Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Motion
Enviado por
api-340406981Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Motion
Enviado por
api-340406981Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME : _______________________
_____________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION
SCORE
: _____________
ACTIVITY # 1
MOMENTUM
Objectives:
calculate the momentum of an object
analyze factors that affects the momentum of an object
Arrange the following
according to increasing magnitude of momentum. Assume that all of them are moving in
their maximum speed.
___Car
___Motorcycle
___Bicycle
___Rabbit
___Bullet airplane
___Horse
___Ant
___Bus
___Turtle
___Skateboard
Problem Solving:
1. A bowling ball of 35.2 kg generates 218 kg m/s units of momentum. What is the
velocity of the bowling ball?
2. What is the momentum of a child and wagon if the total mass of the child and
wagon is 22kg and the velocity is 5.4 km/h?
3. A school bus traveling at 39.96 km/h has a momentum of 152,625 kg m/s. What
is the mass of the bus?
4. What should be the velocity of a 1800 kg bus to have the same momentum as a
car with a mass of 1400 kg moving with a velocity of 120 km/h?
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME : _______________________
_____________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION
SCORE
: _____________
ACTIVITY # 1
COLLISION
Objective:
Solve problems involving the different types of collisions.
1. A 1800kg car is moving at 30m/s eastward. It collides head on with a 2200kg
garbage truck. What is the initial velocity of the truck if the car and the truck move
together after the collision at 12m/s?
2. A 0.25kg ball moving southward at 30m/s collides with a 0.10 kg ball moving
along the same line with a velocity of 15m/s southward. After collision, the 0.25kg
ball attains a velocity of 22m/s southward. What is the velocity of the 0.10kg ball?
3. A 660kg motorcycle moving 20m/s rear-ends a 1017kg car traveling at 16m/s on
a concrete highway in the same direction. If the two vehicles stick together, how
fast did they move immediately after collision?
4. A 0.48 kg ball moves to the left with a speed of 6m/s. It hits a 0.65kg ball that is
at rest. After collision, the second ball moves to the left with a speed of 4m/s.
What is the speed of the first ball after collision?
5. A 1222kg car moves at 25m/s while a second car which has a mass of 1168kg
travels at 22m/s. If the two cars collide head-on and stick together, what will be
their speed after collision?
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME : _______________________
_____________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION
SCORE
: _____________
Differentiate the three types of collisions by completing the table below.
TYPE OF
DIAGRAM
BEHAVIOR OF
CONSERVE
COLLISIO
BEFORE
AFTER
OBJECTS
D QUANTITY
N
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME : _______________________
_____________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION
SCORE
: _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
Activity # 3
Projectile Motion
Part 1
Objective:
Compute for unknown variables using equations for horizontal and angled
projectiles
1. A marble is rolled off the edge of a table 0.75 m high with a horizontal velocity of
1.5 m/s. How far will the marble travel before it hits the ground?
2. A soccer ball is kicked horizontally off a 22.0-meter high hill and lands a distance
of 35.0 meters from the edge of the hill. Determine the initial horizontal velocity of
the soccer ball.
3. A stone is thrown from a 5m high window with an initial velocity of 45 m/s. How
long will the stone reach the ground? How far on the ground will it reach?
4. A golfer on an elevated tee 2.5 m above the green hits the golf ball so that it
leaves the club with a horizontal velocity of 25m/s. How long will the golf ball land
on the green after it leaves the club? How far will the golf ball travel before
striking the green?
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Activity # 3
Projectile Motion
Part 2
Objective:
Compute for unknown variables using equations for horizontal and angled
projectiles
1. A golf ball was hit and projected at an angle of 55 o with the horizontal. If the initial
velocity of the ball was 50 m/s (neglect air friction), then calculate the horizontal
distance the ball traveled and the maximum height the ball reached.
2. Water shoots out from a fountain at 40 m/s at an angle of 55 o above the
horizontal. What is its time of flight? What is its range?
3. A long jumper leaves the ground at an angle of 30 o to the horizontal and at a
speed of 12m/s. How far does he jump?
4. A player kicks a football from ground level with an initial velocity of 32.0 m/s, 60 o
above the ground. Find the maximum height reached by the ball and the
horizontal distance traveled by the ball.
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Activity # 3
Energy
Objectives:
1. illustrate understanding about energy.
2. Solve problems involving different forms of energy
Kinds:
Sources:
Applications:
Occupations:
Problem Solving:
1. A 2-kg toy car moves along a frictionless surface with a uniform speed of 6 m/s.
What is its kinetic energy?
2. Budoy, a junior high school student, lifts a 3-kg book from the floor into a cabinet 2.0
m high. With reference to the floor, how much potential energy does the book acquire?
NAME: _______________________
SECTION : _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
DATE : _______________________
_____________
SCORE
Activity # 4
Heat Cloze
Fill in the blanks with words from the box.
conduction
energy
rise
convection
kinetic
temperature
dense
liquids
thermometer
Earth
radiation
Vibrating
Heat is a form of _________________ that moves from hot things to cold
things. In other words, heat is energy that flows from objects with a high
_________________ to objects with a low temperature. Temperature is
the average _________________ energy of the particles in an object and
is measured using a _________________.
Heat can move from object to object in three ways. One way that heat
flows is called _________________, which occurs when two objects are
Keeping warm by the fire.
touching.
In conduction, the particles in the high temperature object are _________________ quickly compared to the
low temperature object. When the particles in the high temperature object bump into the particles in the low
temperature object, the low temperature objects particles begin to vibrate more quickly. Another form of heat
transfer is _________________, which occurs in _________________ and gases. In convection, the part of the
liquid or gas with high temperature is less_________________ than the part with low temperature so the high
temperature parts _________________ and the low temperature parts sink.
In both conduction and convection, heat is transferred through a material. However, heat energy can also travel
through empty space in a third way called _________________, which is how heat travels from the sun to the
_________________.
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Activity # 4
Efficiency
Compute the efficiency, work input and work output of the given machines below.
MACHINES
Garbage Truck
Racing Car
INPUT WORK
(J)
OUTPUT
WORK
(J)
1800
600
900
Tricycle
Airplane
Motorcycle
75%
110
4000
EFFICIENCY
(%)
51%
3200
400
60%
Solutions:
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________Date: _____
Você também pode gostar
- High School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsNo EverandHigh School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsAinda não há avaliações
- ACT Math Section and SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionNo EverandACT Math Section and SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (3)
- 2.4 Analysing Momentum(s)Documento11 páginas2.4 Analysing Momentum(s)Freddie ChaiAinda não há avaliações
- 1st 9 Week Review 2015bDocumento2 páginas1st 9 Week Review 2015bapi-297287095Ainda não há avaliações
- Force and Acceleration WSDocumento2 páginasForce and Acceleration WSMIS NURUL IMAN JakbarAinda não há avaliações
- FORCES AND MOTION-workbook PDFDocumento13 páginasFORCES AND MOTION-workbook PDFJane DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- DC Honors Physics Final Exam Practice Problems - May 15Documento6 páginasDC Honors Physics Final Exam Practice Problems - May 15webelo1998Ainda não há avaliações
- AccelerationDocumento1 páginaAccelerationAika Mae ArakakiAinda não há avaliações
- Fisika 1Documento1 páginaFisika 1bat.laughAinda não há avaliações
- Test+Review+TMD 2Documento4 páginasTest+Review+TMD 2Deborah OlofinkuadeAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 6 6th Grade CH 6Documento2 páginasExam 6 6th Grade CH 6Maranyelis ArroyoAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam A Review 2014Documento4 páginasFinal Exam A Review 2014api-273978634Ainda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 1 HomeworkDocumento1 páginaTopic 2 1 HomeworkFakha VezirovaAinda não há avaliações
- Semester Exam 2 Study Guide With AnswersDocumento8 páginasSemester Exam 2 Study Guide With Answersapi-277964255Ainda não há avaliações
- ENMA 101 Assignment No. 3 - RELATED RATES/TIME RATES NAME: - ScoreDocumento2 páginasENMA 101 Assignment No. 3 - RELATED RATES/TIME RATES NAME: - ScoreJordan Arellano MacatoAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 - Science - CompleteDocumento19 páginasGrade 10 - Science - CompleteLucille Gacutan AramburoAinda não há avaliações
- 1st PT G9 Physics EditedDocumento4 páginas1st PT G9 Physics EditedAldrin UrbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Cyphersenergyreview 2016 DocxsDocumento4 páginasCyphersenergyreview 2016 Docxsapi-285382578Ainda não há avaliações
- 4 Mastery Test: Momentum Unbalanced Collision Isolated ImpulseDocumento2 páginas4 Mastery Test: Momentum Unbalanced Collision Isolated Impulsejohn Erick JulianAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Sheet in Science q3Documento14 páginasActivity Sheet in Science q3Sherlyn Dela Cruz TiongsonAinda não há avaliações
- Examen de Physics 11 Ordinario Dic 2023Documento7 páginasExamen de Physics 11 Ordinario Dic 2023Camila GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity SheetDocumento18 páginasActivity SheetAnonymous bM3dl8mAinda não há avaliações
- GizmoDocumento9 páginasGizmoAmaan Baloch0% (3)
- Science VDocumento4 páginasScience VRuvelyn AmidoAinda não há avaliações
- q4 summatIVE QUIZ QUEZONDocumento2 páginasq4 summatIVE QUIZ QUEZONcapiendokarljarrens09Ainda não há avaliações
- Collisions Worksheet and ReviewDocumento3 páginasCollisions Worksheet and ReviewHartantoAinda não há avaliações
- Student Exploration: Free Fall TowerDocumento4 páginasStudent Exploration: Free Fall TowerAK - 11ZZ 677996 Mayfield SSAinda não há avaliações
- Shs Periodical ExamDocumento2 páginasShs Periodical ExamRICHARD GASATANAinda não há avaliações
- AccelerationWorksheet 000Documento1 páginaAccelerationWorksheet 000Gerry BritalAinda não há avaliações
- Summative Test Sci8 q1Documento2 páginasSummative Test Sci8 q1jennelyn zamoraAinda não há avaliações
- MT BSMathDocumento2 páginasMT BSMathJeremy RubianesAinda não há avaliações
- IV EXPLANATION OF CONCEPTS: Answer The Ff. Questions Briefly. (3 Points Each Item)Documento9 páginasIV EXPLANATION OF CONCEPTS: Answer The Ff. Questions Briefly. (3 Points Each Item)VaryAinda não há avaliações
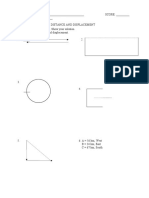
- Distance DisplacementDocumento4 páginasDistance DisplacementRuchi Briam James LagitnayAinda não há avaliações
- Questions About QuestionsDocumento2 páginasQuestions About QuestionsEvan Marey AntoneAinda não há avaliações
- Saint Thomas Development Academy of Bulacan Inc. Third Preliminary Examination in Science 7Documento8 páginasSaint Thomas Development Academy of Bulacan Inc. Third Preliminary Examination in Science 7El CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Physics1-1b Problem SetsDocumento14 páginasPhysics1-1b Problem SetsPogi MedinoAinda não há avaliações
- Student Exploration: Free Fall TowerDocumento4 páginasStudent Exploration: Free Fall TowerOmar MoosaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity SheetDocumento14 páginasActivity SheetMa. Cristina D. MagadiaAinda não há avaliações
- Air Track SEDocumento7 páginasAir Track SEHenry HAinda não há avaliações
- 5b. Newton Olympics LabDocumento3 páginas5b. Newton Olympics LabAna Ats YviAinda não há avaliações
- 2.1 Linear Motion 2012Documento18 páginas2.1 Linear Motion 2012cikgusuriyatiAinda não há avaliações
- Science 8 - Q1 - DW8Documento3 páginasScience 8 - Q1 - DW8Argyll PaguibitanAinda não há avaliações
- ECSDTest - Unit1and2StudyGuideKEY - PDF Force-Motion-Newtons Laws 2020Documento4 páginasECSDTest - Unit1and2StudyGuideKEY - PDF Force-Motion-Newtons Laws 2020paulAinda não há avaliações
- PT 2 - Problem Set Free FallDocumento1 páginaPT 2 - Problem Set Free FallLeila BacayAinda não há avaliações
- GR 7 - POST TEST ON HEAT ENERGYDocumento3 páginasGR 7 - POST TEST ON HEAT ENERGYChielina Lourine LozanoAinda não há avaliações
- Student Exploration: Energy Conversions Part 2Documento2 páginasStudent Exploration: Energy Conversions Part 2yareliAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Activity Sheets in Science7 - No. 1Documento6 páginasLearning Activity Sheets in Science7 - No. 1Cherry Mae MamarilAinda não há avaliações
- Science 4, Q3, Module 6, ReyesDocumento12 páginasScience 4, Q3, Module 6, ReyesIyutaann Kantutan100% (1)
- PhysicsDocumento1 páginaPhysicsyeniAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - Part I: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocumento3 páginasKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - Part I: Potential and Kinetic EnergyChristine Ainah Pahilagao Sales100% (1)
- Acceleration WorksheetDocumento2 páginasAcceleration WorksheetjezzuwafuAinda não há avaliações
- Freefall Towers eDocumento4 páginasFreefall Towers eRyan Pazon0% (1)
- Student Exploration: Free Fall TowerDocumento4 páginasStudent Exploration: Free Fall TowerAlnawaya hassanAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 7 Activity Sheet Week 3 1Documento5 páginasGrade 7 Activity Sheet Week 3 1Bianca MielleAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 4th GradingDocumento3 páginasScience 9 4th GradingedwardAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics and Heat CompleteDocumento4 páginasMechanics and Heat CompleterezaAinda não há avaliações
- NAME: - CLASS: - Chapter 5: Motion 5.1 The Motion of Vehicles On LandDocumento18 páginasNAME: - CLASS: - Chapter 5: Motion 5.1 The Motion of Vehicles On LandCik HidayahAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Math Refresher, 2nd Ed.: Everyday Math for Everyday PeopleNo EverandBasic Math Refresher, 2nd Ed.: Everyday Math for Everyday PeopleAinda não há avaliações
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 3No EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 3Ainda não há avaliações
- From warm-up to handball team play: 75 exercises for every handball trainingNo EverandFrom warm-up to handball team play: 75 exercises for every handball trainingAinda não há avaliações
- VolcanoDocumento8 páginasVolcanoapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- 9 Learning StrategiesDocumento3 páginas9 Learning Strategiesapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Science 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer RubricsDocumento6 páginasScience 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer Rubricsapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- MoleDocumento5 páginasMoleapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemical BondingDocumento5 páginasChemical Bondingapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- ClimateDocumento5 páginasClimateapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Actvity Sheets GeneticsDocumento6 páginasActvity Sheets Geneticsapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Volcanoes 3 FinalDocumento106 páginasVolcanoes 3 Finalapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- GeneticsDocumento28 páginasGeneticsapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity Sheet PhotosynthesisDocumento4 páginasActivity Sheet Photosynthesisapi-34040698140% (5)
- Projectile MotionDocumento11 páginasProjectile Motionapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Impulse Momentum Check ItDocumento38 páginasImpulse Momentum Check Itvenkateshyadav2116Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 Project ProposalDocumento3 páginas8 Project Proposalapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity Sheet Body SystemDocumento8 páginasActivity Sheet Body Systemapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- 0708 EnergyDocumento42 páginas0708 EnergybittuchintuAinda não há avaliações
- ClimateDocumento14 páginasClimateapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- ConstellationsDocumento85 páginasConstellationsDivya NayakaAinda não há avaliações
- Bonding Types Ionic Covalent MetallicDocumento43 páginasBonding Types Ionic Covalent Metallicapi-236069914100% (1)
- Structure of Organic CompoundsDocumento27 páginasStructure of Organic CompoundsBetty Weiss100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocumento22 páginasCirculatory SystemAliAshalAinda não há avaliações
- ExtinctionsDocumento20 páginasExtinctionsapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- The Mole ConceptDocumento8 páginasThe Mole Conceptapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratorysystem 16Documento35 páginasRespiratorysystem 16api-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Ubd 3rd VolcanoDocumento1 páginaGrade 9 Ubd 3rd Volcanoapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical BondingDocumento34 páginasRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical Bondingapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Ubd 4th Heat ElectricityDocumento15 páginasGrade 9 Ubd 4th Heat Electricityapi-340406981100% (14)
- Grade 9 Ubd 4th Motion EnergyDocumento1 páginaGrade 9 Ubd 4th Motion Energyapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Ubd 3rd Climate ConstellationDocumento1 páginaGrade 9 Ubd 3rd Climate Constellationapi-340406981Ainda não há avaliações
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter MoleDocumento23 páginasRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Moleapi-340406981100% (1)
- Modelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidDocumento13 páginasModelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidKaram JaradatAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo Sample ProblemsDocumento5 páginasThermo Sample ProblemsDeniel AndalAinda não há avaliações
- SAP BI BO Presentation TorrentDocumento36 páginasSAP BI BO Presentation TorrentRajab Ali Jiwani100% (1)
- Get TRDocDocumento185 páginasGet TRDockfrisch1229Ainda não há avaliações
- On Windows Syscall Mechanism and Syscall Numbers Extraction MethodsDocumento26 páginasOn Windows Syscall Mechanism and Syscall Numbers Extraction MethodsqdwqdAinda não há avaliações
- Allpile ManualDocumento103 páginasAllpile ManualKang Mas WiralodraAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Seismic Force On BuildingDocumento12 páginasDesign of Seismic Force On BuildingAjay DalviAinda não há avaliações
- c3 PDFDocumento29 páginasc3 PDFHrithik IGAinda não há avaliações
- 3M Festool Catalog - 60-4402-7925-9Documento25 páginas3M Festool Catalog - 60-4402-7925-9Kaled VásquezAinda não há avaliações
- EMM 3514 - Numerical MethodDocumento33 páginasEMM 3514 - Numerical MethodAdhar GoodAinda não há avaliações
- User Acceptance and System Test Checklist Proven Practice v1Documento5 páginasUser Acceptance and System Test Checklist Proven Practice v1skeezixxAinda não há avaliações
- Be Form 3 - Resource Mobilization FormDocumento3 páginasBe Form 3 - Resource Mobilization FormDherick RaleighAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic: VvinuDocumento528 páginasSeismic: VvinuLucas ScartonAinda não há avaliações
- BrochureDocumento4 páginasBrochureChristina MaierAinda não há avaliações
- AICTE Registered Management Colleges in IndiaDocumento67 páginasAICTE Registered Management Colleges in IndiaChandra Shekar100% (1)
- Earthquake Design Presentation (M.sleiman)Documento20 páginasEarthquake Design Presentation (M.sleiman)JunnoKaiserAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1:: Preliminary EstimatesDocumento22 páginasTopic 1:: Preliminary EstimatesRajan RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Rexroth CDB01 CSB01 CSH01 Project Planning ManualDocumento198 páginasRexroth CDB01 CSB01 CSH01 Project Planning Manualdhanita yAinda não há avaliações
- BOP Shear Pressure Calculations Rev 1Documento3 páginasBOP Shear Pressure Calculations Rev 1unduh100% (1)
- Electrically Controlled Deluge Valve With Remote Reset Model FP 400Y - 3UDocumento4 páginasElectrically Controlled Deluge Valve With Remote Reset Model FP 400Y - 3Upedro torresAinda não há avaliações
- Microwave JunctionsDocumento20 páginasMicrowave JunctionsSaraswathi Asirvatham100% (2)
- Dimethylamine PDFDocumento2 páginasDimethylamine PDFangelofgloryAinda não há avaliações
- JUMONG General (JMPS) Installation Manual - en - CMP200 - 20181129Documento44 páginasJUMONG General (JMPS) Installation Manual - en - CMP200 - 20181129Juan Alberto RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocumento10 páginasVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalAinda não há avaliações
- Mhi (Humicool Industrial) : Industrial Evaporative Cooler / HumidifierDocumento2 páginasMhi (Humicool Industrial) : Industrial Evaporative Cooler / HumidifierGraham GunnerAinda não há avaliações
- Bmaxx 4400 JindalDocumento76 páginasBmaxx 4400 JindalRakesh Karan Singh0% (1)
- Loctite Instant Adhesives: Instant Solutions in Every DropDocumento9 páginasLoctite Instant Adhesives: Instant Solutions in Every DroptejassidhpuraAinda não há avaliações
- Sikadur®-42 PC: Product Data SheetDocumento4 páginasSikadur®-42 PC: Product Data SheetMohammed AwfAinda não há avaliações
- Backup of Submitil CraneDocumento17 páginasBackup of Submitil CraneAhmed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Datasheet Sunedison 330W PDFDocumento2 páginasDatasheet Sunedison 330W PDFDarilho Batista IgnacioAinda não há avaliações