Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
BCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering) - Question 35-32
Enviado por
Shekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed100%(19)100% acharam este documento útil (19 votos)
7K visualizações23 páginasBCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering)- Question 35-32
Título original
BCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering)- Question 35-32
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoBCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering)- Question 35-32
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
100%(19)100% acharam este documento útil (19 votos)
7K visualizações23 páginasBCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering) - Question 35-32
Enviado por
Shekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedBCS BCS Preliminary Question (Civil Engineering)- Question 35-32
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 23
¥
Mark
(a) What is meant by river training? List the jectives. Explain 8
only te dict mechs ely a ee ea
@ Design surface drainage channel in non-alluvial soil to cary a7
discharge of 10m’/s with a velocity of m/s, Assume side si
0 , bed slope | : 5000 and manning’s n = 0.0225, wv
@
of a catchment
() Explain the principal causes of flood and possible remedial 5
‘measures for flood Control.
(©) A pump is installed on a wel to it water and to itrigate rie crop 5
sown over 35 hectare of land, Ifthe duty of rice is 850 hectare
‘ounce on the field and pump efficiency is 50%, determine the
‘minimum required impute HLP. the pump. The lowest well water
level is 9m below the highest portion of the field. Assume
‘negligible field channel losses,
(@ Explain the different methods of water distribution with relative 5,
advantages and disadvantages of each method,
(©) Explain the factors to be kept in view in the design of water 3
distribution system.
(©) Discuss the st involved for calculating the flow in a looped sf
network using cross method. =
(@). Write notes on the followings == 6
() Aerobie and anerobi decomposition of sewage.
(ii) Gray sewage and dark sewage.
(i Solid wastemanasement.
ist the properties thal ae required tobe analyzed ifsoid wastes 3
are to be used as resources.
(€) Calculate BOD) ay at 37°C of a sewage whose standard BOD is 6
10mg, Assume Kye 0
(a) = discuss the transmission rates of water and waste related 7
isa
(©) sewer ith an isosceles (wo sides equal) tingulr section. 8
having side of 10. feet with n SE eosin
(@ What is the capacity ofthe sewer when the depth of flow is
$ fet? ci What wll be the velochy wen ine Sesh of Now i
3 feet and the section is circular with a diameter of 3/4 of the
ivangular same side?
fa) Differentiate =
& Flexible and rigid pavement;
ii) Base and sub-base;
(Stopping Ste dance (sd) and ovtaking sight distance (OSD),
(6) What are the necessity and objects of highway planning? Discuss in 4
the planning survey of a highway project.
(© Calculate the safe stopping sight distance for design speed of 5
50 kav fr @) two way traf on a two lane road i) two way
trafic ona single lan oad
o
3x26
[Please turn over
It
B.
4
15
a
eo
©
@
o
©
ww
o
@
o
@
o
©.
@
0)
©
soam
‘What is high ‘alignment? Explain’ the: ote
conmolig aigumcsrola neat
List the various types of transition curves used is highway.
Explain the factors to be eonsidered while designing the length of
transition curve.
Define the fem tafe volume Explain the diferent methods or
carrying out trafic volume studies.
Write short notes —
() Points and crossing in Railway; ;
(i), Hee! divergence; z
(iit) CTC, o
‘Gv) Broad gauge and Metre gauge:
(9) Conerete slepner.
Sate the neces of flat in Rallway Expl he forts of
Screcring of tla Why fe tlt tod in etna ek 1 be
renewed from time to time?
Define equilibrium cant. curve of 5° js situated on a section of
broad guage, The maximum permissible speed in the section is
50 knv/hr. Find out the amount of equilibrium cant.
‘What are the principal objectives of soil exploration? Write dawn
the most common types of in-situ test, can
‘A state cone penetration test was performed in a cohesive soil at
a depth of 7-0m with a tip resistance q, of | MPa and friction
ratio 39%, The soil is intensive and plasticity index of 15%, What
is the undrained shear strenath of the soil?
‘Show with diagram the different modes of slope failures.
Find the center of the ettcal circle for B =78%. 11 = 60" and
D= 18’ and toe circle failure.
EstimatesF for a slope having H.= 20m, D = 40m, B = 25,
Y=19 KNIMP, Cu=50 KPa.
What is your idea about cross-border issue? Write in brief
‘What do you understand by regional connectivity? What ae t's
avai and isavamtages? =
What dosou mens BIN? api 2
What is meant by co-efficicut of permeability of soil? List the
fees ting he pom afsai
‘Discuss the effect of water table on the bearing capacity of
Differentiate between normally consolidated and _ over
analiza soi A chy sot Sm chick bas initial oii of
il.
‘30 andthe effective, a A Ne We
ao is subjected to an increased pressure of 120 KN’
coefficient of
edi 144,
— voli ci i et
CIVIL ENGINEERING “GS
Finst PArER
Subject Code : 881
Time allowed—3 hours
Full marks—100
INB—he figures inthe right margin indicate full marks]
Section A—Structure (A wal yf,
put CAmalysis)
(Answer any two questions)
Marks.
1. @ Define stiffness and yover factor of a structural member. Ss
Derive the expression si aitees el Ge
prismatic beam when the far end is fixed.
() Analyse the frame shown in Fig 1(b) by moment distribution 15
mnethod. Daw SPD & BMDorthe hone”
A
Sm
JOKN
* 2 fe 100KN =
hy o o a
@ 10m
2.” (@) Define influence line (IL) diagram ofa structure. State its practical 4
aspects in structural analysis,
(@) State Brelau Principle regarding IL diagram. Explain its practical” 4
application,
(©) Draw IL diagram for shear atD of the continuous beam ABC shown 12
in Fig2 (C). Compute the IL ordinates at 10f interval. Elis constant.
& D B A
2 poo 20, sy 0 20°
Fig2 (©)
[Please turn over
Fig 3 (b)
(®) List the methods available
for approximate analysis of building
frame subjected to lateral loads. Mention, the assumptions
‘Section B—Water Resources Engineering
Marks—30
(Answer
4. Write short notes on
‘any two questions)
(i) Water losses in irrigation canal;
Jay Bee counter berms;
fii) Lining of ircigation canals;
(iy) Balancing depth;
Z (4). Meffects of Irigation..
54" (a). What is meant by river training? State the objectives of river
training,
(®) What are cutoffs and how are they artificially induced? What are
the advantages and disadvantages?
(©) Determine the size of a cite
ular tile drain, draining 6 hectares of a
drainage area if the drainage coefficient is 1-5 om and grade is
4%. Assume rugosity coefficient forthe tile material is 0-013,
6 @
)
©
7)
©
8 @
&
©
0)
©
909m
‘What is meant by water logging? Explain principal causes and
effects of water logging in a irrigation canal.
Define flood. State the various causes of flood. What is meant by
design flood?
Design a regime channel for a discharge of 60 cumecs. Assume
silt factor = 1-10. Assume any reasonable value of missing data.
Section C—Environmental Engineering
Marks—30
‘(Answer any two questions)
What do you mean by filtration of water? Discuss briefly the
theories of filtration,
Draw a chlorination curve and explain the reaction zones,
‘Also explain the break point chlorination.
A slow sand filtration unit is producing 1500 m? of water/day.
How much bleaching powder with 30% available chlorine will be
required per day to treat this water with a chlorine dose of 0-5
mg/L.
What are the main types of water distribution networks? State
their relative advantages and disadvantages.
How can water demand of a community be estimated? Explai
Mention step by step procedure to calculate the flow of water in a
looped network Using Hardy Cross Method.
Discuss the types of sewer.
A 15" sewer with n = 0.015 is laid on a slope of 0-018. What is
the discharge and velocity of the sewer when flowing (i) half full
and (ii) when the depth of flow is 5-0".
Define the functional elements of waste management. State the
effect of solid waste management.
2 aaa
frre oe
civ ENGINFERING
Fst Paes
Subject Coe 881
Tine allowed-—3 hous
Fall marks —100
INB—Pieures in th aren Indica ul rs
Section A—Sirueture( Awa lysis)
Marks—40
(Answer ny tv qktions)
Marks
Analyze the frame shown below by the moment distribution method. 20
Draw the bending moment diagram and sketch the deflected shape of
the structure,
aK
| sa
1 400 int 250 int?
a T= $00 i
20K —
an
mm
f+-— 151 +} 12n —+|
A truss as shown below consists of 8 panels cach 35 metre long. 20
Find the maximum tension and compression in the member AB,
‘when a concentrated load of 10 tonnes rolls over the tras.
A
ate
+
DOOR ens
[Please turn over
08 309
foornt
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Fist PaPer 3 2-8
Subject Code : 881
Time allowed—3 hours
Full marks—100
[N.B.—Figures in the right margin indicate full marks.]
Section A—Structure (Awolys} 5)
Marks —40
(Answer any two questions)
Marks
(a Determine the reaction components and then draw the shear 10
force and bending moment diagrams for the beam loaded as
shown in Fig. 1 —
2h) 2R | 28 Bn aft
Fig. 1
@) Analyze the frame, as shown in Fig. 2, by the moment — 10
distribution method. ‘E” is same for all members,
a 50 KN
B
A fs
3m
80 KN
3m.
D
6m 3m 2m
Fig.2
[Please turn over
forces and reaction components of the space
pwn in Fig. 3 -—
Poa
Fig.3
3. (@ Mention the assumptions made in the Portal method of
structural analysis for frames subjected to lateral loads,
Mlustrate with sketches,
(6) Determine the maximum bending moments and shear forces in
‘column *CG" and girder “JK’ of the frame subjected to lateral
load as shown in Fig 4. Also draw the shear force and bending
‘moment diagrams for these two members. Use Portal method
we
Marks
20
15'.0"
20'.0"
(b)
2 @
()
3 @)
)
L @
o
2 @
o
3. (@)
oe
886m
3
Section B—Water Resources Engineering
Marks—30
(Answer any two questions)
‘Name the important types of river training method and indicate
the purposes for which each type is adopted.
Give a typical plan and sections of a Guide Bank and discuss
its design procedure step by step.
Explain the terms : (i) Flood management; (7i) Flood proofing;
Gil) Controlled flooding; and (iv) Design flood.
Discuss the advantages and illeffects of embankment as a
measure for flood management.
‘What is spur? Explain the different types of spur based on their
alignment with neat sketches.
Design a conerete lined channel to carry a discharge of 350
‘cumecs by a slope of 1 in 5000. The side slopes of the channel
are 1-5 #1 and Manning's m value may be taken as 0-014,
Assume the limiting velocity in the channel as 2m/sec.
Section C—Environmental Engineering
Marks—30
(Answer any two questions)
Explain the mechanism of filtration,
What are the operational difficulties in Rapid Sand Filter? How
can you overcome those? Explain.
Define the following terms :
@ Break point chlorination;
(ii) Critical setting velocity;
(it) Aquifer.
What is meant by free available chlorine and combined
available chlorine? Explain their mechanism with proper
reactions. How these destroy bacteria and viruses of polluted
water?
Describe the functional elements of solid waste management,
What are the methods of sanitary land filling of final disposal
of solid waste? Describe,
10
@
@
©
- (a)
@
©
@
eis
‘Time aliowed —3 hours
Full marks—100
INB—The figures in the right margin indicate full marks.)
Section A—Structure (2.0, £)
(Answer any two questions)
Marks —40
Explain the different methods for approximate analysis of
building frame subjected to lateral loads,
How does the effect of earthquake load differ from wind load
‘when imposed to structures?
In designing an interior panel of a flat plate slab with Direct
Design Method the total static moment in the long direction
is found to be 410.k-ft, Design the reinforcement for the
Panel in the column strip. Consider width of. column strip =
10ft and effective depth = 7-5 in. Use fe =4 ksi and fe= 60
ksi. Assume any reasonable data if required.
What are diagonal tension cracks in beam? How does the
formation of diagonal cracks cause the redistribution of
internal stresses in RC beam?
Explain strength interaction diagram of RC column. Also
State the necessity of using unsymmetrical reinforcement in
RC column.
A rectangular RC/beam having b = 10 in, h= 22 in, spans 18
ft of simple support. It is reinforced for flexure with 3 # 8 §
bar and is to camry a service DL = 1 31/8 (excluding self wt)
and service LL = 2-2 k/ft, both uniformly distributed along the
Span. Material strengths are : f'c = 3 ksi and fy = 60'ksi.
(@ What part of the beam to be web reinforced?
(Design the web reinforcement for the beam,
CIVIL ENGINEERING
‘SECOND PAPER
Subject Code : 882
Marks
12
ul
[Please turn over
©
(a)
0
(7
. (a)
o)
©
(a)
o
©
. (a)
o
©
classification of pre-stressed concrete
any two.
conerete with reinforced concrete with
to serviceBbility, safety and economy.
‘A 15 in brick wall supports a DL = 12 k/ft and LL = 8K/E.
‘The wail footing is to be placed at 5'-0" below the G. L and
Qa = 4 ksf is reported at that level. Design a RC footing using
fc=3-5 ksi and fy = 60 ksi.
Sectioh B—Transportation Engineering
(Answer any two questions)
Marks—30
‘What is right of way? State the factors governing the land
width of a highway.
What do you mean by highway allignment? Discuss the
factors controlling the allignment of a highway.
State the objectives of highway planning. Explain briefly the
planning survey for a highway project.
State the importance of geometric design of a highway.
Briefly discuss the geomeiric design elements of a highway.
Define the term ‘traffic volume’. Explain the different
‘methods for carrying out traffic volume studies.
isite properties of aggregates in
re-s
‘What is coning of rails? Why coning of wheels is mainly done.
Write the requirements of an ideal sleeper. Write the
advantages of sizel sleeper over wooden sleeper.
Draw the cross-section of ballast in railway. Write the
function of ballast.
Section C—Foundation Engineering
‘(Answer any two questions)
Marks—30
‘What do you mean by active and passive earth pressure?
Draw a neat diagram showing the variation of different
co-efficient of earth pressures.
A cclay stratum 5 m thick has the initial void ratio of 1-50 and
the effective overburden pressure of 120 KN/m2. When the
sample is subjected to an increased pressure of 120. KN/m?,
the void ratio reduces to 1-44. Determine the co-efficient of
volume compressibility and final settlement of the stratum,
Marks
10
9 a)
yes 00 AE
CIVIL ENGINEERING 4
Sconp Parer
Subject Code : 882 3
Time allowed—3 hours
Full marks—100
[NB.—The figures in the margin indicate full marks]
Section A—Structure € Rec)
Marks—40
(Answer any two questions)
Marks
1. Answer any five from the following questions -— 4x5=20
(@) What are the criteria that required to the design of tall buildings?
Explain them with their requirements for the Same
@) What are the different methods available for
reinforced structures? Write down the suitabi
‘methods according to BNBC.
(©) List the methods available for the design of flat plate/slab. State
ic design of
of different
the restrictions for the”use of direct design "method in flat
plate/stab design
(@ Mention the reduction factors (@) for the followings :
(flexure; (i) shear; (iti) torsion; (?v) spiral column.
‘Also state the reasons for variation of the above mentioned
‘@ values.
(©) What are the various structural forms of tall buildings? Explain
the assumptions made in analysing by factor method,
@ “Concrete of substantially higher compressive strength and
hhigher strength of steel should be used for prestressed eonerete
construction”. Justify the statement,
@ @ What do you mean by preliminary and final design of
prestressed concrete flexural member?
My
Gi) How Mo ratio influences the flexural design of a
prestressed concrete structital element?
(hy What is partial prestressing?: How ‘cart"it be done? State the
advantages and disadvantages of partial prestressing of
prestressed concrete structures,
(@ What do you mean by inflection point? Write down the
assumptions needed for analysing of building frame sibjected to
vertical load. ib
{Please turn over
Marks
coy tem consists of parallel T-beam spaced 10ft on 20
32ft between supports. The 6 inch thick slab is
ly with T-beam webs having width bw = 14 inch
ured from the top of the slab of h = 28 inch. In
‘addition to its ow weight. each T-beam must carry a superimposed
dead load of S0¥psf and service live load of 225 psf, Material
strength fy = 60 ksi and f,' = 3 ksi, Determine the required tensile
steel arealand needed rebars for atypical member.
(@) What is tap splices? What are the ACI code requirements for: 4#6=10
Lap splices in tension;
il) Compression splices;
(ati) Column splices.
@) & 13" long and 10° wide uniformly loaded slab is simply 10
Supported along two short sides; the long sides are unsupported.
The slab thickness is 8" with #5 @ bar spaced 6° de as main
‘flexural steel. Calculate the maximum uniformly load that the
slab ean carry. Given fy’ = 4 ksi and f, = GO ksi.
Section B—Transportation Engineering
Marks—30...,
(Answerany two questions)
(@) Write down the function of Ballast in a railway track.
@) Define Yard. Discuss the important points needs to be =
considered in designing Marshalling Yard,
(©) “Design the rate of super elevation for a curve of radius 400m 6
and speed of 80kivh, Also check the co-efficient of lateral
frictions.
‘Answer any three from the following questions Sedal5
@ ‘What is transportation system? What are its various functional
‘elements? Explain.
(0) What do you mean DHY? Discuss with neat sketch, What are
the specifications of this for urban area?
(@) What are the various types of regulatory speeds?'Explain them
with neat sketch
@
©
@
0)
©
we OO
a
CIVIL ENGINEERING
i Second Paper oe
Subject Code: 882 3
Time allowed—3 hours
Full marks—i00
Section A—Structure Ci c)
(Answer any two questions)
Marks—40
‘A rectangular beam having b= 12" and d=22" spans 20' face
{0 face of simple supports. It has to carry service dead load
1°63 K/f and service live load of 3-10 W/ft, both uniformly
‘istributed along the span. Design the shear reinforcement
using # 3 bar as vertical U stirrups. Material strengths are
Fe= 4000 psi and fy = 60,000 psi
Define the following terms —
Bar cutoff, Development length and Bond stress.
‘Write down the factors influencing development length of bar.
320
ncs
Marks
12
3
Discus the sittations in which ea of the following types of 6¥3-9
retaining wal is ysed? Also draw heat sketches of them:-
(© Gravity wall: i Cantilever wall and (i) Coumtefort wal
Write down the main requirements of ACI code for designing
‘cantilever retaining wall
Design the stem of a cantilever retaining wall to’ support a
bank of earth 20ft high. The top of the earth isto be level with
8 surcharge of $00 psf. Given that $=36°, allowable soil
bearing capacity = 4 ksf, fc = 3-5 ksi, fy = 60 ksi, y soil =
18 psf and ground water level is 10 ft below top level of FGL.
[Please turn over
o
@
o
©
@)
o
o
@
o
‘Why spiral column is shorter than tied column? Explain
Seeffbn B—Transportation Engineering
(Answer any two questions)
Marks—30
‘Why joints are provided in rigid pavement? What do. you
‘mean by slip form paving?
What are the factors affecting structural design of rigid
pavement? Why do we need to blend the agareuates?
Explain the following term: —
@ Apron; (i) Taxiway; (iii) Runway; (iv) Hanger; (v) Arca
Traffic Control (ATC),
What is meant by gauge of rail? What are the gauges used in
Bangladesh Railway? Would you advocate one uniform gauge
throughout the country? Why?
Explain with neat sketches the various devices used in
‘railways to divert trains from one track to another.
Discuss briefly the causes and remedies for ereep of rails.
Pilate bearing test was carried out on subgrade and base layers
Of the pavement. Plate diameter was adopted 30 em and
thickness of base layer 20 cm. The developed pressure at
0-5 em deflections are 1.0 and 4 kg/em? on sub-grade and
base-layer respectively. Design pavement for 5443 kg whee! load.
‘Tyre pressure is 6 kalem:? fora permissible deflection of 5 em.
Write short notes on:
( Plash Paint; (it) Fire Point; (it) Loss on heating test
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- IBC1997-UBC2000 Structural Comparison and Cross ReferenceDocumento240 páginasIBC1997-UBC2000 Structural Comparison and Cross Referencerobersasmita100% (1)
- Linear Static Seismic Force Procedures <40Documento28 páginasLinear Static Seismic Force Procedures <40alfieAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Static Seismic Force Procedures <40Documento28 páginasLinear Static Seismic Force Procedures <40alfieAinda não há avaliações
- A Time History Analysis Method-4689Documento8 páginasA Time History Analysis Method-4689Shekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Section DesignerDocumento191 páginasSection DesignergreatwellwisherAinda não há avaliações
- Plaxis Tutorial 01Documento33 páginasPlaxis Tutorial 01Duc Tran0% (2)
- Major Utilities Relocation For UndergroundDocumento2 páginasMajor Utilities Relocation For UndergroundShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- UG Water Line RelocationDocumento1 páginaUG Water Line RelocationShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Getting Started PDFDocumento14 páginasGetting Started PDFCeliz MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Large Underground Station ConstructionDocumento2 páginasLarge Underground Station ConstructionShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- WALLPRES ExcavationDocumento11 páginasWALLPRES ExcavationShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Hydro Utility Relocation For Laird StationDocumento2 páginasHydro Utility Relocation For Laird StationShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Utilities Relocation For Underground StationDocumento1 páginaAdvance Utilities Relocation For Underground StationShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Underground Station ConstructionDocumento1 páginaUnderground Station ConstructionShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- International Lateral LoadsDocumento38 páginasInternational Lateral LoadsRamilArtates100% (1)
- Pile DetailsDocumento1 páginaPile DetailsShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Data Interpolation From Table Using ExcelDocumento1 páginaData Interpolation From Table Using ExcelShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- ConstructionPracticesAnsProceduresManual PDFDocumento64 páginasConstructionPracticesAnsProceduresManual PDFAnonymous 2BfRGloP9iAinda não há avaliações
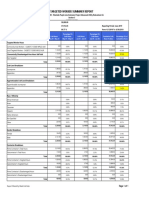
- Targeted Worker Summary Report: Economically Disadvantaged Area Hours SubtotalDocumento1 páginaTargeted Worker Summary Report: Economically Disadvantaged Area Hours SubtotalShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Diaphragm Wall ConstructionDocumento9 páginasDiaphragm Wall ConstructionShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- ELECTRICAL PLAN LEGENDDocumento3 páginasELECTRICAL PLAN LEGENDShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Channai MetroDocumento11 páginasChannai MetroShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Osha 3115Documento30 páginasOsha 3115aaa206Ainda não há avaliações
- Under Ground Reservoir DetailsDocumento1 páginaUnder Ground Reservoir DetailsShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Column Layout PlanDocumento1 páginaColumn Layout PlanShekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed0% (1)
- Pile DetailsDocumento1 páginaPile DetailsShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- b2b SpliceDocumento5 páginasb2b SpliceShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Structural steel beam dimensions and properties tableDocumento42 páginasStructural steel beam dimensions and properties tableShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Structural steel beam dimensions and properties tableDocumento42 páginasStructural steel beam dimensions and properties tableShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Torsional Irregularity Plan ASCE 7-10 EC8Documento11 páginasTorsional Irregularity Plan ASCE 7-10 EC8Shekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedAinda não há avaliações