Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
ATPL Inst Contents PDF
Enviado por
Koustubh VadalkarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ATPL Inst Contents PDF
Enviado por
Koustubh VadalkarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Instrumentation
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Table of Contents
Section 1 Air Data Instruments
Chapter 1.1 - Air Temperature Measurement
Introduction
Direct Reading Thermometer
Electrical Thermometer
Static Air Temperature Sensor
Total Air Temperature Probe
1.1.1
1.1.2
1.1.2
1.1.3
1.1.4
Chapter 1.2 - Pitot-Static System
Introduction
Pitot Tube
Static Source
Alternate Static Source
Combined Pitot-Static (Pressure) Head
Operating Problems
Pitot/Static System Errors
1.2.1
1.2.1
1.2.1
1.2.2
1.2.4
1.2.4
1.2.4
Chapter 1.3 - Pressure Altimeter
Introduction
Pressure Altitude
Density Altitude
The Simple Altimeter
Datum Sub-scale Settings
The Sensitive Altimeter
Altimeter Displays
Design Errors
Errors due to Calibration
Blockages and Leakages
Servo Altimeters
Operation of a Servo-Altimeter
Servo-Altimeter Power Failure
Altitude Encoding
Advantages of Servo-Altimeters
1.3.1
1.3.1
1.3.1
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
1.3.4
1.3.6
1.3.6
1.3.7
1.3.8
1.3.9
1.3.10
1.3.10
1.3.10
Chapter 1.4 - Vertical Speed Indicator
Introduction
Principle of Operation
Operation of the VSI
Errors of the VSI
Faults of the VSI
Instantaneous Vertical Speed Indicator (IVSI)
Operation of the IVSI/ILVSI
1.4.1
1.4.1
1.4.1
1.4.2
1.4.2
1.4.2
1.4.2
Chapter 1.5 - Airspeed Indicator
Introduction
Principle of the Airspeed Indicator (ASI)
Operation of a Simple ASI
Sensitive and Servo Airspeed Indicators
Calibration of the ASI
Colour Coding of the ASI
ASI Errors
1.5.1
1.5.1
1.5.1
1.5.1
1.5.2
1.5.2
1.5.3
ii
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
ASI Faults
Calculation of CAS to TAS (up to 300 knots)
1.5.4
1.5.6
Chapter 1.6 - Machmeter
Introduction
Critical Mach Number (MCRIT)
Principle of Operation
Machmeter Construction and Operation
Calibration
Errors
Blockages and leakages
Accuracy
Serviceability Checks
1.6.1
1.6.1
1.6.1
1.6.3
1.6.4
1.6.4
1.6.5
1.6.5
1.6.5
Chapter 1.7 - Mach Airspeed Indicator
Introduction
Display
VMO Pointer
Driven Cursor
Bugs
Linkages
Errors
1.7.1
1.7.1
1.7.1
1.7.1
1.7.1
1.7.2
1.7.2
Chapter 1.8 - Central Air Data Computer
Introduction
The Central Air Data Computer
Conversion of Sensing Pressures
Digital Air Data Computer
1.8.1
1.8.1
1.8.2
1.8.4
Section 2 Magnetism and Aeroplane Compasses
Chapter 2.1 - Basic Magnetism
Introduction
Magnetic Properties
Fundamental Laws of Magnetism
Characteristics of Lines of Magnetic Flux
Magnetic Materials
Permeability
Electromagnetism
An Electromagnet
Magnetic Moments
Period of Oscillation of a Suspended Magnet
2.1.1
2.1.1
2.1.2
2.1.3
2.1.5
2.1.5
2.1.5
2.1.6
2.1.7
2.1.8
Chapter 2.2 - Terrestrial Magnetism
Introduction
Magnetic Dip
Earths Total Magnetic Force
Magnetic Variation
2.2.1
2.2.2
2.2.4
2.2.5
Chapter 2.3 - Aeroplane Magnetism
Introduction
Types of Aeroplane Magnetism
Components of Hard Iron Magnetism
Components of Soft Iron Magnetism
2.3.1
2.3.1
2.3.1
2.3.4
iii
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Determination of Deviation Coefficients
Minimum deviation
Maximum Deviation
Joint Airworthiness Requirements (JAR) Limits
Compass Swinging
The Compass Swing procedure
An Example of A Compass Swing
Deviation Compensation Devices
2.3.5
2.3.6
2.3.6
2.3.7
2.3.8
2.3.9
2.3.10
2.3.11
Chapter 2.4 - Direct Reading Magnetic Compass
Introduction
Properties of a Direct Reading Compass
E Type Compass
Pre-flight Checks
Principle of a Pendulum
Acceleration Errors
Turning errors
2.4.1
2.4.1
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.3
2.4.4
2.4.7
Chapter 2.5 Remote Indicating Compass
Introduction
RIC Architecture
Principle of a Flux Detector Element
Flux Detector unit
Operation of the Remote Indicating Compass System
Gyroscope Element
Heading Indicator
Modes of operation
Synchronising Indicators
Manual Synchronisation
Operation of an RIC in a Turn
Advantages of a Remote Indicating Gyro Magnetic Compass
Disadvantages of a Remote Indicating Gyro Magnetic Compass
2.5.1
2.5.1
2.5.1
2.5.4
2.5.4
2.5.7
2.5.7
2.5.8
2.5.8
2.5.9
2.5.9
2.5.10
2.5.11
Section 3 Gyroscopic Instruments
Chapter 3.1 - Gyroscopic Principles
Introduction
Principle of Construction
Gyroscopic Properties
Types of Gyroscope
Power Sources for Gyroscopes
The Disadvantages and Advantages of Air Driven Gyros
The Disadvantages and Advantages of Electrically Driven Gyros
Gyro Wander
Examples of Gyro Wander
3.1.1
3.1.1
3.1.2
3.1.4
3.1.5
3.1.6
3.1.6
3.1.7
3.1.10
Chapter 3.2 - Direction Indicator
Introduction
Basic Description of the Direction Indicator
Operation of the Direction Indicator
Errors Associated with the Air Driven Direction Indicator
Use of the Direction Indicator
Advanced use of the Direction Indicator
Sample Calculation
3.2.1
3.2.1
3.2.2
3.2.3
3.2.4
3.2.4
3.2.5
iv
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Chapter 3.3 - Artificial Horizon
Introduction
Construction of an Air Driven (Classic) Artificial Horizon
Operation of an Air Driven Artificial Horizon
The Air Driven Artificial Horizon Erection System
Errors Associated with the Air Driven Artificial Horizon
Construction of an Electrically Driven Artificial Horizon
Torque Motor and Levelling Switch System
Electrical Fast Erection
Errors Associated with the Electrically Driven Artificial Horizon
Remote Vertical Gyro
Standby Attitude Indicator
3.3.1
3.3.2
3.3.3
3.3.4
3.3.5
3.3.6
3.3.7
3.3.7
3.3.8
3.3.9
3.3.9
Chapter 3.4 - Turn and Balance Indicator
Introduction
Construction and Principle of Operation of a Turn Indicator
Operation of the Turn Indicator
Errors Associated with the Turn Indicator
Pre-flight Check
Construction and Operation of the Balance Indicator
Limitations and Errors Associated with the Balance Indicator
Pre-flight Check
Electrically Driven Turn and Balance Indicators
Typical Indications on a Turn and Balance Indicator
3.4.1
3.4.1
3.4.2
3.4.3
3.4.3
3.4.3
3.4.4
3.4.4
3.4.4
3.4.5
Chapter 3.5 - Turn Co-ordinator
Introduction
Principle of Operation
3.5.1
3.5.1
Section 4 Flight Navigation Systems
Chapter 4.1 - Inertial Navigation System
Introduction
The Principle and Construction of an Accelerometer
Performance
Operation of a Gyro-Stabilised Platform
Setting-up Procedures
Levelling
Alignment
Levelling and Alignment
Corrections
Acceleration Corrections
Wander Azimuth System
The Schuler Tuned Platform
Errors
The Advantages and Disadvantages of an INS
Mode Selector Panel
Control Display Unit
4.1.1
4.1.1
4.1.3
4.1.3
4.1.6
4.1.6
4.1.7
4.1.7
4.1.7
4.1.8
4.1.9
4.1.9
4.1.11
4.1.12
4.1.12
4.1.14
Chapter 4.2 - Inertial Reference System
Introduction
Description of the Strap-Down System
Solid State Gyros
4.2.1
4.2.1
4.2.2
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Advantages and Disadvantages of RLGs
Alignment of the Inertial Reference System
Performance
The Control, Display and Output from an IRS
Description of a Typical IRS
IRS Transfer Switch
IRS Alignment
Loss of Alignment in Flight
4.2.3
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.4
4.2.5
4.2.7
4.2.7
4.2.7
Section 5 Electronic Flight Systems
Chapter 5.1 - Radio Altimeter
Introduction
The Radio Altimeter System
Principle of Operation of a Radio Altimeter
Performance and Accuracy of a Radio Altimeter
Errors Associated with a Radio Altimeter
The Advantages of a Radio Altimeter
5.1.1
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.1.3
5.1.3
5.1.4
Chapter 5.2 - Electronic Flight Instrument System
Introduction
EFIS Architecture
Attitude Director Indicator (ADI)
The Horizontal Situation Indicator (HSI)
EFIS/IRS Interface
Heading Reference Switch
HSI Symbology
5.2.1
5.2.1
5.2.3
5.2.5
5.2.8
5.2.9
5.2.10
Chapter 5.3 - Flight Management System
Introduction
The Flight Management Computer System
Command Display Unit
Control Panels
CDU and FMC Terminology
The Flight Management Computer Memory
General FMS Operation
Pre-Flight
En-Route
Lateral Navigation (LNAV)
Vertical Navigation (VNAV)
Operational Notes
Fuel Monitoring
Flight Control and Management Summary
5.3.1
5.3.2
5.3.4
5.3.5
5.3.6
5.3.8
5.3.10
5.3.11
5.3.12
5.3.12
5.3.12
5.3.14
5.3.15
5.3.15
Section 6 Automatic Flight Systems
Chapter 6.1 - Flight Director System
Introduction
Flight Director Architecture
Flight Director Control Inputs
Flight Director Computer
Mode Control Unit
Flight Director Displays
6.1.1
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.1.3
vi
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Flight Director Modes of Operation
Mode Annunciator
Operation of the Attitude Director Indicator
The Horizontal Situation Indicator Flight Director Commands
6.1.4
6.1.10
6.1.10
6.1.11
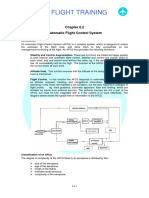
Chapter 6.2 - Automatic Flight Control Systems
Introduction
Classification of an AFCS
Control Channels
Inner Loop Control (Stabilisation)
Operation of an Inner Loop Pitch Stabilisation System
Outer Loop Control (Stabilisation)
Roll Modes
Pitch Modes
Combined Roll and Pitch Modes
Attitude Sensing
The AFCS Computer (Signal Processor)
Servomotor Actuators
Autopilot Terminology
Cross Coupling
ILS Coupling
VOR Coupling
Stability Problems
Yaw Damper
Mach Trim System
Automatic Pitch Trim Control
Interlocks
Synchronisation
Instinctive Cut-Out
6.2.1
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.3
6.2.4
6.2.6
6.2.6
6.2.7
6.2.8
6.2.9
6.2.10
6.2.11
6.2.11
6.2.13
6.2.13
6.2.13
6.2.15
6.2.15
6.2.17
6.2.18
6.2.18
Chapter 6.3 - Automatic Landing system
Introduction
Basic Requirements for an Automatic Landing System
Automatic Landing System Terminology
Automatic Landing System Equipment Requirements
Automatic Approach, Flare and Landing Sequence
Weather minima
ICAO Categorisation for Low Visibility Landing Capabilities
The Fundamental Landing Requirement
System Reliability and Integrity
6.3.1
6.3.1
6.3.1
6.3.2
6.3.3
6.3.5
6.3.5
6.3.6
6.3.7
Chapter 6.4 - Thrust Management Systems
Introduction
Determining the Thrust Required
Calculation of Climb and Cruise Thrust
Cruising Methods
Electronic Engine Control (EEC)
Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC)
Auto-throttle (A/T)
Thrust Lever Operation
Thrust Management via the Auto-throttle
Thrust Management Computer (TMC)
Thrust Mode Select Panel (TMSP)
6.4.1
6.4.1
6.4.2
6.4.2
6.4.2
6.4.3
6.4.6
6.4.7
6.4.7
6.4.8
6.4.8
vii
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Section 7 Warning and Recording Systems
Chapter 7.1 - Central Warning System
Introduction
Central Warning System Annunciator Panel
Aural Warnings
7.1.1
7.1.1
7.1.2
Chapter 7.2 - Altitude Alerting System
Introduction
Altitude Alerting System Operation
7.2.1
7.2.1
Chapter 7.3 - Ground Proximity Warning System
Introduction
GPWS Architecture
GPWS Modes
Warning System
GPWS Control Panel
Discretionary Response
Warning Inhibition
The Reporting of GPWS Events
Operation of the GPWS
Joint Aviation Requirements
7.3.1
7.3.1
7.3.2
7.3.3
7.3.4
7.3.5
7.3.5
7.3.5
7.3.5
7.3.11
Chapter 7.4 - Traffic Collision Avoidance System
Introduction
Aeroplane Installation
Operation of TCAS II
TCAS Aural Warnings
Information Display
Resolution Advisory / Vertical Speed Indicator (RA / VSI)
TCAS Control Panel
Operating Restrictions
7.4.1
7.4.2
7.4.3
7.4.5
7.4.6
7.4.6
7.4.7
7.4.7
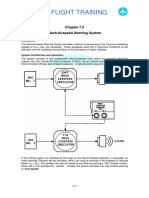
Chapter 7.5 - Mach/Airspeed Warning System
Introduction
System Architecture and Operation
Maximum Operating Airspeed schedule
7.5.1
7.5.1
7.5.1
Chapter 7.6 - Stall Warning
Introduction
Light Aeroplane Stall Warning Device
Transport Category Aeroplane Stall Warning Device
7.6.1
7.6.1
7.6.1
Chapter 7.7 - Recording devices
Introduction
Flight Data Recorder (FDR) Requirements
FDR Design
Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) Requirements
CVR Design
7.7.1
7.7.1
7.7.2
7.7.3
7.7.3
Section 8 Engine and System Instrumentation
Chapter 8.1 - General Engine Instrumentation
Introduction
viii
8.1.1
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Piston Engines
Turbo Propeller Engines
Gas turbine Engines
8.1.1
8.1.1
8.1.2
Chapter 8.2 - Pressure and Temperature Sensors
Introduction
Pressure Measurement
Temperature Measurement
8.2.1
8.2.1
8.2.3
Chapter 8.3 - Pressure and Temperature Indicators
Introduction
Pressure Indicators
Temperature Indicators
8.3.1
8.3.1
8.3.3
Chapter 8.4 - RPM Indicators & Propeller Synchroniser Systems
Introduction
Tachometers
Propeller Auxiliary Systems
Synchronisation System
Synchrophasing System
Operation of a Synchrophasing System
8.4.1
8.4.1
8.4.5
8.4.5
8.4.6
8.4.6
Chapter 8.5 - Engine Torque measurement
Introduction
Torque Meter
Negative Torque Sensing
8.5.1
8.5.1
8.5.2
Chapter 8.6 - Vibration Monitoring
Introduction
Vibration Monitoring System
8.6.1
8.6.1
Chapter 8.7 - Fuel Gauging
Introduction
Measurement of Fuel Quantity
Fuel Totaliser
Fuel Flow
8.7.1
8.7.1
8.7.4
8.7.4
Chapter 8.8 - EICAS
Introduction
EICAS Architecture
Engine Displays
Crew Alerting
Master Warning/Caution Light
Inhibits
Display Messages
Status
Maintenance
EICAS Failure Modes
8.8.1
8.8.1
8.8.2
8.8.3
8.8.4
8.8.4
8.8.4
8.8.5
8.8.6
8.8.7
Chapter 8.9 - ECAM
Introduction
Engine / Warning (E/W) CRT Display
The System / Status (S/S) CRT Display
ECAM System Architecture
ECAM Control Panel (ECP)
Attention Getters
8.9.1
8.9.1
8.9.2
8.9.3
8.9.4
8.9.5
ix
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Display Colour Coding
ECAM System Failure
Failure Categorisation
System Operation
8.9.5
8.9.5
8.9.5
8.9.6
WILJAM FLIGHT TRAINING
Intentionally Left Blank
xi
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- King Air C90 A-BDocumento342 páginasKing Air C90 A-BBruno Graziano Almeida Migliavacca94% (18)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Learning To Fly With Flight SimulatorDocumento130 páginasLearning To Fly With Flight Simulatorkyoobum100% (4)
- ATPL Inst 5.1 PDFDocumento4 páginasATPL Inst 5.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.9 PDFDocumento12 páginasATPL Inst 8.9 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.7 PDFDocumento6 páginasATPL Inst 8.7 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.8 PDFDocumento8 páginasATPL Inst 8.8 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.5 PDFDocumento4 páginasATPL Inst 8.5 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 6.2 PDFDocumento20 páginasATPL Inst 6.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.3 PDFDocumento4 páginasATPL Inst 8.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.6 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 8.6 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 3.2 PDFDocumento6 páginasATPL Inst 3.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.2 PDFDocumento6 páginasATPL Inst 8.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.4 PDFDocumento8 páginasATPL Inst 8.4 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 5.3 PDFDocumento18 páginasATPL Inst 5.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.6 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 7.6 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 4.1 PDFDocumento16 páginasATPL Inst 4.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 8.1 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 8.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.5 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 7.5 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.4 PDFDocumento8 páginasATPL Inst 7.4 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 6.4 PDFDocumento10 páginasATPL Inst 6.4 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.7 PDFDocumento4 páginasATPL Inst 7.7 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 3.3 PDFDocumento10 páginasATPL Inst 3.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 6.3 PDFDocumento8 páginasATPL Inst 6.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 3.4 PDFDocumento6 páginasATPL Inst 3.4 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.3 PDFDocumento12 páginasATPL Inst 7.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.2 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 7.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 3.5 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 3.5 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 3.1 PDFDocumento10 páginasATPL Inst 3.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 4.2 PDFDocumento8 páginasATPL Inst 4.2 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 7.1 PDFDocumento2 páginasATPL Inst 7.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 2.5 PDFDocumento12 páginasATPL Inst 2.5 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- ATPL Inst 2.4 PDFDocumento10 páginasATPL Inst 2.4 PDFKoustubh VadalkarAinda não há avaliações
- Law Exam 1Documento15 páginasLaw Exam 1momanbh100% (1)
- Aeronautical Engineering PDFDocumento137 páginasAeronautical Engineering PDFsabbithiAinda não há avaliações
- Aerofoil Decision MatrixDocumento2 páginasAerofoil Decision MatrixDanAinda não há avaliações
- (IAC) Ils Z Rwy 35L: Alt, Elev, HGT: FT Dist: NM BRG: Mag VA/CHG: 06'WDocumento1 página(IAC) Ils Z Rwy 35L: Alt, Elev, HGT: FT Dist: NM BRG: Mag VA/CHG: 06'WGuilherme Kazuo OgawaAinda não há avaliações
- Piper PA44 180 POH PDFDocumento354 páginasPiper PA44 180 POH PDFJayson FowlerAinda não há avaliações
- EASA-TCDS-A.059 Piaggio Aero Industies Spa P.180!07!11102012Documento19 páginasEASA-TCDS-A.059 Piaggio Aero Industies Spa P.180!07!11102012Anonymous ucJM9AGdaAinda não há avaliações
- UPRT (Upset Prevention & Recovery Training) : Background InformationDocumento3 páginasUPRT (Upset Prevention & Recovery Training) : Background InformationKonstantinos AIRMANAinda não há avaliações
- MCQs ME6604 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineeringDocumento93 páginasMCQs ME6604 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineeringrameshneupane33% (3)
- Damage Tolerant Design in HelicoptersDocumento23 páginasDamage Tolerant Design in HelicopterspozolabAinda não há avaliações
- ApolloDocumento68 páginasApolloBob Andrepont100% (6)
- Aerospace Vehicle DesignDocumento1 páginaAerospace Vehicle DesignMasuda AkterAinda não há avaliações
- Change of RVSM Approval StatusDocumento2 páginasChange of RVSM Approval StatusHugo Clemente100% (1)
- AanDocumento9 páginasAanPocs MadarAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper For Internal Assessment Examination (Theory) - Credit 4 / 45Documento6 páginasQuestion Paper For Internal Assessment Examination (Theory) - Credit 4 / 45Garkal AjinkyaAinda não há avaliações
- Real Life Drama in The AirDocumento6 páginasReal Life Drama in The AirAbdul NaeemAinda não há avaliações
- SHORT SD3-360 - SKYbrary Aviation SafetyDocumento3 páginasSHORT SD3-360 - SKYbrary Aviation SafetyAnonymous d8N4gqAinda não há avaliações
- Esa Electric Propulsion PerspectiveDocumento24 páginasEsa Electric Propulsion PerspectiveAndreescu Anna-Maria TheodoraAinda não há avaliações
- Business Jet Monthly JP MorganDocumento37 páginasBusiness Jet Monthly JP MorganEric JacobAinda não há avaliações
- Designing, Implementation of Test Bench With Pid Control For Variable Pitch Propeller SystemDocumento8 páginasDesigning, Implementation of Test Bench With Pid Control For Variable Pitch Propeller SystemMMAinda não há avaliações
- A320 - Command Upgrade - Trainee1 01 Jan 24Documento19 páginasA320 - Command Upgrade - Trainee1 01 Jan 24Ankit YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Fictional Aircraft in Dale Brown NovelsDocumento33 páginasFictional Aircraft in Dale Brown NovelsPeterD'Rock WithJason D'Argonaut67% (6)
- Training Report On Airport Authority of INDIA (A.A.I)Documento43 páginasTraining Report On Airport Authority of INDIA (A.A.I)Ruatfela PachuauAinda não há avaliações
- CH-47F Chinook: Description & PurposeDocumento2 páginasCH-47F Chinook: Description & PurposeSonnet XavierAinda não há avaliações
- Circling Approach Briefing - English VersionDocumento12 páginasCircling Approach Briefing - English Versionözgür TanriverdiAinda não há avaliações
- A350 XWB Family & TechnologiesDocumento52 páginasA350 XWB Family & TechnologiesAlberto CañaverasAinda não há avaliações
- Bombardier CRJ 200-Hydraulic PowerDocumento17 páginasBombardier CRJ 200-Hydraulic PowerGazpachoesi100% (3)
- ATP CTP BrochureDocumento2 páginasATP CTP BrochureFikredingil MulugetaAinda não há avaliações
- 65 - Aerospace Engineering E-Books ListDocumento48 páginas65 - Aerospace Engineering E-Books ListKabir Sai Prasanna Suryavansh100% (2)