Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ecg Cookbook
Enviado por
Calin PopaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ecg Cookbook
Enviado por
Calin PopaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
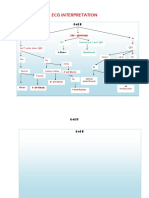
Question
1. Rhythm
Answer
Criteria for sinus rhythm:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Are the P waves positive in I and II?
Is there a QRS after each P wave?
Are the PR intervals constant?
Are the RR intervals constant?
2. Heart rate
Estimate heart rate: 300 / number of large boxes between two QRS
complexes
3. P waves
Large P wave amplitude (> 2.5mm in II, III or aVF)
Prolonged negative part of P wave in V1 (>1mm) and P wave with 2
peaks in II, P wave duration > 0.12 sec
4. PR Interval
a)
> 0.2 sec (if PR interval constant for all beats & each P wave is
followed by a QRS complex
Sinus rhythm or
no sinus rhythm?
Heart rate in beats per min.
Right atrial enlargement
Left atrial enlargement
I AV block
b) < 0.12 sec & QRS complex normal
LGL syndrome
c)
WPW syndrome
< 0.12 sec & visible delta wave
5. QRS Axis
Determine the axis according to Leads I, II and aVF
6. QRS Duration
a)
0.12 sec (always think of the WPW syndrome as a differential)
b) > 0.1 and < 0.12 sec with typical bundle branch block appearance (notching)
7. Rotation
Diagnosis
Rotation is defined according to the hearts transition zone. Normally
the transition zone is located at V4, which means that right ventricular
myocardium is located at V1-V3 and left ventricular myocardium is at
V5-V6.
Normal axis
Left axis deviation
Right axis deviation
North-West axis
complete bundle
branch block
incomplete bundle
branch block
transition zone at V5-V6:
clockwise rotation
transition zone at V1-3:
counter-clockwise rotation
CAVE: dont evaluate rotation
in the setting of myocardial
infarction, WPW syndrome or
bundle branch block
8. QRS amplitude
a)
QRS amplitude <0.5 mV in all standard leads
b) Positive criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy
c)
9. QRS infarction signs
low voltage
left ventricular hypertrophy
Positive criteria for right ventricular hypertrophy
right ventricular hypertrophy
abnormal Q waves, QS waves, missing R wave progression
myocardial infarction localization according to
affected leads
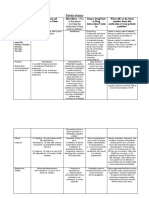
10. ST-T segment
tall T wave
ST depression ST depression
ST elevation
negative T
QRS normal
hyperkalemia,
vagotonia
QRS normal
probably ischemia
(DD: Digitalis)
QRS normal
non-specific repolarization
abnormality
acute ischemia,
myopericarditis
Variant angina
QRS normal
STEMI in resolution
QRS normal
STEMI in resolution
NSTEMI, myopericarditis
QRS normal
STEMI acute and in resolution
QRS with Q wave
left ventricular hypertrophy
with abnormal repolarization
QRS: left ventricular
hypertrophy
In these situations an ST segment deviatiation is almost
always present and cannot be
interpreted in and of itself.
It has to be left out in the
ECG report
QRS: right ventricular
hypertrophy, bundle
branch block or WPW
syndrome
11. QT duration,
T-U waves
a)
QT shortening
Hypercalcemia
b) QT prolongation
Hypocalcemia
c)
Hyperkalemia
tall and peaked T wave
d) U wave, ST depression, T wave flattening or a combination of
these
Hypokalemia
Você também pode gostar
- EKG Basic Analysis GuideDocumento1 páginaEKG Basic Analysis Guideskeebs23Ainda não há avaliações
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocumento69 páginasEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraAinda não há avaliações
- Ekg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurDocumento59 páginasEkg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurArum MaharaniAinda não há avaliações
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsAinda não há avaliações
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookAinda não há avaliações
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Ainda não há avaliações
- Heart Block, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandHeart Block, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandAbnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocumento31 páginasECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani KayedAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideDocumento14 páginasCardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideShawn Gaurav Jha100% (1)
- Dysrhytmia NotesDocumento11 páginasDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfAinda não há avaliações
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyDocumento66 páginasDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Ainda não há avaliações
- CG B Ook: Rapid FindDocumento25 páginasCG B Ook: Rapid FinddellaAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Quiz Prep: Key Points for Interpreting RhythmsDocumento7 páginasECG Quiz Prep: Key Points for Interpreting RhythmsAAAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ECG Reading GuideDocumento63 páginasBasic ECG Reading GuideJofandAndrea MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocumento16 páginas11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhAinda não há avaliações
- EKG Clep TestDocumento13 páginasEKG Clep TestElissa LafondAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesDocumento102 páginasECG Guide: Anatomy, Physiology, Interpretation and AbnormalitiesMustafa A. DawoodAinda não há avaliações
- EKG - Assignment Without AnswersDocumento10 páginasEKG - Assignment Without AnswersJon Millhollon100% (1)
- ECG Master Class-2Documento138 páginasECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Ecg Reading NotesDocumento17 páginasEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Rythum Study Guide PDFDocumento9 páginasECG Rythum Study Guide PDFArtika MayandaAinda não há avaliações
- Interpret ECG Rhythms & Manage ArrhythmiasDocumento6 páginasInterpret ECG Rhythms & Manage Arrhythmiasjh_ajjAinda não há avaliações
- EKG Cheat Sheet - Henry Del RosarioDocumento1 páginaEKG Cheat Sheet - Henry Del RosarioanwarAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Master Class-1Documento132 páginasECG Master Class-1Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Sinus Rhythm DisturbancesDocumento3 páginasSinus Rhythm DisturbancesMarcus Philip GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- EkgDocumento67 páginasEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sAinda não há avaliações
- PR-QRS-TwavesDocumento3 páginasPR-QRS-TwavesKelly PrattAinda não há avaliações
- Rhythm Strip ReviewDocumento8 páginasRhythm Strip ReviewDouglas Greg Cook100% (2)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorDocumento77 páginasElectrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Jovel Balaba Tangonan InstructorNecky AlbaciteAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial NodeDocumento80 páginasNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Nodesiusiuwidyanto100% (2)
- Basic Arrythmia AnalysisDocumento60 páginasBasic Arrythmia AnalysisZakky KurniawanAinda não há avaliações
- ECG MonitoringDocumento96 páginasECG MonitoringJey BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac pacing guide for beginnersDocumento89 páginasCardiac pacing guide for beginnerssandwhale056Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG Interpretation TheoryDocumento4 páginasECG Interpretation TheorySteph PiperAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Interpretation: Gel PDocumento2 páginasEcg Interpretation: Gel PjuliperAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ECGDocumento152 páginasBasic ECGTuấn Thanh VõAinda não há avaliações
- ECG InterpretationDocumento40 páginasECG InterpretationMuhammad BadrushshalihAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocumento29 páginasElectrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramMihaela PrisacaruAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyDocumento87 páginasCardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyummimalikihamidAinda não há avaliações
- Ventricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)Documento3 páginasVentricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)goobyyplssAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocumento8 páginasNormal Sinus RhythmRosalyn YuAinda não há avaliações
- How To: Read ECG?Documento63 páginasHow To: Read ECG?Let BAinda não há avaliações
- DIT High Yield Questions PDFDocumento13 páginasDIT High Yield Questions PDFjoshAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Final Study GuideDocumento14 páginasCardiac Dysrhythmia Final Study GuideBSNNursing101100% (2)
- BBB EcgDocumento33 páginasBBB EcgLokbre YoasAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07Documento60 páginasECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07ampogison08Ainda não há avaliações
- Heartbeat Irregularities ExplainedDocumento5 páginasHeartbeat Irregularities ExplainedKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- Pre - and Post Test Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocumento6 páginasPre - and Post Test Cardiac ArrhythmiasEköw Santiago JavierAinda não há avaliações
- EKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Documento10 páginasEKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Saidel ElizondoAinda não há avaliações
- Megacode Testing Checklist Scenarios 4-7-10 Tachycardia, VF, PEA, PC...Documento1 páginaMegacode Testing Checklist Scenarios 4-7-10 Tachycardia, VF, PEA, PC...krgduraiAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg 1Documento40 páginasEcg 1doctorhanifAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Guide - Qw5620Documento16 páginasOperation Guide - Qw5620powerfmsAinda não há avaliações
- Infectious Disease Essentials HandbookDocumento157 páginasInfectious Disease Essentials HandbookCalin Popa100% (3)
- Arterele CarotideDocumento11 páginasArterele CarotideCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- ECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookDocumento118 páginasECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookOana Anghel100% (7)
- Japan CreativityDocumento67 páginasJapan CreativityCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- CHIP Romania - Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients: March 29-30, 2019, Hotel Hilton Garden Inn, BucharestDocumento2 páginasCHIP Romania - Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients: March 29-30, 2019, Hotel Hilton Garden Inn, BucharestCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Chest X Ray Diagnostic AlgorithmDocumento10 páginasChest X Ray Diagnostic AlgorithmCalin Popa100% (1)
- Rudolf Breuss - Tratament Cancer PDFDocumento71 páginasRudolf Breuss - Tratament Cancer PDFCalin Popa88% (8)
- Basic Clinical Massage TherapyDocumento654 páginasBasic Clinical Massage Therapykkism100% (11)
- Femei Obeze StudiuDocumento6 páginasFemei Obeze StudiuCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Infective Endocarditis EhemDocumento47 páginasInfective Endocarditis Ehemyoga_buanaAinda não há avaliações
- AritmiileDocumento78 páginasAritmiileCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Stress QuestionnaireDocumento2 páginasStress QuestionnaireCalin Popa100% (1)
- Easy-to-Use ECG Features Comprehensive FunctionsDocumento6 páginasEasy-to-Use ECG Features Comprehensive FunctionsCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- PericarditisDocumento120 páginasPericarditisCalin Popa100% (1)
- Bone Tissue: Supportive Connective Tissue: CellsDocumento52 páginasBone Tissue: Supportive Connective Tissue: CellsCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Studies in Teacher Education PsychologyDocumento260 páginasStudies in Teacher Education PsychologyYasmina HassaineAinda não há avaliações
- ESC Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary HypertensionDocumento45 páginasESC Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary HypertensionCalin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal Screening For The 35delg GJB2Documento2 páginasPrenatal Screening For The 35delg GJB2Calin PopaAinda não há avaliações
- 336 EngDocumento158 páginas336 EngMahdi HayAinda não há avaliações
- Definition - Mecical Term - KEYDocumento4 páginasDefinition - Mecical Term - KEYKieu AnhAinda não há avaliações
- The Small Intestine - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum - TeachMeAnatomyDocumento4 páginasThe Small Intestine - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum - TeachMeAnatomyFelix Oriono100% (1)
- University of Glasgow ECG Analysis Program OverviewDocumento4 páginasUniversity of Glasgow ECG Analysis Program OverviewMSAinda não há avaliações
- Classifying Electrocardiograph Waveforms Using Trained Deep Learning Neural Network Based On Wavelet RepresentationDocumento9 páginasClassifying Electrocardiograph Waveforms Using Trained Deep Learning Neural Network Based On Wavelet RepresentationIAES IJAIAinda não há avaliações
- AmiodaroneDocumento2 páginasAmiodaroneEmmil BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Vijayalakshmi 2008Documento7 páginasVijayalakshmi 2008Rakesh DashAinda não há avaliações
- SLICC/ACR Damage Index GlossaryDocumento1 páginaSLICC/ACR Damage Index GlossarySilvana Chimá BustilloAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Jahshan Oet CollectionDocumento398 páginasReading Jahshan Oet CollectionMaria del CarmenAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Pain DDDocumento79 páginasChest Pain DDkashmala afzalAinda não há avaliações
- Borras 2019Documento7 páginasBorras 2019Hill kanjinAinda não há avaliações
- NCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingDocumento3 páginasNCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingCedie BarcaAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Chemical Pathology Lipid Profile: DesirableDocumento1 páginaDepartment of Chemical Pathology Lipid Profile: DesirableSanan AsifAinda não há avaliações
- Cholesterol Guidelines SummaryDocumento52 páginasCholesterol Guidelines Summaryi_top3Ainda não há avaliações
- Physiology-Based Electrocardiographic Criteria For Left Bundle Branch CaptureDocumento9 páginasPhysiology-Based Electrocardiographic Criteria For Left Bundle Branch CaptureVojislavSajicAinda não há avaliações
- Medications For ObDocumento9 páginasMedications For ObMaria Cecilia Pereyra SulzerAinda não há avaliações
- MF3 - CardiomyopathyDocumento51 páginasMF3 - CardiomyopathyAnnbe BarteAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationDocumento21 páginas1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationNuno CoelhoAinda não há avaliações
- Non Q - Wave Myocardial InfarctionDocumento18 páginasNon Q - Wave Myocardial InfarctionOlga GoryachevaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterDocumento30 páginasScience Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterIan BelgaAinda não há avaliações
- Kidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureDocumento50 páginasKidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureKevin MontoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Ijc Heart & Vasculature: SciencedirectDocumento8 páginasIjc Heart & Vasculature: SciencedirectFerdi YuanAinda não há avaliações
- Uttam Maheshwari Ji Gau Ke Chamatkari AushadhiDocumento2 páginasUttam Maheshwari Ji Gau Ke Chamatkari Aushadhiसुमित भारत भूषण वर्मा83% (6)
- DRUG ACTIONDocumento3 páginasDRUG ACTIONGwyn RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology of Cardiovascular SystemDocumento75 páginasPathology of Cardiovascular Systemefri100% (2)
- HeartIndia54157-4958724 134627 PDFDocumento3 páginasHeartIndia54157-4958724 134627 PDFGagandeep Singh ShergillAinda não há avaliações
- Blood TransfusionDocumento41 páginasBlood TransfusionajAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Internal Medicine PDFDocumento388 páginas1-Internal Medicine PDFAbdulaziz AlQahtani100% (1)
- MMDSDocumento1.222 páginasMMDSUlsi Haibara100% (1)
- Basic EchocardiographyDocumento63 páginasBasic EchocardiographyStella CooKeyAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary System-WPS OfficeDocumento6 páginasUrinary System-WPS OfficeClara ZirimAinda não há avaliações