borne DiseasesaringkinkingAinda não há avaliações
- English Paper "Gastroenteritis": Manado Health PolytechnicDocumento8 páginasEnglish Paper "Gastroenteritis": Manado Health Polytechnicprayitno tabraniAinda não há avaliações
- Reporting Draft For PPT InputsDocumento2 páginasReporting Draft For PPT InputsPhaestus ReverseAinda não há avaliações
- Acute gastroenteritis causes and treatmentDocumento4 páginasAcute gastroenteritis causes and treatmentChrisette Cenizal LoreñaAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 3 GIT BudiDocumento67 páginasPemicu 3 GIT BudiGrace KahonoAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 3 GIT GraceDocumento67 páginasPemicu 3 GIT GraceGrace KahonoAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis causes, symptoms, treatmentDocumento6 páginasGastroenteritis causes, symptoms, treatmentMikael AlmstrongAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoid Feve1Documento9 páginasTyphoid Feve1Jonas Galeos100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Tract Diarrhea Nausea Viral Infection BacteriaDocumento60 páginasGastrointestinal Tract Diarrhea Nausea Viral Infection BacteriawakuyllibAinda não há avaliações
- Faeco-Oral DiseasesDocumento46 páginasFaeco-Oral DiseasesNatukunda DianahAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Gastroenteritis: Defnition and Etiology/Clinical ManifestationsDocumento13 páginasAcute Gastroenteritis: Defnition and Etiology/Clinical ManifestationsMia EstadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis: Presented by BSCN - Krchn. Paul Mutie Cyrus Pwani UniversityDocumento35 páginasGastroenteritis: Presented by BSCN - Krchn. Paul Mutie Cyrus Pwani UniversityAleeya rizviAinda não há avaliações
- Acute and Chronic Diarrhea - نسخةDocumento49 páginasAcute and Chronic Diarrhea - نسخةHero StoreAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Gastroenteritis GuideDocumento42 páginasAcute Gastroenteritis Guideroizen bagamaspadAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea: DefinitionDocumento13 páginasDiarrhea: Definitionudaybujji100% (1)
- GastroenteritisDocumento2 páginasGastroenteritisIanne MerhAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea Written OutputDocumento5 páginasDiarrhea Written Outputrobertvaliente471Ainda não há avaliações
- Shigella June 2014Documento2 páginasShigella June 2014Nur IffahAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Presentation On ADDDocumento39 páginasClinical Presentation On ADDSREEDEVI T SURESHAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Gastroenteritis (AGE) Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and PreventionDocumento9 páginasAcute Gastroenteritis (AGE) Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and PreventionKristine Jade OdtujanAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocumento2 páginasBacterial Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentabhieghailAinda não há avaliações
- GastroenteritisDocumento2 páginasGastroenteritisJoanna Marie M. dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation GastroenteritisDocumento58 páginasCase Presentation GastroenteritisShereen Manabilang100% (3)
- Acute Gastroenteritis: Acute Inflammation of The Stomach Small IntestineDocumento6 páginasAcute Gastroenteritis: Acute Inflammation of The Stomach Small IntestineJha FernandoAinda não há avaliações
- AGE ReadingsDocumento6 páginasAGE ReadingseljhayrosAinda não há avaliações
- Acute GastroenteritisDocumento11 páginasAcute GastroenteritisrubyjoysasingAinda não há avaliações
- Dysente RY: ALVAREZ, Ronilyn A. BSN Ii-BDocumento20 páginasDysente RY: ALVAREZ, Ronilyn A. BSN Ii-BRonilyn Mae AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteritis ME PresentasiDocumento7 páginasGastroenteritis ME Presentasibayu kuberaAinda não há avaliações
- Symptoms of DiarrhoeaDocumento6 páginasSymptoms of DiarrhoeaPhoenixAinda não há avaliações
- Acute GastroenteritisDocumento35 páginasAcute GastroenteritisAdil ShabbirAinda não há avaliações
- ShigellosisDocumento14 páginasShigellosisMuhammad GetsoAinda não há avaliações
- Strointestinal / GastroenterologyDocumento6 páginasStrointestinal / GastroenterologyLeizel ApolonioAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea Crampy Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting: Gastroenteritis CausesDocumento7 páginasDiarrhea Crampy Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting: Gastroenteritis CausesClefford TagapanAinda não há avaliações
- Viral Gastroenteritis-1Documento17 páginasViral Gastroenteritis-1Abdus SubhanAinda não há avaliações
- Counseling on DiarrheaDocumento4 páginasCounseling on Diarrheakristelaaa guevarraAinda não há avaliações
- Control of Diarrheal Diseases: Marife A. Reyes M W 2 - 1 Mdwy 21Documento13 páginasControl of Diarrheal Diseases: Marife A. Reyes M W 2 - 1 Mdwy 21Kieth SeresulaAinda não há avaliações
- DiseasesDocumento13 páginasDiseasesJaypee SaturnoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 45: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDocumento14 páginasChapter 45: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (3)
- Infectious Diseases: Infectious Diarrhea Causing BacteriaDocumento3 páginasInfectious Diseases: Infectious Diarrhea Causing BacteriaVivek ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- DiarrheaDocumento3 páginasDiarrheaSusana Lopez MontoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrheaseminare3 180503115906Documento65 páginasDiarrheaseminare3 180503115906yersiniapestismorAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric CardiomyopathyDocumento60 páginasPediatric CardiomyopathyPaul A IBattledaily ScavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury - Junior Medicine ClerkshipDocumento18 páginasAcute Kidney Injury - Junior Medicine ClerkshipPaul A IBattledaily ScavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento32 páginasAcute Kidney InjuryPaul A IBattledaily ScavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury - Junior Medicine ClerkshipDocumento18 páginasAcute Kidney Injury - Junior Medicine ClerkshipPaul A IBattledaily ScavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem 10A Lab QuestionsDocumento6 páginasBiochem 10A Lab QuestionsPaul A IBattledaily Scavella100% (1)
- PDA: Patent Ductus Arteriosus GuideDocumento48 páginasPDA: Patent Ductus Arteriosus GuidePaul A IBattledaily ScavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric Emergencies GuideDocumento50 páginasPsychiatric Emergencies GuidePaul A IBattledaily Scavella33% (3)
- Psychiatric Emergencies GuideDocumento50 páginasPsychiatric Emergencies GuidePaul A IBattledaily Scavella33% (3)
- Teratogenic Pregnancy RisksDocumento40 páginasTeratogenic Pregnancy RisksVonny RiskaAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Assessment Form-DECADocumento3 páginasRisk Assessment Form-DECAHill CordialAinda não há avaliações
- Newborn Eye Prophylaxis and Vaccines ExplainedDocumento14 páginasNewborn Eye Prophylaxis and Vaccines ExplainedJoiz Rivera100% (2)
- Spib SEDocumento6 páginasSpib SErosieAinda não há avaliações
- (Teaching Public Health) Jennifer Beard - Teaching Public Health Writing-Oxford University Press (2022)Documento177 páginas(Teaching Public Health) Jennifer Beard - Teaching Public Health Writing-Oxford University Press (2022)Suyogya WagleAinda não há avaliações
- ContraceptionDocumento156 páginasContraceptionLorenn DacpanoAinda não há avaliações
- Hydatidiform Mole Diagnosis and ManagementDocumento19 páginasHydatidiform Mole Diagnosis and ManagementAndre Karl FaculinAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Management Quiz: True FalseDocumento2 páginasStress Management Quiz: True FalseLady Ann HondoAinda não há avaliações
- Iligan Medical Center College College of Nursing and Midwifery Mid 104 (Final Long Quiz)Documento1 páginaIligan Medical Center College College of Nursing and Midwifery Mid 104 (Final Long Quiz)Rohanisah AdapAinda não há avaliações
- SDG 4. HospitalDocumento215 páginasSDG 4. HospitalMuki SimonAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotic treatment guidelines for common infectionsDocumento21 páginasAntibiotic treatment guidelines for common infectionsnovaAinda não há avaliações
- (2013) Principles and Practice of Modern Radiotherapy Techniques in Breast CancerDocumento360 páginas(2013) Principles and Practice of Modern Radiotherapy Techniques in Breast CancerSamir BenAinda não há avaliações
- Infant Feeding in The Context of HIV InfectionDocumento37 páginasInfant Feeding in The Context of HIV InfectionDengAwutAinda não há avaliações
- Who GMP 1221037407Documento478 páginasWho GMP 1221037407Đặng Hoàng50% (2)
- Diphtheria Disease Reporting and Surveillance GuidelinesDocumento10 páginasDiphtheria Disease Reporting and Surveillance GuidelinesAgustin IskandarAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Methods of Family PlanningDocumento24 páginasModern Methods of Family PlanningGeneen GelvoleoAinda não há avaliações
- UploadDocumento7 páginasUploadAlif algifariAinda não há avaliações
- Welton 2019Documento8 páginasWelton 2019Mahanani Edy PutriAinda não há avaliações
- SRSG Keeping The PromiseDocumento106 páginasSRSG Keeping The PromisesofiabloemAinda não há avaliações
- PoliomyelitisDocumento46 páginasPoliomyelitisBareera Nudrat100% (1)
- Placenta Previa GuideDocumento7 páginasPlacenta Previa GuideMargaret AssilasAinda não há avaliações
- Step 1-5 Malnutrition Risk AssessmentDocumento3 páginasStep 1-5 Malnutrition Risk AssessmentM Rendy RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Longevity British English Teacher Ver2Documento6 páginasLongevity British English Teacher Ver2Anna PerepechaevaAinda não há avaliações
- Madurai RoadDocumento3 páginasMadurai RoadSiva NatAinda não há avaliações
- Complaint Letter Assignment 10 18 2Documento4 páginasComplaint Letter Assignment 10 18 2api-584907991Ainda não há avaliações
- ErasinfographicDocumento1 páginaErasinfographicapi-641786123Ainda não há avaliações
- Infection Prevention EssentialsDocumento32 páginasInfection Prevention EssentialsBeamlak Getachew WoldeselassieAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Hiv 101Documento42 páginas2 Hiv 101Francis AbadAinda não há avaliações
- D.S.S Aiims Prepration Test Series - 1 DR - SANJAY (7014964651)Documento17 páginasD.S.S Aiims Prepration Test Series - 1 DR - SANJAY (7014964651)Dr-Sanjay SinghaniaAinda não há avaliações
- 2009 Red Book 7th EdDocumento96 páginas2009 Red Book 7th EdRashid AlahmerAinda não há avaliações
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNo EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNo EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsAinda não há avaliações
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNo EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (31)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossNo EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (8)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNo EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (22)