Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Scotch Yoke Mechanism
Enviado por
faizan997Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Scotch Yoke Mechanism
Enviado por
faizan997Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1
Experiment 3
Statement:
To Draw the Displacement, Velocity and acceleration Diagrams of
Scotch Yoke. (Slotted Link Mechanism).
Apparatus:
Scotch yoke mechanism
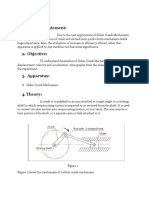
Diagram:
Theory:
Scotch yoke mechanism:
The Scotch yoke (also known as slotted
link mechanism) is a reciprocating motion mechanism, converting the linear
motion of a slider into rotational motion, or vice versa.
Working principle:
The piston or other reciprocating part is directly
coupled to a sliding yoke with a slot that engages a pin on the rotating
part. The location of the piston versus time is a sine wave of constant
amplitude, and constant frequency given a constant rotational speed
Construction:
It is constructed with iron bars. Here crank is made in some
length and yoke is made using same material. It should be noted that
minimum length of yoke should be twice of length of crank. The crank and
yoke is connected with pin. Iron bars are welded to both sides of the yoke
to get reciprocating motion. The yoke with iron bars is fixed on display
board with the help of c clamp .
Advantage:
Its advantage over crank shaft mechanism is that
it has lesser moving parts
smoother operation.
Disadvantages:
Its disadvantages are:
Rapid wear of slot in the yolk caused by sliding friction and
high contact pressures.
Increased hest loss during combustion due to extended dwell
at top dead centre offset any constant volume combustion
improvement in real engines.
Applications:
Control valve actuators:
This setup is most commonly used in
control valve actuators in high-pressure oil and gas pipelines.
Crude shapers:
Although not a common metalworking machine
nowadays, crude shapers can use Scotch yokes.
Internal combustion engines:
Under ideal engineering conditions, force is applied directly in the
line of travel of the assembly. The sinusoidal motion, co sinusoidal
velocity, and sinusoidal acceleration (assuming constant angular
velocity) result in smoother operation. The higher percentage of
time spent at top dead center (dwell) improves theoretical engine
efficiency of constant volume combustion cycles. It allows the
elimination of joints typically served by a wrist pin, and near
elimination of piston skirts and cylinder scuffing, as side loading
of piston due to sine of connecting rod angle is mitigated. The
longer the distance between the piston and the yoke, the less
wear that occurs, but greater the inertia, making such increases
in the piston rod length realistically only suitable for lower RPM
(but higher torque) applications
Observations And Calculations:
Degrees
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
240
Displacem
ent
3.2
5
16
33.
2
51
64
69
64.5 53
270
300
330
34.7 17.5 4.5
360
0
Conclusions:
The scotch yoke advantages and disadvantages are
discussed .its motion characteristics are studied.
It is concluded that this mechanism is great choice can
be used in direct injection engines like diesel engine to
convert rotating motion into reciprocating motion
because of fewer moving parts and smooth operation.
Você também pode gostar
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationNo EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Scotch Yolk Mechanism Lab Report 2010-ME-206Documento7 páginasScotch Yolk Mechanism Lab Report 2010-ME-206Syed Imtinan Ahmed0% (1)
- Scotch Yoke Mechanis1Documento17 páginasScotch Yoke Mechanis1Saravanan ViswakarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Slider Crank Mechanism Term Project ReportDocumento16 páginasSlider Crank Mechanism Term Project ReportAnis Badshah88% (24)
- Scotch Yoke MechanismDocumento5 páginasScotch Yoke MechanismSurendran Sai50% (4)
- Scotch Yoke Mechanism FinalDocumento12 páginasScotch Yoke Mechanism FinalsathyasonyAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics of Scotch-YokeDocumento11 páginasKinematics of Scotch-YokeAhmad Bin Sadiq100% (1)
- Epicyclic Gear Train ApparatusDocumento8 páginasEpicyclic Gear Train ApparatusGurmeet Mehma83% (6)
- Slotted Link Mechanism SHM ExperimentDocumento6 páginasSlotted Link Mechanism SHM ExperimentShawn Waltz50% (2)
- Slider CrankDocumento3 páginasSlider CrankAnonymous GGtvR65MR100% (1)
- Experiment #1: Whirling of ShaftsDocumento7 páginasExperiment #1: Whirling of ShaftsJibran Ansari0% (1)
- Slider Crank Mechanism Lab Report Ms Word ... 2017me162Documento11 páginasSlider Crank Mechanism Lab Report Ms Word ... 2017me162Binya meen50% (2)
- LAB MEC424-Slider CrankDocumento7 páginasLAB MEC424-Slider CrankAhmad Fadzlan93% (15)
- Scotch Yoke Experiment Motion AnalysisDocumento4 páginasScotch Yoke Experiment Motion Analysissharjeel100% (2)
- ExperimentsDocumento4 páginasExperimentsRohitGuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Quick return mechanism cuts idle timeDocumento1 páginaQuick return mechanism cuts idle timeShreyasi17Ainda não há avaliações
- Cam and FollowerDocumento12 páginasCam and Followerkulkajinkya100% (2)
- Exp 1Documento6 páginasExp 1Muhammad Moin KhanAinda não há avaliações
- How to animate a Scotch-Yoke mechanism in MATLAB (38 charactersDocumento4 páginasHow to animate a Scotch-Yoke mechanism in MATLAB (38 charactersMohammed A Isa0% (1)
- Porter Governor Speed vs Load DisplacementDocumento16 páginasPorter Governor Speed vs Load DisplacementShahir Afif Islam50% (2)
- Upto 2010 KomDocumento36 páginasUpto 2010 KomRajueswarAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Dynamics Lab ReportDocumento10 páginasEngineering Dynamics Lab ReportMian Abdul RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Whitworth Quick Return MechanismsDocumento39 páginasWhitworth Quick Return MechanismsJack jackson25% (4)
- Cam Follower Lab ReportDocumento16 páginasCam Follower Lab ReportAustin Williams80% (5)
- Bell CrankDocumento5 páginasBell CrankRajuKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cam Jump Phenomenon-1Documento10 páginasCam Jump Phenomenon-1Dhairyasheel Bhutkar100% (1)
- Whirling of ShaftDocumento5 páginasWhirling of ShaftGauthamSarang0% (1)
- 4 Bar MechanismsDocumento49 páginas4 Bar MechanismsFrank SandorAinda não há avaliações
- Gear Trains - Lecture 10Documento22 páginasGear Trains - Lecture 10priyankar007Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Mechanism and KinematicsDocumento24 páginasIntroduction To Mechanism and Kinematicsboonjie100% (1)
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 3Documento27 páginasJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 3Adib AzharAinda não há avaliações
- Slider Crank Chain ExperimentDocumento10 páginasSlider Crank Chain ExperimentNazim Jamali100% (2)
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Documento9 páginasCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1 Almost Complete Full ReportDocumento16 páginasLab 1 Almost Complete Full ReportMuhammad Taufiq YusofAinda não há avaliações
- Cam Analysis Apparatus ExperimentDocumento2 páginasCam Analysis Apparatus ExperimentGaurav KumarAinda não há avaliações
- KDM 6Documento54 páginasKDM 6KarthikeyanRamanujamAinda não há avaliações
- Scotch YokeDocumento7 páginasScotch YokeSandeela NaveedAinda não há avaliações
- Single Slider Crank MechanismDocumento2 páginasSingle Slider Crank MechanismDeepika Machina0% (1)
- Assemble and Analyze a 4-bar MechanismDocumento9 páginasAssemble and Analyze a 4-bar MechanismJigneshAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 2: Slider Crank MechanismDocumento6 páginasExperiment No. 2: Slider Crank MechanismLovekeshAinda não há avaliações
- Screw JackDocumento10 páginasScrew JackNarasimhaPrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Cam Analysis ManualDocumento4 páginasCam Analysis ManualNishant B MayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Gears and Gear Trains 19 PDFDocumento37 páginasChapter 3 Gears and Gear Trains 19 PDFMITTAPALLI PAVAN KUMAR REDDYAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics Lab Manual - ME6511Documento66 páginasDynamics Lab Manual - ME6511vinothAinda não há avaliações
- Scotch Yoke MechanismDocumento12 páginasScotch Yoke MechanismAhmad Bin SadiqAinda não há avaliações
- Epicyclic Gear TrainDocumento5 páginasEpicyclic Gear TrainRachan PancheAinda não há avaliações
- Scott Russell mechanism motion studyDocumento15 páginasScott Russell mechanism motion studyNABIL HUSSAINAinda não há avaliações
- Belt DrivesDocumento17 páginasBelt DrivesAbebe AyingdaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment:04 Cam Jump Analysis: Kinematics and Dynamics Lab Manual (ME406ES)Documento15 páginasExperiment:04 Cam Jump Analysis: Kinematics and Dynamics Lab Manual (ME406ES)Akshay PolasAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineDocumento8 páginasReport On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineshazedislamAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Machinery 2 - Balancing of Rotating MassesDocumento11 páginasMechanics of Machinery 2 - Balancing of Rotating MassesAhmed Zawad ShovonAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration Lab 2 Belt Friction Lab ReportDocumento15 páginasVibration Lab 2 Belt Friction Lab ReportYann YeuAinda não há avaliações
- Synchromesh Gearbox - Construction, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications (PDF)Documento7 páginasSynchromesh Gearbox - Construction, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications (PDF)Kyle LabileAinda não há avaliações
- Scotch Yoke MechanismDocumento4 páginasScotch Yoke MechanismIshak EnginerAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No 3 DynamicsDocumento7 páginasExperiment No 3 DynamicsAliAinda não há avaliações
- Scotch YokeDocumento3 páginasScotch YokeiiitianAinda não há avaliações
- Project ReportDocumento9 páginasProject Reportanilkumar529283% (12)
- Experiment of Mechanical EgineeringDocumento66 páginasExperiment of Mechanical EgineeringAmin MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Double Acting Hacksaw Machine Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDocumento32 páginasDouble Acting Hacksaw Machine Using Scotch Yoke Mechanismbalaji67% (12)
- MECHANICS OF MACHINES LAB Experiments on Linkage MechanismsDocumento43 páginasMECHANICS OF MACHINES LAB Experiments on Linkage MechanismsMuhammad HammadAinda não há avaliações
- 15 Questionnaire PDFDocumento11 páginas15 Questionnaire PDFfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Indicators of Motivation and Employee Satisfaction in Public Enterprise - Case Study of PE "Post of Serbia"Documento19 páginasIndicators of Motivation and Employee Satisfaction in Public Enterprise - Case Study of PE "Post of Serbia"rajmanit49Ainda não há avaliações
- Four Stroke Diesel Engine PresentationDocumento29 páginasFour Stroke Diesel Engine Presentationfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Forging of SwordsDocumento29 páginasForging of Swordsfaizan997100% (2)
- P Sheet BM Diagrams-2Documento7 páginasP Sheet BM Diagrams-2faizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- CAD/CAM Principles and Applications: CH 4 Geometric ModellingDocumento76 páginasCAD/CAM Principles and Applications: CH 4 Geometric Modellingantony1993Ainda não há avaliações
- Preventive MaintenanceDocumento19 páginasPreventive Maintenancefaizan9970% (1)
- 3x3determinants by DR Julia AdamsDocumento4 páginas3x3determinants by DR Julia AdamsNabeel AmeerAinda não há avaliações
- SURFACE ROUGHNESS TERMINOLOGY AND PARAMETER DEFINITIONSDocumento2 páginasSURFACE ROUGHNESS TERMINOLOGY AND PARAMETER DEFINITIONSfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Gears: Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & ClassificationDocumento12 páginasGears: Types, Advantages, Disadvantages & Classificationfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Discomfort ChecklistDocumento1 páginaDiscomfort Checklistfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Belts DesignDocumento16 páginasBelts Designfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch. 26Documento14 páginasCh. 26faizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Zipcar Case StudyDocumento3 páginasZipcar Case Studyfaizan997100% (2)
- Carbon Steels PDFDocumento9 páginasCarbon Steels PDFfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbon Steels: ME 215/205:materials Science LaboratoryDocumento9 páginasCarbon Steels: ME 215/205:materials Science Laboratoryfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Understanding Lathe Machine Parts, Operations and Tool-Workpiece ContactDocumento12 páginasUnderstanding Lathe Machine Parts, Operations and Tool-Workpiece Contactfaizan997Ainda não há avaliações
- Pronet Plus User ManualDocumento159 páginasPronet Plus User ManualJJ LópezAinda não há avaliações
- POWER GENERATION FROM OCEAN WAVESDocumento14 páginasPOWER GENERATION FROM OCEAN WAVESChersey DoctorAinda não há avaliações
- IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and EngineeringDocumento9 páginasIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and EngineeringMahesh MAinda não há avaliações
- Ee242 Lect06 TwoportsDocumento32 páginasEe242 Lect06 TwoportsZyad IskandarAinda não há avaliações
- Información de Transmisión CVT ToyotaDocumento151 páginasInformación de Transmisión CVT ToyotaMauricio Exequiel Chavez93% (15)
- No.1 PrestressedDocumento10 páginasNo.1 PrestressedKristin ArgosinoAinda não há avaliações
- Kill Sheet CalculationsDocumento16 páginasKill Sheet CalculationsYash SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Harduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh SharmaDocumento66 páginasHarduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh Sharmageeteshaccurate100% (1)
- 3G Commands in EricssonDocumento2 páginas3G Commands in EricssonKeshav Singh0% (1)
- Rigid PavementDocumento100 páginasRigid PavementJAY GANDHI100% (1)
- Solution to Tutorials 1-4: Shock Absorber, Crane, SDOF Vibration, Landing GearDocumento19 páginasSolution to Tutorials 1-4: Shock Absorber, Crane, SDOF Vibration, Landing GearPearlyn Tiko TeoAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYDocumento12 páginas11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYkAinda não há avaliações
- Rac NotesDocumento16 páginasRac NotesJohnRay LominoqueAinda não há avaliações
- DCT Dual Clutch TransmissionDocumento16 páginasDCT Dual Clutch TransmissionSudharshan SrinathAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Correcao Exercicios FixacaoDocumento3 páginas03 Correcao Exercicios FixacaoRodrigoAinda não há avaliações
- Fiziks: Basic Properties and Tools of ThermodynamicsDocumento28 páginasFiziks: Basic Properties and Tools of ThermodynamicsSURAJ PRATAP SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDocumento5 páginas1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Equilibrium Updated WorksheetDocumento22 páginasChemical Equilibrium Updated Worksheetmehwish razaAinda não há avaliações
- Network of Global Corporate Control. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in ZurichDocumento36 páginasNetwork of Global Corporate Control. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurichvirtualminded100% (2)
- DL-H61M-VG4: Motherboard User ManualDocumento52 páginasDL-H61M-VG4: Motherboard User ManualSutripti Bardhan100% (1)
- SE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFDocumento799 páginasSE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFBenigno Tique Jonasse100% (1)
- Ch01Documento33 páginasCh01sakali aliAinda não há avaliações
- Active Heating and CoolingDocumento16 páginasActive Heating and Coolinga_j_sanyal2590% (1)
- Self-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueDocumento376 páginasSelf-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueBill Frisch100% (1)
- Excerpt From Surely Youre Joking, Mr. FeynmanDocumento4 páginasExcerpt From Surely Youre Joking, Mr. FeynmanElbis Santos CardosoAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes HSCDocumento107 páginasBiology Notes HSCGouri DasAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardDocumento11 páginasCalculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardibmmoizAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engineering Conference ProgramDocumento40 páginasMechanical Engineering Conference Programirinuca12Ainda não há avaliações
- Essay For Villa Savoye AbstractDocumento1 páginaEssay For Villa Savoye AbstractFrancis PohAinda não há avaliações
- Truth Without ObjectivityDocumento4 páginasTruth Without ObjectivityMetafisco Parapensante0% (1)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNo EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (50)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNo EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationAinda não há avaliações
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNo EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (18)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsNo EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNo EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNo EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (10)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNo EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandIntroduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringNo EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Quantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationNo EverandQuantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNo EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- Waves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastNo EverandWaves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines: Integrity and Safety HandbookNo EverandOil and Gas Pipelines: Integrity and Safety HandbookAinda não há avaliações
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachNo EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsNo EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryAinda não há avaliações
- Machinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeNo EverandMachinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (4)