Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Answer To Practice Problems #4 PDF
Enviado por
ddubbah0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações19 páginasTítulo original
Answer to Practice problems #4.pdf
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações19 páginasAnswer To Practice Problems #4 PDF
Enviado por
ddubbahDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 19
Problem 8.144
‘Avweight W = 21eN ix support dby a cable that pasar over frictionless palleys
‘at D and F. The cable i atached to awinch at G, and cable segment DC
isvertical Member ABC is builtin at A. and members ABC. DCEF. and
[BE we attached sing pine at points B.C,and E. Neglecting the weighes of
individual members, detcrmin: the internal forces acting on: Cross sections
‘Land Q, located immediaely t the eft of pint C and the right of paint D,
‘respectively
Solution
We take a cut through cross section [, and draw the FED to the left My 7
‘ofthe crots section ta determine te ier Foret. weet &
TEN + Ni = 0, ay Ye
=> Mp=—2kN, a aN
—2eN— y= 0. ®
= h=-nN, w
AML ML =0, ®
+ M,=-320INm 6)
summa -
Me=—2EN, Vi Mi = —3.0EN-m. 0
(We take a cut through crs ction © and draw the FED to the IR of the
‘crore mection t dewrmine the inaeral forces.
TAN +NQ=0,
+ No=-20N,
TEN Vo =0, any
e3
ay
Problem 6.184
"A machine for ifing kowy cbjects on an assembly line ixshows. consists of
stnight member ABC. a quare.circular member CDE, and a hydraulic cylinder
[BD. In the position shown, the hydronic cylinder te vertical. If W = 800 Tp, and
neglecting the weight ofthe components of the mackie, determine the imrnal
(forces acting ore Cross sections Hand [, located immediately ta the left of point
1 and tthe right of point C, mexpectively.
‘Solution
Wedraw the PRD of member ABC to determine te reaction force at pint B
ElMe=0: Fao (2 AMeor30")— (B00 18Kt coe 30") = 0, o
> Feo = 100m. o
Werte 2 cut through cross ction Hf and draw the PRD to the right
‘ofthe cross section tn determine te internal foros.
LR =0: | -Wy—(te008)( V=-20N, (©) A, = aston
MeO: “ye tao, »
= w= Cmo0Nts. 6
Summary
fe 0 eo
‘Weta acutatan arbitrary postion etwarn points Band C anddrow te FD
‘to the right of the cut to determine the shear and moment 2s functions of position for 4
Imsrsdm qa
bmi wv oh
VE 6O7N, M=(CO6INKdm—x), for Imex =ém ay
(Using them salts the shear and moment diagrams may he drawn as follows
von 4m)
8
* 248) °
Problem 8.384
We tae a cut at an arbitrary position between points A and C and draw the FD unfane
tothe left of the cut © determine the shear and moment as functions of postion. H
o
. oo | (ny
Problem 8.434
‘One of the beams that supports balcony is shown. To design a beam for this
[purpos it is common to we a uniformly disiribeied load that inclades the
‘dead leads (og, weight of materials) and live loads (e..weight of » large, bat
reasonable nursber of people distributed over the balcony ) If the uniformly
\dicributed load ix 2500.N/m, determine the shear and moment as funetions of
position, and draw the shear and moment diagrams. Idealire the supports at BA!
land € to bea rllerand pin, wspectively.
Solution
Wecdraw the HD ofthe beam AIC to determine the reacions fesc0 3) (am) = 00
rr G0 @ |
Bim = 0: -29(2m) + O00N)(1.5m) =0, @ a ro
= sasN, » Ie
Eno: By + Cy 75008 = 0, «
WEN.)
Wetake acutat an arbitrary position tetween points A and Bandra the FAD tothe (2808) 5
leftofthe cutis detrmine the shear and moments functions of position for Q |@=tn'p,
o
Problem 9.171
"A wedge is used to vel a structure. All contact surfaces have coeficients|
of static and kinetic friction of 0.3 and 0.25, respectively, and W = SOON.
‘Assume the dimensions ofthe wedge are small. Determine the value of P to 4
cause impending motion of the wedge:
(@) Tothe left
(b) Totte righ,
Solution
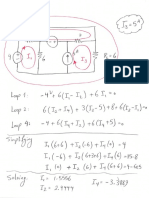
Part (a) Wedge C slides to the left, which allows the the Fs shown,
atthe right to be drawn.
BeamAB: >My =0: —(500N)(00mm)
+2608 15°(600mm) — N sin 15°(G0mm)
— Fcos 15°@0mm) — Fa sin 15° (600 mm
1 motion is impending. then
Fr=nM= (030M, and F2=p,N2=(03)N2.
Solving Eqs. (1) and (2) for Nz and F provides
Nz =3067N, f= 9201N. °
. @
Wedge C: > F, = 0: Mi —Nacosis? + Fysinis® =o,
Seno: A+ msinis? + Frewis"— P =o.
Using Eqs. (2) and (3), i, (4) is sotved to obtain
Mj =224N, Fy =8L73N,
and Eq. (5) i solved to obtain
wo
o
©
@
Statics 26 1353
Problem 9.184
[Blocks A and B each have 2kg mass. All contact surfaces have the same coefficient
rns Drm an Pm imp on
SRS Be
Solution
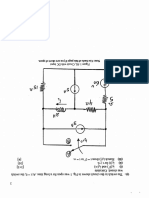
ach block has weight IV. = (2kg) (9.81 m/s?) = 19.62N. With block B »
sliding to the left and block 4 sliding upward, the FBDs are shown a the right.
Block A: > Fy = 0: Nzcos20"— Fy sin20°— Fy—W = 0
Soe = 0: —Nysin20°— Fc0s20° 4s
© A
1M, — Nzcos20° + Fzsin20°—W = 0, G) rr
Fy 4Nzsin20° + F,c0s20°— P= 0. (4) M
Fy= mM =O4)N, Fr=psNa=(04N2, amd Fy=,Ny= (04. )
‘While there ae seven equations with seven unknowns, these are easily solved, as follows. Using Fa. (5),
Eqs. (1) and 2) become, respectively,
‘Nacos20” — (0.4)Nasin 20° — (0.4)Na—W
= Nzsin20°— (0.4)N 2008 20° + Ns
©
0
‘Maltpying Eq. (7) by 4 and adding this to Eq (6 provides one equation where Ni the only unknown,
‘and solving for this provides Na — 38.04N. Substituting N3 into the other equations then provides the
‘remaining unknowns, with the sults
Ny =5016N, Fy ®
N2=3808N, Fo o
Na=2731N, Fa a0)
P=ATAN, an
Você também pode gostar
- Tutorial Question 0711Documento3 páginasTutorial Question 0711ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Making Sense of Pump Testing Standards - How Understanding Standards Can Impact The Bottom Line PDFDocumento24 páginasMaking Sense of Pump Testing Standards - How Understanding Standards Can Impact The Bottom Line PDF1sympatyagaAinda não há avaliações
- مضخة الطرد المركزى- كتيب للتحميلDocumento128 páginasمضخة الطرد المركزى- كتيب للتحميلGrundfosEgypt100% (4)
- L 00112Documento76 páginasL 00112ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- PV776 TSP194907Documento62 páginasPV776 TSP194907acido4020100% (1)
- FormulationDocumento40 páginasFormulationNitin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Formula Sheet-Midterm 2015Documento2 páginasFormula Sheet-Midterm 2015ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Gates CoolingSystemTroubleshootingGuide Manual enDocumento76 páginasGates CoolingSystemTroubleshootingGuide Manual enddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Programming OptimizationDocumento37 páginasLinear Programming OptimizationlaestatAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management Case Study Group AssignmentDocumento9 páginasProject Management Case Study Group AssignmentddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- CH 09Documento114 páginasCH 09ddubbah100% (2)
- Me C 323 Solution 2016Documento4 páginasMe C 323 Solution 2016ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Answer To Practice Problems #4 PDFDocumento19 páginasAnswer To Practice Problems #4 PDFddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Final Winter 2015 PDFDocumento27 páginasSolutions Final Winter 2015 PDFddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Final Winter 2015Documento27 páginasSolutions Final Winter 2015ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions April21 ExamDocumento18 páginasSolutions April21 ExamddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Binder EEs512 Midterm SolutionDocumento14 páginasBinder EEs512 Midterm SolutionddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- CH 12Documento13 páginasCH 12ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- CH02 1Documento26 páginasCH02 1ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Answer To Practice Problems #4 PDFDocumento19 páginasAnswer To Practice Problems #4 PDFddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- IND 605 - Lab SummaryDocumento3 páginasIND 605 - Lab SummaryddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- 605 Excel Lab 1Documento2 páginas605 Excel Lab 1ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Practice MidtermDocumento5 páginasPractice MidtermddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Alternate Candidate For Branching: (10 4)Documento3 páginas1 Alternate Candidate For Branching: (10 4)ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- CH 09Documento15 páginasCH 09ddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Ecn801 MT p2015 Ver - A - FullDocumento12 páginasEcn801 MT p2015 Ver - A - FullddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Reading sample task – Matching informationDocumento5 páginasAcademic Reading sample task – Matching informationKabilan MuthukannanAinda não há avaliações
- Summarizing MethodsDocumento8 páginasSummarizing MethodsddubbahAinda não há avaliações
- 1000 Most Common Words (SAT)Documento70 páginas1000 Most Common Words (SAT)grellian95% (20)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)