Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Volcano Guided Notes
Enviado por
api-330490538Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Volcano Guided Notes
Enviado por
api-330490538Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
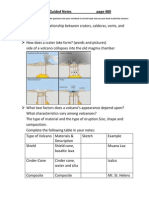
What is the relationship between craters, calderas,
vents, and magma?
Lava erupts through an opening in the crust called a
vent, around the vent is a bowl-shaped depression
called a crater, large depressions are called calderas,
magma flows through the volcano and comes out of
the peak as lava.
How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures)
When the summit or the side of a volcano collapses
into the magma chamber that once fueled the
volcano, thats how Crater Lake was formed.
What two factors does a volcanos appearance
depend upon? What characteristics vary among
volcanoes?
The type of material that forms the volcano and the
type of eruptions that occur.
Complete the following table in your notes:
Type of
Volcano
Shield
Materials &
Description
Forms when
layers build
up during
nonexplosive
volcanic
eruptions
Cinder-Cone
Material is
Sketch
Example
Mauna Loa
Izalco
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
ejected into
the air, falls
back onto the
earth, and
gathers
around the
vents
Composite
Layers of
(Stratovolcano volcanic
)
fragments
and lava
Mt. St.
Helens
How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and
slope?
Shield is the largest; gentler slopes; straight
Cinder-Cone is the smallest; steeper slopes; caved
What factors cause differences in size and slope?
The differences in size and slope are caused by the
eruptions, when the lava hardens it builds up the
volcano.
What is tephra?
Fragments of rock thats ejected in the air during an
eruption.
What is a pyroclastic flow?
The movement of volcanic material.
Where are most volcanoes found?
Volcanoes are found at plate boundaries
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific
Belt and the Mediterranean Belt where convergent
volcanism occur and (2) the Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic
Chain.
How do hotspots form?
When the mantle is hotter than normal
What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates?
Volcanoes form as a plate moves over a hotspot
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
Você também pode gostar
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesNo EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento5 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330464848Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento5 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050027Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento5 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050095Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento4 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049909Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento2 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264220672Ainda não há avaliações
- Volcanoes NotesDocumento4 páginasVolcanoes Notesapi-264874516Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento4 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330042011Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1Documento4 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1api-330067833Ainda não há avaliações
- Voolcanoes Guided NotesDocumento3 páginasVoolcanoes Guided Notesapi-264885511Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of VolcanoesDocumento3 páginasTypes of Volcanoesapi-265544103Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento3 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264099976Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento3 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264090670Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento5 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049903Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento4 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330102217Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento5 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330092916Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocumento4 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330085018Ainda não há avaliações
- Byjus Com Physics Types of VolcanoesDocumento6 páginasByjus Com Physics Types of VolcanoesEren YeagerAinda não há avaliações
- Australian volcano guideDocumento14 páginasAustralian volcano guideTulika ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano Term PaperDocumento6 páginasVolcano Term Paperafmzmajcevielt100% (1)
- VOLCANOESDocumento10 páginasVOLCANOESYesha ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualDocumento11 páginasEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (32)
- Volcanic EruptionsDocumento7 páginasVolcanic EruptionsmusicatworkAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Main Types of VolcanoesDocumento1 página4 Main Types of VolcanoesbjmandiaAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano WebquestDocumento3 páginasVolcano WebquestRichard Muchow100% (1)
- Quarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESDocumento39 páginasQuarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESRubeliza LawengAinda não há avaliações
- Six Types of Volcanoes ClassifiedDocumento3 páginasSix Types of Volcanoes ClassifiedBenes Salamanca BolascoAinda não há avaliações
- Science Power PointDocumento18 páginasScience Power PointpatriciangbenaohanAinda não há avaliações
- Mary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateDocumento11 páginasMary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateMary DruryAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano WorksheetDocumento1 páginaVolcano WorksheetJavier100% (1)
- Term Paper On VolcanoesDocumento9 páginasTerm Paper On Volcanoesea6mkqw2100% (1)
- Wonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaNo EverandWonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaAinda não há avaliações
- Unlocking Volcano SecretsDocumento4 páginasUnlocking Volcano SecretsRiaAinda não há avaliações
- Earth's Structure in 40 CharactersDocumento56 páginasEarth's Structure in 40 CharactersTHE HATE FARMERAinda não há avaliações
- Types of VolcanoesDocumento21 páginasTypes of VolcanoesAgaManlapazMacasaquitAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Volcanoes Based On StructureDocumento48 páginasTypes of Volcanoes Based On StructureJhayAinda não há avaliações
- Prepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber HussienDocumento127 páginasPrepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber Hussienmalakelghamry743Ainda não há avaliações
- VolcanoesDocumento75 páginasVolcanoesMeleen ConstantinoAinda não há avaliações
- The Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo EverandThe Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceAinda não há avaliações
- Volcanoes: Openings that allow hot magma to escapeDocumento84 páginasVolcanoes: Openings that allow hot magma to escapeJM LomoljoAinda não há avaliações
- Science VolcanoDocumento48 páginasScience Volcanojosemaria tabliganAinda não há avaliações
- P PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"Documento4 páginasP PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"bpmojapeloAinda não há avaliações
- HGGGGDocumento8 páginasHGGGGBea Ashley VosotrosAinda não há avaliações
- G9 Science Q3 Week 1 Volcanoes 1Documento49 páginasG9 Science Q3 Week 1 Volcanoes 1Mark Joseph AndresAinda não há avaliações
- Mountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsNo EverandMountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsAinda não há avaliações
- VolcanoDocumento78 páginasVolcanoGen BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano Features & TypesDocumento8 páginasVolcano Features & TypesShah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Types of VolcanoesDocumento26 páginasTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalAinda não há avaliações
- Everything You Need to Know About VolcanoesDocumento6 páginasEverything You Need to Know About VolcanoesRoger Corre RivaAinda não há avaliações
- Competency 9 Ay 2023 2024Documento18 páginasCompetency 9 Ay 2023 2024chaibalinAinda não há avaliações
- VolcanoDocumento3 páginasVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganAinda não há avaliações
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDocumento83 páginasVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Volcanic LandformDocumento12 páginasVolcanic LandformJoseph ZotooAinda não há avaliações
- Science9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleDocumento18 páginasScience9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleGrace OroAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano - Parts, Types, EruptionDocumento33 páginasVolcano - Parts, Types, EruptionenriquezryzellaAinda não há avaliações
- lecturemodule1-2volcanoq3G9Documento4 páginaslecturemodule1-2volcanoq3G9John Carlo MiclatAinda não há avaliações
- VOLCANOESDocumento65 páginasVOLCANOESPrincess Alyssa BarawidAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable Energy Look at Notes On WebsiteDocumento1 páginaRenewable Energy Look at Notes On Websiteapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Climate Change WebquestDocumento3 páginasClimate Change Webquestapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Wastewater Treatment ActivityDocumento3 páginasWastewater Treatment Activityapi-330050095Ainda não há avaliações
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocumento2 páginasAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264228415100% (1)
- Climate NotesDocumento2 páginasClimate Notesapi-264874516Ainda não há avaliações
- Freshwater Pollution Guided NotesDocumento3 páginasFreshwater Pollution Guided Notesapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Climate NotesDocumento2 páginasClimate Notesapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Alien InvadersDocumento2 páginasAlien Invadersapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Water Cycle WebquestDocumento6 páginasWater Cycle Webquestapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Watersheds and River Basin ActivityDocumento3 páginasWatersheds and River Basin Activityapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Meatrix QuestionsDocumento2 páginasMeatrix Questionsapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 "Waste" Notes-Guiding QuestionsDocumento3 páginasChapter 12 "Waste" Notes-Guiding Questionsapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Coastal Protection ManagementDocumento3 páginasCoastal Protection Managementapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is MiningDocumento1 páginaWhat Is Miningapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Tsunami Hazard Worksheet/CGSDocumento5 páginasTsunami Hazard Worksheet/CGSapi-3304905380% (1)
- Foresty Guided NotesDocumento1 páginaForesty Guided Notesapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocumento3 páginasEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Tsunami NotesDocumento2 páginasTsunami Notesapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- Yellowstone SupervolcanoDocumento1 páginaYellowstone Supervolcanoapi-330490538Ainda não há avaliações
- PlateTectonics PDFDocumento35 páginasPlateTectonics PDFJhon JipcAinda não há avaliações
- Origin and Structure of Earth's SpheresDocumento4 páginasOrigin and Structure of Earth's SpheresCazandraShynne RabinoAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of The EarthquakeDocumento23 páginasParts of The EarthquakeIan ELAinda não há avaliações
- 1.introduction To Engg. Geology & SeismologyDocumento32 páginas1.introduction To Engg. Geology & SeismologyZindai WazirAinda não há avaliações
- Geography guide to earth's interior, processes, and climateDocumento15 páginasGeography guide to earth's interior, processes, and climatemotu179Ainda não há avaliações
- Sea-Floor SpreadingDocumento63 páginasSea-Floor SpreadingMyyo TabunoAinda não há avaliações
- Mahanjane - 2012 - A Geotectonic History of The Northern Mozambique Basin Including The BeiraDocumento12 páginasMahanjane - 2012 - A Geotectonic History of The Northern Mozambique Basin Including The BeiraShelton UamusseAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Quiz Bee ReviewerDocumento17 páginasScience 10 Quiz Bee ReviewerChynna Mei A. BongalosAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Module in Science 10: The Science of Plate Tectonics and Disaster PreparednessDocumento18 páginasLearning Module in Science 10: The Science of Plate Tectonics and Disaster PreparednessChekahay ni 'Cher Ojie ug 'Cher Alven DiazAinda não há avaliações
- ES 2nd Quarter Week 7 Rock Behaviors Under Stress PDFDocumento25 páginasES 2nd Quarter Week 7 Rock Behaviors Under Stress PDFNoval, Christine Joy T.Ainda não há avaliações
- Petrology - New Perspectives and ApplicationsDocumento236 páginasPetrology - New Perspectives and ApplicationsKuncoro Yw50% (2)
- The Geosphere: Layers, Tectonic Plates and Relief StructuresDocumento13 páginasThe Geosphere: Layers, Tectonic Plates and Relief StructuresMarieta DomínguezAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science Mod 10Documento13 páginasEarth and Life Science Mod 10Jonna RizaAinda não há avaliações
- Objectives: Internal Heat of The EarthDocumento5 páginasObjectives: Internal Heat of The EarthLeslie Ann Pobeda RoceroAinda não há avaliações
- Mantle Convection Pamhplet For Ghianne ErfeDocumento2 páginasMantle Convection Pamhplet For Ghianne ErfePATRICIA ANGELICA VINUYA100% (1)
- The Evolution of Ocean BasinDocumento4 páginasThe Evolution of Ocean BasinJun Gabriel BornalesAinda não há avaliações
- Sulu Sea BasinDocumento15 páginasSulu Sea Basinafterc82Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hellenides A Complicated, Multiphase Deformed Alpine Orogenic Belt - Compression Vs Extension, The Dynamic Peer For The Orogen Making 18 - KiliasDocumento5 páginasThe Hellenides A Complicated, Multiphase Deformed Alpine Orogenic Belt - Compression Vs Extension, The Dynamic Peer For The Orogen Making 18 - KiliasDimitrios KostopoulosAinda não há avaliações
- Activity-4 2Documento5 páginasActivity-4 2Gidion GinoyAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Structure of The Earth and LithosphereDocumento16 páginasInternal Structure of The Earth and LithosphereMangam RajkumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Adam and Eve StoryDocumento43 páginasThe Adam and Eve StoryYori DamiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy OAEDocumento38 páginasAnatomy OAEscweemeraweertAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!VOLCANOESDocumento46 páginasSCIENCE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!VOLCANOESlicarl benitoAinda não há avaliações
- Allen, Et Al., (2015)Documento24 páginasAllen, Et Al., (2015)chris17tianAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Magnetic Reversal?: Wegener Had GuessedDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Magnetic Reversal?: Wegener Had GuessedLhaika Maureen CasisAinda não há avaliações
- Rock Cycle QuizDocumento2 páginasRock Cycle QuizKizzi Kye Edelweiss BalmoresAinda não há avaliações
- Geology For Engineers (Week 1,2,3)Documento24 páginasGeology For Engineers (Week 1,2,3)kimberlyjoyregaladoAinda não há avaliações
- EAL Q1-Module 10 Plates, Folds, Faults STRESS - RemovedDocumento20 páginasEAL Q1-Module 10 Plates, Folds, Faults STRESS - RemovedJohn Partrick PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Asad Seismic Zones of PakistanDocumento5 páginasAsad Seismic Zones of PakistanM Baqir IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- 3D MT Spain Weerachai CodeDocumento5 páginas3D MT Spain Weerachai CodegpsglonassAinda não há avaliações