Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cell Modifications That Lead To Adaptation
Enviado por
John Barry IbanezDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cell Modifications That Lead To Adaptation
Enviado por
John Barry IbanezDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
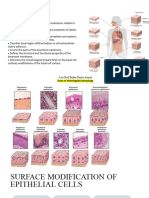
CELL MODIFICATIONS THAT LEAD TO
ADAPTATION
Kinds of Cell Modifications
APICAL MODIFICATIONS (top)
BASAL MODIFICATIONS (bottom)
LATERAL MODIFICATIONS (sides)
APICAL MODIFICATIONS
Hemidesmosome
protein filaments interlock with filaments of
the adjacent cell which forms a dense
intermediate line between the cells
found beneath the zonula adherens
cytoplasmic
face
is
connected
to
microfilaments extending into the cytoplasm
LATERAL MODIFICATIONS
Tight Junctions (Zonula Occludens)
Microvilli
a band near the apical surface forms a seal,
also called brush/striated border
appearing to be fused
finger-like cytoplasmic extensions of the
there is 15-20 nm space between epithelium
apical surface which increase surface area for
cells
absorption
tight junction occludes/separates the
numerous, often regularly arranged, and
compartments
found in absorptive epithelia
Adhering
Junctions (Zonula Adherens)
Cilia
the actin filaments which make up zonula
motile, function in movement
adherens maintain integrity of the cell to
beats in a coordinated rhythmical wave-like
better bind
manner, promoting movement of materials
found just beneath the tight junction
over the surface
cytoplasmic
face
is
linked
to
appear as short hair-like structures or
the actin cytoskeleton
projections
Gap
Junctions
each cilium is connected to a basal body and
connexons of one membrane aligns with
extends from the free surface
connexon of adjacent membrane so that
core is composed of microtubules arranged
hydrophilic material can be transported
in a specific manner
important in cell communication
can be found in the lining of the trachea
adjacent cells are 2-3 nm apart
(windpipe) or in the Fallopian tube
Desmosome (Macula Adherens)
Stereocilia
protein filaments interlock with filaments of
long microvilli that function in increasing
the adjacent cell which forms a dense
absorption
intermediate line between the cells
non-motile
help to resist shearing forces and are found
found in sensory cells in ear and male
in simple and stratified squamous epithelium
reproductive tract
does not have the true characteristic of the
SPECIALIZED MODIFICATIONS
true cilia or flagella
Nerve cells, or neurons are very specialized
Flagella
cells of the nervous system. Since an electrical
are also concerned with movement
signal needs to travel relatively long distances
same axial structure with cilia but much
to parts of the body, nerve cells have
longer
specialized structures called dendrites, which
present in the tail of the spermatozoa
receive an electrical signal from another
BASAL MODIFICATIONS
neuron, and axons, which transmit an
electrical signal to another neuron.
Basal Infoldings
Muscle cells are made up primarily of a pair of
often found in epithelium that are known to
special proteins called actin and myosin which
transport fluid (kidney)
allows the muscle to contract.
will often see mitochondria in the basal
Red blood cells are anucleate, and thus are
infoldings; suggests that active transport is
produced from bone marrow, but contain large
occurring
amounts of hemoglobin to transport oxygen
very important in epithelial polarization and
throughout the body.
stability
Sperm cells are haploid and contain a
support the epithelium and also functions as
flagellum in order to swim through the vagina.
a passive molecular sieve or ultrafilter
Plant cells have large amounts of the organelle
if basal lamina is destroyed (trauma,
chloroplast, which allows the cell to undergo
infections, burns), the epithelium will not be
photosynthesis. Plant cells are also covered by
repaired but substituted with a scar
a cell wall.
(connective tissue)
Você também pode gostar
- Cell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationDocumento1 páginaCell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationChris EismaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M4Documento15 páginasBiology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M4Hera VictrixAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcDocumento34 páginasChapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcCristel BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocumento44 páginasMechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsEvangelene Esquillo SanaAinda não há avaliações
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasDocumento2 páginasCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals GasJohn Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocumento18 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- General Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GDocumento6 páginasGeneral Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GJackylyn Evangelista100% (2)
- Lesson 1 - Cell TheoryDocumento26 páginasLesson 1 - Cell TheoryJoy's Faith Marata100% (2)
- 5.transport MechanismDocumento10 páginas5.transport Mechanismdiane recintoAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesDocumento5 páginasGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesJohn Brylle UrsuaAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1 NotesDocumento4 páginasGeneral Biology 1 NotesKrisha GatocAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Documento24 páginasModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- GB2 11 q3 Mo5 wk5 Unique Characteristics of Specific Taxon Relative To Other Taxa Phylis Langakan BGDocumento22 páginasGB2 11 q3 Mo5 wk5 Unique Characteristics of Specific Taxon Relative To Other Taxa Phylis Langakan BGDustin AgsaludAinda não há avaliações
- Module 11 Calvin CycleDocumento14 páginasModule 11 Calvin CycleCandice LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Types & Cell ModificationDocumento41 páginasCell Types & Cell ModificationShane Marcande Calicdan78% (18)
- Basic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationDocumento28 páginasBasic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationKaela Sophia AndalisAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Documento23 páginasGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenAinda não há avaliações
- Bio 1 Module 4Documento8 páginasBio 1 Module 4yhajj jamesAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Documento20 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Pril Gueta100% (2)
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocumento39 páginasChemical and Nervous ControlElizabeth Alvear100% (1)
- Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDocumento23 páginasDevelopment of Evolutionary ThoughtCrow HoganAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology Q4 M7Documento19 páginasGeneral Biology Q4 M7Mubin AbdulkarilAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3: Cell Modifications: General Biology 1Documento3 páginasWeek 3: Cell Modifications: General Biology 1Florene Bhon GumapacAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleDocumento11 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleAron Chua FababeirAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocumento6 páginasGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Module 3Documento21 páginasBiology Module 3Joemmel MagnayeAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 2 - AngieDocumento9 páginasGeneral Biology 2 - AngiePrincess Mejarito MahilomAinda não há avaliações
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2Documento21 páginasSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2James Aringo100% (1)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Documento17 páginasSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- UNIT I (Cell - Transport Mechanisms)Documento20 páginasUNIT I (Cell - Transport Mechanisms)Rex Daniel Tingson100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Learning Activity Sheet: Cell ModificationsDocumento15 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Learning Activity Sheet: Cell ModificationsKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Documento6 páginasGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - Module 1Documento11 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - Module 1Regine Ann ViloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient Procurement and ProcessingDocumento62 páginasNutrient Procurement and ProcessingClara Mae100% (2)
- Cell ModificationDocumento28 páginasCell ModificationIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 General Biology 1 - IntroductionDocumento6 páginas1 General Biology 1 - IntroductionKay JusonAinda não há avaliações
- Energy TransformationDocumento28 páginasEnergy Transformationmaria genioAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTDocumento21 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTJean Raziel MantesAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Key Card Gen Bio 1 Quarter 2 Module 1 For PostingDocumento3 páginasAnswer Key Card Gen Bio 1 Quarter 2 Module 1 For PostingKarl Patrick Pacheco50% (4)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 1 - Cell TheoryDocumento22 páginasSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 1 - Cell TheoryEmer PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Study This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Documento70 páginasStudy This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Rose MendizabalAinda não há avaliações
- Cladogram CH 19 Part ADocumento3 páginasCladogram CH 19 Part AJasmine lee100% (1)
- (PDF) GenBio2 Module Week04Documento26 páginas(PDF) GenBio2 Module Week04Ramon VillotaAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 2 - 4QT - Week 1 4editedDocumento69 páginasGeneral Biology 2 - 4QT - Week 1 4editedJanel FloresAinda não há avaliações
- GENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemDocumento15 páginasGENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemBea Bayona JoloAinda não há avaliações
- GENBIO1 - MOD5 - Q1 - Cell Modifications What Fits In.Documento23 páginasGENBIO1 - MOD5 - Q1 - Cell Modifications What Fits In.Ennyliejor YusayAinda não há avaliações
- PLANTS and AnimalS Development and NutritionDocumento64 páginasPLANTS and AnimalS Development and NutritionRhyian Arma100% (2)
- DISORDERS AND DISEASES CELL CYCLE - EllaDocumento9 páginasDISORDERS AND DISEASES CELL CYCLE - EllaKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- Chlorophyll and Other PigmentsDocumento19 páginasChlorophyll and Other PigmentsMeghan Old67% (3)
- General Biology1 - Q1 - Module 15 - Oxidation-and-Reduction-ReactionsDocumento18 páginasGeneral Biology1 - Q1 - Module 15 - Oxidation-and-Reduction-ReactionsSyrine Myles Sullivan0% (2)
- General Biology ModuleDocumento16 páginasGeneral Biology ModuleKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- Cell Cycle ModuleDocumento28 páginasCell Cycle ModuleDuaneAinda não há avaliações
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 3 Module 5 - Cell ModificationDocumento16 páginasSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 3 Module 5 - Cell ModificationEmer Perez100% (3)
- Grade 12: Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationships: Cladistics and PhylogenyDocumento14 páginasGrade 12: Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationships: Cladistics and PhylogenyDrew MalubagAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 1 Gen Bio 2 PDFDocumento4 páginasMODULE 1 Gen Bio 2 PDFEzekielAinda não há avaliações
- 2ND QTR MODULE 1-StudentsDocumento12 páginas2ND QTR MODULE 1-StudentsDimple MontemayorAinda não há avaliações
- Sir FayyazDocumento49 páginasSir FayyazSara ZaraAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1: Cell TypesDocumento4 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Cell TypesClauriz Keith Ashley SanicoAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Basal Lateral Apical Modifications and Connective TissueDocumento84 páginas2 Basal Lateral Apical Modifications and Connective TissueDeniz asmazAinda não há avaliações
- All Document Reader 1713202404640Documento34 páginasAll Document Reader 1713202404640kanyangakapusu72Ainda não há avaliações
- EAP Group CompilationDocumento5 páginasEAP Group CompilationJohn Barry Ibanez100% (4)
- Properties of SolutionsDocumento33 páginasProperties of SolutionsJohn Barry Ibanez100% (2)
- Qualitative Research MethodsDocumento3 páginasQualitative Research MethodsJohn Barry IbanezAinda não há avaliações
- CellsDocumento1 páginaCellsJohn Barry IbanezAinda não há avaliações
- Earthquake Preparedness: Before During and After An EarthquakeDocumento2 páginasEarthquake Preparedness: Before During and After An EarthquakeJohn Barry IbanezAinda não há avaliações
- Embriologi Organ Genital Dan Sistim Reproduksi Wanita Dan Payudara - DR SilphiaDocumento18 páginasEmbriologi Organ Genital Dan Sistim Reproduksi Wanita Dan Payudara - DR SilphiaSamuel SiagianAinda não há avaliações
- PEC28 Formaldehyde 153 393Documento241 páginasPEC28 Formaldehyde 153 393Nouhaila YahdihAinda não há avaliações
- 01-Paper 2 Biology O LevelDocumento2.829 páginas01-Paper 2 Biology O LevelP ElgamalAinda não há avaliações
- Teens 4 Paper 1Documento3 páginasTeens 4 Paper 1English Training Studio -ETSAinda não há avaliações
- Tomato BreedingDocumento12 páginasTomato BreedingYASHPAL SINGH100% (2)
- Genetic Manipulation of Host PlantDocumento15 páginasGenetic Manipulation of Host PlantDeza Grace Lobigas GerelingoAinda não há avaliações
- I. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyDocumento94 páginasI. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyAradani Ongchi Frena100% (1)
- Clinical BacteriologyDocumento123 páginasClinical Bacteriologykurotsukki todoroki100% (1)
- EMBO Short-Term Fellowships: Application GuidelinesDocumento15 páginasEMBO Short-Term Fellowships: Application GuidelinesFernando Fernández GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocumento6 páginasDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Cell Division GizmoDocumento3 páginasCell Division Gizmoapi-522847737Ainda não há avaliações
- TaqMan Gene Expression Assay ProtocolDocumento69 páginasTaqMan Gene Expression Assay ProtocolsamarqandiAinda não há avaliações
- (BOTAFUN) Life From LightDocumento2 páginas(BOTAFUN) Life From LightBen Joshua MancileAinda não há avaliações
- The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Documento9 páginasThe Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Chloe Miel Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Structure Prediction Final ReportDocumento27 páginasProtein Structure Prediction Final ReportNithiyaraj VAinda não há avaliações
- Tuesday, October 13, 2020 Tuesday: HolidayDocumento9 páginasTuesday, October 13, 2020 Tuesday: HolidayMemoona GullAinda não há avaliações
- Material Inglés Grado 10Documento7 páginasMaterial Inglés Grado 10Isabella Acevedo SierraAinda não há avaliações
- Munchkin Cat: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocumento6 páginasMunchkin Cat: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFullsun LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Genome MappingDocumento22 páginasGenome MappingVarshika SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Examination in BIOLOGY I. Multiple ChoiceDocumento6 páginasMidterm Examination in BIOLOGY I. Multiple ChoiceMa.Janice GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Straight Is To Gay As Family Is To No FamilyDocumento4 páginasStraight Is To Gay As Family Is To No FamilyPreesha ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Prevalence and Characterization of Shiga Toxin O157 H7 and Non O157 H7 Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli Isolated From Different SourcesDocumento10 páginasPrevalence and Characterization of Shiga Toxin O157 H7 and Non O157 H7 Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli Isolated From Different SourcesSABA YOUNASAinda não há avaliações
- In Vitro Models of Bone Remodelling and Associated DisordersDocumento22 páginasIn Vitro Models of Bone Remodelling and Associated DisordersedricAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsDocumento13 páginasTest Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsJohn Rigby100% (32)
- Form 2.1 (Temporary) Monthly Barangay Consolidated Monitoring Report On Outcome and Output IndicatorsDocumento3 páginasForm 2.1 (Temporary) Monthly Barangay Consolidated Monitoring Report On Outcome and Output Indicatorsmariegold mortola fabelaAinda não há avaliações
- Medicinal Biochemistry 1st Pharm D Quistion BankDocumento7 páginasMedicinal Biochemistry 1st Pharm D Quistion BankAnanda Vijayasarathy0% (1)
- 20 Mechanisms of Injuries (MOI) : How COVID - 19 Injections Can Make You Sick... Even Kill YouDocumento24 páginas20 Mechanisms of Injuries (MOI) : How COVID - 19 Injections Can Make You Sick... Even Kill YouEphrayim Odor100% (1)
- Monoclonal Antibody ProductionDocumento18 páginasMonoclonal Antibody ProductionNina TrươngAinda não há avaliações
- RECEPTORS Sexl MorigglDocumento45 páginasRECEPTORS Sexl Morigglabhishek talokarAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Informatics: Assignment No 03Documento3 páginasBio Informatics: Assignment No 03rafiullahAinda não há avaliações
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNo EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (517)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNo EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (18)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNo EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (52)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNo EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (393)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNo EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (812)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNo EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNo EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeAinda não há avaliações
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNo EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (66)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNo EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNo EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (216)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNo EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorAinda não há avaliações
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindNo EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (93)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)No EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (411)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNo EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignNo EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (39)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNo EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNo EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (115)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNo EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperNo EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (16)