Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Diagram 1.1: Revision For Year End Examination
Enviado por
sookchinTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Diagram 1.1: Revision For Year End Examination
Enviado por
sookchinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
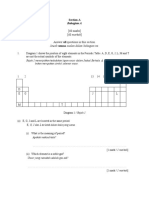
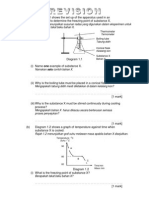
1. Diagram 1.1 shows the symbols for atoms of element W, X and Y.
Diagram 1.1
(a) Based on Diagram 1, answer the following questions.
(i) Write the electron arrangement of atom Y.
[1 mark]
(ii) What is the number of neutron for atom X?
[1 mark]
(iii) What is the atomic mass of atom W?
[1 mark]
(b) Diagram 1.2 shows the set up of the apparatus of an experiment where a drop of potassium manganate
(VII) crystal is dropped into a test tube containing water and is left for a few minutes.
Water
Potassium manganate (VII) crystal
Diagram 1.2
(i) State the name of process involved in this experiment.
[1 mark]
(ii) State one observation in the test tube after a few minutes.
[1 mark]
(iii) Explain the observation in 1(b)(ii) based on the kinetic theory of matter.
[3 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(c) Substance Z has a melting point of 80oC. Draw the particles arrangement of substance Z at 60oC and
85oC
At 60oC
At 85oC
[2 marks]
2. Diagram 2.1 shows the structural formula of compound P
Diagram 2.1
(a) What is the meaning of molecular formula?
[1 mark]
(b) Write the molecular formula of compound P.
[1 mark]
(c) Write the empirical formula of compound P.
[1 mark]
(d) Can molten compound P conduct electricity? Explain your answer.
....
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(e) One molecule of stearic acid contains 75.7% of carbon, 12.8% of hydrogen and 11.5% of oxygen by mass.
[Relative atomic mass of C: 12; H: 1; O:16]
(i) Find the empirical formula of stearic acid.
[3 marks]
(ii) If the molar mass of stearic acid is 284gmol-1, find its molecular formula.
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
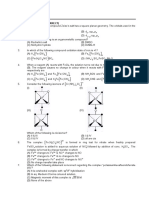
3. Diagram 3.1 shows the position of several elements in the Periodic Table of Elements. The
letter do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Diagram 3.1
Using the letters in the Periodic Table of the Elements, answer the following questions.
(a) Write the electron arrangement for an atom of element A.
[1 mark]
(b) Draw the electron arrangement in the compound formed between A and D.
[2 marks]
(c) Which element forms an amphoteric oxide?
[1 mark]
(d) Arrange A, B,C, D, E, F according to the increase in the size of atoms.
[1 mark]
(e) Write the formula of ion formed from an atom of C.
[1 mark]
(f) Atom of element E exists as monoatomic gas. Explain why.
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(g) State one special characteristic of element F.
[1 mark]
(h) When a small piece of element A is put into water, AOH is formed and hydrogen gas is released. State one
observation when a few drops of pheneolphthalein is added into the solution formed.
[1 mark]
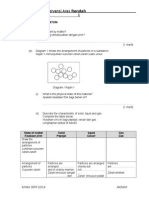
4. A series of experiment were carried out to investigate the tendency of metals to donate
electrons. The results of the experiment are shown in Table 1.1.
Solution
W(NO3)2
X(NO3)2
Y(NO3)2
Z(NO3)2
Metal
W
ppppppppppppp
X
x
ppppppppppppp
x
x
Displacement of metal occurs
ppppppppppppp
x
ppppppppppppp
x Displacement of metal does not occur
Table 1.1
(a) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between X(NO3)2 and Z.
[1 mark]
(b) Arrange the four metals in ascending order of electropositivity.
[1 mark]
(c) What is the precaution step for this experiment?
[1 mark]
(d) What is the role of metal Y when react with W(NO3)2?
[1 mark]
(e) If X is copper, state two observations for the reaction between metal Y and X(NO3)2.
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(f) If 25.0cm3 of 2.0moldm-3 X(NO3)2 solution reacts completely with 0.5g of metal Y. calculate the mass of
metal X is produced. [ Relative atomic mass of X: 64; Y:24]
[2 marks]
(g) The tendency of metals to donate electron also can be study by another experiment.
Pair of metal
Z-W
Z-X
Y-X
W-Y
Potential difference/ V
0.2
0.8
2.6
x
Negative terminal
W
Z
Y
y
Based on table 1, predict the value of X and negative terminal, y.
...
[2 marks]
5. Diagram 4 shows the setup of the apparatus for the titration of 25.0cm3 sodium hydroxide solution and
2moldm-3 of vinegar using phenolphthalein as indicator.
2moldm-3 of vinegar
Sodium hydroxide solution +
phenolphthalein
Diagram 4
(i) Complete the table 1 below.
Final burette reading/ cm3
Initial burette reading/ cm3
Volume of vinegar/ cm3
Titration 1
0.00
23.20
Titration 2
23.30
46.50
Titration 3
0.00
23.30
Table 1
[1 mark]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(b) Vinegar is an aqueous ethanoic acid. Ethanoic acid is a weak acid. What is meant by a weak acid?
[1 mark]
(c) Write the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction.
[1 mark]
(d) Calculate the average volume of 2moldm-3 of vinegar to neutralize with 25.0cm3 sodium hydroxide.
[1 mark]
(e) Calculate the number of mole of vinegar reacted.
[1 mark]
(f) Calculate the molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution.
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(g) The experiment is repeated by using same concentration of barium hydroxide to replace sodium
hydroxide solution.
(i) Predict the volume of the barium hydroxide solution needed to react with vinegar.
..
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain your answer in (e) (i)
..
..
[2 marks]
6. Diagram 5 shows the apparatus setup for the preparation of copper (II) chloride from copper(II) oxide and an
acid.
Diagram 5
(a) What is meant by salt?
[1 mark]
(b) (i) Draw a labeled diagram for step II in the box provided.
[2 marks]
(ii) What is the purpose of carrying out step II?
..
[1 mark]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(c) (i) Name the acid used.
..
[1 mark]
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
..
[1 mark]
(iii) Calculate the maximum mass of the salt formed, when 50cm3 and 1moldm-3 of acid named in c(i) is
used.
[Relative atomic mass of Cu: 64; Cl: 35.5]
[3 marks]
(d) Name another substances that can react with acid named in (c)(i) in order to form copper(II) chloride.
....
[1 mark]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
7. (a) Table 2.1 shows the pH value of two alkali with the same concentration.
Type of alkaline
Ammonia solution
Sodium hydroxide solution
Concentration
0.1moldm-3
0.1moldm-3
pH value
9.0
13.0
Table 2.1
Explain why the pH values of these two alkalis are different.
[4 marks]
(b) Table 2.2 shows the observation when copper(II) oxide reacts with nitric acid in two different solvent X
and Y.
Experiment
I
II
Reaction
Copper(II) oxide reacts with
nitric aicd in solvent X
Copper(II) oxide reacts with
nitric aicd in solvent Y
Observation
No change
-
Black solid dissolves
Colourless solution turns blue
Table 2.2
(i) Suggest solvent X and Y
[2 marks]
(ii) Compare the observation in Experiment I and Experiment II. Explain your answer
and include an ionic equation involved.
[8 marks]
10
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(c) Experiment II in 7(b) is repeated by using same concentration of acid P. It is found that the volume of acid
P required to completely react with copper(II) oxide has reduced to half.
Suggest an acid P and explain your answer.
[4 marks]
(d) Hydrochloric acid is a type of monoprotic acid and it can be prepared by reacting chlorine gas with water.
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between chlorine gas and water.
[1 mark]
(ii) State the observation when the product in d(i) is tested with blue litmus paper.
[1 mark]
11
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
12
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
9.
(a)
The empirical formula of copper(II) oxide can be determined by reduction using
hydrogen gas.
(i)
State two reactants which can be used to produce hydrogen gas to react with
copper(II) oxide.
[1 mark]
(ii)
Write the chemical equation for the production of hydrogen gas using the
reactants stated in (a)(i)
[2 marks]
(iii) Describe how you confirm that hydrogen gas has been produced.
[2 marks]
(b)
A carbon compound X contains 24g of carbon and 5g of hydrogen. The relative
molecular mass of X is 58.
[Relative atomic mass: C=12, H=1]
Find the molecular formula of this compound.
[5 marks]
13
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(c)
14
Describe how you can determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide in the
laboratory. Your description should include:
Chemical equation
Procedure of experiment
Precautionary steps
Tabulation of data
[10 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
10. Diagram 9 shows the apparatus set up of electrolysis.
Carbon
electrode
Y
electrode
Carbon
electrode X
Cell P
Copper
electrode
Zinc
electrode
Copper(II) sulphate solution
Cell Q
Diagram 9
(i)
State the function of Cell Q.
(ii)
Table 4 shows the voltage obtained from voltaic cell using different pair of metal.
Metal pairs
Zinc and copper
Magnesium and copper
Magnesium and zinc
Predict the value a.
15
[1 mark]
Voltage/ V
a
2.6
0.8
Positive terminal
Copper
Copper
Zinc
[1 mark]
(iii)
State the anode for both Cell P and Cell Q. Explain the reaction occurred at anode of Cell P and
Cell Q.
Your answer should include the following aspects:
Half equation
Observation
[6 marks]
(iv)
Change of electrolyte in Cell P and Cell Q is the same. State the observation and explain your
answer.
[2 marks]
REVISION FOR YEAR END EXAMINATION
(v)
Describe an experiment to construct a simple voltaic cell if you are given magnesium plate,
silver plate and dilute sulphuric acid.
Your answer should include of the following:
List of material and apparatus
Procedures
Half equation
Observation
[10 marks]
16
Você também pode gostar
- Chemistry Form 4-Paper 2Documento19 páginasChemistry Form 4-Paper 2adikmuk50% (2)
- Science Form 3 July TestDocumento7 páginasScience Form 3 July TestNorafiza Hashim100% (1)
- RCD Beam Analysis and DesignDocumento33 páginasRCD Beam Analysis and DesignJayChristian Quimson50% (12)
- Awwa C115 - A2c115 (1999)Documento23 páginasAwwa C115 - A2c115 (1999)kumarvizayin100% (1)
- Chemical reactions and propertiesDocumento14 páginasChemical reactions and propertiesHan LingAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDocumento49 páginasSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 Kim F4-AdahDocumento16 páginasPaper 2 Kim F4-AdahNOR ATIKAH BINTI TAKRUDDIN MoeAinda não há avaliações
- SOALANnnDocumento13 páginasSOALANnnKeertanaAinda não há avaliações
- Form Four Revision on Chemistry Section A QuestionsDocumento17 páginasForm Four Revision on Chemistry Section A Questionspatkhsheng@hotmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerDocumento36 páginasUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- spm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Documento14 páginasspm2003p2 120131100349 Phpapp01Suriati Bt A RashidAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 4 Quiz AnswerDocumento8 páginasChemistry Form 4 Quiz Answerkhangsiean89Ainda não há avaliações
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Documento16 páginasSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- The Periodic Table of Elements ExplainedDocumento5 páginasThe Periodic Table of Elements Explained301 Dhia JaharahAinda não há avaliações
- 2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Documento15 páginas2018f5s9ex4chemistry 2Nicholson NicholsonAinda não há avaliações
- Revision - Chem - F4 Chapter 1-4Documento8 páginasRevision - Chem - F4 Chapter 1-4HaziraAzlyAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Intensive Revision Program Set 2 QuestionsDocumento22 páginasChemistry Intensive Revision Program Set 2 QuestionsrajaAinda não há avaliações
- Panduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaDocumento12 páginasPanduan & Teknik Menjawab Kimia Yang Berkesan: Program Perfect Score SPM Sekolah Menengah Negeri MelakaChew Boon WeiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocumento12 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiEmily VinciAinda não há avaliações
- Form 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberDocumento8 páginasForm 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberAzie Nurul AkhtarAinda não há avaliações
- Topical Test Chapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDocumento3 páginasTopical Test Chapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoeAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Documento13 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgAinda não há avaliações
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMDocumento32 páginasUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMMThana BalanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2Documento8 páginasChemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2andrew silungweAinda não há avaliações
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Documento15 páginasLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Farah Aisyah AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Projek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Documento9 páginasProjek Skor Kimia 2014 Siri 3Zul BaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 1 BK2-Intervensi Aras 1: RendahDocumento36 páginasModul 1 BK2-Intervensi Aras 1: RendahijaAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesDocumento14 páginasSPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesTee Xin Rui50% (2)
- Chemistry Form 5 DoneDocumento7 páginasChemistry Form 5 DoneTee Xin RuiAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMISTRY FORM 3 PAPER II EXAMDocumento5 páginasCHEMISTRY FORM 3 PAPER II EXAMHomok NokiAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Documento19 páginasSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Aras RendahDocumento35 páginasModul Aras RendahNurul Hasmah HarunAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionDocumento32 páginasElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 5070 End of YearDocumento7 páginasChemistry 5070 End of Yearsamuelbandamiracle20Ainda não há avaliações
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Documento27 páginasStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Selaras Kimia4 2010Documento3 páginasSelaras Kimia4 2010ida_komeAinda não há avaliações
- KIMIA Paper 2Documento23 páginasKIMIA Paper 2Fadzil RashidAinda não há avaliações
- Chem F2Documento8 páginasChem F2Festus NanokAinda não há avaliações
- Form 3 Chemistry End Term Exam - March 2016 Time: 2 HoursDocumento12 páginasForm 3 Chemistry End Term Exam - March 2016 Time: 2 HoursKevin NdanyiAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Structure and Chemical BondsDocumento19 páginasAtomic Structure and Chemical BondsRaymond Cheang Chee-CheongAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Documento9 páginasSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangAinda não há avaliações
- STPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2Documento13 páginasSTPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (1)
- 2013 ChemistryDocumento13 páginas2013 ChemistryGaneshwaran KumaresenAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Documento14 páginasFinal Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Norzilah MazaharAinda não há avaliações
- Sns Paper 2 KimiaDocumento16 páginasSns Paper 2 KimiaDuong Han CalebAinda não há avaliações
- (60 Marks) (60 Markah) Answer All Questions in This Section. 1Documento5 páginas(60 Marks) (60 Markah) Answer All Questions in This Section. 1LELA RELAZIMAHAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Kimia f4Documento6 páginasRevision Kimia f4Abdul ManafAinda não há avaliações
- pg10 12Documento3 páginaspg10 12Melor DihatiAinda não há avaliações
- Air Composition and RespirationDocumento9 páginasAir Composition and RespirationAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocumento12 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiSakinah Saad100% (3)
- Chemistry Test 2Documento2 páginasChemistry Test 2Daniel Ngenokesho WandyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Chemical in IndustryDocumento8 páginasChapter 8 Chemical in IndustryADY2022Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsDocumento16 páginasScience Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsLouis Lim0% (1)
- SPM 2013 Chemistry Paper 2 ReviewDocumento17 páginasSPM 2013 Chemistry Paper 2 ReviewMohamad Fazdir SallehAinda não há avaliações
- CHE Perlis Modul Juss ADocumento162 páginasCHE Perlis Modul Juss ALim Wai Wai SmktpAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, CDocumento45 páginasChapter 2: Matter: Temperature, CsookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 4-1 Introduction To ChemistryDocumento2 páginas4-1 Introduction To ChemistrysookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 0653 s06 Ms 3Documento10 páginas0653 s06 Ms 3sookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 Chemistry Example Candidate Responses Booklet 2012Documento158 páginas0620 Chemistry Example Candidate Responses Booklet 2012sookchin100% (2)
- 0620 m15 Ms 22Documento6 páginas0620 m15 Ms 22sookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Specimen Paper 2 PDFDocumento18 páginas2016 Specimen Paper 2 PDFPepz SupitchaAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE 2016 Specimen Paper 6Documento12 páginasIGCSE 2016 Specimen Paper 6ashathtAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 Y16 SP 4Documento20 páginas0620 Y16 SP 4sookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 Y16 SM 2 PDFDocumento2 páginas0620 Y16 SM 2 PDFsookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFDocumento4 páginas0620 Y16 SM 6 PDFsookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocumento6 páginas2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemelolismAinda não há avaliações
- 2.0 Experimental TechniquesDocumento4 páginas2.0 Experimental TechniquessookchinAinda não há avaliações
- 2.0 Experimental TechniquesDocumento4 páginas2.0 Experimental TechniquessookchinAinda não há avaliações
- List of notifications prepared as of 22 March 2018Documento13 páginasList of notifications prepared as of 22 March 2018Anonymous F1xtU2RAinda não há avaliações
- Alkali-Activated Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers With Zeolite or BentoniteDocumento7 páginasAlkali-Activated Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers With Zeolite or BentoniteSo Thu DaiAinda não há avaliações
- Training Overview: Presented by Akash KarpeDocumento22 páginasTraining Overview: Presented by Akash KarpeMukesh Kumar VaishnavAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Chemicals for the Polyurethane IndustryDocumento8 páginasPerformance Chemicals for the Polyurethane IndustrySiriluck NevestAinda não há avaliações
- NTA ABHYAS I P-Block Elements I VERMA SIRDocumento5 páginasNTA ABHYAS I P-Block Elements I VERMA SIRarslaan8799Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Manufacturing Question SampleDocumento2 páginasAdvanced Manufacturing Question SampleBakul RoyAinda não há avaliações
- UTP A 8051 Ti: ClassificationsDocumento1 páginaUTP A 8051 Ti: ClassificationsGustavo OrozcoAinda não há avaliações
- Aspen Aerogel Pyrogel XT-DSDocumento2 páginasAspen Aerogel Pyrogel XT-DSkflimAinda não há avaliações
- 21.coordination Compound, D & F Block Transition ElementsDocumento21 páginas21.coordination Compound, D & F Block Transition ElementsQwerty100% (1)
- Drainage Pump 50HzDocumento20 páginasDrainage Pump 50HzashishkkrAinda não há avaliações
- Investment Casting Process and ApplicationsDocumento28 páginasInvestment Casting Process and ApplicationsKristin Louise Agbulos100% (1)
- Wash Care Label RequirementsDocumento11 páginasWash Care Label Requirementsnishkarsh mauryaAinda não há avaliações
- General Chemistry NotesDocumento7 páginasGeneral Chemistry Notesdeveravanessa01Ainda não há avaliações
- The Book of Random Tables Science Fiction 2Documento48 páginasThe Book of Random Tables Science Fiction 2xihoxam66475% (4)
- Basement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckDocumento3 páginasBasement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckPhanithAinda não há avaliações
- Lesoon Equipment Catalogue 2015Documento28 páginasLesoon Equipment Catalogue 2015Jason PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Parameters For Hyperbolic Model of SoilsDocumento13 páginasDetermination of Parameters For Hyperbolic Model of SoilsRamiro ChairezAinda não há avaliações
- On-Site Electrolytic Chlorination Skid-Mounted OSEC B-Pak SystemDocumento4 páginasOn-Site Electrolytic Chlorination Skid-Mounted OSEC B-Pak SystemgohviccAinda não há avaliações
- Power Infrastructure - 170220 LowDocumento25 páginasPower Infrastructure - 170220 LowrajamasaAinda não há avaliações
- Metals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetDocumento5 páginasMetals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetHappy NthakomwaAinda não há avaliações
- Urban Ae Paper - 20669792 - 2023 - 07 - 28 - 16 - 48Documento14 páginasUrban Ae Paper - 20669792 - 2023 - 07 - 28 - 16 - 48Rabi DasAinda não há avaliações
- 2022faoziah J.il - Tan.LinkDocumento6 páginas2022faoziah J.il - Tan.LinkHuáng GuozhiAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Issues in Materials Processing: Yogesh JaluriaDocumento14 páginasThermal Issues in Materials Processing: Yogesh JaluriarahulAinda não há avaliações
- Process Scheme Mechanical & Electrical Equipments & Guidlines For DesignDocumento24 páginasProcess Scheme Mechanical & Electrical Equipments & Guidlines For DesignPravin BoteAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Vitae: I Personal DataDocumento10 páginasCurriculum Vitae: I Personal DataRachmat SirojudinAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Slipforming: A Cost-Effective Formwork TechniqueDocumento117 páginasConcrete Slipforming: A Cost-Effective Formwork Techniqueparamarthasom1974Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 Concrete Works CompuDocumento14 páginas2 Concrete Works CompuALFONSO RAPHAEL SIAAinda não há avaliações
- Wrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll OnDocumento3 páginasWrb-Air Barrier - Parex Usa Weatherseal Spray and Roll Onsaffronbuilders9Ainda não há avaliações