Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Plants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall Phagocytic
Enviado por
Hara Prasad Mohapatra0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
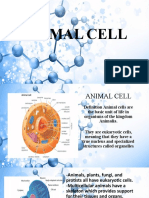
12 visualizações1 páginaAll animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts found in plant cells, and have a variety of shapes due to their lack of a cell wall. Animal cells contain organelles such as a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria and ribosomes. There are over 200 different cell types in the human body, and animal cells can engulf other structures through phagocytosis.
Descrição original:
Animal Cells
Título original
Animal Cells
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoAll animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts found in plant cells, and have a variety of shapes due to their lack of a cell wall. Animal cells contain organelles such as a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria and ribosomes. There are over 200 different cell types in the human body, and animal cells can engulf other structures through phagocytosis.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
12 visualizações1 páginaPlants Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell Wall Phagocytic
Enviado por
Hara Prasad MohapatraAll animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts found in plant cells, and have a variety of shapes due to their lack of a cell wall. Animal cells contain organelles such as a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria and ribosomes. There are over 200 different cell types in the human body, and animal cells can engulf other structures through phagocytosis.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
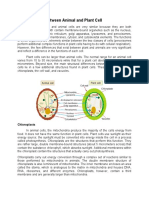
All animals consist of eukaryotic cells.
Animal cells are distinct from those of other eukaryotes, most
notably plants, as they lack cell walls and chloroplasts and have smaller vacuoles. Due to the lack of
a cell wall, animal cells can adopt a variety of shapes. Aphagocytic cell can even engulf other
structures.
There are many other types of cell. For instance, there are approximately 210 distinct cell types in the
adult human body.
The following are examples of structures and organelles that can be found in typical animal
cells:
Cell (Plasma) Membrane - thin, semi-permeable membrane that surrounds
the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosing its contents.
Centrioles - cylindrical structures that organize the assembly of microtubules
during cell division.
Cilia and flagella - specialized groupings of microtubules that protrude from some
cells and aid in cellular locomotion.
Cytoplasm - gel-like substance within the cell.
Cytoskeleton - network of fibers throughout the cell's cytoplasm that gives the cell
support and helps to maintain its shape.
Endoplasmic Reticulum - extensive network of membranes composed of both
regions with ribosomes (rough ER) and regions without ribosomes (smooth ER).
Golgi Complex - also called the Golgi apparatus, this structure is responsible for
manufacturing, storing and shipping certain cellular products.
Lysosomes - sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules such as nucleic
acids.
Microtubules - hollow rods that function primarily to help support and shape the cell.
Mitochondria - cell components that generate energy for the cell and are the sites
of cellular respiration.
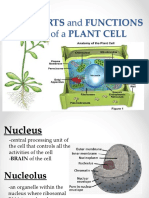
Nucleus - membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information.
Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of
ribosomes.
Nucleopore - tiny hole within the nuclear membrane that allows nucleic
acids and proteins to move into and out of the nucleus.
Peroxisomes - enzyme containing structures that help to detoxify alcohol, form bile
acid, and break down fats.
Ribosomes - consisting of RNA and proteins, ribosomes are responsible for protein
assembly.
Você também pode gostar
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksNo EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocumento2 páginasPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocumento15 páginasPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyAinda não há avaliações
- The Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNADocumento2 páginasThe Animal Cell: Eukaryotic Cells DNAEstefanía ElizondoAinda não há avaliações
- CellDocumento5 páginasCellapi-267979304Ainda não há avaliações
- All About Animal CellsDocumento2 páginasAll About Animal CellsJether Marc Palmerola GardoseAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento2 páginasAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento3 páginasAnimal CellKent Orriele FadriquelAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of Animal CellDocumento27 páginasParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocumento5 páginasNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeAinda não há avaliações
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocumento8 páginasScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedAinda não há avaliações
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocumento5 páginasThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocumento46 páginasLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocumento5 páginasBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724Ainda não há avaliações
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento14 páginasAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoAinda não há avaliações
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 páginasAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinAinda não há avaliações
- CellDocumento3 páginasCellLeordan SanimAinda não há avaliações
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocumento15 páginasParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento3 páginasAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisAinda não há avaliações
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocumento9 páginasMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatAinda não há avaliações
- NucleusDocumento10 páginasNucleusjhariesargente05Ainda não há avaliações
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocumento6 páginasThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocumento4 páginasLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSAinda não há avaliações
- All About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysDocumento8 páginasAll About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysRishikesh BhintadeAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocumento8 páginasKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryAinda não há avaliações
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocumento39 páginasForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Documento30 páginasCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- CellDocumento7 páginasCellnik29569Ainda não há avaliações
- ASDFASDFASDocumento17 páginasASDFASDFASChristian Cyril RoldanAinda não há avaliações
- Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumDocumento3 páginasRough and Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumAnna Mae DollenteAinda não há avaliações
- Functions of A CellDocumento4 páginasFunctions of A CellyayayanizaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Key TermsDocumento3 páginasBiology Key TermsTia TiaAinda não há avaliações
- CYTOLOGYDocumento3 páginasCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloAinda não há avaliações
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocumento13 páginasThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocumento9 páginasCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento7 páginasAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocumento8 páginasAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento2 páginasAnimal CellPaul Sotto NgujoAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell PrintoutDocumento3 páginasAnimal Cell Anatomy: Plant Cell Printout Bacterium Cell Printoutjallie niepesAinda não há avaliações
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocumento5 páginasCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodAinda não há avaliações
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDocumento5 páginasAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusAinda não há avaliações
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocumento14 páginasOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasAinda não há avaliações
- BIO ReviewerDocumento14 páginasBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento7 páginasComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocumento7 páginasAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Physiology-1Documento32 páginasCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaAinda não há avaliações
- CELLSDocumento6 páginasCELLSFenny May SebonAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocumento9 páginasCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology ReviewerDocumento6 páginasGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraAinda não há avaliações
- Animal CellDocumento11 páginasAnimal CellDaryl De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Cells PDFDocumento107 páginasCells PDFida hadiAinda não há avaliações
- Diagram of Plant CellDocumento4 páginasDiagram of Plant CellekongAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocumento12 páginasCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocumento12 páginasCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliAinda não há avaliações
- فاينل انسجة نظريDocumento40 páginasفاينل انسجة نظريحسن القاضيAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Biology PresentationDocumento14 páginasCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento51 páginas2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONDocumento6 páginas1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONOlamide KoleAinda não há avaliações
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocumento10 páginasUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- STM123 OutlineDocumento19 páginasSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliAinda não há avaliações
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNo EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (52)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNo EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNo EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (18)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNo EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeAinda não há avaliações
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNo EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (517)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNo EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (597)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNo EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNo EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorAinda não há avaliações
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNo EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (812)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouNo EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (62)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNo EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (216)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNo EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (111)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceNo EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (633)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (393)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNo EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (397)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessNo EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (18)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNo EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (116)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNo EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (38)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateNo EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (24)