Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
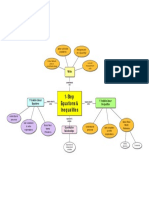
Vocabulary Terms-One Step Equations
Enviado por
api-302577842Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Vocabulary Terms-One Step Equations
Enviado por
api-302577842Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
An equation is like a balance because both sides are
equal values.
The idea of balance can help me solve an equation by making sure to
keep both sides equal. I can use tables and diagrams to help me understand and represent
real situations using proportions, equations and inequalities. I can write, interpret and
manipulate proportions, equations, and inequalities using rules, tables and graphs. I can
solve a proportion, equation or inequality using addition and multiplication. I can tell the
difference between an expression, equation and an inequality by the presence or absence of
an equal or inequality symbol. Proportions can be used to solve problems. Proportional
relationships can be described using the equation y = kx by realizing that k is the
proportion y / x. Proportional relationships can be represented using rules, tables, and
graphs. The graph of y = kx be interpreted for different contexts such as the cost per
gallon of gasoline. A change in one variable affects the other variable in a given situation.
A table, a graph or a formula can tell me everything I want to know about a variable
relationship.
Key Words
Addition Property of Equality: Adding the same number to each side of an equation
produces an equivalent expression.
Constant of Proportionality: The constant value of the ratio of two proportional
quantities x and y; usually written y = kx, where k is the constant of proportionality.
In a proportional relationship, y = kx, k is the constant of proportionality, which is
the value of the ratio between y and x.
Direct Proportion (Direct Variation): The relation between two quantities whose
ratio remains constant. When one variable increases the other increases
proportionally: When one variable doubles the other doubles, when one variable
triples the other triples, and so on. When A changes by some factor, then B changes
by the same factor: A=kB, where k is the constant of proportionality.
Division Property of Equality: States that when both sides of an equation are
divided by the same number, the remaining expressions are still equal
Equation: A mathematical sentence that contains an equal sign
Inequality: A mathematical sentence that contains the symbols >, <, , or .
Inverse Operation: A mathematical process that combines two or more numbers
such that its product or sum equals the identity.
Multiplication Property of Equality: States that when both sides of an equation are
multiplied by the same number, the remaining expressions are still equal.
Proportion: An equation which states that two ratios are equal.
Subtraction Property of Equality: States that when both sides of an equation have
the same number subtracted from them, the remaining expressions are still equal.
Term: A number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables.
Variable: A letter or symbol used to represent a number or quantities that vary.
Você também pode gostar
- On Unit 4 VocabDocumento1 páginaOn Unit 4 Vocabapi-347092840Ainda não há avaliações
- EquationsDocumento5 páginasEquationsRida AabidAinda não há avaliações
- Inverse Proportionality Jump To Navigation Jump To Search ProportionalityDocumento6 páginasInverse Proportionality Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Proportionalitytormenta90Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary - Rate Ratio ProportionDocumento11 páginasSummary - Rate Ratio ProportionSwatiAinda não há avaliações
- EquationDocumento2 páginasEquationJef FreyAinda não há avaliações
- Math Reviewer Pt. 1Documento3 páginasMath Reviewer Pt. 1Alyah Jannah HiñolaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Correlation and Their Specific ApplicationsDocumento25 páginasTypes of Correlation and Their Specific ApplicationsRajesh KannaAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra I Vocab CardsDocumento15 páginasAlgebra I Vocab Cardsjoero51Ainda não há avaliações
- Equations and Word ProblemsDocumento2 páginasEquations and Word ProblemsBernadeth MontardeAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Relationship Analysis: Correlation & RegressionDocumento4 páginasQuantitative Relationship Analysis: Correlation & RegressionInamullah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Africa Beza College: Chapter 2: Correlation Theory Pre-Test QuestionsDocumento11 páginasAfrica Beza College: Chapter 2: Correlation Theory Pre-Test QuestionsAmanuel GenetAinda não há avaliações
- Stearns Msa UnitplanDocumento10 páginasStearns Msa Unitplanapi-281469512Ainda não há avaliações
- Proportionality (Mathematics)Documento4 páginasProportionality (Mathematics)OmarGarciaAinda não há avaliações
- BSEE Calculus ReviewDocumento13 páginasBSEE Calculus ReviewRonalyn ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation and covariance explainedDocumento11 páginasCorrelation and covariance explainedSrikirupa V MuralyAinda não há avaliações
- Graphs in Economics ExplainedDocumento28 páginasGraphs in Economics ExplainedYahya MakarimAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Variation Form 2-WPS OfficeDocumento1 páginaDirect Variation Form 2-WPS OfficeMarlvin PrimeAinda não há avaliações
- Untitled PresentationDocumento10 páginasUntitled PresentationAyesha MurtazaAinda não há avaliações
- CORRELATION ANALYSIS: MEASURING RELATIONSHIPSDocumento8 páginasCORRELATION ANALYSIS: MEASURING RELATIONSHIPSGanesh BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Proportionality (Mathematics)Documento4 páginasProportionality (Mathematics)Stojan SavicAinda não há avaliações
- Ordering Numbers and Absolute Value: A and B Are Two Real Numbers Such ThatDocumento4 páginasOrdering Numbers and Absolute Value: A and B Are Two Real Numbers Such ThatMuhammad ShamoeelAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation: DefinitionsDocumento24 páginasCorrelation: DefinitionsBhawna JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Httpsgacbe - ac.Inpdfematerial18BPS34A U4 PDFDocumento27 páginasHttpsgacbe - ac.Inpdfematerial18BPS34A U4 PDFBaljeet KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Regression and CorrelationDocumento37 páginasRegression and Correlationmahnoorjamali853Ainda não há avaliações
- Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 páginasEureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip Sheetapi-324380772Ainda não há avaliações
- BRM - 4.4 Measures of Linear RelationshipDocumento3 páginasBRM - 4.4 Measures of Linear RelationshipSasin SasikalaAinda não há avaliações
- SLHT Math9 - Q2 Wk2aDocumento6 páginasSLHT Math9 - Q2 Wk2amerryjoey heranaAinda não há avaliações
- LinearDocumento16 páginasLinearAmalina ZulkifleeAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation Coefficient DefinitionDocumento8 páginasCorrelation Coefficient DefinitionStatistics and Entertainment100% (1)
- 3rd Term Math ReviewerDocumento7 páginas3rd Term Math ReviewerRaf FlorendoAinda não há avaliações
- Butol, Michael Jordan P. QUANTI (Friday, 4:00PM - 5:30PM) Assignment No: 1Documento3 páginasButol, Michael Jordan P. QUANTI (Friday, 4:00PM - 5:30PM) Assignment No: 1Jordan P HunterAinda não há avaliações
- SampleDocumento11 páginasSampleGodson OnophurhiAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Equations NotesDocumento3 páginasLinear Equations NotesKeshavAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation AnalysisDocumento20 páginasCorrelation AnalysisVeerendra NathAinda não há avaliações
- MidtermreviewprojectpptxDocumento37 páginasMidtermreviewprojectpptxapi-553954607Ainda não há avaliações
- Algebra Terms and DefinitionsDocumento5 páginasAlgebra Terms and DefinitionsIftikhar AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation: (For M.B.A. I Semester)Documento46 páginasCorrelation: (For M.B.A. I Semester)Arun Mishra100% (2)
- Variation: Direct Proportion (Or Variation)Documento4 páginasVariation: Direct Proportion (Or Variation)Alex LeeAinda não há avaliações
- BBA - 106 - Lecture Notes On Regression AnalysisDocumento2 páginasBBA - 106 - Lecture Notes On Regression AnalysisTanmay Chakraborty67% (3)
- Correlation & Regression Analysis in StatisticsDocumento21 páginasCorrelation & Regression Analysis in Statisticssara sibyAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary List for AlgebraDocumento6 páginasVocabulary List for Algebrakemuel juadiongAinda não há avaliações
- Business Math Week 4Documento10 páginasBusiness Math Week 4Patrick TaboradaAinda não há avaliações
- Algebraic ExpressionDocumento3 páginasAlgebraic Expressionapi-150539480Ainda não há avaliações
- Iskak, Stats 2Documento5 páginasIskak, Stats 2Iskak MohaiminAinda não há avaliações
- FL G8 M04 Family+LetterDocumento2 páginasFL G8 M04 Family+Letterahmed5030 ahmed5030Ainda não há avaliações
- (English) How To Use The Quadratic Formula in Chemistry (DownSub - Com)Documento5 páginas(English) How To Use The Quadratic Formula in Chemistry (DownSub - Com)ikhsania utamiAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Equation - WikipediaDocumento24 páginasLinear Equation - WikipediaChristine Mae BetangcorAinda não há avaliações
- Mca4020 SLM Unit 08Documento36 páginasMca4020 SLM Unit 08AppTest PI0% (1)
- Chapter 7 Vocabulary Addition Property of EqualityDocumento3 páginasChapter 7 Vocabulary Addition Property of EqualityStephanie MaherAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocumento2 páginasLinear Equations in Two VariablesShubham KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of EqualitiesDocumento13 páginasProperties of EqualitiesMyla VelascoAinda não há avaliações
- Direct VariationDocumento4 páginasDirect VariationMa Fretchie Cabale MendovaAinda não há avaliações
- Correlation Between Plant Height and YieldDocumento15 páginasCorrelation Between Plant Height and YieldGAYATHRI NATESHAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Ratio and ProportionDocumento9 páginasUnderstanding Ratio and ProportionrajanrajguruAinda não há avaliações
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocumento14 páginasPair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesAnulina17Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u4 Vocab CardsDocumento12 páginasM6u4 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Here are the key steps:1) Divide both sides by -32) Reverse the inequality sign since we divided by a negative number3) Graph the solution on a number lineTherefore, the solution is: x < -4Documento26 páginasHere are the key steps:1) Divide both sides by -32) Reverse the inequality sign since we divided by a negative number3) Graph the solution on a number lineTherefore, the solution is: x < -4Adrian JulianAinda não há avaliações
- Rational ExplorationsDocumento2 páginasRational Explorationsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u1 Flyswatter Vocabulary Review 1Documento19 páginasM6u1 Flyswatter Vocabulary Review 1api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u7 ArizonaexDocumento8 páginasM6u7 Arizonaexapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Key Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student EditionDocumento2 páginasKey Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student Editionapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u1 Vocab CardsDocumento24 páginasM6u1 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u4 ConceptmapDocumento1 páginaM6u4 Conceptmapapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u6 Sample Concept MapDocumento1 páginaM6u6 Sample Concept Mapapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u7 Outline Overview 2016Documento20 páginasM6u7 Outline Overview 2016api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u7 Sample Concept Map 5Documento1 páginaM6u7 Sample Concept Map 5api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1Documento5 páginasM6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u4 Outline Overview 2017Documento24 páginasM6u4 Outline Overview 2017api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u1 Sample Concept Map 2 1Documento1 páginaM6u1 Sample Concept Map 2 1api-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u4 Vocab CardsDocumento12 páginasM6u4 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- M6u4 ArizonaexDocumento10 páginasM6u4 Arizonaexapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 HomeworkDocumento6 páginasUnit 2 Homeworkapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- GCF and LCMDocumento1 páginaGCF and LCMapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Solving Equations 12 ProblemsDocumento1 páginaSolving Equations 12 Problemsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- 08 Math Homework-Taken From Students WorkbookDocumento1 página08 Math Homework-Taken From Students Workbookapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Number Line Practice-OlDocumento2 páginasNumber Line Practice-Olapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Integer Addition Practice ADocumento1 páginaInteger Addition Practice Aapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Sweet Algebra TaskDocumento10 páginasSweet Algebra Taskapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 9 Post Test ReviewDocumento3 páginasUnit 9 Post Test Reviewapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Ixl-Week of 5-2 Multiplydivide IntegersDocumento1 páginaIxl-Week of 5-2 Multiplydivide Integersapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Numberline Practice-OlDocumento2 páginasNumberline Practice-Olapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Ixl-Week of 4-24 Addsubtract IntegersDocumento1 páginaIxl-Week of 4-24 Addsubtract Integersapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Ws Distributive Combine-Like-TermsDocumento2 páginasWs Distributive Combine-Like-Termsapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Gams Review OverallDocumento3 páginasGams Review Overallapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Whiz Unit 7 MCDocumento3 páginasMath Whiz Unit 7 MCapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Gams Review OverallDocumento3 páginasGams Review Overallapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Whiz Unit 6 MCDocumento1 páginaMath Whiz Unit 6 MCapi-302577842Ainda não há avaliações