Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ChE125 Quiz 3 - 2016
Enviado por
Emmanuel PlazaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ChE125 Quiz 3 - 2016
Enviado por
Emmanuel PlazaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
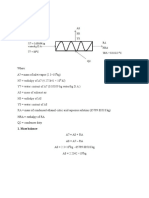
ANSWERS TO THE QUIZ (01 SEPTEMBER 2016) WITH DISCUSSION
ChE125 Quiz 3
September 2016
This is a closed notes, closed book, closed e-book quiz. Find the solution to the following problems. Show the process. For
problems requiring numerical answers instead of expressions, numerical values in the course of the solution must be limited to
three decimal places and report final answer in 2 decimal places. You may discuss your answer if deemed necessary. Write your
solutions in YELLOW PAPER. Excel files may also be submitted (file name: ChE125_surname_quiz3_problem number (e.g.
ChE125_Medrano_quiz3_1)). Attach this questionnaire to your answer sheet upon submission.
1.
Write the rate law for the reaction
2 +
If the reaction is
a. second order in B and overall third order,
b. zero order in A and first order in B,
c. zero order in both A and B, and
d. first order in A and overall zero order.
Answer:
General form of the rate law:
= , = +
If the reaction above were elementary, rate law would be
= 2 , = 3
But the rate low being asked for each letter above does not correspond to the rate law of an elementary reaction,
Write the rate law according to the specified order for each component and overall order.
a.
second order in B and overall third order
= 2
b.
zero order in A and first order in B
c.
zero order in both A and B
d.
first order in A and overall zero order
=
=
= 1
Given the low pressure gas-phase reaction with rate
=
= 1 2.2 2 0.5
with p in atm, C in
3 , t in hours, and 1 = 17.3, 2 = 0.2. The reaction takes place at 72 1 .
2.
a.
b.
What are the units of 1 2 ?
With the rate equation in the following form, find 1 2 , value and units.
=
= 1 2.2 2 0.5
Answer:
a. What are the units of 1 2 ?
The unit for rate is
. Each of the terms in the equation should give the same unit. Unit for a given term is still the
same: ( )1 ()1
1
1 :
1.2
( )()
0.5
2 :
b.
With the rate equation in the following form, find 1 2 , value and units.
=
= 1 2.2 2 0.5
For each term in the right side of the equation, this corresponds to . Relating partial pressure and
concentration to get values and units for 1 2 must be done term by term.
For 1 ,
For 2 ,
Finding the values and units,
3.
At 500 , the rate of a bimolecular reaction is ten times the rate at 400 K. Find E of the reaction from Arrhenius Law.
Solution:
500 = 10400
Relationship of rates at two temperatures of the same reaction from Arrhenius Law:
2 1
1
ln = ( )
1 1 2
Substituting above equation with values from the problem and = 8.31447
,
500
1
1
ln
= (
)
400 400 500
10400
ln
400
= 8.31447
(
)
1
1
(
)
400 500
= 38289.549
= .
4.
At 250 the stoichiometry of the first order gas-phase decomposition of A shows 0.96 + 0.04 . We suspect that
this stoichiometry is better explained by considering the competing decomposition paths
1
with
1
2
= 24. Further experiments are planned for 300. What ratio of rate constants would we expect to find if
hypothesis of competing paths is correct?
Answer:
For the hypothesis of competing paths to be correct, the ratio of rate constants would be expected to be the same,
provided that the activation energy of both reactions are the same.
5.
The initial reaction rate for the elementary reactor
2 +
0.002
0.046
0.72
( 3 )
()
26.85
46.85
66.85
was measured as a function of temperature when the concentration of A was 2M and that B is 1.5 M.
a.
b.
c.
Hint:
8.33
86.85
What is the activation energy?
What is the frequency factor?
What is the rate constant as a function of temperature using = 300 as the base case?
Apply Arrhenius Law to the temperature dependency factor of the rate law.
Develop an equation into a form = + , where y and x are functions of and T.
Plot the given data above, and utilize the equation of the line (e.g. slope is equal to which variable, etc.).
Consistent units should be used.
Solution:
Rate Law:
= 2
From the hints above:
a. Apply Arrhenius Law to the temperature dependency factor of the rate law.
= ( ) 2
b.
c.
Develop an equation into a form = + , where y and x are functions of and T.
1
ln( ) = ( ) + ln( 2 )
Plot the given data above, and utilize the equation of the line (e.g. slope is equal to which variable, etc.).
1
A plot of ln( ) . .
d.
Consistent units should be used.
Compare units of all parameters/variables (e.g. concentration, temperature, etc.)
Questions and Answers:
1. What is the activation energy?
The equation of the plot is
= 14999 + 43.786
which corresponds to
1
( ) + ln( 2 )
Slope corresponds to , so to solve for the activation energy,
= 14999
= 14999 (8.31447
)
= 124708.736
= .
ln( ) =
2.
What is the frequency factor?
ln( 2 ) = 43.786
43.786
ko = 2
43.786
=
(2)2 (1.5)
= 1.729 1018
= .
3.
What is the rate constant as a function of temperature using = 300 as the base case?
= ( )
= 1.729 1018
124708.736
(300 )
8.31447
(
= 3.346 104
= .
Você também pode gostar
- Time ManagementDocumento1 páginaTime ManagementEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Prayer and Fasting ExplainedDocumento1 páginaTypes of Prayer and Fasting ExplainedEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Silence and SolitudeDocumento1 páginaSilence and SolitudeEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- 4.7 Notes and ExercisesDocumento4 páginas4.7 Notes and ExercisesaswaniexpressAinda não há avaliações
- Preliminary ExamDocumento1 páginaPreliminary ExamEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Intro CSTRDocumento6 páginasIntro CSTREmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- References For Citric AcidDocumento1 páginaReferences For Citric AcidEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Abstract AlgebraDocumento2 páginasAbstract AlgebraEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Quadrilaterals in The Real WorldDocumento22 páginasQuadrilaterals in The Real WorldEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Position For Ungrouped DataDocumento1 páginaMeasures of Position For Ungrouped DataEmmanuel Plaza83% (6)
- Capitol University College of Education Cagayan de Oro City Course Syllabus in Probability VisionDocumento7 páginasCapitol University College of Education Cagayan de Oro City Course Syllabus in Probability VisionEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Hs Stats Sample Version 1Documento19 páginasHs Stats Sample Version 1Emmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Capitol University College of Education Cagayan de Oro City Course Syllabus in Probability VisionDocumento7 páginasCapitol University College of Education Cagayan de Oro City Course Syllabus in Probability VisionEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Probabilty 2Documento1 páginaProbabilty 2Emmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Perimeter QuadrilateralsDocumento2 páginasPerimeter QuadrilateralsEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Pag117 Pag126 PDFDocumento5 páginasPag117 Pag126 PDFLucia LorenziniAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization of supercritical fluid extractionsDocumento2 páginasOptimization of supercritical fluid extractionsEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Isolation of Essential OilDocumento58 páginasIsolation of Essential OilEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- CONDENSING DUTYDocumento3 páginasCONDENSING DUTYEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Distillation Matlab CodeDocumento8 páginasDistillation Matlab CodeSaurab Devanandan0% (1)
- 03 Extractor&CondenserDocumento29 páginas03 Extractor&CondenserEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- VLE Data for MeOH/H2O System at 1 atmDocumento2 páginasVLE Data for MeOH/H2O System at 1 atmEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- ReferencesDocumento1 páginaReferencesEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Energy Balance AnalysisDocumento23 páginasPlant Energy Balance AnalysisEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Godsitoffee EditedDocumento10 páginasGodsitoffee EditedEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6 DataDocumento29 páginasExperiment 6 DataEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Extraction of Essential From LavenderDocumento6 páginasExtraction of Essential From LavenderEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- A Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsDocumento17 páginasA Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsEmmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6 Data2Documento4 páginasExperiment 6 Data2Emmanuel PlazaAinda não há avaliações
- Super Critical Fluid Extraction in Plant Essential and Volatile Oil AnalysisDocumento23 páginasSuper Critical Fluid Extraction in Plant Essential and Volatile Oil Analysismyrtarom100% (4)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- LCP SpanlockDocumento8 páginasLCP SpanlockGarfieldAinda não há avaliações
- Wear Plate SpecsDocumento4 páginasWear Plate SpecsJuan Carlos EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Indirect RestorationsDocumento32 páginasIndirect RestorationsNaji Z. Arandi100% (1)
- Construction Materials For Marine Diesel EnginesDocumento5 páginasConstruction Materials For Marine Diesel EnginesVijay AAinda não há avaliações
- Product Information Sheet: Phytotechnology Laboratories®Documento1 páginaProduct Information Sheet: Phytotechnology Laboratories®Jiovanni AmbAinda não há avaliações
- Set 2 MSDocumento7 páginasSet 2 MSsanjith4arisAinda não há avaliações
- Philips NMR and MRIDocumento98 páginasPhilips NMR and MRItsram90Ainda não há avaliações
- Research Paper March 10 2019Documento12 páginasResearch Paper March 10 2019vincent jancarlo ricarteAinda não há avaliações
- Empirical and Molecular Formulas ExplainedDocumento16 páginasEmpirical and Molecular Formulas ExplainedangelaAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Properties of SolutionDocumento3 páginasPhysical Properties of SolutionRhye Tabaday LopezAinda não há avaliações
- ASTM C-1196-09 Standard Test Method For in Sity Compressive Stress Within Solid Unit Masonry Estimated Using Flatjack Measurements PDFDocumento6 páginasASTM C-1196-09 Standard Test Method For in Sity Compressive Stress Within Solid Unit Masonry Estimated Using Flatjack Measurements PDFAlejandro JiménezAinda não há avaliações
- FDA Guidance on Dosage Delivery Devices for Liquid OTC DrugsDocumento14 páginasFDA Guidance on Dosage Delivery Devices for Liquid OTC DrugsmkyousufAinda não há avaliações
- EndocrineDocumento3 páginasEndocrinePotato HeadAinda não há avaliações
- Nu 5100 5100eg HalfDocumento19 páginasNu 5100 5100eg HalfCristian AedoAinda não há avaliações
- Bollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialDocumento48 páginasBollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialAce Industrial SuppliesAinda não há avaliações
- Method Statement For Installation of Water Recticulation SystemDocumento18 páginasMethod Statement For Installation of Water Recticulation SystemRabi'atul Adawiyah Ismail100% (2)
- Novenco Cnd-Cnf-Cat-Gb-Mu15467-0317Documento20 páginasNovenco Cnd-Cnf-Cat-Gb-Mu15467-0317budayaAinda não há avaliações
- Heat TreatmentDocumento53 páginasHeat TreatmentIqbal Muhammad HusainiAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Paper 2Documento12 páginasSample Paper 2Sheereen AiyazAinda não há avaliações
- Bond Length: Measuring the Average Distance Between Atoms in a Covalent BondDocumento9 páginasBond Length: Measuring the Average Distance Between Atoms in a Covalent BondMiteigiAinda não há avaliações
- Internship ReportDocumento31 páginasInternship ReportShashidhara AEAinda não há avaliações
- EP0070932B1Documento5 páginasEP0070932B1bayuAinda não há avaliações
- Refining and Petrochemicals CourseworkDocumento9 páginasRefining and Petrochemicals CourseworkMichael GregoryAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8Documento44 páginasChapter 8Oscar Espinosa BonillaAinda não há avaliações
- Coway water purifiers product collectionDocumento10 páginasCoway water purifiers product collectionSyida NaufalAinda não há avaliações
- NORD-Painting CodeDocumento3 páginasNORD-Painting CodeubabAinda não há avaliações
- Dungs ATEX en 161 Solenoid ValvesDocumento12 páginasDungs ATEX en 161 Solenoid Valvesstefan-romocki-4927Ainda não há avaliações
- Enzyme Assay Units: Amylase Units Lactase UnitsDocumento4 páginasEnzyme Assay Units: Amylase Units Lactase UnitsDaniel RincónAinda não há avaliações
- Hy-Pro Air BreathersDocumento7 páginasHy-Pro Air BreathersImam WahyudiAinda não há avaliações
- COMPACT 99B Inlet Valve ManualDocumento4 páginasCOMPACT 99B Inlet Valve Manualalwill09Ainda não há avaliações