Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lecture7 - Substituion Reaction For Alkyl Halides
Enviado por
xavierTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lecture7 - Substituion Reaction For Alkyl Halides
Enviado por
xavierDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 9
Substitution
Reactions of
Alkyl Halides
Paula Yurkanis Bruice
University of California,
Santa Barbara
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Families of Group II
Substitution Reactions of Alkyl Halides
alkyl halides:
the first of the families
in Group II
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Compounds in Group II Are Electrophiles
All the compounds in Group II
have an electron withdrawing atom or group
that is attached to an sp3 carbon.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Because Group II Compounds are Electrophiles,
They React with Nucleophiles
Substitution reactionthe electronegative group is replaced by another group.
Elimination reactionthe electronegative group is eliminated along with a hydrogen.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Alkyl Halides
This chapter discusses the substitution reactions of alkyl halides.
Alkyl halides have good leaving groups.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
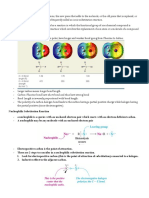
A Substitution Reaction
More precisely called a nucleophilic substitution reaction
because the atom replacing the halogen is a nucleophile.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
What is the Mechanism of the Reaction?
The kinetics of a reactionthe factors that affect the rate of the reaction
can help determine the mechanism.
an SN2 reaction
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Relative Rates of an SN2 Reaction
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Inverted Configuration
If the halogen is bonded to an asymmetric center,
the product will have the inverted configuration.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of the Experimental Evidence
for the Mechanism of an SN2 Reaction
1. The rate of the reaction is dependent on the concentration
of both the alkyl halide and the nucleophile.
2. The relative rate of the reaction is
primary alkyl halide > secondary alkyl halide > tertiary alkyl halide.
3. The configuration of the product is inverted compared to
the configuration of the reacting chiral alkyl halide.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Mechanism
back-side attack
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why Bimolecular?
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why Back-Side Attack?
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
If Front-Side Attack
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why Do Methyl Halides React the Fastest
and Tertiary the Slowest?
steric hindrance
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why Steric Hindrance Decreases the Rate
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Both are Primary Alkyl Halides
but They React at Different Rates
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Although it is Primary, it Reacts Very Slowly
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why the Configuration of the Product
is Inverted
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Weakest Base is the Best Leaving Group
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Rate of an SN2 Reaction
is Affected by the Leaving Group
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Base Strength and Nucleophile Strength
If atoms are in the same row, the strongest base is the best nucleophile.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Base Strength and Nucleophile Strength
A negatively charged atom is a stronger base and a better nucleophile
than the same atom that is neutral.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Polarizability
As you go down a row in the
periodic table the larger
atoms are more polarizable,
so they are better
nucleophiles but they are
weaker bases.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
IonDipole Interactions
Stronger bases form stronger iondipole interactions.
Iondipole interactions have to be broken before the nucleophile can react.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Base Strength and Nucleophile Strength
F is the best nucleophile in
a protic solvent because it is
the strongest base.
I is the best nucleophile in
an aprotic solvent because
it more polarizable and it is
poorly solvated.
The strongest base is the best nucleophile unless
1.they differ in size.
2.they are in a protic polar solvent.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
DMF and DMSO
They can solvate a cation (+) better than they can solvate an anion ().
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Steric Hindrance Decreases Nucleophilicity
Even though the tert-butoxide ion is a
stronger base, it is a poorer nucleophile
because nucleophilic attack is more
sterically hindered than proton removal.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
SN2 Reactions Can Be Used to Make
a Variety of Compounds
The reactions are irreversible because a strong base displaces a weak base.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Synthesizing an Amine
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
A Substitution Reaction
A tertiary alkyl halide and a poor nucleophile
The reaction is surprisingly fast, so it must
be taking place by a different mechanism.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Rate Depends Only on the
Concentration of the Alkyl Halide
an SN1 reaction
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Relative Rates of an SN1 Reaction
Generally only tertiary alkyl halides
undergo SN1 reactions.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Product is a Pair of Enantiomers
If the halogen is bonded to an asymmetric center,
the product will be a pair of enantiomers.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of the Experimental Evidence
for the Mechanism of an SN1 Reaction
1. The rate of the reaction depends only on the
concentration of the alkyl halide.
2. Tertiary alkyl halides react the fastest.
3. If the halogen is attached to an asymmetric center
the product will be a pair of enantiomers.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Mechanism
The leaving group departs before the nucleophile approaches.
Most SN1 reactions are solvolysis reactions; the nucleophile is the solvent.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Slow Step is Formation of the Carbocation
Tertiary alkyl halides react the fastest; they form the most stable carbocations.
Secondary and primary alkyl halides do not undergo SN1 reactions.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why a Pair of Enantiomers?
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Why More Inverted Product
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Front Side is Partially Blocked
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Weakest Base is the Best Leaving Group
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Benzylic and Allylic Halides
Undergo SN2 Reactions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Benzyl and Phenyl Groups
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Benzylic and Allylic Halides
Undergo SN1 Reactions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The SN1 Reaction of Allylic Halides
Can Form Two Products
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Vinylic and Aryl Halides
Cannot Undergo SN2 Reactions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Vinylic and Aryl Halides
Cannot Undergo SN1 Reactions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Comparing SN2 and SN1 Reaction
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Alkyl Halide Reactivity
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Rate Law for an SN2 Reaction + Rate Law for an SN1 Reaction
The rate law for a reaction that can undergo both SN2 and SN1 reactions.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Common Solvents
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Solvation
The dielectric constant is a measure of how the solvent
can insulate opposite charges from one another.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
One of the Reactants is Charged
If a reactant is charged, the charge on the
reactants will be greater than
the charge on the transition state.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
If One of the Reactants is Charged,
Increasing the Polarity of the Solvent Decreases the Rate
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Reactants are Neutral
If the reactants are neutral, the charge
on the reactants will be less than
the charge on the transition state.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
If the Reactants are Neutral,
Increasing the Polarity of the Solvent Increases the Rate
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Rate of an SN1 Reaction of an Alkyl Halide Increases
as the Polarity of the Solvent Increases
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Intermolecular versus Intramolecular
SN2 Reactions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Intramolecular Reaction is Favored When
a Five- or Six-Membered Ring Can Be Formed
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
3-Membered and 4-Membered Rings
are Less Stable
Three-membered rings are generally formed faster than 4-membered rings.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Methylation by a Chemist
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Methylation by a Cell
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Nordrenaline to Adrenaline
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
One Phospholipid is Converted
to Another Phospholipid
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Você também pode gostar
- CHEM 2445 Lab Practical 1 Part ADocumento4 páginasCHEM 2445 Lab Practical 1 Part AKAR100% (1)
- Declaration Page Sample Homeowners 12Documento1 páginaDeclaration Page Sample Homeowners 12Keller Brown JnrAinda não há avaliações
- COLLOIDAL GOLD RECIPE - CitrateDocumento9 páginasCOLLOIDAL GOLD RECIPE - CitrateDevon Narok100% (4)
- The List InditexDocumento126 páginasThe List InditexRezoanul Haque100% (2)
- Alkyl Halides SN1,2 and E1,2,1cbDocumento45 páginasAlkyl Halides SN1,2 and E1,2,1cblorrainebarandonAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento62 páginasChapter 6NURULAIN NIZAMUDINAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Lecture Sustitution EliminationDocumento120 páginas09 Lecture Sustitution EliminationangelaAinda não há avaliações
- Substitution and Elimination Reactions: Paula Yurkanis Bruice University of California, Santa BarbaraDocumento141 páginasSubstitution and Elimination Reactions: Paula Yurkanis Bruice University of California, Santa BarbaraShi PeterAinda não há avaliações
- SN ReactionsDocumento60 páginasSN Reactionsnur ainiAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocumento9 páginasFactors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionchuasioklengAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocumento49 páginasChapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesThanh NguyênAinda não há avaliações
- CH14Documento52 páginasCH14James GigaquitAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Substituents On ReactivityDocumento30 páginasThe Effect of Substituents On ReactivityAbhimanyu GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry 6 Edition: Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Competition Between Substitution and EliminationDocumento65 páginasOrganic Chemistry 6 Edition: Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Competition Between Substitution and Eliminationpawan kumar guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 4 Alkylhalide-Sn eDocumento59 páginasLec 4 Alkylhalide-Sn eNida Nur FadhilahAinda não há avaliações
- SN1, SN2, E1, E2Documento39 páginasSN1, SN2, E1, E2Dian AnggrainiAinda não há avaliações
- Solomons Ch6 AlkilHalida PDFDocumento41 páginasSolomons Ch6 AlkilHalida PDFFitria RamadantiAinda não há avaliações
- The Reactions of Alkynes: An Introduction To Multistep SynthesisDocumento70 páginasThe Reactions of Alkynes: An Introduction To Multistep SynthesisshahjafferAinda não há avaliações
- Unit1 ClickersDocumento23 páginasUnit1 ClickersYara HaidarAinda não há avaliações
- 13.2 Characteristic Organic ReactionsDocumento45 páginas13.2 Characteristic Organic Reactionssafiya_91Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Substitution ReactionDocumento41 páginasChapter 4 Substitution Reactionahmedmustefa773Ainda não há avaliações
- A Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement Reactions of Aryl HalidesDocumento5 páginasA Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement Reactions of Aryl HalidesSAGNIK PALAinda não há avaliações
- Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and EliminationsDocumento70 páginasReactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and EliminationsIrfan ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry-2FDocumento61 páginasOrganic Chemistry-2FChristine Jirah Duca - DeañoAinda não há avaliações
- Water-1 Acetate-500. Ammonia-700. Chloride-1000 Hydroxide-10,000 Methoxide-25000 Iodide-1,00,000 Cyanide-1,25,000 Hydrosulfide-1,25,000Documento2 páginasWater-1 Acetate-500. Ammonia-700. Chloride-1000 Hydroxide-10,000 Methoxide-25000 Iodide-1,00,000 Cyanide-1,25,000 Hydrosulfide-1,25,000Kartik ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocumento18 páginasNucleophilic SubstitutionShivam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento35 páginasClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes Haloalkanes and HaloarenesAshish rathoreAinda não há avaliações
- McMurry9e PPT CH14Documento59 páginasMcMurry9e PPT CH14Abdel RawashdehAinda não há avaliações
- SN1, SN2 PDFDocumento7 páginasSN1, SN2 PDFYoucef José FredAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFDocumento13 páginasNucleophilic Substitution Reactions PDFBhushan Dravyakar100% (6)
- Radicals Reactions of Alkanes: Paula Yurkanis Bruice University of California, Santa BarbaraDocumento56 páginasRadicals Reactions of Alkanes: Paula Yurkanis Bruice University of California, Santa BarbaramooreB_93Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit1 Worked ExamplesDocumento16 páginasUnit1 Worked ExamplesYara HaidarAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 7 - HaloalkanesDocumento42 páginasCHAPTER 7 - HaloalkanesPaolo NaguitAinda não há avaliações
- Substitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocumento71 páginasSubstitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDaniel McDermottAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in OrgDocumento18 páginasReviewer in OrgMichael Josh RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Solvent, Leaving Group, and Nucleophile On Unimolecular SubstitutionDocumento5 páginasEffects of Solvent, Leaving Group, and Nucleophile On Unimolecular SubstitutionRafly HidayatAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 7 - Haloalkanes PDFDocumento42 páginasCHAPTER 7 - Haloalkanes PDFPaolo NaguitAinda não há avaliações
- Nuceleophilic Substitution ReactionDocumento7 páginasNuceleophilic Substitution ReactiondayhunterAinda não há avaliações
- Nuceleophilic Substitution ReactionDocumento7 páginasNuceleophilic Substitution ReactiondayhunterAinda não há avaliações
- Hasham Anas PresentationDocumento14 páginasHasham Anas PresentationirfansaeedAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento5 páginas10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesVansh VaibhavAinda não há avaliações
- Deciding SN1 - SN2 - E1 - E2 (2) - The Nucleophile - Base - Master Organic ChemistryDocumento26 páginasDeciding SN1 - SN2 - E1 - E2 (2) - The Nucleophile - Base - Master Organic ChemistryKinjal Busa100% (1)
- CH 07Documento42 páginasCH 07Samantha Louise MondonedoAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, and An Introduction To Reactivity - Thermodynamics and KineticsDocumento59 páginasAlkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, and An Introduction To Reactivity - Thermodynamics and KineticslebchemAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Note 4Documento5 páginasChem Note 4Gee BandongAinda não há avaliações
- Reaksi Alkilasi Friedel-Crafts: Kimia Organik II Jurusan Pendidikan KimiaDocumento10 páginasReaksi Alkilasi Friedel-Crafts: Kimia Organik II Jurusan Pendidikan KimiaEkanisaKurniawatiAinda não há avaliações
- 12 SubstitutionsDocumento68 páginas12 Substitutionshuykhiem50% (2)
- Nucleophilicity of AminesDocumento22 páginasNucleophilicity of AminesAnonymous k7jIVoaqBAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1, SN2) AND Elimination Reactions (E1, E2)Documento11 páginasNucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1, SN2) AND Elimination Reactions (E1, E2)Makhdoom JahaniaAinda não há avaliações
- KNC1063 Organic Chemistry: DR Md. Rezaur RahmanDocumento19 páginasKNC1063 Organic Chemistry: DR Md. Rezaur RahmanKunashiny RamashAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsDocumento41 páginasNucleophilic Substitution Reactionseva982205Ainda não há avaliações
- 12-Aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution PDFDocumento68 páginas12-Aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution PDFVenkatraj Gowdas100% (1)
- Chem 351 Study GuideDocumento10 páginasChem 351 Study Guidesamantha davidsonAinda não há avaliações
- P0 DienesDocumento25 páginasP0 DienesbluepeninmypocketAinda não há avaliações
- Orgchem TransDocumento16 páginasOrgchem TransScyrah Allana RiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Organic PresentationDocumento25 páginasOrganic PresentationsaheedvkAinda não há avaliações
- UNITIII SN1andSN2reactionsDocumento24 páginasUNITIII SN1andSN2reactionsRams ChanderAinda não há avaliações
- Class Slides Jan 2023Documento105 páginasClass Slides Jan 2023Prarabdha SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry - Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsDocumento58 páginasOrganic Chemistry - Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsNatalie EnriquezAinda não há avaliações
- CM134-1L Experiment 2.1Documento8 páginasCM134-1L Experiment 2.1Christian JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Tetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40No EverandTetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40Derek BartonAinda não há avaliações
- The Chemistry of Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine and Astatine: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 7No EverandThe Chemistry of Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine and Astatine: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 7Nota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryNo EverandHard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- AIPMT 2009 ExamDocumento25 páginasAIPMT 2009 ExamMahesh ChavanAinda não há avaliações
- Level 9 - Unit 34Documento7 páginasLevel 9 - Unit 34Javier RiquelmeAinda não há avaliações
- Study On Optimization and Performance of Biological Enhanced Activated Sludge Process For Pharmaceutical Wastewater TreatmentDocumento9 páginasStudy On Optimization and Performance of Biological Enhanced Activated Sludge Process For Pharmaceutical Wastewater TreatmentVijaya GosuAinda não há avaliações
- 006R5-WMS-JI-MI-MAU-ACS-II-23 Working Method - Pile CapDocumento20 páginas006R5-WMS-JI-MI-MAU-ACS-II-23 Working Method - Pile CapEko Budi HartantoAinda não há avaliações
- Esomeprazol Vs RabeprazolDocumento7 páginasEsomeprazol Vs RabeprazolpabloAinda não há avaliações
- Ronnel Del RioDocumento5 páginasRonnel Del Rioamity balweg100% (2)
- Annual Sustainability Report 2022-23 FinalDocumento93 páginasAnnual Sustainability Report 2022-23 FinalLakshay JajuAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Safety: Good Servant But A Bad MasterDocumento143 páginasFire Safety: Good Servant But A Bad MasterernmrajaAinda não há avaliações
- Blessing of The Advent WreathDocumento3 páginasBlessing of The Advent WreathLloyd Paul ElauriaAinda não há avaliações
- 621F 721F Op's ManualDocumento362 páginas621F 721F Op's ManualMilAuto87100% (1)
- Molecular MechanicsDocumento26 páginasMolecular MechanicsKarthi ShanmugamAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Marketing of ArecanutDocumento22 páginasReport On Marketing of ArecanutsivakkmAinda não há avaliações
- Monitor Zoncare - PM-8000 ServicemanualDocumento83 páginasMonitor Zoncare - PM-8000 Servicemanualwilmer100% (1)
- WWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenaDocumento6 páginasWWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenapotoculAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Accounts On Business CombinationDocumento2 páginasTheory of Accounts On Business CombinationheyAinda não há avaliações
- CSF LeaksDocumento3 páginasCSF LeaksDrTarek Mahmoud Abo KammerAinda não há avaliações
- Muet Topic 10 City Life Suggested Answer and IdiomsDocumento3 páginasMuet Topic 10 City Life Suggested Answer and IdiomsMUHAMAD FAHMI BIN SHAMSUDDIN MoeAinda não há avaliações
- Hedayati2014 Article BirdStrikeAnalysisOnATypicalHeDocumento12 páginasHedayati2014 Article BirdStrikeAnalysisOnATypicalHeSharan KharthikAinda não há avaliações
- Air Pollution Emissions 2008-2018 From Australian Coal Mining: Implications For Public and Occupational HealthDocumento11 páginasAir Pollution Emissions 2008-2018 From Australian Coal Mining: Implications For Public and Occupational HealthMaria Stephany CalisayaAinda não há avaliações
- EC Type-Examination Certificate: Reg.-No.: 01/205/5192.02/18Documento11 páginasEC Type-Examination Certificate: Reg.-No.: 01/205/5192.02/18Orlando Ortiz VillegasAinda não há avaliações
- Nepal Health Research CouncilDocumento15 páginasNepal Health Research Councilnabin hamalAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental Unit of Life 1-25Documento25 páginasFundamental Unit of Life 1-25Anisha PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Zemoso - PM AssignmentDocumento3 páginasZemoso - PM AssignmentTushar Basakhtre (HBK)Ainda não há avaliações
- Business-Plan (John Lloyd A Perido Grade 12-Arc)Documento4 páginasBusiness-Plan (John Lloyd A Perido Grade 12-Arc)Jaypher PeridoAinda não há avaliações
- Peseshet - The First Female Physician - (International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, Vol. 32, Issue 3) (1990)Documento1 páginaPeseshet - The First Female Physician - (International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, Vol. 32, Issue 3) (1990)Kelly DIOGOAinda não há avaliações
- DoDough FriedDocumento7 páginasDoDough FriedDana Geli100% (1)
- Vinegar Intake Reduces Body Weight Body Fat Mass and Serum Triglyceride Levels in Obese Japanese SubjectsDocumento8 páginasVinegar Intake Reduces Body Weight Body Fat Mass and Serum Triglyceride Levels in Obese Japanese SubjectsZaphan ZaphanAinda não há avaliações