Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Feb. 8, 1966 L.. H. Smith 3,233,345: Filed July Lí 1964 2 Sheets-Sheet L
Enviado por
cvkkkk1Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Feb. 8, 1966 L.. H. Smith 3,233,345: Filed July Lí 1964 2 Sheets-Sheet L
Enviado por
cvkkkk1Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Feb.
8, 1966
l.. H. SMITH
3,233,345
EDUCATIONAL DEVICES
Filed July l 1964
2 Sheets-Sheet l
ATTORNEY
Feb. 8, 1966
L_. H, SMITH
'
3,233,345
EDUCATIONAL DEVICES
Filed July l, 1964
2 Sheets-Sheet 2
BY
ATTORNEY
United States Patent O
ICC
the device to teach the inverse relationship of addition
3,233,345
This invention relates to improvements in educational
devices and is more particularly addressed to an improved
basic mathematics teaching and learning aid. The pres
Patented Feb. 8, i966
2
and subtraction, both said views showing the partial
EDUCATIGNAL DEVICES
Lelia H. Smith, 1529 W. Lane St., Lakeland, Fla.
Filed .Iuly 1, 1964, Ser. No. 379,579
6 Claims. (Cl. 35-31)
3,233,345
or answer covers in their raised or answer-exposing
positions; and
Ul
FIGS. 7 and 8 are views similar to FIGS. 5 and 6 set
up to teach not only multiplication and division as such
but also the inverse relationship of one such operation to
the other.
Referring to the drawings in greater detail, a mathe
ent application for Letters Patent for such a device is
matics learning aid or device as herein contemplated,
a continuation-in-part of my application Serial No. 10 in its structural aspects, comprises: a preferably square
208,175, tiled June 21, 1962 (now abandoned).
card or plate 10 of rigid material, such as stit cardboard,
Among the objects of the present invention may be
noted the provision of an improveai, simplied device
designed to aid children and others in learning the basic
addition, subtraction, multiplication and division com
binations of arithmetic; the provision of such a device
of indicators l2, 14, one disposed on one face and the
other on the opposite face of said plate and being con
nected `to one another for rotary movement in unison
which further provides an effective aid to the learning
16 extending through the middle-length points of said
which constitutes the body member of the device; a pair
about the center of said plate both by a common pivot
and understanding of the inversely related operations
indicator and the center oi the plate and by an indicator
on numbers, i.e. subtraction as the inver-se of addition,
division as the inverse of multiplication, and vice versa,
not as separate and unrelated operations but, instead, as
from said center and which passes through an arcuate
sets of very denitely related operations; the provision
of an improved dial-type mathematics learning aid char
acterized by its ability to spell out a plurality of dilerent
mathematical sentences for solution and ultimate verifi
cation by the user thereof; the provision of an improved
connecting rivet or pin 13 spaced radially outwardly
slot 2li provided in the plate; and partial covers 22, 24
(to be hereinafter referred to as answer covers) hinged
ly secured to the opposite side edges of said plate 10 for
25 raising and lowering motion with respect thereto by
hinge means generally designated 22a, 24a. Preferably,
dial-type mathematics learning aid characterized by dials,
said hinge means 22a is of a type as to bias the partial
cover 22 with which it is associated towards one face
indicators and information on or associated with the
of the plate, and said hinge means 24a is similarly of
opposite faces of a card- or plate-form body member,
a type as to bias the partial cover plate 24 against the
and which is so constructed and arranged as to be ca
opposite face of said plate. A simple hinge means pro
pable, upon corresponding rotary movement of the indi
cators with respect to the dials, of spelling out inversely
related mathematical sentences on said opposite faces;
the provision of a dial-type mathematics learning aid as
aforesaid employing a novel arrangement and mounting
of cover plates serving normally to mask the answer por
tion of said mathematical sentences but which can be
raised to an answer-exposing position enabling the learner
viding the requisite bias on each said cover plate as
aforesaid is shown to comprise a plurality of endless
rubber bands which are threaded through aligned holes
in the edge of each partial cover plate and the edge
of the body plate to which the latter connects, said rub
ber bands being sutlciently small that they always snug
the cover plates against the body plate as shown in
FIG. 3. It will of course be understood that any other
or user to verify his answers for said sentences; and the 40 hinge means having cover plate to body plate biasing
provision of an effective basic mathematics learning aid
as aforesaid of simple construction and of a design lend
ing itself to inexpensive manufacture, and which is tho
roughly dependable in its operation.
The above and other objects and features of advantage
of a basic mathematics learning aid according to the in
vention will appear from the following detailed descrip
tion, in which reference is had to the accompanying
drawings illustrating preferred physical embodiments
thereof, wherein
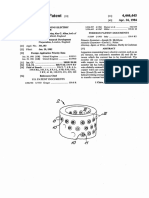
FIG. 1 is a perspective View generally illustrating the
constructional details and partial cover arrangement of
a mathematics learning aid or device accor-ding to the
invention, the covers being shown in full lines in their
normal answer-masking position, and in broken lines in
their answer-exposing position;
function may be substituted for said endless rubber bands.
According to the invention, each face of the plate 19
is imprinted or otherwise provided with two sets of di
ametrically opposed numbers arranged in connecting right
' and left-hand semi-circles of like radius struck from the
center of the plate 10, the numbers of each set being
spaced equally apart and the diametrically opposed num
bers of the two sets being disposed on diameters of the
full circle defined by said two semi-cylindrical sets of
numbers. Preferably, the indicators 12 and 14 have
slightly less length than the diameter of said circle and
are provided with pointed ends, thus to facilitate the set
ting of the indicators and the reading of the diametrically
opposed numbers of the semi-circular sets thereof to
which the opposite ends of the indicators point. Thus,
each face of the plate 10 resembles a circular dial and
each rotary indicator (12 or 14) associated therewith gen
the lower edge thereof;
erally resembles a diameter-like hand or pointer turning
FIG. 3 is an enlarged section taken on line 3--3 of
about the center of said dial.
FIG. 1, which is intended to illustrate that the rotatable 60
Preferably, the aforesaid arcuate slot 20 in which the
indicators associated with the opposite faces of the de
non-centrally disposed indicator-connecting pin 18 op
vices are mounted to turn in unison;
erates extends along a vertical arc of approximately 180.
FIG. 4 is a detail view illustrating a slightly modied
Accordingly, the action of said pin and its slot 2t) is to
form of indicator characterized by a radially enlarged
limit the rotary motion of the indicators to a range such
hub portion designed to cover its pivoting and motion
that the mathematical operations capable of being per
limiting means;
formed by the device are always accurate and meaning
FIG. 5 is a plan view of a mathematics learning aid
ful, as will be hereinafter more fully explained. The
or device as herein proposed designed for use in teach
slot 20 may be left exposed as in FIG. 1, or it may be
ing addition and FIG. 6 is a similar view showing the
masked through the provision of cover sheets on the
outer faces of the large diameter hub portions 12a, 14a
reverse .side of the device adapted to teach subtraction,
said ligures taken together further showing the use of
provided on the indicators 12, 1li, as shown in FIG. 4.
FIG. 2 is an edge view looking onto said device from
3,233,345
3
The aforesaid partial covers 22, 24 are provided in their
14, 8, 16, 9, ll, 17, 13, 10 and l5 (reading upwardly)
free edges with semi-circular cut-outs 28, 30, respectively,
are placed so as to make up the left-hand semi-circle.
of radius such as to permit motion of the indicators 12,
14 within their respective ranges without interference
from said covers, while at the same time leaving the
covers each with a circular edge portion configured and
Although the indicator 14, as was the indicator 12, is im
printed or otherwise provided with the number S, the op
erational symbol for subtraction is of course the negative
located so as to mask. the right-hand semi-circular set of
numbers on each face of the plate when said covers are
clockwise movement of the indicator 14 up the left-hand
in their respective lowered positions.
(_) rather than the positive (-1-) sign. Thus, with
semi-circular set of numbers, the device is adapted to spell
out the mathematical sentences 12-8=4, 14-8=6,
According to a further feature of the invention, the
8-8=0, etc., the learning of which aids the user in ac
indicator 12, 14 each has impressed or otherwise provided
quiring a knowledge of the basic principles of subtraction,
thereon an operational symbol and a number, which are
such that when they are combined with any two diamet
the answer cover 24 further assisting in this respect as it
enables the user to test out his so acquired knowledge.
rically opposed numbers of the semi-circular sets thereof,
But at least equally importantly, the device enables the
user to acquire the further understanding of the inverse
there is spelled out a complete mathematical sentence.
Thus, it is possible for as many mathematical sentences
to be spelled out on each face of the device as there are
related numbers in the opposed semi-circular sets thereof.
relationship of subtraction to addition, and vice versa,
merely by flipping the device 180 labout ya vertical axis
extending through same. ln explanation of this important
function of the device, the transposition of the numbers
' The manner of applying a device having the structural
features as just _described as an aid to learning the basic 20 making up the semicircular sets thereof on the opposite
faces of the device, taken with the fact that the indicators
addition, subtraction, multiplication and division combina
move in unison, provide that a mathematical sentence of
tions of numbers, as well as to a proper understanding of
addition and an inversely related sentence of subtraction
the inversely related operations involved in the addition
are invariably disposed back-to-back. That is to say, if
and subtraction, and in the multiplication and division of
numbers, will now be explained. Referring iirst to FIGS. 25 the addition face is up and the indicator 1?. spells out the
5 and 6, which show the device set up for both simple
mathematical sentence, 4-l-8=12, for example, the in
addition and subtraction problems on each of its opposite
versely related sentence of subtraction, 12-8=4, is
faces and also in manner as to illustrate the inverse rela
spelled out by the indicator 14 on the opposite face of
tionships involved in the operations of addition and sub
the device. Since this same back-to-back disposition ob
traction of numbers, it will be noted that the face of 30 tains for all mathematical sentences of addition and sub
the card or plate 10 shown in FIG. 5 has imprinted there
traction capable of being spelled out by the device, the
on a left-hand semi-circle A made up of the Whole num
bers 0 through 9 arranged at random; that the opera
tional symbol appearing on the indicator 12 associated
with said face is -{-8=, such being the addition or plus
sign, the number 8 which it will be understood is typical
of any of the whole numbers 0-9, etc. which is to be
added to the numbers of the semi-circle A, and the equa
tion sign; and a right-hand semi-circle B of numbers,
being those which correctly complete the mathematical
sentences represented respectively by the number of the
left-hand semi-circle to which the left end of the indicator
12 may point, plus the number 8 appearing on said indi
cator. For example, if the numbers of the left-hand cir
cle are (reading downwardly) the randomly related num
bers, 4, 6, 0, 8, 1, 3, 9, 5, 2 and 7, the numbers making
up the right-hand semi-circle thereof (reading upwardly)
will be 12, 14, 8, 16, 9, l1, 17, 13, l0 and 15, since these
user thereof can establish the inverse relation of one sen
tence to its inversely related sentence simply by ilipiping
the device over from right-to-left or from left-to-right,
as the case may be.
Referring now to FGS. 7 and 8, such illustrate a math
ematical learning aid according to the invention set up
to teach both simple problems of multiplication and di
vision, and an understanding `as well of the inverse rela
tion that multiplication and division bear to one another.
More particularly, FG. 7 shows a device structurally
similar in all respects to that previously described in con
nection with FIGS. 1_3, for example, and which differs
from the device described in connection with FIGS. 5 and
6 only in that mathematical sentences of multiplication
and division are substituted for those of addition and sub
traction characterizing said lower numbered views. Thus,
in FlG. 7 the face of the plate termed the multiplication
latter numbers are the answer portions (sums) of the
face has a left-hand semi-circle E of the whole numbers
mathematical sentences i4-8:12, 6-}-8=14, 0-|-8=8,
50 0-9, inclusive, shown as arranged in the random order
etc. capable of being spelled out by the device as the in
dicator is turned throughout the range of its permissible
180 turning motion in counterclockwise direction.
However, it will be understood that these answer por
tions are normally masked by the partial cover 22 which
thus serves as an answer cover but which is capable of
being very simply raised to expose said answer. Ac
cordingly, the user of the device has at hand the means
of 0, 6, 9, 7, 2, 3, 5, l, 4 and 8; the indicator 12 bears
the operational symbol ><6= indicating respectively
the operation of multiplication `and that the number 6 has
been selected as the multiplier; and a right-hand semi
circle F of answer or product numbers, which are of
course the numbers which complete the respective math
ematical sentences `of multiplication, for example,
to test his ability to correctly complete the sentence and
thereupon to verify his answer or solution simply by lift
00 capable of being spelled out by the device With move
ing said cover, thus to expose the number toward which
ment of the indicator to positions in which its left end
the pointed right end of the indicator 12 is then pointing.
points to a number of the left-hand semi-circle. Thus,
To adapt the device as just described for use not only
the numbers of the right-hand semi-circle are, reading
as an aid to the learning of simple problems of subtrac
downwardly, 48, 24, 6, 30, 18, 12, 42, 54, 36 and 0,
tion as well as addition but also to a proper understand
which are of course the respective (normally covered)
ing of the inverse relationship that subtraction bears
products of the sentences of multiplication capable of be
to addition, and vice versa, the opposite or so-called sub
ing spelled ou-t by the illustrated device.
traction face of the plate or card 10 is imprinted or other
The so-calle-d division face, shown in FIG. 8, bears the
wise provided with the identical semi-circular sets of
identical numbers appearing on the multiplication face,
numbers as the rst described or addition face, but as will 70 but such are arranged as sentences of division and also
be seen from FIG. 6, the sets of numbers (designated C
to show the inverse relation that division bears to multi
and D) are transposed from right to left and from left
plication, by arranging the inversely related sentences in
to right. T hat is to say, on said subtraction face, the 4,
back-to-back relation with respect to one another. Thus,
6, 0, 8, 1, 3, 9, 5, 2 and 7 series of numbers are placed so
as seen in FIG. 8, the product numbers of FlG. 7 are
as to make up the right side semi-circle, whereas the 12,
here the dividend numbers, being arranged in the left
3,233,345
hand semi-circle G; Vthe multiplicand numbers of FIG. 7
are here the quotient numbers, being arranged in the nor
mally right-hand semi-circle H; and of course-the opera
tional symbol is the division (+) rather than the multi
plication sign as in-FIG. 7.
indicator in either direction past the vertical diameter line
of the circle, said indicator having operational symbols
and a number impressed thereon which are readable left
to right along the length thereof, the aforesaid numbers
and operational symbols bearing a mathematical relation
'
Thus, in addition to establishing by proper use of the
device that 54+6=9, 30-:-6=5, and so on, a child or
As above
such that when the indicator is turned to any one num
ber of the left-hand semi-circular set thereof said num
ber in concert With the operational symbols, the number on
the indicator and the diametrically opposed number of the
right-hand set thereof spell out a complete mathematical
sentence, and a partial cover hingedly connected by
hinge means to a side edge of said base member adja
explained, such follows from the baek-to-back disposi
tion of the inversely related sentences of multiplication
and division capable of being spelled out by the device.
cent one semi-circular set of numbers and having a free
edge portion which is configured so as to mask all num
bers of said one set `from vieW While permitting turning
other user can also learn the inverse relationshipof such
sentences of division to the above set forth sentences of
multiplication, i.e. 9X6=54, M5><6=3O (and vice versa)
simply by flipping the device about a'vertical axis to bring
one or the other face of the device to view.
movement of the indicator throughout its permissible
While the hinge means 22a, 24a normally serve to bias
range of movement, said hinge means biasing said partial
the partial covers 22, 24 to positions in which they cover
cover to aposition in Which it lies substantially flat against
the answer portions ofthe mathematical sentences cap
said base member and thereby masks said one set of num
able of being spelled out by the subject learning aid on
only one face thereof, preferably said hinge means are 20 bers from View, but permitting movement of said par
tial cover to a raised position in which it exposes said
each of a type such that they are also capable of bias
one set of numbers and thereby renders fully visible any
ing the partial covers to positions in which they overlie
one complete mathematical sentence spelled out by the
the opposite dial face, thus to cover the identical semi
device as aforesaid.
circular set of numerals appearing on said opposite dial
2. A mathematics learning aid according to claim 1,
face. Such a two-face cover positioning means thus pro 25
wherein said one semi-circular set of mathematical num
vides, when applied to the addition and subtraction learn
bers-represent the solution portions of the mathematical
ing aid shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, not only for the study
sentence capable of being spelled out by the device, and
and learning of mathematical sentences such as 4-}-8=12,
wherein said partial cover is hingedly connected by hinge
6-I-8=14, 0-l-8=8, etc. or 12h-8:4, 11i-8:6, 8-8=0,
etc. as previously explained, but also, by swinging the 30 means to a side edge of the base member adjacent to said
one set of numbers, thereby normally masking the solu
partial covers 22, 24 to positions in which they lie against
tion portions of said mathematical sentences from view.
the opposite dial face, for the study and solution of the
3. A mathematics learning aid comprising: a plate-form
opposed incomplete sentences of addition and subtraction,
base member; each of the opposite faces thereof having
impressed thereon two sets of numbers extending along
connected right- and left-hand semi-circles which together
namely, ?-l-8=l2, {Lf-8:14, Thi-8:8, etc. or ?-8=4,
?--8=6, .7-8=0, etc.
Similarly, the device shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, assum
define a circle and the numbers making up each semi
circular set being circumferentially spaced from one an
other and diametrically opposed to the numbers of the
ing the partial-cover hinge means 22a, 24a permit the
cover plates to swing against the respective opposite faces
of the device, will, in addition to spelling out sentences'
of multiplication and addition as above, also be capable 40 other semi-circular set; the circles defined by the semi
circular sets of numbers having the same radius and being
of presenting for study the opposed, incomplete sentences
struck
from a common center and the numbers of the
of multiplication and division, such as ?><6=54, ?><6=30,
semi-circular sets thereof on said opposite faces being ar
etc. or ?+6=9, ?+6\=2; ?-:-6l=5, and so on.
ranged back-to-back with respect to one another; a pair of
It will of course be understood that while for purpose
indicators, one on each of said opposite faces, pivotally
of simple disclosure mathematical Isentences of addition,
connected to the base member for turning movement about
subtraction, multiplication and division built upon the
said center and being connected to one another in back
one-digit numbers 0-9 inclusive, and similarly that the
to-back relation and for movement in unison, said indi
one-digit numbers 8 and 6 have been used in association
cators having the same length which is slightly less than
with the operational symbols placed on the indicators 12
the diameter of said circles defined by each two semi-cir
and i4, plural-digit and fraction numbers can be used in
cular sets of numbers and terminating in points where
stead, and of course will be used in accordance with the
by each said indicator is adapted to visually couple the
progress made by the child or user of the device in his
diametrically opposed numbers of said connected semi
study of basic mathematics through the use of the device.
circular sets thereof; stop means carried by said base
As many changes could be made in carrying out the
above constructions without departing from the `scope of 55 member for limiting motion of said connected indicators
in either direction past the vertical diameter of said cir
the invention, it is intended that all matter contained in
cles; each said indicator having operational symbols and
the above description or shown in the accompanying draw
a number impressed thereon which are readable left-to
ings shall be interpreted as illustrative and not in a limit
ing sense.
I claim:
l. A mathematics learning aid comprising: a plate
form base member, two sets of numbers impressed on a
face of said base member, said sets extending along con
nected right- and left-hand semi-circles and the numbers
making up each set being circumferentially spaced from
one another and diametrically opposed to numbers of the
other set, an indicator pivotally connected to said base
member for turning movement about an axis extending
therethrough on the center of the circle defined by said
two sets of numbers, said indicator having length which
is slightly less than the diameter of said circle and ter
minating in points thereby serving to visually couple the
diametrically opposed numbers of the sets thereof with
which the indicator is aligned at any one time, stop means
carried by said base member for limiting motion of the
right along the length thereof; the aforesaid diametrical
60
ly opposed numbers of the connected semi-circular sets
thereof on each face and the symbols and the number
impressed on the indicator for said face bearing a mathe
matical relation such that when the said indicator is turned
to a position visually coupling any two of said diarnetrical
ly opposed numbers, said indicator in concert with said
coupled numbers Will spell out a complete mathematical
sentence; said numbers and symbols being such that the
indicators together spell out sentences on said opposite
faces which are inversely related mathematically.
4. A mathematics learning aid according to claim 3,
70
wherein the numbers of one semi-circular set thereof im
pressed on each of the opposite faces of the device repre
sent the respective solutions of the mathematical sentences
capable of being spelled out on said face as aforesaid, and
wherein partial covers are hingedly connected by hinge
31,233,345
8
means to the opposite side edges of the device, one said
partiall cover being adapted normally to mask the solu
tions of the mathematical sentences capable of being
spelled out on the one face and the other said partial
cover being adapted normally to mask the solutions of
of the device in which it covers the numerals of the sen
tences opposite the answers thereof while leaving the an
swers exposed.
References Cited by the Examiner
the mathematical sentences capable of being spelled out
on the other face of the device.
'
5. A mathematics learning aid according to claim 4,
wherein said hinge means are constructed and arranged
as normally to bias the partial covers to lowered posi
tions against said opposite faces of the device in which
they mask said solutions, while permitting raising of said
covers to solution-exposing positions.
6. A mathematics learning aid according to claim 5,
wherein said hinge means are also constructed and ar- 15
ranged as to permit each said partial cover plate which is
connected thereby to an edge of the device to swing ap
proximately 360 to a position against said other face
UNITED STATES PATENTS
416,639
1,161,381
12/1889
Mullins ____________ __ 281-36
11/1915 Duffy.
2,234,075
3/1941
Carolin ________ __ 3_5-35.5 X
2,693,362
3,027,073
11/1954
3*/ 1962
Ford ____________ __ 35-73 X
Handelman ________ __ 23S-S3
165,225
FOREIGN PATENTS
6/ 1921 Great Britain.
EUGENE R. CAPOZIO, Primary Examiner.
LAWRENCE CHARLES, Examiner.
Você também pode gostar
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationNo EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Mst121 Chapter A2Documento60 páginasMst121 Chapter A2radu20122012Ainda não há avaliações
- Predictive Astro M N KedarDocumento388 páginasPredictive Astro M N KedarPrasan Nanda71% (7)
- MST121 HandbookDocumento48 páginasMST121 HandbookJon WilkesAinda não há avaliações
- T-Splines ChesapeakeDocumento6 páginasT-Splines ChesapeakeBill Erick CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Gravity and Magnetics WorkbooksDocumento63 páginasGravity and Magnetics WorkbooksSutthisrisaarng Pholpark100% (2)
- Areas and VolumesDocumento114 páginasAreas and VolumesAztec Mayan100% (2)
- Unit 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1.introduction 1.2.objectives PDFDocumento341 páginasUnit 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1.introduction 1.2.objectives PDFtoshugo100% (1)
- LEKX6306 Torque CurvesDocumento11 páginasLEKX6306 Torque Curvesmijael1393100% (1)
- Design of An Energy Efficient High Performance Drive Train: Loek MarquenieDocumento116 páginasDesign of An Energy Efficient High Performance Drive Train: Loek MarqueniePratik PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Karnaugh Map ExerciseDocumento21 páginasKarnaugh Map ExerciseAzman Ahmad100% (1)
- Gilson Slide Rule Circular Manual of OperationDocumento17 páginasGilson Slide Rule Circular Manual of OperationhughnileAinda não há avaliações
- Wind EnergyDocumento33 páginasWind Energysebascian100% (3)
- HW #3 - 2D Motion and Projectiles Mastering Physics AnswersDocumento41 páginasHW #3 - 2D Motion and Projectiles Mastering Physics AnswersQusizle72% (18)
- Common Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeDocumento171 páginasCommon Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeJessicaAinda não há avaliações
- Dividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 RatioDocumento9 páginasDividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 RatioTahirMehmood0% (1)
- RCS Characterization of A Finite Ground Plane With Perforated Apertures: Simulations and MeasurementsDocumento11 páginasRCS Characterization of A Finite Ground Plane With Perforated Apertures: Simulations and MeasurementsiamnbroneAinda não há avaliações
- Perimeter Chains Performance Standard (8A/8B/8C) .EDocumento8 páginasPerimeter Chains Performance Standard (8A/8B/8C) .EAlenAinda não há avaliações
- Essentials of Aerial Surveying and Photo InterpretationNo EverandEssentials of Aerial Surveying and Photo InterpretationAinda não há avaliações
- Dividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 RatioDocumento9 páginasDividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 Ratioleonbone0% (1)
- Parting Directions For Mould and Die Design: Lin-Lin Chen, Shuo-Yan Chou and Tony C WooDocumento7 páginasParting Directions For Mould and Die Design: Lin-Lin Chen, Shuo-Yan Chou and Tony C WooDeepak SrivastavAinda não há avaliações
- Talyrond 51 Operating InstructionsDocumento44 páginasTalyrond 51 Operating InstructionsAnenomeAinda não há avaliações
- The Robinson CalculatorDocumento13 páginasThe Robinson CalculatorRobert Adams100% (1)
- Folding AparatusDocumento4 páginasFolding AparatusUbunterAinda não há avaliações
- Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares ProceduresDocumento13 páginasSmoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares ProceduresMadan LakshmananAinda não há avaliações
- M © JG) - B) John Garlic/9r.: Sept-3, 1959 J. Gallo, SR 2,902,815Documento3 páginasM © JG) - B) John Garlic/9r.: Sept-3, 1959 J. Gallo, SR 2,902,815James LindonAinda não há avaliações
- Additional Mathematics Project WorkDocumento35 páginasAdditional Mathematics Project WorkRaakeshTharmanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 28 - Higher SurveyingDocumento4 páginasLab 28 - Higher Surveyingdevilene nayazakoAinda não há avaliações
- Go To The Homep-WPS OfficeDocumento24 páginasGo To The Homep-WPS OfficelanceAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanDocumento7 páginas6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanBecky JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Dividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 RatioDocumento4 páginasDividing Head Calculator 40 To 1 RatioDavid Cerveaux100% (1)
- Level 0 or Known As A Traditional Method of Conducting Laboratory ActivitiesDocumento9 páginasLevel 0 or Known As A Traditional Method of Conducting Laboratory ActivitiesMohamad HaziqAinda não há avaliações
- I Can Math 6Documento6 páginasI Can Math 6api-365969613Ainda não há avaliações
- 5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuarterDocumento3 páginas5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuartermrkballAinda não há avaliações
- 4024 Y04 SW 5Documento6 páginas4024 Y04 SW 5mstudy123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Grade 5 08 11Documento6 páginasMath Grade 5 08 11api-246939068Ainda não há avaliações
- Divide and Conquer For Convex HullDocumento8 páginasDivide and Conquer For Convex HullJournal of Computing100% (1)
- Examen de Auditor InternoDocumento4 páginasExamen de Auditor InternoJavier CastañedaAinda não há avaliações
- K MappingDocumento72 páginasK MappingMark Albea100% (1)
- GraphicsDocumento30 páginasGraphicsAmanya AllanAinda não há avaliações
- Oxford University Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To The MonistDocumento6 páginasOxford University Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To The Monistjuan perez arrikitaunAinda não há avaliações
- Mesh Plate PDFDocumento4 páginasMesh Plate PDFskc3128Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Ch7 ParentDocumento78 páginasGrade 8 Ch7 ParentAmaya RiceAinda não há avaliações
- Itt ProjectDocumento112 páginasItt ProjectVinay AroraAinda não há avaliações
- GMH 02 NoRestrictionDocumento5 páginasGMH 02 NoRestrictionKarma Pema DorjeAinda não há avaliações
- Apl'il 7, 1959 W. Settele ' v2,880,518Documento4 páginasApl'il 7, 1959 W. Settele ' v2,880,518राजकुमार यादवAinda não há avaliações
- Surveying Practical Lab 3Documento11 páginasSurveying Practical Lab 3FikrilAzimAbdulSani67% (3)
- Symmetry: Training by Kishor BhatiaDocumento14 páginasSymmetry: Training by Kishor BhatiaKishor kumar Bhatia100% (2)
- "I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade MathDocumento6 páginas"I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade Mathapi-303193556Ainda não há avaliações
- Wa/fer W/Mayfie/a: Dec. 28, 1937. W. W. Mayfield 2,103,332Documento6 páginasWa/fer W/Mayfie/a: Dec. 28, 1937. W. W. Mayfield 2,103,332NathanAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Math Common Core I Can StatementsDocumento6 páginas6th Grade Math Common Core I Can Statementsapi-233930784Ainda não há avaliações
- Chart Analysis Enhanced With Mathcad: Flexible General-Purpose Mathematics Software Can Be Customized For RF Design WorkDocumento6 páginasChart Analysis Enhanced With Mathcad: Flexible General-Purpose Mathematics Software Can Be Customized For RF Design WorkAldern FoxgloveAinda não há avaliações
- E N Gineering Computers: Offsets of Curves On Rational B-Spline SurfacesDocumento8 páginasE N Gineering Computers: Offsets of Curves On Rational B-Spline Surfacespeterpans01Ainda não há avaliações
- "The Map Method For Synthesis of Combinational Logic Circuits" Karnaugh, Maurice (November 1953)Documento7 páginas"The Map Method For Synthesis of Combinational Logic Circuits" Karnaugh, Maurice (November 1953)inExcelsisDeo100% (1)
- Bendixen Guide To Correspondence AnalysisDocumento15 páginasBendixen Guide To Correspondence Analysisdhaya88Ainda não há avaliações
- Mesh PlateDocumento4 páginasMesh PlateAyodele Oluwaseyi DinaAinda não há avaliações
- Mesh Plate PDFDocumento4 páginasMesh Plate PDFAyodele Oluwaseyi DinaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics-Experiment 1-Lab-ReportDocumento8 páginasPhysics-Experiment 1-Lab-Reportgacc4sitesAinda não há avaliações
- Volumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar FiguresDocumento15 páginasVolumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar Figuresmasyuki1979Ainda não há avaliações
- cmp3 GlossaryDocumento66 páginascmp3 Glossaryapi-299469383Ainda não há avaliações
- Pinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsNo EverandPinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsAinda não há avaliações
- United States Patent 1191: Davies Et A1Documento4 páginasUnited States Patent 1191: Davies Et A1cvkkkk1Ainda não há avaliações
- Sept. 4 - , 1956 A. Cherkin 2,761,445: Filed May 3, 1952 2 Sheets-Sheet 1Documento5 páginasSept. 4 - , 1956 A. Cherkin 2,761,445: Filed May 3, 1952 2 Sheets-Sheet 1cvkkkk1Ainda não há avaliações
- Gli55 User ManualDocumento126 páginasGli55 User Manualcvkkkk1Ainda não há avaliações
- TCC31 One-Way SlabsDocumento43 páginasTCC31 One-Way SlabsMuscadin MakensonAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word - 4-State of Matter - Gaseous StateDocumento5 páginasMicrosoft Word - 4-State of Matter - Gaseous StateSatya KamAinda não há avaliações
- Maglev PDFDocumento1 páginaMaglev PDFmichyimAinda não há avaliações
- Mainak Majumder: Mainak Majumder, PHD (Curriculum Vitae) Page1/12 Monash UniversityDocumento12 páginasMainak Majumder: Mainak Majumder, PHD (Curriculum Vitae) Page1/12 Monash UniversityanifaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Complex Numbers in TrigonometryDocumento13 páginasComplex Numbers in TrigonometryHimanshu TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- BCS 012Documento92 páginasBCS 012RishabhAinda não há avaliações
- Thin Walled Pressure Vessels: ASEN 3112 - StructuresDocumento11 páginasThin Walled Pressure Vessels: ASEN 3112 - Structuresaap1Ainda não há avaliações
- Matigo Mocks Uace Phy 2 GuideDocumento22 páginasMatigo Mocks Uace Phy 2 Guidebuuleivan8Ainda não há avaliações
- Rolleicord V InstructionsDocumento56 páginasRolleicord V InstructionsFranck PowellAinda não há avaliações
- Intensity LED Lights Flyer RETAIL 1013Documento2 páginasIntensity LED Lights Flyer RETAIL 1013Jole WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento4 páginasAssignment 1Jean100% (1)
- AUSPOS - Online GPS Processing ServiceDocumento7 páginasAUSPOS - Online GPS Processing ServiceRanjith KumarAinda não há avaliações
- IJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchDocumento6 páginasIJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Ainda não há avaliações
- Hazard MapsDocumento5 páginasHazard MapsSaaz ZeeAinda não há avaliações
- RESUME Marjan Shameem QTRDocumento5 páginasRESUME Marjan Shameem QTRsophist1Ainda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Forces On WiresDocumento4 páginasMagnetic Forces On WiresasiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Activity No. 3Documento2 páginasLab Activity No. 3Vannareneal SalesaAinda não há avaliações
- State Space Model Nptel ModDocumento30 páginasState Space Model Nptel ModBarathAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Conveying in Vane Extruder For Polymer Processing: Effects On Pressure EstablishmentDocumento10 páginasSolid Conveying in Vane Extruder For Polymer Processing: Effects On Pressure EstablishmentИгорь БезукладниковAinda não há avaliações
- Random Process PDFDocumento91 páginasRandom Process PDFramakant.savranAinda não há avaliações
- Insulation Condition During Transformer Manufacturing: by Study Committee A2Documento4 páginasInsulation Condition During Transformer Manufacturing: by Study Committee A2Pruthvi KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Encoder Data SheetDocumento13 páginasEncoder Data SheetKylo RenAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies On Nonlinear Control Theory of The Inverted PendulumDocumento28 páginasCase Studies On Nonlinear Control Theory of The Inverted PendulumDragan ErcegAinda não há avaliações
- Panasonic TX L32C10P 10PS Chassis GLP24Documento38 páginasPanasonic TX L32C10P 10PS Chassis GLP24yacosAinda não há avaliações
- BSOSR6X0907Documento20 páginasBSOSR6X0907xuanhungyteAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrostatic PressureDocumento13 páginasHydrostatic Pressureapi-2859151810% (1)