Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Flocculation - Merge Suspended Solid Yeast and Fungi Are Not Common in Waste Water
Enviado por
Nicko Jay Bajao0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
6 visualizações1 páginaFlocculation involves merging suspended solids. Methane is a colorless, odorless, flammable gas that is the main component of natural gas and is used as fuel. Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate, and is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process that reduces nitrate and may ultimately produce nitrogen gas through intermediate nitrogen oxides. Acidophiles thrive in highly acidic conditions below pH 2.0, while alkaliphiles can survive in alkaline environments around pH 8.5-11 and grow optimally at pH 10.
Descrição original:
NOTHING
Título original
Flocculation
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoFlocculation involves merging suspended solids. Methane is a colorless, odorless, flammable gas that is the main component of natural gas and is used as fuel. Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate, and is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process that reduces nitrate and may ultimately produce nitrogen gas through intermediate nitrogen oxides. Acidophiles thrive in highly acidic conditions below pH 2.0, while alkaliphiles can survive in alkaline environments around pH 8.5-11 and grow optimally at pH 10.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
6 visualizações1 páginaFlocculation - Merge Suspended Solid Yeast and Fungi Are Not Common in Waste Water
Enviado por
Nicko Jay BajaoFlocculation involves merging suspended solids. Methane is a colorless, odorless, flammable gas that is the main component of natural gas and is used as fuel. Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate, and is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process that reduces nitrate and may ultimately produce nitrogen gas through intermediate nitrogen oxides. Acidophiles thrive in highly acidic conditions below pH 2.0, while alkaliphiles can survive in alkaline environments around pH 8.5-11 and grow optimally at pH 10.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
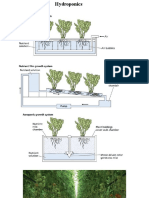
Flocculation merge suspended solid
Yeast and fungi are not common in waste water
METHANE fuel gas: a colorless odorless flammable gas that is the main constituent of natural gas. Use: as fuel.
Formula: CH4
METABOLIC -breakdown, absorption, digestion, uptake, use, metabolic rate
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia or ammonium to nitrite followed by the
oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate. The transformation of ammonia to nitrite is usually the rate
limiting step of nitrification.Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil.
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process of nitrate reduction (performed by a large
group of heterotrophic facultative anaerobic bacteria) that may ultimately produce molecular
nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products.
Ammonia or azane is acompound of nitrogen andhydrogen with the formulaNH3. The
simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent smell. It
contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor
tofood and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis
of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products.
Acidophiles or acidophilic organisms are those that thrive under highly acidic conditions
(usually at pH 2.0 or below). These organisms can be found in different branches of the tree of
life, including Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryotes.
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline (pH roughly
8.511) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10.
Most bacteria prefer pH 6-8
Most fungi prefer pH 4-7
Você também pode gostar
- Environmental Microbiology GRP 4Documento11 páginasEnvironmental Microbiology GRP 4Ayoade opeyemiAinda não há avaliações
- M A N U R e C H e M I S T R y - N I T R o G e N, P H o S P H o R U S, & C A R B o NDocumento4 páginasM A N U R e C H e M I S T R y - N I T R o G e N, P H o S P H o R U S, & C A R B o NRowel GanzonAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento17 páginasNitrogen CycleLeigh Chanelle OngAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento5 páginasNitrogen CycleVamsi K Kuchibhotla100% (1)
- AmmonificationDocumento2 páginasAmmonificationlakadia taylorAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogenous FertilizersDocumento8 páginasNitrogenous FertilizersSadia UroojAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento7 páginasNitrogen CycleAfina ShsAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento10 páginasNitrogen Cyclejarina jeydAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenDocumento3 páginasChem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenshshbshshsjsjAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen FixationDocumento6 páginasNitrogen FixationAxel Andrus ClapisAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient CyclingDocumento24 páginasNutrient CyclingSofia Dicen100% (1)
- Nitrogen in The BiosphereDocumento39 páginasNitrogen in The BiosphereAzizi D'adventurerAinda não há avaliações
- Mineral NutritionDocumento16 páginasMineral NutritionPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanAinda não há avaliações
- 162 Ecological Processes AmmonificationDocumento4 páginas162 Ecological Processes AmmonificationGilingan PastaAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento52 páginasNitrogen CycleHardik100% (2)
- Jimma Institute of Technology Advanced Wastewater TreatmentDocumento40 páginasJimma Institute of Technology Advanced Wastewater TreatmentyaredAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental of Ecology Lec09 Nitrogen and Phosporus Cycles Hand2003Documento6 páginasFundamental of Ecology Lec09 Nitrogen and Phosporus Cycles Hand2003Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.Ainda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento21 páginasNitrogen CycleAfaq AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen MetabolismmmmDocumento11 páginasNitrogen MetabolismmmmAngelica Malacay RevilAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento17 páginasNitrogen CyclejosevitorromualdoAinda não há avaliações
- Assimilation: Edit Assimilation (Biology) Nitrogen AssimilationDocumento5 páginasAssimilation: Edit Assimilation (Biology) Nitrogen AssimilationSNS-12 PAVITHRAA TAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento2 páginasNitrogen CycleKalsoom AsadAinda não há avaliações
- DOC040.52.10005.Oct12 Nutrients - Web PDFDocumento8 páginasDOC040.52.10005.Oct12 Nutrients - Web PDFKari ConwayAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical Cycles Compatibility ModeDocumento52 páginasBiogeochemical Cycles Compatibility ModeAkshay EtwareeaAinda não há avaliações
- Iso 14000 & 18000Documento11 páginasIso 14000 & 18000Suchiey Mei SaaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient Cycles: Prof. Murray, Univ of Illinois at ChicagoDocumento35 páginasNutrient Cycles: Prof. Murray, Univ of Illinois at Chicagomahesh nagarAinda não há avaliações
- 4500 NitrogenoDocumento6 páginas4500 NitrogenoPenelope MeloAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen Cycle: Submitted By, Sreejith P S EEE ROLL NO:-54Documento19 páginasNitrogen Cycle: Submitted By, Sreejith P S EEE ROLL NO:-54Jobin VargheseAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen and Sulphate Assimilation PresentationDocumento55 páginasNitrogen and Sulphate Assimilation PresentationSri HayuniAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento10 páginasNitrogen CyclekilaxxdmaxAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento15 páginasNitrogen CycleZoya ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical Cycle Nitrogen Gaseous Earth's Atmosphere NitrogenDocumento20 páginasBiogeochemical Cycle Nitrogen Gaseous Earth's Atmosphere NitrogenaradhyaAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical CycleDocumento29 páginasBiogeochemical CycleAsep SaefumillahAinda não há avaliações
- Practices To Maintain Soil FertilityDocumento15 páginasPractices To Maintain Soil FertilityNogaraAinda não há avaliações
- DENITRIFICATIONDocumento3 páginasDENITRIFICATIONmishti3001Ainda não há avaliações
- Nat Sci 2Documento2 páginasNat Sci 2Pamela Ellaine PlarizaAinda não há avaliações
- V. Nitrogen Transformations in Soil: Required ReadingsDocumento13 páginasV. Nitrogen Transformations in Soil: Required ReadingsMandaviAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen Cycle: Ecological FunctionDocumento8 páginasNitrogen Cycle: Ecological FunctionApam BenjaminAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen MetabolismDocumento7 páginasNitrogen MetabolismNida saleemAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical CycleDocumento29 páginasBiogeochemical CycleAsep SaefumillahAinda não há avaliações
- NASIRDocumento8 páginasNASIRapi-26413035Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemical Fertilizers: Lesson 12Documento42 páginasChemical Fertilizers: Lesson 12Ngô Minh AnhAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocumento17 páginasBiogeochemical CyclesSudeeksha RavikotiAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento5 páginasNitrogen CycleTufel Noorani100% (1)
- The Making of Ammonia: Name - Date - ClassDocumento2 páginasThe Making of Ammonia: Name - Date - ClassJoseph ScottAinda não há avaliações
- Production Technology of Agrochemicals-FertilizerDocumento81 páginasProduction Technology of Agrochemicals-FertilizerBereket TadesseAinda não há avaliações
- Nitro CompoundDocumento5 páginasNitro CompounddearbhupiAinda não há avaliações
- Bioremediation of Polynitrated Aromatic Compounds: Plants and Microbes Put Up A FightDocumento7 páginasBioremediation of Polynitrated Aromatic Compounds: Plants and Microbes Put Up A FightLuis CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Biology PresentationDocumento21 páginasBiology PresentationWalid Hasan JoyAinda não há avaliações
- Environment - Nitrogen CycleDocumento5 páginasEnvironment - Nitrogen CycleMugal AslamAinda não há avaliações
- Enzymology and Ecology of The Nitrogen CycleDocumento4 páginasEnzymology and Ecology of The Nitrogen CyclespongebobAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Muhammad Ishaq Paper: Environemental Biology ID NO: 15312 M.SC (Botany) 4 Semester DATED: 14/06/2021Documento20 páginasName: Muhammad Ishaq Paper: Environemental Biology ID NO: 15312 M.SC (Botany) 4 Semester DATED: 14/06/2021Sajid RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Biogeochemical CycleDocumento57 páginasBiogeochemical Cyclebiboy maganAinda não há avaliações
- Proceedings of the Conference on Nitrogen as a Water Pollutant: Volume 8.4No EverandProceedings of the Conference on Nitrogen as a Water Pollutant: Volume 8.4S. H. JenkinsAinda não há avaliações
- Flowsheet LabsDocumento10 páginasFlowsheet LabsNisaMardiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen CycleDocumento15 páginasNitrogen CycleKenji AlbellarAinda não há avaliações
- 1.1 General:: Biological Nutrient RemovalDocumento21 páginas1.1 General:: Biological Nutrient Removalವಿನಯ್ ಎಮ್. ಆರ್Ainda não há avaliações
- 1.1 General:: Biological Nutrient RemovalDocumento21 páginas1.1 General:: Biological Nutrient Removalವಿನಯ್ ಎಮ್. ಆರ್Ainda não há avaliações
- Chem 3Documento4 páginasChem 3Cristyl Vismanos GastaAinda não há avaliações
- Derivatives of AlcoholDocumento5 páginasDerivatives of AlcoholEcho MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Att14-Effective Asphalt Content of Mix 01-07 PDFDocumento1 páginaAtt14-Effective Asphalt Content of Mix 01-07 PDFNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- PlumbingDocumento31 páginasPlumbingNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Design of RC Rectangular Section NSCP ACI 318Documento5 páginasDesign of RC Rectangular Section NSCP ACI 318Nicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Turbine: Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber Steam Power Plant Compressor EnergyDocumento6 páginasGas Turbine: Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber Steam Power Plant Compressor EnergyNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- VerseDocumento3 páginasVerseNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Related Review LiteratureDocumento3 páginasRelated Review LiteratureNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Steel BarsDocumento4 páginasSteel BarsNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- 02 - Design of Steel Tension MembersDocumento15 páginas02 - Design of Steel Tension MembersMayur PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter IDocumento5 páginasChapter INicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Sedl/ : "Suspended Organic Matter": Floating Organic Particles Derived From The Decomposition of Dead OrganismsDocumento7 páginasSedl/ : "Suspended Organic Matter": Floating Organic Particles Derived From The Decomposition of Dead OrganismsNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Truss Roof: University of Engineering & Technology, TaxilaDocumento42 páginasDesign of Truss Roof: University of Engineering & Technology, TaxilaNicko Jay BajaoAinda não há avaliações
- Reinforced Concrete Design FormulasDocumento6 páginasReinforced Concrete Design FormulasNicko Jay Bajao83% (6)