Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NT1330 Lab 2 Ans Key
Enviado por
addislibroTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NT1330 Lab 2 Ans Key
Enviado por
addislibroDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
LAB 2 ANSWER KEY
CONFIGURING DNS AND
DHCP
This lab contains the following exercises:
Exercise 2.1
Designing a DNS Namespace
Exercise 2.2
Creating a Zone
Exercise 2.3
Creating Domains
Exercise 2.4
Creating Resource Records
Exercise 2.5
Creating a Scope
Exercise 2.6
Confirming DHCP Server Functionality
Exercise 2.7
Configuring DHCP Reservations
Workstation Reset: Returning to Baseline
Estimated lab time: 100 minutes
Exercise 2.1
Designing a DNS Namespace
Overview
You have been tasked with creating a test DNS namespace structure for
your organization. Your first task is to design that namespace by specifying
appropriate domain and host names for the computers in the division.
Completion time
15 minutes
1.
Design a DNS namespace for your organization that conforms to the following
guidelines.
a. The root domain name for the test DNS namespace is Contoso##.com, where ## is the
number assigned to your computer by your instructor. All of the additional domains that
you create must be subordinate to this domain.
b. The internal network must be located in a different domain from the external
network.
c. The organization consists of three internal divisions: Sales, Human Resources, and
Production. Each division must be represented by a separate subdomain in the
namespace.
d. Each division has departmental servers performing various roles and as many as 200
workstations, only some of which are shown in the diagram. Your host names should
identify the function of each computer.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
e. Three servers on an external perimeter network host the companys Internet services:
Web, FTP, and e-mail. These servers must be in the domain Contoso##.com.
2.
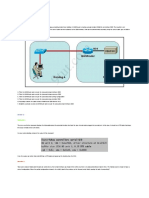
In the diagram provided in Figure 2-1, write both the domain names and the fully
qualified domain names that you have selected for the computers in the appropriate
spaces.
Figure 2-1
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Exercise 2.2
Creating a Zone
Overview
You will now configure the DNS Server Role you installed in lab 1.4 by
creating zones. A zone is the administrative division that DNS servers use
to administer domains. The first step in implementing the DNS namespace
that you designed is to create a zone representing your root domain.
Completion time
10 minutes
1. Turn on the Server##A computer and log on using your Student## account and the
password P@ssw0rd.
2. If the Initial Configuration Tasks (ICT) screen window opens automatically, place a
checkmark next to Do not show this window at logon, and click Close.
3. If the Server Manager window appears automatically, close it.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
4. Click Start, and then click Administrative Tools > DNS. Click Continue in the User
Account Control message box, and the DNS Manager console appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
5. Expand the SERVER##A node in the DNS console.
6. Right-click the Forward Lookup Zones folder and, from the context menu, select New
Zone. The New Zone Wizard appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
7. Click Next to bypass the Welcome page. The Zone Type page appears.
Question
1
Why is the Store the zone in Active Directory checkbox
grayed out? Answer: Because Active Directory is not
installed on this machine
8. Leave the Primary Zone option selected, and click Next. The Zone Name page appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
9. In the Zone name text box, key the root domain name from the diagram you created in Exercise
2.1, and click Next. The Zone File page appears.
10. Click Next to accept the default zone file name. The Dynamic Update page appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
11. Select the Allow both nonsecure and secure dynamic updates option, and click Next. The
Completing the New Zone Wizard page appears.
12. Click Finish. The new zone appears in the Forward Lookup Zones folder in the console.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Question
2
What resource records appear in the new zone you
created by default? Answer: The Start of Authority (SOA)
and the Name Server (NS) resource records appear in the
new zone you created by default.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
13. Repeat steps 3 to 9 to create another zone by using the internal domain name you specified
in the diagram in Exercise 2.1.
14. Leave the DNS Manager console open for the next exercise.
Exercise 2.3
Creating Domains
Overview
A single zone on a DNS server can encompass multiple domains as long as
the domains are contiguous. In this exercise, you create the departmental
domains you specified in your namespace design.
Completion time
10 minutes
1. In the DNS Manager console, right-click the zone you created using the internal domain
name from your namespace in Exercise 2.3. From the context menu, select New Domain.
The New DNS Domain dialog box appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
NOTE
2. In the Type the new DNS domain name text box, key the name of the Human Resources
domain you specified in your namespace design, and click OK.
When you create a domain within a zone, you specify the name for the
new domain relative to the zone name. For example, to create the
qa.contoso.com domain in the contoso.com zone, you would specify
only the qa name in the New DNS Domain dialog box.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
3. Repeat steps 1 to 2 to create the domains for the Sales and Production departments from your
namespace design.
Question
3
What resource records appear in the new domains you
created by default? Answer: There are no resource records
in the domain by default.
4.
Leave the DNS Manager console open for the next exercise.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Exercise 2.4
Creating Resource Records
Overview
Now that you have created the zones and domains for your namespace,
you can begin to populate them with the resource records that the DNS
server uses to resolve host names into IP addresses.
Completion time
15 minutes
1. In the DNS Manager console, right-click the root domain zone you created in Exercise 2.3.
From the context menu, select New Host (A or AAAA). The New Host dialog box appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
2.
In the Name text box, key the host name of the Internet Web server you specified in your
namespace design.
3.
In the IP Address text box, key 172.17. xx.201, where xx is the number assigned to your
computer by your instructor.
4. Click Add Host. A DNS message box appears, stating that the resource record was created.
Question
4
What must you do before you can select the Create
associated pointer (PTR) record checkbox in the New
Host dialog box? Answer: Before you can select the Create
associated pointer (PTR) record checkbox in the New Host
dialog box you must create a Reverse Lookup Zone.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
5. Click OK. A new, blank Add Host dialog box appears.
6. Repeat steps 2 to 4 to create Host records for the Internet FTP and e-mail servers in your namespace
design. For each resource record, use a different IP address on the 172.17. xx subnet.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
7. In the three domains you created in Exercise 2.3, create Host resource records for all of the
remaining computers in your namespace design, using the names you specified in your diagram
and a different IP address in the 172.16. xx (start from 172.16.##.9) subnet for each record.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
NOTE
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
For the purposes of this exercise, the actual IP addresses you use when
creating your resource records do not matter. In an actual DNS deployment,
you must either specify an appropriate IP address for each host, based on
the subnet to which the computer is connected, or rely on DHCP to create
8.
Click Done to close the Add Host dialog box.
9.
Press Ctrl+Prt Scr to take a screen shot of the DNS Manager console, showing the
resource records you created in the Human Resources domain, and then press Ctrl+V to
paste the resulting image into the lab02_worksheet file in the page provided.
10. Close the DNS Manager console.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Creating a Scope
Overview
In this exercise you will configure the DHCP Server Role you installed in
lab 1.5 by creating a scope. A scope is a range of IP addresses that a DHCP
server uses to supply clients on a particular subnet with IP addresses. In
this exercise, you create a scope on your DHCP server.
Completion time
15 minutes
NOTE
Exercise 2.5
Ensure that your virtual machines network settings are set to Host-only
before beginning this exercise.
1. On Server##A click Start, and then click Administrative Tools > DHCP. Click Continue in
the User Account Control message box, and the DHCP console appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
2. Expand the Server##A node.
3. Right-click the IPv4 node and, from the context menu, select New Scope. The New Scope Wizard
appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
4. Click Next to bypass the Welcome page. The Scope Name page appears.
5. In the Name text box, key Student## Scope, where ## is the number provided by your
instructor and click Next. The IP Address Range page appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
6. In the Start IP address text box, key 172.16.##.240, where ## is the number assigned to your
computer by your instructor.
7. In the End IP address text box, key 172.16.##.250.
Question
5
Notice that the wizard automatically adds a value to the
Subnet mask text box.Where did this value come from?
Answer: The subnet mask is based on the class of the address you
entered in the IP address range boxes.
8. In the Subnet mask text box, key 255.255.255.0, and then click Next. The Add Exclusions
page appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
9. In the Start IP address text box, key 172.16.##.245.
10. In the End IP address text box, key 172.16.##.245.
11. Click Add. The address appears in the Excluded address range list.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
12. Click Next. The Lease Duration page appears.
13. Click Next to accept the default value. The Configure DHCP Options page appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
14. Click Next to accept the Yes, I want to configure these options now option. The Router (Default
Gateway) page appears.
15. In the IP address text box, key 172.16.##.100 and then click Add.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
16. Click Next to continue. The Domain Name and DNS Servers page appears.
17. In the Parent domain text box, key the name of the internal domain you specified in your
namespace design in Exercise 2.1.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
18. In the Server name text box, key Server##A, where ## is the number assigned to your computer
by your instructor, and click Resolve. Your computers IP address appears in the adjacent text
box.
19. Click Add, and then click Next. The WINS Servers page appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
20. Click Next to bypass the page. The Activate Scope page appears.
21. Click Next to accept the default Yes, I Want To Activate This Scope Now option. The Completing
the New Scope Wizard page appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
22. Click Finish. The scope is added to the console.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
23. Expand the IPv4 node and the new scope, and then select the Address Pool folder.
24. Press Ctrl+Prt Scr to take a screen shot of the DHCP console, showing the contents of the
Address Pool folder, and then press Ctrl+V to paste the resulting image into the lab02_worksheet
file in the page provided.
25. Close the DHCP Server console.
26. Leave the computer logged on for the next exercise.
Exercise 2.6
Confirming DHCP Server Functionality
Overview
In this exercise you will test the functionality of your DHCP Server using
your Windows 7 virtual machine.
Completion time
10 minutes
1. Turn on the Workstation## computer and log on using your Student## account and the
password P@ssw0rd.
*Note
In order to log in you may have to click switch user and enter
Workstation##\Student## as the username.
2. Click Start and then click Control Panel. The Control Panel window appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
3. Click Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. The Network and Sharing
Center control panel appears.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
4. In the Network and Sharing Center control panel select Change Adapter Settings. The
Network Connections window appears.
5. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and, from the context menu, select
Properties. The Local Area Connection Properties sheet appears.
6. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties. The Internet Protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties sheet appears.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
Question
6
What IP addressing settings are currently configured?
Answer: It should be set to a static address, but it may be set
to obtain automatically.
7. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically radio button.
8. Click OK twice to close the two Properties sheets. Close the Network Connections
window.
9.
Click Start, key cmd, and press Enter.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
10.
At the command prompt, key ipconfig /release.
11.
At the command prompt, key ipconfig /renew.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
NOTE
12. At the command prompt, key ipconfig /all.
You may have to execute the ipconfig /release and /renew commands
more than once in order for your client machine to obtain an IP Address
from your DHCP server.
Question
7
Question
Is the computer currently configured for DHCP? How
can you tell? Answer: Yes DHCP is enabled, the DHCP
enabled line indicates that it is enabled.
What is the IP address of the DHCP server from which
Configuring DNS and DHCP
Workstation## has obtained its IP address? Answer: This
8
Question
9
Question
10
answer depends on the DHCP range you created in the
previous exercise.
If the answer to #8 was not the IP address of the
Server##A computer, why might this have happened?
Answer: Another DHCP server received and serviced the
request.
What DNS Server address was Workstation XX
assigned? Answer: This answer depends on the DNS Server
address you configured in the earlier exercise.
13. Record the Physical address of WorkstationXX for use in the next exercise.
14. At the command prompt, key exit, and press Enter to close the command prompt
window.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
Exercise 2.7
Configuring DHCP Reservations
Overview
In this exercise you will configure a DHCP reservation for your Windows
7 virtual machine. A DHCP reservation enables the DHCP server to always
assign a specific address to a client machine. You will test the DHCP
reservation using your Windows 7 virtual machine.
Completion time
15 minutes
1. On Server ##A Click Start, and then click Administrative Tools > DHCP. Click Continue
in the User Account Control message box, and the DHCP console appears.
2. Expand the Server##A node, followed by IPv4, followed by Scope [<address>].
Configuring DNS and DHCP
3. Click Reservations. Right-click Reservations, and select New Reservation.
4. In the Reservation Name text box, enter Workstation##.
5. In the IP Address: field, enter an available IP address within the scope that you defined in
exercise 2.5.
6. In the MAC address: field, enter the physical address of the even-numbered computer as
indicated in the ipconfig /all output from Workstation##.
7. Click Add, and then Close.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
8. Expand the Reservations node. Right-click the reservation you just created, and click
Configure Options.
Configuring DNS and DHCP
9. Place a checkmark next to 006 DNS Servers. Enter the IP address you assigned to
Server##A.
10. Click Add, and then click OK.
11. Close the DHCP MMC.
12. Log on to the Workstation## computer. Open a command prompt, key ipconfig /release,
and press Enter.
NOTE
13. At the command prompt, key ipconfig /renew, and press Enter.
You may have to execute the ipconfig /release and /renew commands
more than once in order for your client machine to obtain an IP Address
from your DHCP server.
Windows Server 2008 70-646 Administrator and 70-642 Network Infrastructure
Configuration
14. On Server##A open the DHCP Server console and click on the Address Leases node.
15. Press Ctrl+Prt Scr to take a screen shot of the DHCP Server console, showing the reservation you
created is active, and then press Ctrl+V to paste the resulting image into the lab02_worksheet file
in the page provided.
16. Log off of both machines.
WORKSTATION RESET: RETURNING TO BASELINE
Completion time
10 minutes
To return the computer to its baseline state, complete the following procedures.
1.
Open the Server Manager console.
2. Remove the DNS Server and DHCP Server roles you installed during the course of the lab.
Restart the computer.
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Ccna TroubleshootingDocumento7 páginasCcna TroubleshootingaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna-Lab-Sim (CCNA Access List Sim 2)Documento6 páginasCcna-Lab-Sim (CCNA Access List Sim 2)addislibroAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna Drag and Drop QuestionsDocumento11 páginasCcna Drag and Drop QuestionsaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- 64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionDocumento3 páginas64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna Drag and Drop 4Documento2 páginasCcna Drag and Drop 4addislibroAinda não há avaliações
- 59 Ccna Configuration Sim QuestionDocumento2 páginas59 Ccna Configuration Sim QuestionaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- Configuring The User and Computer Environment Using Group PolicyDocumento41 páginasConfiguring The User and Computer Environment Using Group PolicyaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- Global Catalog and Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) RolesDocumento30 páginasGlobal Catalog and Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) RolesaddislibroAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Enterprise Resourse Planning: Assignment 2Documento7 páginasEnterprise Resourse Planning: Assignment 2priyalAinda não há avaliações
- Ipc620-35plc - User Manual1 PDFDocumento68 páginasIpc620-35plc - User Manual1 PDFman_y2k50% (2)
- Bank Management SystemDocumento54 páginasBank Management SystemJuNaid Sheikh100% (1)
- FTTH Handbook - 2014 V6.0Documento160 páginasFTTH Handbook - 2014 V6.0Anonymous 8EHYu9FiM100% (1)
- ICs Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsDocumento4 páginasICs Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsMichael Vincent MonteroAinda não há avaliações
- PC Engines ALIX.1C/1D System BoardDocumento20 páginasPC Engines ALIX.1C/1D System BoardZainuddin JusohAinda não há avaliações
- Comm Project ProposalDocumento2 páginasComm Project ProposalRakesh Sonu PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Core ArchitectureDocumento90 páginasCore Architecturehuthaifa0% (1)
- ZinioDocumento28 páginasZinioDougAinda não há avaliações
- Hiren'S Bootcd 15.1: All in One Bootable CD Which Has All These UtilitiesDocumento10 páginasHiren'S Bootcd 15.1: All in One Bootable CD Which Has All These UtilitiesManjunath NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Instagram Reading: 6 Unit: ComprehensionDocumento1 páginaInstagram Reading: 6 Unit: ComprehensionSoma HamidAinda não há avaliações
- FAQ On Printing at ComCen UTown PDFDocumento3 páginasFAQ On Printing at ComCen UTown PDFrevo17Ainda não há avaliações
- A Deepdive Into Splunk Ebook Edureka Splunk Certification Training - OriginalDocumento61 páginasA Deepdive Into Splunk Ebook Edureka Splunk Certification Training - OriginalK Kunal Raj100% (1)
- 3PAR Technical For PDFDocumento52 páginas3PAR Technical For PDFandroidperaAinda não há avaliações
- Hostel Management DocumentationDocumento49 páginasHostel Management Documentationindira induAinda não há avaliações
- White Paper Idirect Transec in Ip Vsat ArchitectureDocumento5 páginasWhite Paper Idirect Transec in Ip Vsat ArchitectureAriel TituañaAinda não há avaliações
- Vahid Digitaldesign ch04Documento89 páginasVahid Digitaldesign ch04Mauricio AlvesAinda não há avaliações
- HostsDocumento585 páginasHostsScott Foster100% (1)
- Creating A Windows DLL With Visual BasicDocumento12 páginasCreating A Windows DLL With Visual Basicoghenez100% (1)
- EBS Proxy User ManagementDocumento6 páginasEBS Proxy User ManagementdbaahsumonbdAinda não há avaliações
- SAMSUNG Confidential: Application ProcessorDocumento1.482 páginasSAMSUNG Confidential: Application ProcessorjulioAinda não há avaliações
- 07 17 17 PDFDocumento15 páginas07 17 17 PDFGrimlight PursuerAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Implementation of VLSI SystemsDocumento42 páginasDesign and Implementation of VLSI SystemsLê Bá Phước LongAinda não há avaliações
- M-4206 Operator ManualDocumento168 páginasM-4206 Operator ManualarylessenceAinda não há avaliações
- 09 - VAS Vodafone TrainingDocumento25 páginas09 - VAS Vodafone Trainingsrm057Ainda não há avaliações
- CCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullDocumento14 páginasCCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullSándor PetrócziAinda não há avaliações
- Sony DVX-11A Service Manual (P.N. - 987735203)Documento56 páginasSony DVX-11A Service Manual (P.N. - 987735203)tm5u2rAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ's For Operating SystemsDocumento11 páginasMCQ's For Operating SystemsYussif AliAinda não há avaliações
- Module H Information Systems Auditing Learning ObjectivesDocumento26 páginasModule H Information Systems Auditing Learning ObjectivesYvonne TotesoraAinda não há avaliações
- 323 1059 190.1Documento402 páginas323 1059 190.1Tim WalkerAinda não há avaliações