Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
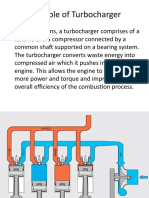
Turbochargers in Diesel Engines
Enviado por
Srini VasanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Turbochargers in Diesel Engines
Enviado por
Srini VasanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Turbochargers in Diesel Engines Marine
Engineering
November 25, 2015 3:43 pm | Leave a Comment | Frozee
Supercharging is the process of the increasing of the weight of the charged air
by increasing the density of the charged air.
Turbocharging is one kind of supercharging by using exhaust gas turbocharger. In which
the energy in the exhaust gas expelled from the engine cylinder is utilized in driven in
gas turbine, which is connected to a centrifugal air blower and air is supplied to
scavenge air trunk.
Constant Pressure System Turbocharging
Exhaust gas from all cylinders into a common large manifold where pulse energy
is largely dissipated.
The gas flow will steady rather than intermittent and at a constant pressure at
turbine inlet.
Turbocharger Arrangement in Constant Pressure System
No exhaust grouping
Exhaust gases enter into large common manifold and then to turbine
Firing order not considered
Advantages and Disadvantages for Constant Pressure System
Advantages
1.
Good performance in high load (Efficient when Bmep is above 8 bar)
2.
3.
More suitable for high output engine.
There is no need to group the cylinders exhaust into multiple of three. (Simple
piping system)
4.
No exhaust grouping
5.
6.
High turbine efficiency due to steady flow of exhaust.
The work transfer at the turbine wheel is smooth.
7.
Reduction in SFOC (Specific Fuel Oil Consumption) of 5% 7%
Disadvantages
1.
When running at reduced speed and starting up low available energy at turbine.
Thus it supplies inadequately air quantity of the scavenge pressure necessary for
efficient scavenging and combustion.
2.
It require scavenge assistant (Auxiliary Blowers).
3.
Poor response in changing load.
Pulse System of Turbocharging
Makes full use of the higher pressure and temperature of the exhaust gas during
the blow down period
While rapidly opening the exhaust valves, exhaust gas leave the cylinder at high
velocity as pressure energy is converted into kinetic energy to create the pressure
wave or pulse in exhaust
These pressure waves or pulses are lead directly to the turbocharger
Exhaust pipe, so constructed in small diameter, is quickly pressurized and
boosted up to form pressure pulse or wave
Pressure waves reach to turbine nozzles and further expansion takes place.
Turbocharger Arrangement in Pulse System
Interference exists between exhausting and scavenging among cylinders
To prevent this, cylinders are grouped relatively with connections to two or more
exhaust pipes
Pipes are arranged, in small diameter to boost up pressure pulse and in short,
straight length to prevent energy loss
Number of exhaust branch depends upon firing order, number of cylinders and
turbocharger design
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pulse System
Advantages
1.
At low load and low speed it is more efficient (Still efficient when Bmep is < 8
bar)
2.
No need assistant of scavenge pump and blower at any load change.
3.
4.
5.
It is highly response to change engine condition giving good performance of all
speed of engines.
High available energy at turbine
Good turbocharger acceleration
Disadvantages
1.
The exhaust grouping is complicated.
2.
3.
Different sizes of exhaust pipes are needed for spare.
High pressure exhaust from one cylinder would pass back into another cylinder
during the low pressure scavenging period thus adversely effecting the combustion
efficiency.
Under Piston Pressure Supercharging
It is a type of constant pressure charging system
Air charged by turbocharger is passed through CAC into first stage manifold, and
then through non-return valves into second stage and under piston space
In down stroke, piston under side compress further the scavenge air
Differential pressure shuts the inlet non-return valves as scavenge ports are
uncovered, and a pulse effect is given to cylinder
Advantages
Assist tangential swirl and ensure complete evacuation of remaining exhaust gas
No auxiliary blower may be required, during manoeuvring
Turbocharger Surging
When the discharge volute pressure exceed the pressure built up in the diffuser
and the impeller, it produces a back flow of air from discharge to suction and it is
characterized by noise and vibration of turbocharger.
Causes of Turbocharger Surging
1.
2.
Suddenly load change by heavy sea
Scavenge space fire / Exhaust trunking fire
3.
4.
Poor power balance
Dirty nozzle and blades
5.
6.
Individual cylinder misfire
Chocked scavenge /exhaust ports
7.
8.
Incorrect matching of turbocharger to engine.
Poor scavenging or leaky exhaust valve
What is exhaust tuning ?
Exhaust tuning means arranging the exhaust pipes with suitable length and
suitable valve timing to exhaust into the same pipe without disturbance.
When the exhaust valve of a diesel engine opens, the cylinder rapidly expands,
and gain velocity and kinetic energy as they pass into the exhaust pipe.
The kinetic energy of the mass of exhaust gas carries it along the exhaust pipe,
and causes a pressure build up ahead of the mass of gas and a partial vacuum
behind it.
This principle is used in a tuned exhaust system. The partial vacuum created by
exhaust from one cylinder is used to help exhaust expulsion from the following
cylinder.
Grouping of exhaust pipes depends upon the firing order, length & diameter of
exhaust pipe.
Advantages of Inter Cooling the Charged Air
The effect of cooling reduces the scavenge air temperature and increase the
density of air delivered to the cylinders, thus increasing the power out put delivered
by the engine.
It can increase the output by about 10%.
Cooled scavenge air reduces cylinder and exhaust gas temperature at a given
power level and these temperatures thus remain within the acceptable limits.
Types of Turbocharger Lube Oil System
1.
2.
Own sump
External lube oil supply system
Types of Turbocharger Bearings
Ball type bearing (rolling type)
These are used in turbocharger lube oil from the sumps on both air and exhaust
sides is sprayed onto the bearing by means of attached rotor driven gear type
pumps.
Sleeve type bearings
These are lubricated by external L.O supply system.
By gravity from independent header tank situated about six meters above
the bearings. The tank capacity must supply for about 15 minutes after engine is
stopped or
From a main L.O pump lead to the bearings with a separate L.O pipe line. It has
also gravity tank incase of failure of L.O supply. (Under main engine L.O system)
Function of Labyrinth Seals
The bearings are separated from the blower and turbine by labyrinth seals.
These seals are sealed by air supply from the discharge of blower to prevent oil
entering the blower and to prevent contamination of the oil by the exhaust gas.
In case of defective labyrinth seals on blower side, oil is leaked into the air
system the cooling surfaces are covered with oil which are insulators and the
cooling efficiency will be reduced. Also there will be deposits on the blower and the
blower efficiency will be reduced.
In case of defective labyrinth seals on turbine side, the oil is leaked into the
exhaust side and there will be carbon deposits on the nozzle and turbine
blades. Reduce blower efficiency and fire in the exhaust piping. It will cause
turbocharger surging. Oil will contaminate with exhaust gas.
How will you know turbocharger air filter chocked ?
It can be known by comparing the manometer difference. If manometer
difference is greater than normal, turbocharger air filter may be choke.
It can cause reduced engine power
Black smoke will emit from the funnel
Scavenge pressure will reduce
Function of nozzle ring in turbocharger
To change pressure energy to velocity (kinetic energy)
Function of shroud ring in turbocharger
Shroud ring is a component in turbochargers which forms a part of the inner
exhaust gas casing adjacent to the turbine.
The area around the turbine is always in contact with highly corrosive exhaust
gases. If no shroud ring is fitted, the turbine inner casing will be slowly wasted and
complete housing to be renewed for repair. Otherwise only shroud ring can be
replaced with new one.
Minimize maintenance cost.
The radial clearance between turbine blades and shroud ring to be maintained
within manufacture tolerance limits. This is very difficult in absence of shroud ring
since casing can go for uneven wear.
Purpose of inducer in turbochargers ?
To feed the shock less air flow to the impeller or
To guide the air smoothly into the eye of impeller
Function of Diffuser in turbochargers ?
To direct the air smoothly into volute casing
Convert kinetic energy to pressure energy inlet air
What is K value in turbochargers ?
It is a distance between the rotor shaft end and the flange of bearing cover
measured by blower side.
Purpose of K value in turbochargers ?
To ensure that rotating impeller does not to touch the stationary blower casing
cover in case of thrust bearing worn out.
How will you run engine in case of turbocharger failure ?
Rotor to be blocked
Exhaust gas to be by-passed the turbocharger
Run engine with reduced speed with remaining turbocharger
Use Auxiliary Blower
Maintain all temperature and pressure of fuel, cooling water and lubrication
within limit
How to Cut off Damaged Turbochargers for Engine Operation
Engines with one turbocharger (Engines with exhaust by-pass)
1.
2.
Stop the engine.
Lock the turbocharger rotor.
3.
4.
Remove the blanking plate from the exhaust by-pass pipe.
Remove the compensator between the compressor outlet and the scavenge air
duct. This reduces the suction resistance.
5.
Run engine with 15% of MCR load and 53% speed.
Engines with one turbocharger (Engines without exhaust by-pass)
1.
2.
Stop the engine.
Remove the rotor and nozzle ring of the turbocharger.
3.
4.
Insert blanking plates.
Remove the compensator between the compressor outlet and the scavenge air
duct. This reduces the suction resistance.
5.
Run engine with 15% of MCR load and 53% speed.
Engines with two or more turbochargers
1.
2.
3.
Stop the engine.
Lock the rotor of the defective turbocharger.
Insert orifice plates in the compressor outlet and the turbine inlet. (A small air
flow is required to cool the impeller, and a small gas flow is desirable to prevent
corrosion)
4.
Run engine with 20% of MCR load and 58% speed.
Você também pode gostar
- Turbochargers in Diesel EnginesDocumento5 páginasTurbochargers in Diesel Enginesmister_no34Ainda não há avaliações
- Turbo Charger NoteDocumento9 páginasTurbo Charger NoteShovon SanaAinda não há avaliações
- Twin-Scroll TurbochargerDocumento24 páginasTwin-Scroll TurbochargerJih Yan LaiAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger 2NDDocumento6 páginasTurbocharger 2NDkyaw yaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 TurbochargerDocumento14 páginas12 TurbochargerAisha Zaheer100% (5)
- Boost engine power with turbochargersDocumento18 páginasBoost engine power with turbochargerscleousAinda não há avaliações
- Locomotive - Charge Air SystemDocumento4 páginasLocomotive - Charge Air SystemArpan MaheshwariAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharging and Supercharging ExplainedDocumento51 páginasTurbocharging and Supercharging ExplainedYoseph MershaAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineDocumento10 páginasTurbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineYasewn KALAWANTAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Forced Induction?Documento15 páginasWhat Is Forced Induction?Fugaru Paul - AlexandruAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 Supercharging TurbochargingDocumento33 páginasChapter 12 Supercharging Turbochargingdesie yalewAinda não há avaliações
- 2.3 Turbo Chargers (WGT, VGT), Engine Emission Control by Three Way Catalytic Converter System, Emission Norms (Euro and BS) .Documento20 páginas2.3 Turbo Chargers (WGT, VGT), Engine Emission Control by Three Way Catalytic Converter System, Emission Norms (Euro and BS) .DEEPAK S SEC 2020Ainda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger Principles and Components for Marine EngineersDocumento14 páginasTurbocharger Principles and Components for Marine EngineersDodi SuhendraAinda não há avaliações
- Engineer M. A. HamidDocumento14 páginasEngineer M. A. HamidAbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- BCMEDocumento9 páginasBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyAinda não há avaliações
- Operating PrincipleDocumento6 páginasOperating PrincipleGedan CristianAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger: Presented byDocumento26 páginasTurbocharger: Presented byYasewn KALAWANTAinda não há avaliações
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocumento16 páginasDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerNazrul Aizat ZunaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger Design Criteria, Selection and Failure: Rajvardhan NalawadeDocumento4 páginasTurbocharger Design Criteria, Selection and Failure: Rajvardhan NalawadeFloyd PriceAinda não há avaliações
- TurbochargerDocumento21 páginasTurbochargerJo VialAinda não há avaliações
- Turbo Tech 101 (Basic) : How A Turbo System WorksDocumento24 páginasTurbo Tech 101 (Basic) : How A Turbo System WorksAapo YritysAinda não há avaliações
- ICE Engineering IDocumento16 páginasICE Engineering Izhafran1513Ainda não há avaliações
- Supercharger VS TurbochargerDocumento25 páginasSupercharger VS TurbochargerAllen CastorAinda não há avaliações
- Final Edition of Automotive QBDocumento15 páginasFinal Edition of Automotive QByoussef faroukAinda não há avaliações
- LP-2 Factors Influencing Power DoneDocumento5 páginasLP-2 Factors Influencing Power DoneKashif UsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocumento16 páginasTurbocharger and SuperchargerPrajwal ZinjadeAinda não há avaliações
- Turbocharger: - Power of A Two Stroke Diesel EngineDocumento28 páginasTurbocharger: - Power of A Two Stroke Diesel EngineShraddha Kant SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Engine Lubrication System: The Importance of LubricationDocumento4 páginasEngine Lubrication System: The Importance of LubricationPyae Sone LonnAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Principle of TurbochargerDocumento19 páginas03 Principle of TurbochargerSky RAinda não há avaliações
- Below Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationDocumento8 páginasBelow Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationchigauAinda não há avaliações
- TurbochargerDocumento17 páginasTurbochargerAravindhRaj100% (1)
- Steam TurbineDocumento50 páginasSteam TurbineNikhil ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Turbo ChargerDocumento23 páginasTurbo Chargerselvaraj9223100% (1)
- Turbo Tech 101 (Basic) : How A Turbo System WorksDocumento6 páginasTurbo Tech 101 (Basic) : How A Turbo System Workscogit0Ainda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About TurbochargersDocumento12 páginasEverything You Need to Know About TurbochargersGeorge JankoAinda não há avaliações
- How A Turbo WorksDocumento2 páginasHow A Turbo WorksSubhojit SamontaAinda não há avaliações
- Expert Systems For Diagnostics of Marine Diesel EnginesDocumento11 páginasExpert Systems For Diagnostics of Marine Diesel EnginesmatianagrabeAinda não há avaliações
- Turbochargers: BY: Muddukrishna C Shetty USN:4AL08ME023Documento25 páginasTurbochargers: BY: Muddukrishna C Shetty USN:4AL08ME023Vinod SubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- ICE Turbocharger BasicsDocumento18 páginasICE Turbocharger Basicssafwansd750% (2)
- Turbocharger Surging and MatchingDocumento18 páginasTurbocharger Surging and MatchingSky RAinda não há avaliações
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDocumento8 páginasSupercharging and TurbochargingMudassir Hussain100% (1)
- Unit II - Turbo Super ChargerDocumento14 páginasUnit II - Turbo Super ChargerdrkbalaAinda não há avaliações
- Engine 114E-3 Series: 10 Structure, Function and Maintenance StandardDocumento14 páginasEngine 114E-3 Series: 10 Structure, Function and Maintenance StandardGiancarlo Cardenas NinaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas TurbineDocumento57 páginasGas TurbineMajid Sattar100% (1)
- Ad Dit LC B Ti E I Advanced Internal Combustion Engines Mae 589V (Spring 2009)Documento15 páginasAd Dit LC B Ti E I Advanced Internal Combustion Engines Mae 589V (Spring 2009)snmathad2Ainda não há avaliações
- Turbo Super Charger SystemDocumento10 páginasTurbo Super Charger Systemsanju_17Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 2Documento21 páginasModule 2NithinAinda não há avaliações
- Four-Stroke Diesel EngineDocumento18 páginasFour-Stroke Diesel Enginebs esliye me aap ka fan ho gya100% (2)
- GTE Note 3 2023Documento5 páginasGTE Note 3 2023ibrahim ibrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Turbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadDocumento21 páginasTurbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadSumanthAinda não há avaliações
- IC Engine QuestionsDocumento18 páginasIC Engine QuestionswasemAinda não há avaliações
- EX - NO:6 Dismantling of Jet Engine AimDocumento4 páginasEX - NO:6 Dismantling of Jet Engine AimesakkimuthuAinda não há avaliações
- Super ChargingDocumento23 páginasSuper Charginghirenbabaji100% (2)
- Lecture 8 - Steam TurbinesDocumento34 páginasLecture 8 - Steam Turbinesmohamed EldesokyAinda não há avaliações
- Scavenging in 2 Stroke Engine FinalDocumento35 páginasScavenging in 2 Stroke Engine Finalnitin_parwaniAinda não há avaliações
- 5 2020 10 06!03 05 20 AmDocumento10 páginas5 2020 10 06!03 05 20 AmHakim ChelghamAinda não há avaliações
- Turbo PDFDocumento16 páginasTurbo PDFAdnin HakeemAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Turbin Mark VIDocumento42 páginasGas Turbin Mark VIpradeeps2007_1777402100% (3)
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento1 páginaStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento3 páginasStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To ComputerDocumento81 páginasIntroduction To ComputerSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Function 5 OralsDocumento4 páginasFunction 5 OralsAditya Arya0% (1)
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento1 páginaStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- M.V.Oliva - Emergency Procedures - Volume 3, Section C11, GroundingDocumento2 páginasM.V.Oliva - Emergency Procedures - Volume 3, Section C11, GroundingSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento1 páginaStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento2 páginasStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Status of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeDocumento2 páginasStatus of Certificate of Competency of Engineering GradeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Elegibility Criteria For CA CS and CMADocumento2 páginasElegibility Criteria For CA CS and CMASrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Meo Class IV Orals Ques Bank - Mumbai MMDDocumento66 páginasMeo Class IV Orals Ques Bank - Mumbai MMDlalindaAinda não há avaliações
- Crankcase explosions causes and preventionDocumento9 páginasCrankcase explosions causes and preventionSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- M.V.Oliva - Emergency Procedures - Volume 3, Section C12, ExplosionDocumento2 páginasM.V.Oliva - Emergency Procedures - Volume 3, Section C12, ExplosionSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Class IV Part BDocumento31 páginasClass IV Part BSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- PMS Alarms List On Board The ShipDocumento15 páginasPMS Alarms List On Board The ShipSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Checklist For Engine Side On Board ShipDocumento1 páginaChecklist For Engine Side On Board ShipSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- CH Engr Standing InstructionsDocumento2 páginasCH Engr Standing InstructionsSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Hot Work Permit ChecklistDocumento1 páginaHot Work Permit ChecklistSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Immediate Action by Outside Source in Case of Elevator EmergencyDocumento1 páginaImmediate Action by Outside Source in Case of Elevator EmergencySrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Changeover Controls ECR BridgeDocumento2 páginasChangeover Controls ECR BridgeSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- IG System Operating ProcedureDocumento1 páginaIG System Operating ProcedureSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- First Aid For Accident With HFC/HCFCDocumento2 páginasFirst Aid For Accident With HFC/HCFCSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Procedure For Changing Over Main Air Bottle in Case of Low Starting Air Pressure During Manouv.Documento1 páginaProcedure For Changing Over Main Air Bottle in Case of Low Starting Air Pressure During Manouv.Srini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Battery RoutinesDocumento1 páginaBattery RoutinesSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocumento1 páginaSewage Treatment PlantSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Instructions For OWSDocumento1 páginaOperating Instructions For OWSSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Alarm Panel Operating InstructionsDocumento1 páginaFire Alarm Panel Operating InstructionsSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Start Up of Aux. BoilerDocumento1 páginaCold Start Up of Aux. BoilerSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- UMS Changeover ProcedureDocumento1 páginaUMS Changeover ProcedureSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- Incinerator Operating ProcedureDocumento1 páginaIncinerator Operating ProcedureSrini VasanAinda não há avaliações
- MachinaDocumento14 páginasMachinaHSY79Ainda não há avaliações
- Ipocc Configuration enDocumento211 páginasIpocc Configuration enMarthaGutnaraAinda não há avaliações
- Two Story Machine BuildingDocumento11 páginasTwo Story Machine BuildingPravin LokareAinda não há avaliações
- Ch11Integer Goal ProgrammingDocumento54 páginasCh11Integer Goal ProgrammingAngelina WattssAinda não há avaliações
- Gantt ChartDocumento49 páginasGantt ChartJayaram ParlikadAinda não há avaliações
- Hero Honda Motorcycle ProjectDocumento93 páginasHero Honda Motorcycle ProjectSharath HegdeAinda não há avaliações
- Tecnotion Torque Motor Brochure Ver 10120150120Documento16 páginasTecnotion Torque Motor Brochure Ver 10120150120ElectromateAinda não há avaliações
- Sharing The SkiesDocumento357 páginasSharing The SkiesLava R5s2019Ainda não há avaliações
- Eccma February2008Newsletter PDFDocumento19 páginasEccma February2008Newsletter PDFprsiva2420034066Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 02Documento39 páginasCH 02enamislamAinda não há avaliações
- Comsoal: Computer Method For Sequencing Operations For Assembly LinesDocumento30 páginasComsoal: Computer Method For Sequencing Operations For Assembly LinesCarson HungAinda não há avaliações
- Developer Feasibility StudyDocumento9 páginasDeveloper Feasibility Studysam dorilloAinda não há avaliações
- Shale ShakerDocumento3 páginasShale ShakerkosunlucyAinda não há avaliações
- CASE03-ABC-MfgDocumento2 páginasCASE03-ABC-MfgLaura Catalina PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Cam350 810Documento4 páginasCam350 810Frank ZamoraAinda não há avaliações
- Slide Management ContractingDocumento3 páginasSlide Management ContractingFairus IthninAinda não há avaliações
- Bleriot XIDocumento8 páginasBleriot XIAlejandro M. Bianchi100% (1)
- Engineering Economics Chapter 2 & 3Documento14 páginasEngineering Economics Chapter 2 & 3byun baekAinda não há avaliações
- Arch Required FlowchartDocumento1 páginaArch Required FlowchartgullipalliAinda não há avaliações
- 3 D Printing TechnologyDocumento17 páginas3 D Printing TechnologyClassic PrintersAinda não há avaliações
- Cylinders FullDocumento110 páginasCylinders FulltnvishAinda não há avaliações
- TFG A 020Documento81 páginasTFG A 020Sergio FontechaAinda não há avaliações
- AgailDocumento34 páginasAgailnarasakuru79Ainda não há avaliações
- WPD Wpbwall Fans Catalog 4820Documento24 páginasWPD Wpbwall Fans Catalog 4820beemer03Ainda não há avaliações
- Up 11-22Documento91 páginasUp 11-22Tamjid Kabir100% (2)
- EpicorSLS10 MigrateGuide SQL 10.2.100.505100Documento219 páginasEpicorSLS10 MigrateGuide SQL 10.2.100.505100Marianne Hernandez MendietaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 09 - Forces Acting On An AeroplaneDocumento26 páginasChapter 09 - Forces Acting On An AeroplaneRezwan Ahmed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Building EstimateDocumento16 páginasBuilding EstimateMrinal TalukdarAinda não há avaliações
- How Cathay Pacific Leveraged IT to Support Business GrowthDocumento2 páginasHow Cathay Pacific Leveraged IT to Support Business Growthranjeeeth8569100% (1)