Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pain
Enviado por
footballjeinDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pain
Enviado por
footballjeinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
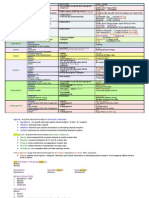
Painunpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with either
actual or potential tissue damage. The processes in the body involved in
perception of pain are called "nociception"
Acute painPain of sudden in onset, usually subsides when treated, &
typically occurs over less than 6-week period of time (injury healing time).
Chronic painPersistent or recurring pain that is often difficult to treat.
Typically lasts longer than 3 months (beyond injury healing time).
Pain thresholdLevel of stimulus needed to produce a painful sensation
Analgesia: Absence of pain
Pain: An unpleasant sensory & emotional experience with actual or potential
tissue damage or described in terms of such damage
Mechanism of pain: Stimulus (cause of pain) detected by pain receptors
(nociceptors) sensory nerve pain centre (perception) emotional
reaction (pain threshold)
Relief of pain
Analgesics
Narcotic analgesics (Opioid analgesics)
Non narcotic analgesics (Non steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs)
Adjuvant analgesics or Co-analgesics
Anaesthetic agents
General anaesthetics
Local anaesthetics
Narcotic analgesics
Used to control moderate to severe pain.
Properties
Control moderate to severe pain by acting on opioid receptors: mu (),
kappa (k), delta (), alters perception of & response to painful stimuli
while producing generalized CNS depression
receptor both spinal & supraspinal analgesia, euphoria,
dependence, respiratory depression and inhibition of gut motility
k receptor analgesia at spinal cord level and dysphoria, do not
contribute to dependence
receptor may contribute to spinal analgesia, respiratory depression
and inhibition of gut motility
Classification of narcotic analgesia
Pure agonists (primarily at , perhaps at k & ): morphine,
methadone
Partial agonist and mixed agonist antagonists: nalorphine(partial
agonist)
Antagonist (all receptors): naloxone
Morphine
Papaver somniferum
prototype of opioids
CNS stimulation (excitation)
Miosis
Vomiting
Mood changes
CNS depression
Sedation
Respiratory depression
Analgesia
Impairs sympathetic vascular reflexes
reduces mental distress
retention of urine
PA
Uses
relieve moderate to serve pain
relive dyspnea
relieve anxiety
Suppressing cough
control of diarrhea
Asthma
drug allergy
Paralytic ileus
Morbid obesity with sleep apnea
Patients with severe head injuries
CI
ADE
Physical & psychological dependence
Tolerance
Respiratory depression
Cerebral vasodilatation
Overdose: coma, pinpoint pupil (miosis), depressed respiration (with injection
morphine > 30 mg)
Treatment: opioid antagonist antidote for opioid poisoning Naloxone
competitively blocks effects of opioids
Naloxone
Pure competitive antagonist
treatment of acute opiate overdose
High first-pass effect (IV)
Codeine
Natural alkaloid
Generalized CNS depression
mild to moderate pain
combination with other analgesics Tylenol with codeine
Methadone
Synthetic opioid
Physical dependence
agonist
Drug of choice for detoxification treatment for opioid addiction
Meperidine(Pethidine)
Synthetic ( & k), with lower analgesic action
has anticholinergic action (dry mouth, blurred vision)
Does not interfere birth or uterine involution
Pethidine differs from morphine in that:
Does not suppress cough
usefully, not constipate
less likely to cause urinary retention
Does not interfere birth or uterine involution
Same uses & adverse effects as morphine
ADE neurotoxic metabolism with chronic use CNS agitation
Hallucinations, Tremors, seizures
Non-narcotic analgesics
Non-steroidal analgesic, antipyretic & anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs)
Classification
Para-aminophenol derivative: paracetamol (acetaminophen)
Salicylic acid derivatives: Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid)
Propionic acid derivatives: Ibuprofen, naproxen
Indoleacetic acids derivatives: Indomethacin diclofenac*,etodolac*
Fenamic acid (Anthranilic acids) derivatives: Mefenamic acid
Oxicams: Piroxicam, meloxicam*
Cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) inhibitors: Celecoxib
Salicylate
PA
Analgesia
Anti-inflammatory action
Antipyretic action
Antiplatelet effect Inhibit platelet aggregation/adhesion
Uses
Systemic administration:
Non-specific relief of certain types of pain headache
To reduce inflammation acute rheumatic fever
Prophylaxis of thromboembolic diseases coronary heart disease
Local application:
Topical application for muscle and joint pain
Oral for ulcerative colitis
ADE
Nausea/vomiting
Salt-water retention
Increased bleeding tendency
hypersensitivity reaction
Reyes Syndrome(Caused by aspirin & other salicylates)
PARACETAMOL
Therapeutic efficacy: equal to aspirin in analgesic
less effect on platelets, on bleeding time and on GI irritation
control pain or fever as substitute for aspirin
ADE
chronic renal failure
hepatic necrosis & failure
INDOMETHACIN
Methylated indole derivatives
relieve pain & inflammation
ADE
anorexia, nausea, abdominal pain
not be used in pregnant women & children
Severe frontal headache
DICLOFENAC
Non-selective COX inhibitor, most used among NSAIDs
Potency against COX-2
Rapidly & completely absorbed
Uses
Long-term symptomatic t/m in moderate pain & inflammation
rheumatoid arthritis
Orally
Short-term treatment in MSK disorders
CELECOXIB
Highly-selective potent COX2 inhibitor
Sulphonamide derivative
Used mainly for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
ADE & CI
Hypertension & oedema.
Selective COX-2 inhibitors depress PGI2 formation by endothelial cells
thrombosis
CI in cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases
INFLAMMATION
Remove harmful stimuli, includi damaged cells, irritants, or pathogens - &
begin the healing process.
CHRONIC autoimmune conditions
damage is too severe to be resolved
CORTICOSTEROID
Suppresses all types of hypersensitivity & allergic phenomenon
Acute short-term therapy Very high single dose
Prolong therapy(> 20 mg prednisolone x > 2 weeks) Only palliative,
NOT curative and used when other measures fall
Gradual withdrawal (after use for 2 weeks), A 50% reduction in dose
may be made on each day
ADE
Fat redistribution
Hypertension
Glucose intolerance
Risk of infection
Cataracts
Infection
Peptic ulcer
Heart disease
CI
GOUT
deposition of Na urate crystals in the joint painful arthritis.
Acute attacks indomethecin, naproxen, or other NSAIDs, but not with
aspirin (plasma urate levels at low doses by inhibiting uric acid
secretion in renal tubules).
Colchicine inhibits phagocytic activity & migration of leukocytes to
the area of uric acid deposition and inflammatory response.
Allopurinol lowers plasma urate by inhibiting xanthine oxidase
(xanthine uric acid).
Uricosuric drugs (probenicid ) inhibit renal tubular reabsorption of uric
acid excretion.
Should drink plenty of H2O
Acute Treatment
NSAIDS (indomethacin)
Corticosteroids
Chronic Treatment
Allopurinol
Uricosuric drugs
Low-dose colchicine
auto-immune
Causes inflammation & swelling
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMRDs) are recommended
for almost all RA patients within 3 months of diagnosis to reduce joint
damage, preserve joint structure & function, improve patients
symptoms & lower health care costs
Steroids are often used along with DMARDs DMARDs may take weeks
to months to have effects. Prednisolone is most often used with
DMARDs
RA
Você também pode gostar
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 1Documento6 páginasQuiz 1footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 1Documento6 páginasQuiz 1footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 1Documento1 páginaQuiz 1footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Sdfefrer 325345634Documento3 páginasSdfefrer 325345634footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetic ToxicityDocumento7 páginasLocal Anesthetic ToxicityfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- NEWRRRDocumento1 páginaNEWRRRfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 1Documento6 páginasQuiz 1footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- DasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsDocumento3 páginasDasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- NEWRRRDocumento1 páginaNEWRRRfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Rtwerejwhfdjkfghdsufghdskjghduigwerhgjkwerghdsjkghdshjkfgdsjkfghsdjkf 2232323 WqerfqwerweqrwerewDocumento3 páginasRtwerejwhfdjkfghdsufghdskjghduigwerhgjkwerghdsjkghdshjkfgdsjkfghsdjkf 2232323 WqerfqwerweqrwerewfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Qwert 77777777777777Documento6 páginasQwert 77777777777777footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Rtwerejwhfdjkfghdsufghdskjghduigwerhgjkwerghdsjkghdshjkfgdsjkfghsdjkf 2232323Documento1 páginaRtwerejwhfdjkfghdsufghdskjghduigwerhgjkwerghdsjkghdshjkfgdsjkfghsdjkf 2232323footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Dasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS1122Documento7 páginasDasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS1122footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Dasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS112233Documento9 páginasDasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS112233footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Dasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS1122Documento7 páginasDasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfdsfdsfdsfdsfdfdsfdsffdfdsf FDSFDS1122footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- DasdsadasfadsgdsgasgDocumento2 páginasDasdsadasfadsgdsgasgfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- NociceptionDocumento8 páginasNociceptionfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- 1233Documento1 página1233footballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- NociceptionDocumento8 páginasNociceptionfootballjeinAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Drugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationDocumento47 páginasDrugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationNavlika DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Acta Anaesthesiol Scand - 2021 - Dokken - Iatrogenic Withdrawal Syndrome Frequently Occurs in Paediatric Intensive CareDocumento8 páginasActa Anaesthesiol Scand - 2021 - Dokken - Iatrogenic Withdrawal Syndrome Frequently Occurs in Paediatric Intensive Carefuka priesleyAinda não há avaliações
- (Osborn) Chapter 15: Osborn, Et Al., Test Item File For Medical-Surgical Nursing: Preparation For PracticeDocumento28 páginas(Osborn) Chapter 15: Osborn, Et Al., Test Item File For Medical-Surgical Nursing: Preparation For PracticeKittiesAinda não há avaliações
- Pain ManagementDocumento25 páginasPain ManagementnurminieAinda não há avaliações
- NEW GUIDELINES - CDC Softens Opioid Prescribing Guidelines For DoctorsDocumento100 páginasNEW GUIDELINES - CDC Softens Opioid Prescribing Guidelines For DoctorsDan LehrAinda não há avaliações
- Pain and Perioperative NursingDocumento28 páginasPain and Perioperative NursingRonica MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- SUBSTANCE DISORDER AND TREATMENT OPTIONSDocumento63 páginasSUBSTANCE DISORDER AND TREATMENT OPTIONSBagus Cahya WibawaAinda não há avaliações
- Knee Osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology and Current Treatment ModalitiesDocumento8 páginasKnee Osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology and Current Treatment ModalitiesHifza ArifAinda não há avaliações
- Research - Drug Rehabilitation CenterDocumento6 páginasResearch - Drug Rehabilitation CenterDan Czar T. JuanAinda não há avaliações
- ICU Sedation and Analgesia GuideDocumento68 páginasICU Sedation and Analgesia GuideAsim KhanAinda não há avaliações
- The Placebo EffectDocumento7 páginasThe Placebo Effectapi-583543995Ainda não há avaliações
- Clin Tox Lab 1Documento4 páginasClin Tox Lab 1Czariana Cassidy MagbanuaAinda não há avaliações
- Acupuncture in Modern MedicineDocumento400 páginasAcupuncture in Modern Medicinepranav100% (2)
- Outpatient SurgeryDocumento7 páginasOutpatient SurgeryJulián David Ríos ZuluagaAinda não há avaliações
- Kratom Feasibility Report SupplementDocumento92 páginasKratom Feasibility Report SupplementMichael_Roberts2019Ainda não há avaliações
- Type Drug ChartDocumento3 páginasType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Drugs Used in CcuDocumento169 páginasDrugs Used in CcuAnusha Verghese100% (3)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Dependence, Withdrawal and Rebound of CNSDocumento23 páginasDependence, Withdrawal and Rebound of CNSHassan AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Physical Therapy For Chronic Pain The Complex Whole Is Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsDocumento4 páginasManual Physical Therapy For Chronic Pain The Complex Whole Is Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsVizaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Guideline Title: Remifentanil: SummaryDocumento11 páginasDrug Guideline Title: Remifentanil: SummaryyafetAinda não há avaliações
- Critical AppraisalDocumento13 páginasCritical AppraisalRatna Widiyanti KAinda não há avaliações
- Tramadol Drug-StudyDocumento3 páginasTramadol Drug-StudyPang ProjectAinda não há avaliações
- Argumentative Essay Medical MarijuanaDocumento7 páginasArgumentative Essay Medical MarijuanaMaxim Dahan100% (1)
- DebateDocumento27 páginasDebateRochelline Rose ParaisoAinda não há avaliações
- LUCEMYRA Fact SheetDocumento2 páginasLUCEMYRA Fact SheetCirca NewsAinda não há avaliações
- Dallas County v. Opioid Drug Makers LawsuitDocumento119 páginasDallas County v. Opioid Drug Makers LawsuitNaomi Martin100% (2)
- Analgesics (Pain Medication)Documento4 páginasAnalgesics (Pain Medication)Frederica DebyAinda não há avaliações
- Anesthprog00276-0033-Summary of The Scientific Literature For Pain and Anxiety Control in Dentistry-Journal Literature, January 1986-December 1987Documento19 páginasAnesthprog00276-0033-Summary of The Scientific Literature For Pain and Anxiety Control in Dentistry-Journal Literature, January 1986-December 1987skyclad_21Ainda não há avaliações
- Alleviating The Access Abyss in Palliative Care and Pain Relief.Documento37 páginasAlleviating The Access Abyss in Palliative Care and Pain Relief.Presentaciones_FKAinda não há avaliações