Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Furosemide Drug Study
Enviado por
You know who0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações2 páginasDireitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações2 páginasFurosemide Drug Study
Enviado por
You know whoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
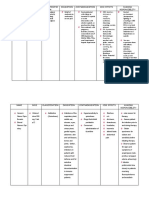
Picture
Generic Name
Brand Name
Classification
Furosemide
Apo-Furosemide (CAN),
Furosemide Special (CAN),
Lasix
Loop diuretic
Action
Furosemide inhibits reabsorption of Na and chloride mainly in the
medullary portion of the ascending Loop of Henle. Excretion of
potassium and ammonia is also increased while uric acid excretion
is reduced. It increases plasma-renin levels and secondary
hyperaldosteronism may result. Furosemide reduces BP in
hypertensives as well as in normotensives. It also reduces
pulmonary oedema before diuresis has set in.
Dosage
Tablets20, 40, 80 mg; oral solution10 mg/mL, 40 mg/5 mL;
injection10 mg/mL
Indication
Oral, IV: Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis, renal disease
IV: Acute pulmonary edema
Oral: Hypertension
Severe sodium and water depletion, hypersensitivity to
sulphonamides and furosemide, hypokalaemia, hyponatraemia,
precomatose states associated with liver cirrhosis, anuria or renal
failure.
Addisons disease.
Contraindicatio
n
Side effects
Drug
interactions
Nursing
responsibilities
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Rashes, photosensitivity, nausea, diarrhoea, blurred vision,
dizziness, headache, hypotension. Bone marrow depression (rare),
hepatic dysfunction.
Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, ototoxicity.
Potentially Fatal: Rarely, sudden death and cardiac arrest.
Hypokalaemia and magnesium depletion can cause cardiac
arrhythmias.
LASIX may increase the ototoxic potential of aminoglycoside
antibiotics, especially in the presence of impaired renal function.
Except in life-threatening situations, avoid this combination.
LASIX should not be used concomitantly with ethacrynic acid
because of the possibility of ototoxicity. Patients receiving high
doses of salicylates concomitantly with LASIX, as in rheumatic
disease, may experience salicylate toxicity at lower doses because of
competitive renal excretory sites.
1. Reduce dosage if given with other antihypertensives; readjust
dosage gradually as BP responds.
2. Administer with food or milk to prevent GI upset.
3. Give early in the day so that increased urination will not disturb
sleep.
4. Avoid IV use if oral use is at all possible.
5. Do not expose to light, may discolor tablets or solution; do not
use discolored drug or solutions.
6. Discard diluted solution after 24 hr.
7. Refrigerate oral solution.
8. Measure and record weight to monitor fluid changes.
9. Arrange to monitor serum electrolytes, hydration, liver and renal
function.
10. Arrange for potassium-rich diet or supplemental potassium as
needed.
11. Blood glucose levels may become temporarily elevated in
patients with diabetes after starting this drug.
Você também pode gostar
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocumento3 páginasDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- AmlodipineDocumento2 páginasAmlodipineMika Kudo100% (2)
- AllopurinolDocumento1 páginaAllopurinolAbigail CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Tramadol UltramDocumento2 páginasTramadol UltramatchiekAinda não há avaliações
- XareltoDocumento2 páginasXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- NitroglycerinDocumento3 páginasNitroglycerinFreisanChenMandumotanAinda não há avaliações
- OfloxacinDocumento2 páginasOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Catapres Clonidine Drug CardDocumento1 páginaCatapres Clonidine Drug CardSheri490Ainda não há avaliações
- Lasix - Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLasix - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoAinda não há avaliações
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Documento2 páginasAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Documento13 páginasDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Flauros Ryu Jabien50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento14 páginasDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaAinda não há avaliações
- ClonidineDocumento2 páginasClonidineFlora Angeli PastoresAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyFloribelle SamaniegoAinda não há avaliações
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDocumento1 páginaVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraAinda não há avaliações
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocumento2 páginasBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunAinda não há avaliações
- Generic NameDocumento2 páginasGeneric NameMichael PalmaAinda não há avaliações
- CefepimeDocumento2 páginasCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonAinda não há avaliações
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaAinda não há avaliações
- AeknilDocumento2 páginasAekniljaycey24Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoAinda não há avaliações
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocumento4 páginasGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocumento5 páginasHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdAinda não há avaliações
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocumento4 páginasAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocumento7 páginasDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyMa R DyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocumento1 páginaClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study AspirinDocumento1 páginaDrug Study AspirinGenierose YantoAinda não há avaliações
- IrbesartanDocumento3 páginasIrbesartanapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- ChlorphenamineDocumento1 páginaChlorphenaminereinaAinda não há avaliações
- OctreotideDocumento3 páginasOctreotideHatim DziauddinAinda não há avaliações
- Humalog Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasHumalog Drug StudyKristinelou Marie ReynaAinda não há avaliações
- Calcium 600/vitamin DDocumento3 páginasCalcium 600/vitamin DE100% (1)
- PropranololDocumento6 páginasPropranololanon_678895677Ainda não há avaliações
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocumento4 páginasMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayAinda não há avaliações
- DRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)Documento1 páginaDRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)rholiboiAinda não há avaliações
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento1 páginaGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocumento4 páginasDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyIrveen Joy Ramirez100% (1)
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocumento2 páginasDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study ICUDocumento5 páginasDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaAinda não há avaliações
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study-Sodium BicarbonateDocumento7 páginasDrug Study-Sodium BicarbonateTrisha Faye OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Name of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesDocumento2 páginasName of The Drug Dosage Indication and Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsbilitiesMiguel Paolo Bastillo MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Losartan Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocumento6 páginasDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaAinda não há avaliações
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Documento3 páginasFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin B ComplexDocumento2 páginasVitamin B ComplexCar_Mi_3606Ainda não há avaliações
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocumento9 páginasAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - FurosemideFeliza Therese A. DeloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Beta BlockersDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Beta BlockersDan Mandig100% (1)
- Drug Ana - FurosemideDocumento3 páginasDrug Ana - FurosemideIngrid Sasha FongAinda não há avaliações
- S 061 LBLDocumento9 páginasS 061 LBLJORGE IRAM BARRAZA ROMEROAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento19 páginasDrug StudyAngelica Bestre De La CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Furosemide DSDocumento2 páginasFurosemide DSjhanrey0810_18768Ainda não há avaliações
- Furosemide (Drug Monograph)Documento1 páginaFurosemide (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanAinda não há avaliações
- IX. Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasIX. Drug StudyAzette AgpiAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocumento6 páginasDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotAinda não há avaliações
- MedicationsDocumento23 páginasMedicationsYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin KDocumento7 páginasVitamin KYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- AminolebanDocumento2 páginasAminolebanYou know who0% (1)
- PonstanDocumento5 páginasPonstanYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Pon StanDocumento5 páginasPon StanYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Norepinephrine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNorepinephrine Drug StudyYou know who100% (9)
- Brain Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento4 páginasBrain Anatomy and PhysiologyYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Peptic Ulcer Disease PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaPeptic Ulcer Disease PathophysiologyYou know whoAinda não há avaliações
- Process Safety - Recommended Practice On KPIsDocumento36 páginasProcess Safety - Recommended Practice On KPIsKB100% (2)
- Documents - Tips Direct Determination of Tin in Whole Blood and Urine by GF AasDocumento5 páginasDocuments - Tips Direct Determination of Tin in Whole Blood and Urine by GF AasRozzy RamanandaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Flow MetersDocumento3 páginasBasic Flow Metersladybuzz89Ainda não há avaliações
- Deligate ExcelFormatDocumento60 páginasDeligate ExcelFormatrashidnyou0% (2)
- Lesson Plan Physical ScienceDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan Physical ScienceRANDOLPH CABAOBASAinda não há avaliações
- Hoeganaes CorporationDocumento11 páginasHoeganaes CorporationjohnhenryyambaoAinda não há avaliações
- Home Assignment-6 (Practice Problem) Chapter-7Documento2 páginasHome Assignment-6 (Practice Problem) Chapter-7Rounak MajumdarAinda não há avaliações
- Fiitjee: Physics, Chemistry & MathematicsDocumento14 páginasFiitjee: Physics, Chemistry & MathematicspranjalAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemicalsDocumento55 páginasOrganic ChemicalsjajajaAinda não há avaliações
- ReviewerDocumento7 páginasReviewerAriel Mark Pilotin50% (2)
- ECV5701 Notes For Concrete Inspection and Assessment-1Documento19 páginasECV5701 Notes For Concrete Inspection and Assessment-1ahmed almhjani100% (1)
- Test To Check Quality of Bitumen For Use in Road WorkDocumento13 páginasTest To Check Quality of Bitumen For Use in Road WorkTajdaarAinda não há avaliações
- Automotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocumento5 páginasAutomotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForSaravanan MAinda não há avaliações
- Influence of Adding Short Carbon Fibers On The Flexural Behavior of Textile-Reinforced Concrete One-Way SlabDocumento18 páginasInfluence of Adding Short Carbon Fibers On The Flexural Behavior of Textile-Reinforced Concrete One-Way SlabShaker QaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Nose Ring & Retaining Ring - Cooling & Refractory DesignDocumento69 páginasNose Ring & Retaining Ring - Cooling & Refractory Designzementhead100% (3)
- Reaction PaperDocumento2 páginasReaction PaperKimberly Molato0% (1)
- Q A CoatingDocumento29 páginasQ A CoatingHau Le100% (1)
- Fluitest Uric Acid AnalyticonDocumento4 páginasFluitest Uric Acid AnalyticonTjakraHarjoWiboewoAinda não há avaliações
- ANTSE Class 6 Previous Year Paper (2008-2013)Documento81 páginasANTSE Class 6 Previous Year Paper (2008-2013)Mota ChashmaAinda não há avaliações
- 000 3DT 00005 000 - 2Documento116 páginas000 3DT 00005 000 - 2anbesivam87Ainda não há avaliações
- Textile PrintingDocumento72 páginasTextile Printingspringstar96% (25)
- 5meo SynthesisDocumento2 páginas5meo SynthesisLuis López PiñeresAinda não há avaliações
- L. Saavedra, E. M. Hebert, C. Minahk, P FerrantiDocumento49 páginasL. Saavedra, E. M. Hebert, C. Minahk, P FerrantiLeidy UribeAinda não há avaliações
- Portfolio - Biological Cell Prepared by 1st Year Mbbs Student-LekshmiDocumento10 páginasPortfolio - Biological Cell Prepared by 1st Year Mbbs Student-Lekshmispillai11Ainda não há avaliações
- Improved Formation Programme For Lead Acid Batteries 1628828706Documento9 páginasImproved Formation Programme For Lead Acid Batteries 1628828706ehsan453Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio FertilizerDocumento15 páginasBio FertilizerAamir SajjadAinda não há avaliações
- Nato - Stanag 4582 - Explosives, Nitrocellulose Based Propellants, Stability Test Procedure and Requirements Using Heat Flow CalorimetryDocumento25 páginasNato - Stanag 4582 - Explosives, Nitrocellulose Based Propellants, Stability Test Procedure and Requirements Using Heat Flow CalorimetryTetis BrionesAinda não há avaliações
- Bell & Gosset PumpDocumento8 páginasBell & Gosset Pumprogel_ganaAinda não há avaliações
- Prime, Tack & Fog 2019 SL PDFDocumento42 páginasPrime, Tack & Fog 2019 SL PDFLucia SaezAinda não há avaliações