Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
15EC205 - Signals and Systems Syllabus
Enviado por
bashyam88Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
15EC205 - Signals and Systems Syllabus
Enviado por
bashyam88Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
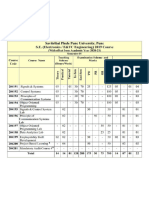
15EC205
Co-requisite:
Prerequisite:
Data Book /
Codes/Standards
Course Category
Course designed by
Approval
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
L T
15MA201
15MA102
NIL
P
PROFESSIONAL CORE
SIGNAL PROCESSING
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
30th Academic Council Meeting 24th March , 2016
PURPOSE
To impart knowledge of fundamentals of signals and systems, and to mathematically analyze
different types of signals and their associated systems.
STUDENT
INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
OUTCOMES
At the end of the course, learner will be able to
H
M
L
1. Acquire knowledge of various classifications Signals and Systems
b
a
2. Utilize the mathematical computing tool for analysis of signals and systems
b
a
k
3. Analyze Periodic and Aperiodic Continuous time Signals using Fourier series.
b
a
4. Analyze and characterize the Continuous time system through Laplace transform and
b
a
c
Fourier transform.
5. Analyze and characterize the Discrete time system through DFT and Z transform and
b
a
c
also realize Discrete time system using Z transform
Sessio
n
Description of Topic
UNIT I: CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
1.
Continuous time signals , Discrete time signals, Basic operations on
Signals, Periodic and Aperiodic signals, Even and odd signals
2.
Energy and power signals, Deterministic and random signals,
Complex exponential and Sinusoidal signals
Unit step, Unit ramp, Unit impulse, Representation of signals in
terms of unit impulse
3.
Contac
t hours
12
C-DI-O
IO
s
Referenc
e
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
4.
Continuous time systems, Discrete time systems, Linear system,
Time Invariant system
C,D
1-4
5.
causal system, BIBO system, Systems with and without memory,
LTI system
C,D
1-4
6.
Programs using mathematical computing tool for mathematical
operations on CT, DT signals
D,I
1,2
12
7.
UNIT-II: ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS TIME SIGNALS
Fourier series: Representation of Continuous time Periodic signals,
Trigonometric
C,D
1-4
8.
Cosine representation and exponential, Symmetry conditions
C,D
1-4
9.
Properties of Continuous time Fourier series, Parsevals relation for
power signals, Frequency spectrum
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
D,I
2,4
C,D
1-4
10. Fourier transform: Representation of Continuous time signals,
Properties of Continuous time Fourier transform, Parsevals relation
for energy signals, Energy density spectrum
11. Analysis of LTI system using Fourier methods
12. Programs using mathematical computing tool for Fourier series and
Fourier transform of CT
UNIT-III: LTI CT SYSTEM
13. System modeling: Solution of Differential equation with initial
conditions, Zero state response and Zero input response
12
3
14. Impulse response, Frequency response
15. Convolution, Convolution integral
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
16. Laplace transform and its properties
17.
Analysis and characterization of LTI system using Laplace transform
C,D
1-4
C,D
1-4
D,I
2,4
1-6
C,D
1-6
C,D
1-6
C,D
1-6
D,I
2,5
C,D
1-6
C,D
1-6
C,D
1-6
C,D
1-6
D,I
2,5
18. programs using mathematical computing tool for CT system
analysis using LT
UNIT-IV: ANALYSIS OF DT SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
12
19. Representation of sequences, Discrete Time Fourier Transform
(DTFT)
20.
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and its properties
21.
Solution of linear constant coefficient difference equations with
initial conditions, Zero state response and Zero input response
22. Impulse response, Convolution sum, Frequency response.
23. Programs using mathematical computing tool for DT system
analysis using DFT
UNIT-V: LTI DT SYSTEM CHARACTERIZATION AND
REALIZATION
24.
Unilateral and Bilateral Z transforms and its properties
12
25. Inverse Z transform: Power series expansion and Partial fraction
methods
26. Analysis and characterization of DT system using Z transform
27. Realization of structures for DT systems, Direct form I, Direct form
II, Parallel, Cascade forms
28. Programs using mathematical computing tool for DT system
analysis using ZT
60
Total contact hours
LEARNING RESOURCES
Sl.
BOOKS / OTHER READING MATERIALS
No.
1.
Alan V Oppenheim, Ronald W. Schafer Signals & Systems, Pearson Education, 2 nd Edition
2015(Imprint).
2.
P.Ramakrishna Rao, Shankar Prakriya, Signals & Systems, McGraw Hill Education, 2nd Edition, 4th
reprint 2015
3.
Simon Haykin and Barry Van Veen, Signals and Systems, John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2nd Edition, 2007.
4.
Lathi B.P, Linear Systems & Signals, Oxford Press, Second Edition, 2009.
5.
John G. Proakis and Manolakis, Digital Signal Processing, Principles, Algorithms and Applications,
Pearson Education, 4th Edition, 2007.
6.
A.Nagoor Kani, , Signals & Systems, McGraw Hill Education, 12th reprint 2015.
Course nature
Assessment Method (Weightage 100%)
Assessment tool Cycle test I Cycle test II
In-semester
Weightage
10%
15%
Theory
Cycle Test III Surprise Test
Quiz
15%
5%
5%
End semester examination Weightage :
Total
50%
50%
Você também pode gostar
- SNS CourseDocumento4 páginasSNS CourseAbhay ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Se Entc (IV Sems - 2019)Documento36 páginasSe Entc (IV Sems - 2019)Chinmay KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- EC or ET or ELDocumento7 páginasEC or ET or ELRam RahimAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech - ECE Syllabus IV Year - Signal and System 3014Documento3 páginasB.Tech - ECE Syllabus IV Year - Signal and System 3014tarang srivasAinda não há avaliações
- RGPV Syllabus 4th Sem Biomedical EngineeringDocumento6 páginasRGPV Syllabus 4th Sem Biomedical Engineeringoliver senAinda não há avaliações
- Btech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Documento38 páginasBtech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Nikhil EdwardAinda não há avaliações
- R 20 Signals and SystemsDocumento174 páginasR 20 Signals and SystemsTHE INDIAN ATLASAinda não há avaliações
- M Tech Syllabus ECEDocumento16 páginasM Tech Syllabus ECEAbhishek BhatnagarAinda não há avaliações
- DSPDocumento5 páginasDSPKarishma SavAinda não há avaliações
- SE E&TC-ELEX - 2015 Course Credit System SyllabusDocumento36 páginasSE E&TC-ELEX - 2015 Course Credit System SyllabusHarshvardhanUpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Course Code Category Hours / Week Credits Maximum Marks AECB63 L T P C CIA SEE TotalDocumento2 páginasCourse Code Category Hours / Week Credits Maximum Marks AECB63 L T P C CIA SEE TotalMr V. Phaninder ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- EC6303 Signals and SystemsDocumento84 páginasEC6303 Signals and SystemsSaffanah ShaukathAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems SyllabusDocumento3 páginasSignals and Systems SyllabusSeema P DiwanAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and SystemDocumento3 páginasSignal and SystemHodec SsecAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento3 páginasGujarat Technological UniversityadamAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and SystemsDocumento174 páginasSignals and Systemsjale charitha reddy50% (2)
- Dynamics of Linear Systems PDFDocumento3 páginasDynamics of Linear Systems PDFBhautik Daxini100% (2)
- EEE 323 - DSP Outline DayDocumento3 páginasEEE 323 - DSP Outline DayGeorge ReavleyAinda não há avaliações
- PEI5I103Documento2 páginasPEI5I103raghavAinda não há avaliações
- Sem 8Documento7 páginasSem 8subineeeAinda não há avaliações
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDocumento25 páginasChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiPiyush KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Plan de EstudiosDocumento12 páginasPlan de EstudiosJosHerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Course Out-Line-1-2Documento2 páginasCourse Out-Line-1-2mandeAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University of Technology, Coimbatore: Regulations 2008Documento8 páginasAnna University of Technology, Coimbatore: Regulations 2008PrethevAinda não há avaliações
- Page 1 of 2: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento2 páginasPage 1 of 2: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Jenny BhadouriyaAinda não há avaliações
- Communication and Networking SyllabusDocumento41 páginasCommunication and Networking SyllabusWesley Moses SamdossAinda não há avaliações
- Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal: BT301 Mathematics-III 3L-1T-0P 4 CreditsDocumento7 páginasRajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal: BT301 Mathematics-III 3L-1T-0P 4 CreditsRachit JainAinda não há avaliações
- 15EC44 NotesDocumento126 páginas15EC44 NoteslathavenkyAinda não há avaliações
- Even Semester Syllabus-ICTDocumento30 páginasEven Semester Syllabus-ICTemailidtofoolAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems 3/0/0/3 Course Pre-RequisitesDocumento2 páginasSignals and Systems 3/0/0/3 Course Pre-RequisitesAjithanieAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University:: Chennai 600 025 Curriculum 2004 B.Tech. Information Technology Semester Iii Code No. Course Title L T P M TheoryDocumento39 páginasAnna University:: Chennai 600 025 Curriculum 2004 B.Tech. Information Technology Semester Iii Code No. Course Title L T P M TheorySutha BalaAinda não há avaliações
- Ec 2204-Signals and SystemsDocumento5 páginasEc 2204-Signals and SystemsragvshahAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento4 páginasPDFursbestfriendAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Signals and SystemsDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To Signals and SystemsFaisal MushtaqAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems: BooksDocumento1 páginaSignals and Systems: Booksfaizan bariAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical TechnologyDocumento51 páginasElectrical TechnologyVaibhav VernekarAinda não há avaliações
- KANNUR UNIVERSITY BTech.S7 EE SyllabusDocumento16 páginasKANNUR UNIVERSITY BTech.S7 EE SyllabusManu K MAinda não há avaliações
- Computer and CommunicationDocumento40 páginasComputer and Communicationrahul cAinda não há avaliações
- CSE SyallbusDocumento126 páginasCSE SyallbusAjay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Signals, Spectra Syllabus PDFDocumento2 páginasSignals, Spectra Syllabus PDFJeffreyBerida50% (2)
- Subject (Theory) : SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: Course ObjectiveDocumento2 páginasSubject (Theory) : SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: Course ObjectivePrafulla Durgadhar GawandeAinda não há avaliações
- AE306 Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento2 páginasAE306 Digital Signal ProcessingPrince ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and Systems - CLODocumento3 páginasSignal and Systems - CLOHamza AyazAinda não há avaliações
- Course Information Sheet: Course Coordinator: Course ObjectivesDocumento2 páginasCourse Information Sheet: Course Coordinator: Course ObjectivesGauri Shanker GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Ci2 CSDocumento2 páginasCi2 CS6 AugAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University - Bio Medical Engineering Syllabus Reg - 2017Documento11 páginasAnna University - Bio Medical Engineering Syllabus Reg - 2017Haem Nahth50% (2)
- 04 B. E. BME Syllabus 2017 Regulation 1 PDFDocumento11 páginas04 B. E. BME Syllabus 2017 Regulation 1 PDFVigneshkAinda não há avaliações
- ECE18R202Documento2 páginasECE18R202Jeya Prakash K0% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento3 páginasGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Saumya LutadeAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and System SyllabusDocumento2 páginasSignal and System SyllabusVinay PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- EE407 Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento2 páginasEE407 Digital Signal ProcessingbibuthomasAinda não há avaliações
- University DepartmentsDocumento33 páginasUniversity DepartmentsPn KrizhhAinda não há avaliações
- I.P (Digital Electronics)Documento10 páginasI.P (Digital Electronics)HarmanWaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Bmi SyllabusDocumento20 páginasBmi SyllabusakhilkpAinda não há avaliações
- CS SyllabusDocumento2 páginasCS SyllabusEEE ACEECAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing: VI SemesterDocumento2 páginasDigital Signal Processing: VI SemesterNagaraju NeelaAinda não há avaliações
- Multicomputer VisionNo EverandMulticomputer VisionS. LevialdiAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesNo EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Petri Nets: Fundamental Models, Verification and ApplicationsNo EverandPetri Nets: Fundamental Models, Verification and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNo EverandDigital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- EE8591 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING SyllabusDocumento2 páginasEE8591 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Syllabussiva100% (1)
- CS010 504-DSPDocumento2 páginasCS010 504-DSPRemya KrAinda não há avaliações
- Z TransformDocumento71 páginasZ TransformSmitha VasAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iii: Analysis of Discrete Time SignalsDocumento22 páginasUnit Iii: Analysis of Discrete Time SignalsAnbazhagan SelvanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Ss Jntuk Dec 2015Documento4 páginasSs Jntuk Dec 2015giribabukandeAinda não há avaliações
- Z-Transforms: Definition: The - Transform of A SequenceDocumento15 páginasZ-Transforms: Definition: The - Transform of A SequenceSudhir RavipudiAinda não há avaliações
- UGRD-ECE6205-Signals-Spectra-and-Signal-Processing-legit-not-quizess MidALLDocumento19 páginasUGRD-ECE6205-Signals-Spectra-and-Signal-Processing-legit-not-quizess MidALLJitlee Papa100% (3)
- Course Name: Digital Signal Processing Course Code: EE 605A Credit: 3Documento6 páginasCourse Name: Digital Signal Processing Course Code: EE 605A Credit: 3nspAinda não há avaliações
- Open 16f8 ECDocumento62 páginasOpen 16f8 ECRitik TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- MITRES 6 008S11 LecurerDocumento267 páginasMITRES 6 008S11 LecureranandintelAinda não há avaliações
- Ecr305 L5 SP 2018Documento37 páginasEcr305 L5 SP 2018Shirazim MunirAinda não há avaliações
- WWW - Vidyarthiplus.in: Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiDocumento18 páginasWWW - Vidyarthiplus.in: Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, Kalavaisharanyameen2704Ainda não há avaliações
- ECE402 Lab4Documento4 páginasECE402 Lab4EDUARD VI DANDAAinda não há avaliações
- EIE410 Digital Control SystemDocumento3 páginasEIE410 Digital Control SystemgurusaravanaAinda não há avaliações
- CCP NotesDocumento101 páginasCCP NoteslvrevathiAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab Expt 4 Manual EECE GITAM-1-6Documento6 páginasDSP Lab Expt 4 Manual EECE GITAM-1-6gowri thumburAinda não há avaliações
- ME PAPER (SEM-1) For E.C. GTUDocumento59 páginasME PAPER (SEM-1) For E.C. GTUGaurang RathodAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus EceDocumento85 páginasSyllabus EceHemanthAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Control (Kannan M. Moudgalya)Documento554 páginasDigital Control (Kannan M. Moudgalya)risovi0% (1)
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Digital Signal Processing A Computer Based Approach 3rd Edition 9780073048376Documento36 páginasSolutions Manual To Accompany Digital Signal Processing A Computer Based Approach 3rd Edition 9780073048376wakeningsandyc0x29100% (53)
- Math Physics: Conformal MappingDocumento4 páginasMath Physics: Conformal MappingEpic WinAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing SlidesDocumento184 páginasDigital Signal Processing SlidesChinmay Anand100% (1)
- DSP - Lecture - Chap 3Documento30 páginasDSP - Lecture - Chap 3Nour Ziad Ibrahim AlkurdiAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Control Systems: Unit - I Sampling and ReconstructionDocumento4 páginasDigital Control Systems: Unit - I Sampling and Reconstructionvamkrishna33% (3)
- Soln hw2Documento28 páginasSoln hw2Hashim Gurmani0% (1)
- Program CC Command ListDocumento12 páginasProgram CC Command ListGabriel BarbachanoAinda não há avaliações
- R 18 Be Ece III To Viii SemestersDocumento171 páginasR 18 Be Ece III To Viii SemestersharshaAinda não há avaliações
- EEE221Documento544 páginasEEE221Tomas KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 12 CSE Syllabus 2012 13Documento57 páginas12 CSE Syllabus 2012 13rickyali_rocksAinda não há avaliações
- BTech IT Curriculum and Syllabus 25.03Documento88 páginasBTech IT Curriculum and Syllabus 25.03pattabirmnAinda não há avaliações