Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Glossary
Enviado por
Crit S AriosaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Glossary
Enviado por
Crit S AriosaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Hematology
Basic dye that stains the acidic part of the cell
(nucleic acids in the nucleus).
The study of blood cells and blood forming tissue,
includes RBCs, WBCs and platelets.
Hemostasis
Eosin
Acidic dye that stains the basic part of the cell
(ribosomes and other cellular parts).
The study of cellular and humoral systems that
controls blood flow, bleeding and clotting.
EDTA
Purple top - prevents clotting by removing
RBCs
Have a lifespan of about 120 days.
Coagulation Proteins
calcium, commonly used in hematology.
Manufactured in liver for forming clots.
Heparin
Platelets
Green top - inactivates thrombin and
AKA thrombocytes; work at a cellular level in
thromboplastin.
regards to hemostasis. Responsible for sealing
wounds, repairing blood vessels, and maintaining
Sodium Citrate
vascular patency.
Blue top - Binds to calcium. 1:9 ratio
Vascular
Microsamples
Keeps the veins intact in regards to hemostasis.
Includes capillary tubes, bullts/microtainers
Assessment of Red Cells and
Morphology
Capillary Sticks
Typically performed in pediatrics
Includes numeric values, cell color, size, shape,
inclusions and distribution patterns.
Unclotted Blood
Does not contain fibrinogen.
Wright Stain
Assessment of White Blood Cells
Includes numeric values, cells counts, differential
counts and flow cytometry. Used for detecting
Polychromatic stain.
leukemia.
Methylene Blue
Assessment of Platelets
Includes numeric counts, functional assays, and
morphology.
Cellularity
Fat to cell ratio, M:E Ratio (myeloid:erythroid)
Automated Hematology Tests
Assessment of Coagulation
Includes hemograms, histograms, scatterplots, auto
Includes platelet function testing,
differentials, interpretative statements and reviews.
coagulation/bleeding disorders, monitor
anticoagulant therapy, thrombosis testing, and
Manual Hematology Tests
Includes microhematocrits, calculated cell indices,
hemacytometer cell counts, microscopic
differentials, and sedimentation rates.
molecular assays.
Megaloblastic Tests
Tests for enlarged RBCs. Includes vitamin B12,
Folate, Intrinsic Factor IF Antibodies, Parietal Cell
Reticulocytes
Young RBCs (immature), tracked during the
process of diagnosis. EX: When someone is
Antibodies, Schilling Test, LDH and Gastrin.
Iron Studies
suffering from low iron, they are given iron and
Includes Iron, TIBC, % Saturation, Ferritin,
their reticulocytes are monitored to see if they
Hemosiderin, Ferritin receptors (CD 71), and Free
recover.
Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin (FEP).
Tests for Hemolytic Disorders
Reticulocyte Counts
Includes Osmotic Fragility, Autohemolysis, G6PD,
Important test where RNA is stained using new
PK, GSH, Ham's, Sucrose Lysis, DAT, Indirect
methylene or brilliant cresyl blue, both manual and
Coombs', Haptoglobin, Plasma Hemoglobin,
automated methods are available.
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis, Solubility Tests,
Fetal Hemoglobin, Hgb H, Heinz Body, LDH, and
Bilirubin.
Assessment of Bone Marrow
Includes cellularity, differentials, iron stores,
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
General screening test for inflammation. Methods
include Modified Westergren and Wintrobe.
Limitations include plasma and red cell factors,
sample integrity, and outside influences.
special techniques (molecular diagnostics and
cytogenetics), and microbiology.
Plasma and Red Cell Factors (ESR)
Inc fibrinogen and Igs will increase ESR. Sickle
cells, acanthocytes, spherocytes will decrease ESR.
Outside Influences (ESR)
Includes temperature, vibrations, tilting and
balance.
Sample Integrity (ESR)
Must be within 2 hrs of blood draw. No clots or
fibrin. Blood/anticoagulant ratio.
Early Lysis
Indicates presence of hemolytic disorders.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Blood Bank Review 2019 PDFDocumento613 páginasBlood Bank Review 2019 PDFCuddles Pingoy100% (1)
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocumento4 páginasDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationHendra SshAinda não há avaliações
- Mtle Tips & RecallsDocumento8 páginasMtle Tips & RecallsJessica OperarioAinda não há avaliações
- CANINE-Mechanism of Thrombocytopenia in Dogs With CancerDocumento11 páginasCANINE-Mechanism of Thrombocytopenia in Dogs With Cancertaner_soysuren100% (1)
- Anemia in The Young and Old Diagnosis and Management (2019)Documento220 páginasAnemia in The Young and Old Diagnosis and Management (2019)asad iraqiAinda não há avaliações
- Symposium Topic: Current Update in Diagnosis & Management of Emergency MedicineDocumento2 páginasSymposium Topic: Current Update in Diagnosis & Management of Emergency MedicineAfriza AnggriniAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Supplies List PDFDocumento3 páginasLaboratory Supplies List PDFjohn02 deanAinda não há avaliações
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocumento2 páginasCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GOAinda não há avaliações
- How To Manage Coagulopathies in Critically Ill Patients: ReviewDocumento18 páginasHow To Manage Coagulopathies in Critically Ill Patients: ReviewDaniel Balderas Anzures100% (2)
- Clinical Pathology - Peripheral Blood Smear - Part 1 (Dr. Carretas)Documento7 páginasClinical Pathology - Peripheral Blood Smear - Part 1 (Dr. Carretas)ashley nicholeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Slides UneditedDocumento103 páginasChapter 8 Slides UneditedavenapopAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocumento2 páginasBlood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchMichelle E. CapacioAinda não há avaliações
- Dade InnovinDocumento7 páginasDade InnovinchaiAinda não há avaliações
- 22012023MU1693RDocumento2 páginas22012023MU1693RmariredrosesAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Pemakaian Dan Lembar Permintaan Reagen (LPLPR)Documento8 páginasLaporan Pemakaian Dan Lembar Permintaan Reagen (LPLPR)Juli Anggarawati ChanelAinda não há avaliações
- Trombosis y Cancer ExpoDocumento31 páginasTrombosis y Cancer Expolia_20ayAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Components and Blood TransfusionDocumento38 páginasBlood Components and Blood TransfusionjosephAinda não há avaliações
- 03.LP Stock Opname Maret-20Documento11 páginas03.LP Stock Opname Maret-20anik cahyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Alteration in OxygenationDocumento8 páginasAlteration in Oxygenationraquel maniegoAinda não há avaliações
- Objectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramDocumento8 páginasObjectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramMarj MendezAinda não há avaliações
- WHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerDocumento2 páginasWHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerKathleen DyAinda não há avaliações
- AnaemiaDocumento7 páginasAnaemiaYousef El3alameyAinda não há avaliações
- Rhesus Isoimmunization: Ishen PerumalDocumento29 páginasRhesus Isoimmunization: Ishen PerumalIshen PerumalAinda não há avaliações
- Thrombin Time ReagentDocumento14 páginasThrombin Time Reagentyousra zeidanAinda não há avaliações
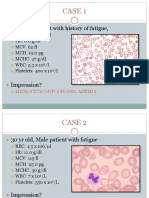
- Case 1: 25 Yr Old Patient With History of FatigueDocumento79 páginasCase 1: 25 Yr Old Patient With History of FatigueMira WryczaAinda não há avaliações
- DMH Blood Safety IndicatorDocumento7 páginasDMH Blood Safety IndicatorCharmaine Corpuz GranilAinda não há avaliações
- Monthly Blood Sugar Log Excel Template: Personal InformationDocumento5 páginasMonthly Blood Sugar Log Excel Template: Personal InformationZeeshan Hyder BhattiAinda não há avaliações
- Blood CellsDocumento10 páginasBlood CellsTItan NainiAinda não há avaliações
- Abc of BloodDocumento7 páginasAbc of Bloodsankalpw358Ainda não há avaliações
- Vox Sanguin Feb 16Documento102 páginasVox Sanguin Feb 16rsdarsono labAinda não há avaliações