Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
6.6-6.7 Reproduction Bio f5
Enviado por
Ct Sophie PheaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
6.6-6.7 Reproduction Bio f5
Enviado por
Ct Sophie PheaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
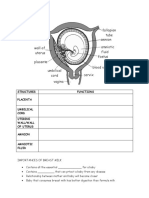
FORMATION FRUIT AND SEED
Importance of double fertilisation
It is unique to angiosperm plants as it give rise to seeds with diploid zygote and
triploid nucleus
Gametes are produced by meiosis contributing to genetic variability in zygote
which is importance for survival of species
Endosperm is a food storage in seed that provide nutrients for development of
embryo. This allows seed to be dispersed to wider areas and to survive for a long
period during unfavourable conditions.
Seeds of angiosperms are protected by fruit wall which is also help in the
dispersal of seeds.
6.6 GROWTH IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS.
An irreversible increase in size of an organism accompanied by an irreversible increase in
mass
May occur in certain parts or all parts of the body
May occur at certain times of an organisms life cycle
3 stages in the growth of multicellular organisms:
1) Cell division- increase in number of cells
Achieved by mitosis which ensure the genetic composition of daughter cell does not
change
The growth rate in this stage is slow
2) Cell elongation: increase in cell size
Achieved by absorption of water and nutrients by cell, from internal environment
The growth rate in this stage is fast
3) Cell differentiation: form a specialised cells with specific functions
Achieved when cell undergoes specific morphological and physiological changes and
become specialised.
The growth rate in this stage is slow
In plants, cells differentiate to form xylem, phloem, cambium, guard cells and
epidermal cells
In animal, cells differentiate to form muscle, nerve, bone, gamete and
epidermal cells
6.7 GROWTH CURVE
Measurement of growth
PARAMETER USED
IN MEASURING
GROWTH
Length or height
Surface area
Volume
ADVANTAGES
- Easy and quick to measure
- Growth may occur in other
- No need to kill organisms
- Repetitive measurement can be
directions
carried out
- More accurate
-
More suitable for organism
that is spherical in shape
Wet mass/ fresh
mass
DISADVANTAGES
Easy to measure
Repetitive measurement can be
carried out
No need to kill microorganism
Difficult and not practical to
carry out
Organism rarely in spherical
in shape
Difficult to calculate if
organism in irregular shape
May be inaccurate due to
fluctuations in water content
in the body of living
Dry mass
A more accurate measurement
of the organic substances in
the body of organism
organisms
Different living organisms
have different amount of
water content in them
All water need to be
removed from organism
Need to kill organisms
GROWTH CURVE
Growth curves are plotted using data from measurements of suitable growth
parameters. For most organisms, a sigmoid or S-shaped curve is obtained when the
growth parameter is plotted against time. This curve can be divided into 5 phases.
HUMAN GROWTH CURVE
-
The growth curve shows two sigmoid
parts that are connected on top of the
other
This is because human growth curve
has two fast growth phases infant
phase and teenage phase
The growth rate in male and female are
slightly different
The growth rate of boys is faster than
of girl after the age of about 4 years
INSECT GROWTH CURVE
Insects undergo intermittent or
discontinuous growth
Insects have a hard, in elastic outer cuticle
(exoskeleton) that restrics growth
1. moulting or ecdysis is the time where
the shedding of exoskeleton of insect
occur
2. an instar is a larval stage between 2
moults. Before moulting, a new cuticle is
formed. Growth occur while new cuticle
is still soft. The insect swallows air or
water which pushes the cuticle
outward. This leaves a gap or growth of
internal tissue.
Once new cuticle is fully hardened, no
further growth occurs until the next moult.
PLANT GROWTH CURVE
Você também pode gostar
- Individual Score SheetDocumento2 páginasIndividual Score SheetCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- SynapseDocumento2 páginasSynapseCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Peka Sains - Iss FormDocumento1 páginaPeka Sains - Iss FormCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Portfolio PekaDocumento1 páginaCover Portfolio PekaCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Type of Neurone-Biology Form 5Documento2 páginasType of Neurone-Biology Form 5Ct Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 3.2 InheritanceDocumento2 páginasExercise 3.2 InheritanceCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Structure of FlowerDocumento1 páginaStructure of FlowerCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceDocumento4 páginasChapter 5.2 Form 1 KSSSM ScienceCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Plant ReproductionDocumento6 páginasPlant ReproductionCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- GENETICSDocumento3 páginasGENETICSCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Fomr 4 4.7Documento3 páginasScience Fomr 4 4.7Ct Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment Form4 BioDocumento2 páginasExperiment Form4 BioCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- PlacentaDocumento2 páginasPlacentaCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 3.2 InheritanceDocumento2 páginasExercise 3.2 InheritanceCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Note Volunt Involun and ReflexDocumento5 páginasNote Volunt Involun and ReflexCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Division f4Documento3 páginasCell Division f4Ct Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocumento13 páginasPHOTOSYNTHESISCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic StructureDocumento4 páginasAtomic StructureCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide TestsDocumento5 páginasProperties of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide TestsCt Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Exercise 3.2 InheritanceDocumento2 páginasExercise 3.2 InheritanceCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Chromosome Movement in Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento3 páginasStages of Chromosome Movement in Mitosis and MeiosisCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Chromosome Movement in Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento3 páginasStages of Chromosome Movement in Mitosis and MeiosisCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2 Inheritance NotesDocumento2 páginas3.2 Inheritance NotesCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Mitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsDocumento2 páginasMitosis:: A Type of Cell Division Occurring in - Cells in Which A Parent Cell Divides Into - Daughter CellsCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- 4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleDocumento22 páginas4.2 Role of Hormone in Menstruation CycleCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- 4.1 Gamete Formation BIOLOGY FORM 4Documento33 páginas4.1 Gamete Formation BIOLOGY FORM 4Ct Sophie Phea100% (1)
- Growth Stages & FactorsDocumento2 páginasGrowth Stages & FactorsCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Rate of Reaction f5Documento4 páginasRate of Reaction f5Ct Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Man and ErthDocumento94 páginasMan and ErthCt Sophie PheaAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Meditations on Ancient Astrology Principles from Brihat Parashari HorāDocumento87 páginasMeditations on Ancient Astrology Principles from Brihat Parashari HorāPrasanna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Anglican Digest - Winter 2022Documento64 páginasThe Anglican Digest - Winter 2022The Anglican Digest100% (1)
- WHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaDocumento2 páginasWHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaTamas ZefferAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme of Valuation and Key for Transportation Engineering ExamDocumento3 páginasScheme of Valuation and Key for Transportation Engineering ExamSivakumarAinda não há avaliações
- A Kitchen in The Corner of The HouseDocumento2 páginasA Kitchen in The Corner of The HousedanielrubarajAinda não há avaliações
- Motherboards Tuf z270 Mark 2Documento70 páginasMotherboards Tuf z270 Mark 2Jonah HexAinda não há avaliações
- Wire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreDocumento8 páginasWire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreQuynh NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Koh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportDocumento7 páginasKoh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportNhoek RenAinda não há avaliações
- Pitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.ADocumento46 páginasPitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.AandreknhAinda não há avaliações
- PartitionDocumento2 páginasPartitionSyed IhyaAinda não há avaliações
- LP Pressure TestingDocumento34 páginasLP Pressure TestinglisaAinda não há avaliações
- Mast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Documento6 páginasMast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Vinay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Function and Definite Integrals ExplainedDocumento7 páginasFunction and Definite Integrals Explainedana maharaniAinda não há avaliações
- Psychoacoustics: Art Medium SoundDocumento3 páginasPsychoacoustics: Art Medium SoundTheodora CristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Homework Helpers - Chemistry PDFDocumento311 páginasHomework Helpers - Chemistry PDFTamby100% (1)
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3, Module 1 Genetic EngineeringDocumento20 páginasGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3, Module 1 Genetic EngineeringRonalyn AndaganAinda não há avaliações
- See Catalog: Get A QuoteDocumento4 páginasSee Catalog: Get A QuoteahnafAinda não há avaliações
- Mahavir Glass Proforma InvoiceDocumento2 páginasMahavir Glass Proforma Invoicemahendra patelAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Systems: Chapter 3: DeadlocksDocumento46 páginasOperating Systems: Chapter 3: DeadlocksManoel Katlib100% (1)
- Chinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariDocumento2 páginasChinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariGauthier Alex Freitas de Abreu0% (1)
- Vectors FoundationDocumento8 páginasVectors FoundationNaning RarasAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeDocumento13 páginasGCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeArchit GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- M700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Documento601 páginasM700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Mert SertAinda não há avaliações
- EC6702-Optical Communication and NetworksDocumento18 páginasEC6702-Optical Communication and Networkskasim_1983Ainda não há avaliações
- This Is Your Presentation TitleDocumento28 páginasThis Is Your Presentation TitleStephanie AcarapiAinda não há avaliações
- Kultura I InteligencijaDocumento15 páginasKultura I InteligencijaToni JandricAinda não há avaliações
- LearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDocumento3 páginasLearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDaniella MensatoAinda não há avaliações
- Alcon Capacitor AC Mp4aDocumento6 páginasAlcon Capacitor AC Mp4aDAC Secretary EEAinda não há avaliações
- Ratana Outdoor FurnitureDocumento107 páginasRatana Outdoor FurnitureNova TechieAinda não há avaliações
- ABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueDocumento56 páginasABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueqwertyAinda não há avaliações