Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
GRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)
Enviado por
Usman Ali Akbar0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações1 páginadad
Título original
GRAM NEGATIVE RODS(5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (a)
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentodad
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações1 páginaGRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)
Enviado por
Usman Ali Akbardad
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
Haemophilus
Bordetella
Leigonella
Genus
Species
Haemophilus influenza
Haemophilus ducrevi
Calymmatobacterium granulomatis
B.pertussis & B. parapertussis
Legionella pneumophila
Important
Properties
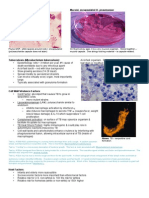
Gmall Gram ve Cocco bacilli
Encapsulated
Req heme( X) & NAD (V) factor for
respiration
Type B (polyribitol phosphate)
Carried in throat
Found only in humans
Infects only humans no
animal reservoir
Enters body through URT
asymptomatic colonization/
infections
Pertussis: small coccobacillary, encapsulated gram ve
rod
Small, silvery,dome-shaped colonies
found only in humans
highly contagious
primarily in infants + young children
Environmental bacteria
Grow in water e.g. air-con cooling units
Airborne droplets produce during severe coughing
episodes
1. Outbreaks when bact grow to high density
in cooling units and spread as aerosol in
air-con mist from cooling tower
2. Colonization of taps, shower heads etc can
give an infective aerosol
person to person dont occur
Portal of entry = respiratory tract
Pathological changes occur primarily in the
lung
Transmission
Pathogenesis
1. Produce IgA protease
2. Degrades secretory IgA
3.
4.
5.
Clinical
facilitate attachment to resp.
mucosa
Enter blood stream, spread to
meninges
Anti-phagocytic capsule +
endotoxin
Most infection occur in
children peak in 6 mth -1
yr: decline in maternal IgG +
inability to generate sufficient
AB against polysaccharide
capsule Ag till 2 yo
Impt cause of URT infection (
otitis media, sinusitis,
epiglottis) and sepsis in
children
Pneumonia in adults esp
1. attach to ciliated epi of URT but dont invade
underlying tissue mediated by filamentous
hemagglutinin on pili
AB against this inhibit attachment + protect against
disease
decrease cilia activity death of ciliated epi cells
2. pertussis toxin stimulate adenylate cyclase via
ADP ribosylation to the inhibitory subunit of
G protein complex
Rise in cAMP
Toxin has domain that mediate binding to Rc on
surface of resp epi cells
Cause lymphocytosis by inhibiting signal
transduction by chemokine Rc via ADP
ribosylation, lymphocytes fail to enter lymphoid
tissue, increase no in blood
3. Synthesize & export adenylate cyclase
inhibit bactericidal activity when taken up by
phagocytic cells
4. Tracheal cytotoxin = fragment of bacterial
peptidoglycan damage ciliated cells of resp
tract
Act in concert with endotoxin to induce NO whch
kills epithelial cells
Whooping cough
Primarily in young children
Adults: paroxysmal cough of varying severity for
wks whoops absent, difficult to diagnose
Acute tracheobronchitis
Major virulence factor:
Lipopolysaccharide endotoxin
No exotoxin produced
Typical candidate:
Old man who smokes & consume substantial
amt of alcohol
Pt with AIDS, CA, transplants (esp renal), on
corticosteroids
3. CMI impt defense mechanism
Range from mild flu like illness to severe
pneumonia, accompanied by mental
confusion, nonbloody diarrhea,
Você também pode gostar
- PlandemicDocumento82 páginasPlandemicOya Soulosophy100% (5)
- DR Vernon Coleman We'Re All Prisoners - With No Signs of ParoleDocumento6 páginasDR Vernon Coleman We'Re All Prisoners - With No Signs of ParoleGeorge KourisAinda não há avaliações
- The Virus Misconception Part 1Documento14 páginasThe Virus Misconception Part 1Zdravlje MarijaS100% (1)
- Micro I ReviewDocumento15 páginasMicro I ReviewEmilee Tu100% (1)
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Documento26 páginasMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovAinda não há avaliações
- Mycobacterium LectureDocumento39 páginasMycobacterium LectureDegee GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Transfusion Practices 2017 PDFDocumento135 páginasNeonatal Transfusion Practices 2017 PDFHarry Febryanto0% (1)
- Animal Experiments in Medical MicrobiologyDocumento70 páginasAnimal Experiments in Medical Microbiologyira_praharaj100% (3)
- Infectious Disease Pathology p31-55Documento25 páginasInfectious Disease Pathology p31-55zeroun2450% (2)
- Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-1Documento24 páginasChapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-1Hillani TadesseAinda não há avaliações
- MycologyDocumento68 páginasMycologyaalipuriaAinda não há avaliações
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!No Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Gram Positive BacilliDocumento6 páginasGram Positive BacilliSteve ShirmpAinda não há avaliações
- Organophosphate Poisoning Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocumento23 páginasOrganophosphate Poisoning Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology: Eukaryotes & ProkaryotesDocumento7 páginasMicrobiology: Eukaryotes & ProkaryotesJohn Christopher Luces100% (1)
- TuberculosisDocumento54 páginasTuberculosisibnbasheer93% (15)
- Microbial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocumento30 páginasMicrobial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemChristopher Eria Santiañez0% (1)
- Midterm Exam Structure of EnglishDocumento2 páginasMidterm Exam Structure of EnglishReñer Aquino BystanderAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Chap 19Documento30 páginasMicro Chap 19Farah ZahidAinda não há avaliações
- BordetellaDocumento54 páginasBordetellatummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Respi-micro-WEEK-10-pdfDocumento4 páginasRespi-micro-WEEK-10-pdfalfonsojo002Ainda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Lecture 3: Respiratory Tract Infections Medicine Ii Dr. Anna Lynda Bellen ZjrnateDocumento9 páginasMicrobiology Lecture 3: Respiratory Tract Infections Medicine Ii Dr. Anna Lynda Bellen Zjrnatezahj nateAinda não há avaliações
- K10 - Important Pathogenic Bacteria During Child (Mikrobiologi)Documento42 páginasK10 - Important Pathogenic Bacteria During Child (Mikrobiologi)Juanto Tio VocAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial Causes of URIDocumento28 páginasBacterial Causes of URIOmar MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- LegionellaDocumento17 páginasLegionellaShubham Pareshkumar KadiwalaAinda não há avaliações
- Immunity To FungiDocumento29 páginasImmunity To FungiNoor NawawraAinda não há avaliações
- Parvobacteria: Dr. Shehab Ahmed LafiDocumento61 páginasParvobacteria: Dr. Shehab Ahmed Lafiقدامه زين العابدين حسان عثمانAinda não há avaliações
- U1T2Documento1 páginaU1T2Jay KayAinda não há avaliações
- Bordetella: Bordetella Organisms Are Small, Gram-Negative Coccobacilli Which Are Strict Aerobes. The ThreeDocumento7 páginasBordetella: Bordetella Organisms Are Small, Gram-Negative Coccobacilli Which Are Strict Aerobes. The ThreeFlor OMAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran Pernafasan BawahDocumento38 páginasInfeksi Saluran Pernafasan BawahajenghalidaAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran Pernafasan BawahDocumento36 páginasInfeksi Saluran Pernafasan BawahMhmd Rifki FaizAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaDocumento49 páginasLecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaHabeeb Ali Baig100% (3)
- 1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionDocumento87 páginas1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionCoy NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- COXIELLADocumento6 páginasCOXIELLAFatima AbasovaAinda não há avaliações
- Haemophilus, Bordetella, Brucella,: and FrancisellaDocumento29 páginasHaemophilus, Bordetella, Brucella,: and FrancisellaDaniel AtiehAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive BacilliDocumento7 páginasGram Positive Bacillieros18Ainda não há avaliações
- Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocumento55 páginasBenito K. Lim Hong III, M.DCoy NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- Pratami Adityaningsari Bag MikrobiologiDocumento55 páginasPratami Adityaningsari Bag MikrobiologiAfnAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocumento44 páginasDiseases of The Respiratory SystemEugenia Ceban100% (2)
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Which Is A Gram-Positive, Acid-Fast Aerobic Bacillus and CanDocumento15 páginasPulmonary Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Which Is A Gram-Positive, Acid-Fast Aerobic Bacillus and CanAIMAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Mechanisms of PathogenicityDocumento48 páginasMicrobial Mechanisms of PathogenicitywfAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology: August 31, 2011 Mary Ann C. Bunyi, MDDocumento4 páginasMicrobiology: August 31, 2011 Mary Ann C. Bunyi, MDLenard PlatonAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Mikrobiologi (Dr. Enny S, M.kes)Documento115 páginas5 Mikrobiologi (Dr. Enny S, M.kes)fitkaAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumocystis CariniiDocumento31 páginasPneumocystis CariniiAayush GhimireAinda não há avaliações
- CLERKS Diagnostic Exam Microbiology 2022Documento10 páginasCLERKS Diagnostic Exam Microbiology 2022Dey SibalAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Last Moment RevisionDocumento16 páginasMicrobiology Last Moment RevisionDeepak MainiAinda não há avaliações
- MICROBIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH - GreenDocumento5 páginasMICROBIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH - GreenBenjamin GaliaAinda não há avaliações
- (SGD) PathologyDocumento6 páginas(SGD) PathologyPaulene RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Part Four - Intro: Bien Ernal, RPHDocumento31 páginasPart Four - Intro: Bien Ernal, RPHTrisha Anne MinoAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Lab Guide Brawijaya University ENT DiseasesDocumento32 páginasMicrobiology Lab Guide Brawijaya University ENT DiseasesfhfebriiAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocumento9 páginasMicrobial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemAnaAinda não há avaliações
- Textbook of Respiratory Disease in Dogs and Cats Bacterial Pneumonia in Dogs and CatsDocumento10 páginasTextbook of Respiratory Disease in Dogs and Cats Bacterial Pneumonia in Dogs and CatsDiego CushicóndorAinda não há avaliações
- Gram-Negative Rods Related To TheDocumento28 páginasGram-Negative Rods Related To ThekebaridukeAinda não há avaliações
- Bordetella: Dr.R.Varidianto Yudo T.,Mkes Laboratorium Mikrobiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hang TuahDocumento16 páginasBordetella: Dr.R.Varidianto Yudo T.,Mkes Laboratorium Mikrobiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hang TuahvenniariskiaAinda não há avaliações
- Bordetella Pertussis Species and Whooping Cough PathogenesisDocumento2 páginasBordetella Pertussis Species and Whooping Cough PathogenesisKat SunicoAinda não há avaliações
- SGL 11Documento29 páginasSGL 11fasdfAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Positive Bacteria ChartDocumento1 páginaGram Positive Bacteria ChartAngelina IafanoAinda não há avaliações
- Childhood Pathogens: Acute Epiglottitis and Whooping CoughDocumento42 páginasChildhood Pathogens: Acute Epiglottitis and Whooping CoughJosephine IrenaAinda não há avaliações
- Haemophilus influenzae: Growth Requirements and PathogenesisDocumento11 páginasHaemophilus influenzae: Growth Requirements and PathogenesisEd Daniel DavisAinda não há avaliações
- P.auroginosa and Bordetalla Pertusiss''''Documento6 páginasP.auroginosa and Bordetalla Pertusiss''''Hisham ChomanyAinda não há avaliações
- Airborne Transmission: Nurul Aqmar Mohd Nor Hazalin Phc454 - Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyDocumento27 páginasAirborne Transmission: Nurul Aqmar Mohd Nor Hazalin Phc454 - Pharmaceutical MicrobiologySuhaila Abdul RahimAinda não há avaliações
- 3b. Fungi ZugerDocumento27 páginas3b. Fungi Zugerbintang25Ainda não há avaliações
- Microbiology UW New by FinalstepsDocumento41 páginasMicrobiology UW New by Finalstepsxinfox11Ainda não há avaliações
- Micro Chap 21Documento50 páginasMicro Chap 21Farah ZahidAinda não há avaliações
- Infeksi Saluran Pernafasan Bawah (MIKRO)Documento36 páginasInfeksi Saluran Pernafasan Bawah (MIKRO)GamarfbajammalAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Chapter 17Documento8 páginasMicro Chapter 17Ana AbuladzeAinda não há avaliações
- Pathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractDocumento28 páginasPathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractLeeShauran100% (2)
- MB DiseasesDocumento12 páginasMB DiseaseslaritzaAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Renal Failure Long CaseDocumento2 páginasChronic Renal Failure Long CaseUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachDocumento3 páginasChronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Tubular Acidosis SummaryDocumento1 páginaRenal Tubular Acidosis SummaryUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- CRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX Pathway - AdjDocumento1 páginaCRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX Pathway - AdjUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Polycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsDocumento1 páginaPolycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Obstructive Airway Diseases ExplainedDocumento53 páginasObstructive Airway Diseases ExplainedUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento2 páginasNephrotic SyndromeUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- CRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX PathwayDocumento1 páginaCRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX PathwayUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisDocumento3 páginasUrinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjDocumento1 páginaRenal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Dialysis Treatment Options: Peritoneal Dialysis vs HemodialysisDocumento2 páginasDialysis Treatment Options: Peritoneal Dialysis vs HemodialysisUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Renal TransplantDocumento2 páginasRenal TransplantUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionDocumento9 páginasGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionDocumento9 páginasGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Ibs Presentation PDFDocumento18 páginasIbs Presentation PDFUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Recurrent Nausea Andor VomitingDocumento8 páginasRecurrent Nausea Andor VomitingUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocumento13 páginasAnaemia in PregnancyUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- King Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Documento40 páginasKing Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Usman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocumento13 páginasAnaemia in PregnancyUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- IBS Pathophysiology & ManagementDocumento18 páginasIBS Pathophysiology & ManagementUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- CORD PROLAPSE GUIDEDocumento2 páginasCORD PROLAPSE GUIDEUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Calendar 2016-2018Documento3 páginasClinical Calendar 2016-2018NickAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Visiting Student Medical Status Form PDFDocumento1 páginaForeign Visiting Student Medical Status Form PDFUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Recurrent VomitingDocumento16 páginasRecurrent VomitingUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Subject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THDocumento1 páginaSubject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- When Hope DiesDocumento2 páginasWhen Hope DiesUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- TSMEntry 2Documento1 páginaTSMEntry 2Usman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Diseases of The StomachDocumento17 páginasDiseases of The StomachUsman Ali AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Try Out II SBMPTN 2018 Paket 320Documento3 páginasSoal Try Out II SBMPTN 2018 Paket 320Siappudan Ni DainangAinda não há avaliações
- ESTERILIZACION s12560-023-09551-6Documento18 páginasESTERILIZACION s12560-023-09551-6Carolina Alveal GaticaAinda não há avaliações
- 203 2021 Article 2248Documento12 páginas203 2021 Article 2248Liam Eiwel ParasAinda não há avaliações
- Tanzania National Strategic Plan For The Control of Viral Hepatitis 2018-19-2022-23Documento72 páginasTanzania National Strategic Plan For The Control of Viral Hepatitis 2018-19-2022-23daniel mwanduAinda não há avaliações
- COVID-19-schools-transmission-August 2020Documento31 páginasCOVID-19-schools-transmission-August 2020FranAinda não há avaliações
- Farmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik Favipirafir Dan RemdesivirDocumento9 páginasFarmakodinamik, Farmakokinetik Favipirafir Dan Remdesiviranggara apAinda não há avaliações
- Commercial Dispatch Eedition 6-28-20Documento24 páginasCommercial Dispatch Eedition 6-28-20The DispatchAinda não há avaliações
- XDVXXDocumento11 páginasXDVXXMarcelis SuryaAinda não há avaliações
- Stock Update 3-4-2023Documento2 páginasStock Update 3-4-2023Classic LoveAinda não há avaliações
- Liječenje zapperom za preko 100 bolestiDocumento7 páginasLiječenje zapperom za preko 100 bolestiMićo RadenovićAinda não há avaliações
- Isolation and purification of bacteriophages from sewage through enrichment, centrifugation and plaque assay techniqueDocumento5 páginasIsolation and purification of bacteriophages from sewage through enrichment, centrifugation and plaque assay techniqueBrilliant SiemaAinda não há avaliações
- Handout Week 1Documento8 páginasHandout Week 1Vien Lovelle Macanip Cabug-osAinda não há avaliações
- Systems Biological Assessment of Immunity To Mild Versus Severe COVID-19 - SMDocumento41 páginasSystems Biological Assessment of Immunity To Mild Versus Severe COVID-19 - SMGabrielaAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Fever PresentationDocumento11 páginasDengue Fever Presentationhira khanAinda não há avaliações
- COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate QR CodeDocumento1 páginaCOVID-19 Vaccination Certificate QR CodeXyrene Del RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Medical Microbiology 6th Edition Patrick R MurrayDocumento3 páginasTest Bank For Medical Microbiology 6th Edition Patrick R MurrayJohnCampbellyacer100% (33)
- Infection and ResponseDocumento26 páginasInfection and ResponseStefaniya Dmitrievna “Stef” DeminetsAinda não há avaliações
- Patient Tests Positive for COVID-19Documento1 páginaPatient Tests Positive for COVID-19HibaAliAinda não há avaliações
- 20.1 Viruses BIODocumento42 páginas20.1 Viruses BIOZac ToglawAinda não há avaliações
- Micro VioletDocumento29 páginasMicro VioletmetAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Testing For COVID-19 - Dr. Trilis Yulianti, M.kesDocumento20 páginasLaboratory Testing For COVID-19 - Dr. Trilis Yulianti, M.kesYayax RakhmanAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On Immune SystemDocumento6 páginasDrugs Acting On Immune SystemSORENI SORENIAinda não há avaliações
- Immunology Assignment DefinitionsDocumento4 páginasImmunology Assignment DefinitionsJuflita Claudya Sweetni RottieAinda não há avaliações