Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
AZ Copyright Long Outline
Enviado por
Shawn AcostaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AZ Copyright Long Outline
Enviado por
Shawn AcostaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
General Principles: Chapter 1
Copyright- The right of an author to control the reproduction of his intellectual creation.
Legal device to give a creator/author/person the right to control a works reproduction
after it has been disclosed (put out into the world)
Restrains a person other than the creator from reproducing the work w/o the owners
consent
Statute of Anne 1710- protected for 14 years.
Constitution
Copyright provision.
o Congress shall have power to promote progress of science and useful arts to
secure for limited times to authors and inventors the exclusive right to their
writings and discoveries. (Inventors and discoveriespatents)
Copyright Law 1790
Assure protection for 14 years (now its authors life plus 70 years).
Copyright 1909*
More comprehensive music just started.
A lot of works copyrighted uner 1909 law and still exist today.
Anything before 1923 is in the public domain. Anything after 1923 aint.
Things published before 1976, 95 years from publication
Used to be 2c for recording a version of a song
Copyright 1976
102(a) Copyright protection subsists in original works of authorship fixed in a
tangible medium of expression
o Original never been expressed in the way you are expressing it before.
Comes from the author
startling, novel, or unusual, a marked departure from the past.
o Work (of authorship) = The intangible creation your mind has formed and the
sum and substance in which you will fix in a medium.
o Fixed= Set in a real/able to touch, see, feel, hear, etc medium of expression
CANNOT GET COPYRIGHT PROTECTION UNTIL THE WORK IS
FIXED
Compulsory Just record the song, contact the copyright office/ person with the copyright
and pay them for each record sold. --- Make your version of it. this is for music.
Bern Conventionwe joined 1989
Burrow- Giles Lithographic v. Sarony
Should photograph be copyrightable?
Rule
Need an original work of authorship for a copyright
Holding:
Some artistic choices being made by the photographer. Therefore, it should be
protected
1
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Bleistein v. Donaldson
Posters for commercial purposes.
Issue
Should you get copyright for promotional lithographs used as advertising for the Great
Wallace Circus sufficiently author-like?
Is it the work of an artist.
Holding
Itd be dangerous to have just persons trained in the law to be judges of what is art.
Need Aesthetic authorship
Copyright Law
Cant get copyright unless created an original work of authorship
o Original startling, novel, or unusual, a marked departure from the past. Work
owes its origin to the author. Fixed medium
Patent- New or useful
New v. Original original simply means you did it! It owes it origin to its
author. New is tough- cant get a patent unless its nonobvious to a person
in the field.
o Work the literary work behind itliteray creation fixed in all the different
formats (book, computer document) (Book is the body). Its not the edition in
which its printed. It's the substance.
Latchesif you are waiting so long so as to prejudice youre opponent, you get fucked.
Does Latches apply in copyright infringement? NO! because of the particular way
copyright law is governed
Patent Law, Trademark Law: The Differences
What does it
protect?
Copyright
Original works of
authorship (17
U.S.C. 102(a) )
Patent
New and useful
processes,
machine,
manufactures, etc.
(35 U.S.C. 101)
Non-obviousness
if anyone having
ordinary skill in the
art would find it
obvious, its not
protected (35
U.S.C. 103)
What are the
prerequisites for
protection?
Has to be an
original work of
authorship (17
U.S.C. 102)
What is the length
of protection?
Authors life plus 70
years
20 years
What is the source
The Constitution
The Constitution
2
Trademark
A word, name,
symbol, or device
(15 U.S.C. 1127)
It must identify and
distinguish the
applicants goods
from those
manufactured or
sold by others and
indicates the source
of goods
Forever, as long as
the trademark is
used
Statutory
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
of the protection?
What is the scope
of the protection?
Where is
jurisdiction
proper?
It protects against
copying of a
substantial portion
of your work
Exclusive federal
jurisdiction
It protects against
any similar
machine, invention,
process, etc. that is
subsequent in time
no requirement to
prove copying
Exclusive federal
jurisdiction
Protects against
anything that
causes confusion in
the marketplace
Federal or state
Cases on Patents/Trademarks
Bell v. Catalda Patent case
Doing what an author does by the scraping process
More than a trivial variationneeds to be authorlike.
How much author like effort must you make?
o You need to do author like things.
Trademark Cases
In order to sue for a trademark, can rely on common law trademark unfair
competition
Under constitution, what allows you to trademark shitCommerce clause
o Interstate commerce meaning was so wide spanning that it made it so
trademark could fall under it.
Priority of appropriation
Peter Rabbit Case
Can trademark the character of Peter Rabbit
Copyright and trademark should be able to overlap
Dastar corp. v. Twentieth Century Fox
False designation of origin. Film version went into the public domain Someone copied
it, set of videos
Origino The person who sold the product or who made the original production
o Court said it was the person who made the original production
Copyright v. Chattel
202: Ownership of Copyright as Distinct from Ownership of Material Object
Ownership of a copyright, or of any of the exclusive rights under a copyright, is distinct
from ownership of any material object in which the work is embodied. Owning the
material object that embodies the work does not give you any rights in the copyrighted
3
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
work that is embodied in the material object. The transfer of ownership of a copyright
(or of any exclusive right under a copyrgith) does not convey property rights in any
material object
o Just because you possess the object in which the copyright was first fixed,
doesnt mean you own the copyright. You just have the rights to that object. The
author still has the copyright right in the substance contained in the object.
Pushmen v. New York Graphics Society Someone sold a painting to the University of Illinois
Holding
Treated like a contractan author who unconditionally transfers ownership in the
chattel embodying the creative work is presumed to have transferred the right of first
publication as well
Forward v. Thorogood
Facts
Forward finances Thorogood & The Destroyers, gets them recordings. In gratitude,
they give him the tape . Then he wants to exploit the tapes
Holding
He has no copyright to the songs the band recorded. The only way he could get it is if
the tapes were, in writing, handed over to him
Sec 109: Limitations on Exclusive Rights: Effect of Transfer of Particular Copy or
Phonorecord (pg 297)
Owner of a particular copy of a book or a phonorecord, is entitled to sell it to someone
elseFirst sale Doctrine
o After you make that first sale, its yours and you can sell it
o You CANNOT make a copy of it. But you can sell the physical object.
109(b)(1)(A) Unless authorized by the owner of the copyright, cant lease or license, or
rent
o Cant lend computer programs. even though you own it (the computer
program) you cant lend it out.
o Cannot lend music either because its so easy to copy
B) This subsection does not apply to-o (i) a computer program which is embodied in a machine or product and which
cannot be copied during the ordinary operation or use of the machine or
product; or
o (ii) a computer program embodied in or used in conjunction with a limited
purpose computer that is designed for playing video games and may be
designed for other purposes.
Andre KerteszFrench has the negatives, but they cant make copies.
Holding
If you own the negative, you don't own the copyright.
Material object that produces the copyright work, but don't own the copyright
Rule
4
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
The only way you convey copyright is through an instrument in writing transfer of
copyright 204. (in whole or in part)
204:Execution of Transfers of Copyright Ownership
(a) A transfer of copyright ownership, other than by operation of law, is not valid
unless an instrument of conveyance, or a note or memorandum of the transfer,
is in writing and signed by the owner of the rights conveyed or such owner's
duly authorized agent.
(b) A certificate of acknowledgement is not required for the validity of a transfer,
but is prima facie evidence of the execution of the transfer if
o (1) in the case of a transfer executed in the United States, the certificate
is issued by a person authorized to administer oaths within the United
States; or
o (2) in the case of a transfer executed in a foreign country, the certificate
is issued by a diplomatic or consular officer of the United States, or by a
person authorized to administer oaths whose authority is proved by a
certificate of such an officer.
If you own the negative, you don't own the copyright.
Material object that produces the copyright work, but don't own the copyright.
Chapter 2: Copyrightable Subject Matter
102: Subject Matter of Copyright: In General
2 Fundamental Criteria: (1) Originality (2) Fixation in tangible form
102: Copyright protection subsists, in accordance with this title, in original works of authorship
fixed in any tangible medium of expression, now known or later developed, from which they
can be perceived, reproduced, or otherwise communicated, either directly or with the aid of a
machine or device. Works of authorship include the following categories:
1. literary works
(1) Written on a white boardIt is a fixed tangible from of expression.
2. musical works, including any accompanying words;
3. dramatic works, including any accompanying music;
4. pantomimes and choreographic works;
(1) write it down- the dance moves and such
5. pictorial, graphic, and sculptural works;
6. motion pictures and other audiovisual works
7. sound recordings; and
8. architectural works (added in 1990).
Five Basic Requirements to look into to decide if something is copyrightable (102)
1. The work has to be original to you
2. It has to be a work of authorship
3. There has to be a modicum of creativity
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
a. Just a slight amountsome but not a lot
b. Feist low threshold
4. It has to be fixed in a tangible medium/form
5. It aslo cannot fall within the prohibition of 102(b) cannot be a fact, idea, process,
instruction, theory.
What is Authorship
A. Original Works of Authorship
I. Authorship: entirely human endeavor. Authors of copyrightable works must be human;
works owning their form to the forces of nature cannot be copyrighted. (Kelley)
You make the workpaintbrushes, typewriters, pens, recording equipment
are the tools in which you use to fix your work.
Burrow-Giles
if the thing in question clearly required some form of artsy work and expression (like
manipulation of light) than it meets constitutional standard for the writing of an
author--- entails form in which the ideas in the mind of the [photographer] are given
visible expression
Kelley v. Chicago Park DistrictNo copyright for planting a garden, even when done artistically because
nature creates the product of your plantingthe actual flowersyou didn't
make the flowers that make up your garden bloom.
No for food either.
Original Works of Authorship
Originality: Don't need to do much. Require originality to justify granting rights.
the work is independently created by the author, and that it possess at least
some minimal degree of creativity.
The Feist Test:
The work is:
1. Independently created by the author
2. Possess some minimal degree of creativity
(Feist v. Rural Telephone Services)
Feist Publications v. Rural Telephone Services (phonebooks)
Sin qua non of copyright is originality
Originality requires independent creaton
Originality requires at least some minimal degree of creativity
o Need to have some creative spark
* FACTS NOT COPYRIGHTABLE
6
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Test for Originality is Low threshold
need to show that it is recognizably your own. The author must
contribute more than a trivial variation of a previous work, (Magic
Marketing)
Does not require novelty, ingenuity, aesthetic merit.
Exceptions:
Short Phrases, titles, typefaces
Cannot copyright instructions (Magic)
Process, Methods of operation
Phrases, Slogans, Mottos and short advertising expressions are not
copyrightable (Sebastian Intl)
o ** HOWEVER, the length of a sentence is NOT dispositive of
whether it is subject to protection
Short Jokes- cannot be copyrighted. They just arent long enough.
o HOWEVER, the whole compilation of jokes can be copyrighted
Magic Marketing v. Mailing Services (Envelopes)
Not enough creativity
o Phrases only describe the contents
o Solid black lines are not enough to constitute designs.
If instructions are part of the process, they cannot be copyrighted.
o Instructions, directions
o Generic in nature!
Labels
Labels on products are copyrightable if the label manifests necessary
modicum of creativity
Sebastian Intl v. Consumer Center
The label was more than just a list of ingredients. It was much more
detailed and there were(are) a lot of ways to describe the product, but the
company chose this one specific way. So copyrightable
Fixation
101: A work is fixed in a tangible medium of expression when its
embodiment in a copy or phonorecord, by or under the authority of
the author, is sufficiently permanent or stable to permit it to be
perceived, reproduced, or otherwise communicated for a period of
more than transitory duration. A work consisting of sounds, images, or
both, that are being transmitted, is fixed for purposes of this title if
a fixation of the work is being made simulataneously with its
transmission.
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Original Work and tangible object must merge through Fixation
A work needs to be Fixed in a tangible medium expression
All you need to do is either write it down or record it if its music (or like a
movie etc)
Only if the author is doing the fixation does it lead to any legal right
o You recording Imogen singing doesn't give you the copyright
Imogen would need to record it (or have her producer record it) in
order for the song to
Book is a copynot a work of authorship
Unfixed Work:
improvision or unrecorded choreographic work
Unfixed work is not protected by 102. BUT are protected under state
common law.
In terms of the constitutional clause for copyright, music, especially live
performances, cannot fit under constitutional definition, but congress made
a law through the commerce clause:
o 1101: Performers Right of Fixation - grants performer of live
musical performance rights against unauthorized fixation, of their
performances, and against distribution or transmission of said
unauthorized fixation.
These rights apply after 1994. Post 1994 sales of pre-1994
fixations apply
o In essence the court created a right to fix a work
o The consequence is the same extent as a copyright infringer.
Fixation in Digital Media
Entry of a work into the random access memory (RAM) of a computer
makes a copy
B. The Idea/ Expression Dichotomy
B. The Idea/ Expression Dichotomy
102(b) In no case does copyright protection for an original work of authorship
extend to any idea, procedure, process, system, method of operation, concept,
principle, or discovery, regardless of the form in which it is described, explained,
illustrated or embodied in such work.
You cannot copyright an idea
You cannot preclude others from using the ideas or information
revealed by the authors work
o Pertains too Literary, Musical, Graphical orArtistic form in which
author expressed intellectual concepts.
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Scene a faire - incidents characters or settings which are as a practical matter indispensible,
or at least standard in the treatment of a given topic. Thus, everybody should be able to use.
Scene a faire as cultural method of operation?
Scene a faire lack originality?
Merger in scene a faire?
Baker v. Seldon
Issue: Can a system of bookkeeping be copyrighted
Holding
Not copyrightable if it has a functional purpose
o Cant copyright complaints or accounting systems.
Can describe things, but cant take the words, but can use the instructions to make it
themselves the charts itself
Morrissey v. Procter & Gamble Co.
Created game and had instructions on how to enter the game. Not copyright
infringement because all of those words were necessary to allow people to enjoy the
game
Judicial Round up
Baker- Cannot copyright if it (the work) has a functional purpose
o No exclusive right/claim to the art/arrangement of columns
o It falls within patent law to try and gain an exclsuvie right to a
bookkeeping set-up
Morrissey- Cannot copyright instructions if all the words in the original were
necessary to allow people to enjoy the game/ necessary for the use of the
product
o The rules were straight forward and simple Copyright doesn't apply
Facts and Compilations
Facts cannot be copyrighted
They fail to meet the constitutional requirement of originality.
Facts are discovered not created
Definition of a law becomes a fact when it it enacted, thus cannot be
102(b): Cannot copyright a theory. In no case does copyright extend to any
idea!
Facts become copyright protected when they are in a compilation-- the indivudual
facts are not copyright protected, but the presentation and arrangement of the
facts (aka the compilation) is.
Compilations
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Test
1. Is there collection and assembly of pre-existing materials, facts, or data?
2. Is there some creativity in the selection and coordination of the materials in
the work
a. Which facts selected
b. how/what order to place them in
c. how to arrange the collected data so that they may be used
effectively by reader
3. If yes, by virtue of a particular selection, coordination or arrangement, the
work taken as a whole constitutes an original work of authorship
Basic Doctrinal Rules
Facts become copyright protected when they are in a compilationthe
individual facts are not copyright protected but the medium in which they
are presented, the compilation, is.
Need to look at all the elements of the work, including text, arrangement of
text, art work, and association between art work and text- Take it as a
whole (Roth Greeting Cards).
The minute a penal code gets enacted into law, it becomes a fact, and a
fact cannot be copyrighted
Merger Doctrine-The idea and the expression have come together
o MD does not apply for soft ideas infused with taste and opinion
o No MD if there are many different ways to express the idea (Maps
case)
101: Definitions: Compilation
A work formed by the collection and assembling of preexisting materials or of data that are
selected, coordinated, or arranged in such a way that the resultin work as a whole constitutes
an original work of authorship. Includes collective works.
Organized/ put together in such an authorly way that it constitutes an original work of
authorship
Need to make a selection --- a compliation of everything is not copyrightable
Examples:
Exercises are not copyrightable Procedure not work of authorship. Exercise is not a
writing so even if you make a compilation you don't get the copyright
Compilation of all the garden supply stores in the town. yes copyrightable
5000 most expensive baseball cards what they are, whose in them, and how much
they cost----- yes copyrightable
May be copyrightable if you select facts to include in the map which are not so
obvious. A map may be a compilation of facts if the selection involves creativity that
overrides the functionality argument.
CASE LAW
Feist v. Rural
10
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Facts: Defendant took listings from plaintiffs white pages when compiling their own white
pages.
Issue
What kind of compilation is protectable?
Rule:
Original means independently created by author and some minimal degree of
creativity.
Holding:
No infringement. There was no (human) creativity. The defendants would put into a
computer new entries and the computer would alphabetize it. This is not original and
therefore not protected by copyright.
Analysis
Collection of facts are not copyrighted per se
Per statute 3 elements:
o 1. Collection and assembly of pre-existing materials, facts, or data.
o 2. The selection, coordination or arrangement of those materials
o 3. The creation, by virtue of a particular selection, coordination or arrangement
of an original work of authorship
Rockfert Map
Its all facts! New have is actually 50 miles from wherever!!
Copyrightable because there is some creativity in which locations you pick to put on
your map
There was no merger between the idea and the expression because there were many
different ways to express that idea
Factual Narratives
Can you have a copyright in a theory? Nash v. CBS
102 (b) in no case does CP extend to any idea! A theory is an idea.
o So no it is not protectable.
Translation s copyrightable creative work of authorship
Nash v. CBS
Dillinger book theorizes hes still alive. Simon & Simon episode copies elements of
this. Can't protect idea, whether it be historical fact or theory. (However, there can be
of factual/historical quotes (Toksvig v. Burce Publ.)
Can you sue someone for infringement for stealing a story that is fake/not real? No
Principle of Law that would be applied--- Estoppel
11
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
o You are estopped (not able to) from suing when you claim something you have
written is based on facts. CLAIMING FACTUAL will ESTOPP
Woman was stopped from denying it was not factual
Person who wrote about Sally Hemings is protected by copyright when someone
copied the entire plot of her book and made it into a play.
Terms of venery--- things we don't just say a group ofslate of candidates, pride of lions, can
of worms not copyrightable
* When you have a compliation copyright, a person has to take the whole thing in
order for it to be infringement
Cases
Matthew Bender v. West Publications
Westlaw adds headnotes, lawyers names, parallel cites, page/vol. #s. Is this enough
for a compilation ? Nolittle if any creative insight
CCC Info v. MacLean Hunter Market Report: Redbook v. bluebook
Put together compilation based on the cars age, mileagea whole series of
evaluations where they had to decide and figure out an actual number on half a dozen
considerations. Wrinkle was insurance companies had to use bluebook for stuff
Holding
Redbook valuations of cars not preexisting factsoriginal creations & thus able The
minute put all together, became subject of copyright.
Analysis
Compendium of used car valuationsNOT like telephone directory creativity involved
in selection & presentation of data.
Merger Doctrine argument failed hereidea & expression are inextricably linked, and
so noCourt rejected:
o Merger doctrine does not apply for soft ideas infused with tast and opinion ( as
opposed to, say, Dewey decimal systemhard facts)
Definition of a law in copyright --- minute it is a law it becomes a fact a fact cannot be
copyrighted
Therefore, cant copyright law
The public must have free access to the law.
New York Mercantile Exchange
Go through elaborate calculation on what the future contracts traded on the exchange
Holding
Merger- the idea and the expression have come together.
o Cant get a copyright if the idea and the expression merge
12
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Merger Example: Sesame Street- Reyher v. Children
o Russian woman says Ses Street copied her story about her son running into town
saying he lost her. Town asks what she looks like. He says the most beautiful woman
in the town or some shit. Moral of the story is what Ses copied, which was that when
you love someone, they seem beautiful SO no infringement because cannot
copyright an idea.
o The idea merges with the method of expressing the idea
American Dental v. Delta Dental
Description of procedure was classified by organization, etc.
Holding
The way they picked where to put the teeth and shit was complex enough for a
copyright or something
o Sufficiently creative endeavor to justify application of
Open Source Yoga v. Choudhury
Putting yoga positions in a certain order does not establish
BELLSOUTH ADVERTISING & PUBLISHING CORP. v. DONNELLEY INFORMATION
PUBLISHING, INC. (1993) (yellow pages)
Facts:
BellSouth publishes a yellow pages advertising directory for the Miami area,
organized into an alphabetical listing of business classifications. Donnelley
Information prepared its own competitive directory, but copied the headings of the
business listings.
Issue:
Does organizing names according to business categories meet the minimum
requirement for originality?
Held:
There is no originality here the arrangement of BellSouths directory is entirely typical
for a business directory and the headings followed industry practices
Textbook questions 147-149
Chart of Stats
Leon thinks stats are unprotectable historical facts
School rating systems
Are all those coprightable? Yes
Consumer reports arentthey are false endorsements. Cant copy the way the set up
their method
Law School directory
Nope. Just too simple
Database Protection
13
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Assessment Tech of Wi v. Wiredata
AT collects data & compiles it.
WireDATA only wants raw data. AT tries to use law to block them. Court says AT has
no ownership right in data (no sweat of the brow, unlike Europe) -- Although the
program itself is copyrighted, the owner had no copyrightable interest in the underlying
data.
Mason v. Montgomery Data
Addition of information to maps precluded application of merger doctrine
selected info from numerous sources, reconciling inconsistencies and
depicting them based on mapmakers skill and judgment. Therefore,
plaintiff has validated
Derivative Work
Derivative Work
A work based upon one or more existing works any other form in wich a work may
be recast, transformed, or apapted
o Movies made from a preexisting work= derivative work
o Recasting, transforming or adaption
Situations Typical of Derivative work
Public Domain Work
Something added to Public Domain Work
Somebody copies what was added.
Originality in Derivative Works- Derivative work must contain sufficient original
material to stand on its own: Original and Substantial
Florida Towels Case
Company marketed towel without copyright notice and protection; later slightly
changed the design and copyrighted the second. Somebody copied the copyrighted
towel. The Court found that the distinguishing details were so minor that they are
virtually unnoticeable and thus that they could not qualify for copyright protection.
Skyy vodka
Photographer loses- dominant feature in both photographs is the bottle, and the
copyright in the bottle itself was owned by Skyy. No copyright in the shadows of the
bottle.
L. Batin v. Snyder
14
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Uncle Sam Bank in the public domain. Manufacturer modifies design (mostly for
functionality / streamilined manufacture). Someone copies this version.
Holding
#1s alterations DID NOT constitute sufficient creativity for
Uncle Sam not artlike as small imitation of Rodins Hand of God. There, the
meticulous reproduction was enough artistic contribution. Here, there is not enough.
There were some very minute details that were different; not perceptible to the casual
observer. That is not sufficient to be an original work. A considerable higher degree
of skills is needed to make it copyrightable so Snyder loses.
Eden Toys v. Floree-Bear (Opposite outcme from ^)
Underlying work, then someone makes a change in the underlying change, and then
someone copies the change. Changed: hat, fingers, etc. -- enough for on what they
added.
Threshold Question:
Is there enough difference and creativity in the modifications that you are entitled to
copyright and nobody can copy it.
So yes, sufficient creativity for
Gracen v. Bradford
2nd plate designers painting of Dorothy from Wizard of Oz almost identical to 1 st
designer.
Holding
No Infringementits purely derivative of the movie still and not able. (This is at elast
in part because the movie isnt public domainits ed and so cant undermine rights
of movie holder by creating a derivative
Schrock v. Learning Curvesame outcome with Thomas the Tank Engine toys
Board games/Games
Have plot might be sufficient for
Cant copyright the rules but the following of the plot itself may be a copyrightable
Visual parts of the game are protectable
If you make a copy of a copyrighted work, your work is not worth ANYTHING if someone
copies it, even if there is great artistic skill in your copying you down hold exclusive rights
Computer Programs
Sec. 117: Copying is not ok unless these two situations:
(1) If you buy a program, and follow the instructions to make it archival copy just so
you have it just in case, that is not an infringement, or
15
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
(2) if you download it onto a harddrive, you are making a copy but that is not an
infringement.
** Argument for infringement is that any other instance than these two, its infringement.
Therefore, a program is copyrightable
Literary work because use letters and numbers to create a work. Suggest addition to
copyright law. (Apple Computer v. Franklin)
Computer programs look like methods of operation
Method of operation if it is the only way to accomplish something
Apple Computer v. Franklin
Holding
Court finds computer program is literary work
Operating system, not an application system. Something is being commuticated
inside.
Object code- binary. Translates in machine to tell it to do things
Source code- Its what operates the system. Uses letters and numbers which makes
it a literary work.
Analysis
Two step argument
o 1. Doesn't fall within statute
yes it does it's a literary work
o 2. Well why isnt it a method of operation
Method of operation if it is the only way to accomplish something
Become method of op if no other way to do it
But here, there are many different ways to do itmany different
operating systems
Rule
Methods of Operation are unable but here, there are many operating--Court is like
they both accomplish soemthign that people can accomplish with different systems
Many operating systems, so this wasn't the only way to run a computer. Therefore, it is
able because the idea can be expressed in a plurality of different manners.
Lotus Development v. Borland Intl
Spreadsheet program copies menu tab order from popular Lotus application.
Obviously, plenty of other variations were possiblecould have used a different order.
But court finds the ordering was NOT able. Its a method of operation.
o There was a circuit split on this, and S.C. split 4-4. So, meh.
Method of operation when you consider program compatibility. Must learn how to do
the same thing for each program used.
Pictorial, Graphical and Sculptural Works
16
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Pictures (Pictorial, Graphical and Sculptural Works
Its how you render the photograph, the lighting and angles.
Special steps taken in using the equipment. The more special steps that are taken, the
more likely we are going to get a result that is copyrightable.
Take something ordinary, but because of your reputation, can get to call it art.
Still used the form which is exactly what copyright protects.
Its not the idea, the photograph is what it is.
Protectable Elements of Photograph
Renditioncamera placement, lens, lighting, etc.
TimingWait for a certain moment (certain reflection from sun; bear
catching salmon in mouth)
Creation of the subjectcreation of original / unique scene
Mannion v. Coors
Coors infringed on Ps copyrighted work where there was many to depict
the same idea
Bridgeman v. Corel
no in photograph of painting which simply tries to reproduce painting
accurately
Rogers v. Koons
Facts: large sculpture copying photo of man and boy holding lots of puppies
on park bench was infringing
Holding: Court here finds unusual lighting and angle, and dark skin
contrasted with light shirt and jewelry might have created uniqueness
meriting --rejects SJ
o Unlike Kaplanthe man with nice shoes standing on ledgetwo
depictions of an unprotectable idea
Bill Diodatorich
infringement
woman
on
toiletlacks
sufficient
originality
for
Functionality: Problem of Applied Art and Functionality
If something is functional, it cannot be copyrighted. Because protected by patent
How do we know whether something is functional or not?
o 1. That can be identified seperately from and
o 2. Being able to existing independently of utilitarian aspects of the article
Functional Aspects
Protected under patent law
17
--no
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
o Even expressive elements are unprotected when they are functional- Baker v.
Seldin
A book describing an accounting system can be protected; the system
itself is not protected; only the authors creative description of such
Instructions and rules may receive protection; but on THIN protection
Useful Articles
Receive protection only if its aesthetic features are separable from its utilitarian
aspects
Copyright and Fashion
A clothing design is protectable only if its aesthetic elements are separable from its
functionfunction and form are generally so intertwined that copyright protection is
negligible
Physical and Conceptual Separability
Physical
o Requires the work to contain separate physical elements
Very tough standard
Conceptual
o Can the author make aesthetic choices that do not affect the functional aspect
of the work
Mazer v. Stein
Facts
The Statue becomes a lamp.
Issue
Could that possibly be copyrightable?
Have to look at statute: 101
o 1. That can be identified seperately from and
o 2. Being able to existing independently of utilitarian aspects of the article
Yes can be able because her utilitarian aspect/function can be separated
What Cannot be separated?
The Zigzag bicycle rack. Not copyrightable. He made the twisty thing as art, but then
someone saw it and was like lets make it a bike rack! If you take away the design, the
bicycle has nothing to sit on. Cannot exist away from utilitarian aspect, as pretty as it
may be
Masquerade costume is clothing, so cant be
o Clothing is functional so it cannot be copyrightable
o Cannot be separated from its utilitarian aspects
Functioning things can be copyrightable
Toy airplane?- Real airplane isnt because it needs a fusal lodge and shit
o But a toy isnt going to be flown and its just a model to play with
Useful articles that cant be copyrighted
18
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Cellinis Salt Shaker
More like lady Lampits capable of existing without the salt shaking partitd still be
a beautiful statue.
Capable of existing separately from the functionality
PIVOT POINT INTL V. CHARLENE PRODS. INC. (P wins)
Facts: Mannequin head to be marketed to hair stylists for use with wigs. Obtained
protection for the design.
Analysis
Three 7th circuit cases that had to be distinguished
o Kielseltiein Cord v. Accessories by Pearl --Fancy belt buckle casevery
elaborate base for where tongue comes out, need the tongue but the base from
where the tongue emerges is not so simple, but a nice design. Yes
copyrgithable.
Dissent: Its not capable of existing separately fromit's the base and the
tongue has nothing to hold onto if you remove it. Dissent was like well as
fancy as it is, you ruin the base
o Barnhart v. Economy CoverDetail model with the chests. Is it capable of
existing without the shirt part? Not copyrightable
o Brandir Intl v. Cascade Pacific Lumber-The Zigzag bicycle rack. Not
copyrightable. He made the twisty thing as art, but then someone saw it and
was like lets make it a bike rack! If you take away the design, the bicycle has
nothing to sit on
Rule
Needs to be conceptually different. It should not be whether its phsycially separable,
but conceptually separable- can your mind look at it and see the different view of it
stimulate in the mind of the beholder a concept that is differnet than the concept
provoked by its utilitarian function.
o The eye of the maker
Really thought it was a beautiful piece of sculpture
o The eye of the seller
o The eye of the ordinary observer
Can you look at it as an aesthetic object
Holding
Conceptual seperability exists when the artistic aspects of an article can be
conceptualize as existing independently of the utilitarian purpose. This independence
is informed by whether the designer was influenced by aesthetic considerations, and
that was his artistic judgment that created it.
Protection granted for mannequin head
Pg 250
Supplement page 15toy car is not useful so it is copyrightable
Tea light candle holder can you separate the candle part from the sails of the ship
the bottom of the ship holds the candlesNOT copyrightable .
19
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
End of each of the chairs was animal figures, decoratve element- you could look at
the chair and look at the decorative element of the animal, the artistic judgment was
sufficiently independentdidn't improve the furnitures utility, but to give the chair a
pretty face . Yes copyrightable
Hookah water holderno copyrightnothing seperable
Typeface designsnot able
Architectural Works
Architectural works
The plans and models that represent the structure AND
The architectural structure itself
Used to be considered useful until 1990s when the law started to recognize as .
Architectural drawings and models were able
o Treated like typical pictures/pictorials, so protection only extended to those
elements in a building that were physically or conceptually seperable.
o Before 1990, a person who had access to the plans or drawings could construct
a building and escape liability if the plans and drawings were NOT copied
o Now, infringement may lie even though access to the 3d work is obtained from
its 2D or 3D depiction
Demetriades v. Kaufmann
SCARSDALE drawings were copied- if you copy the drawings and make new
drawings yourself, that is copyright infringement, but if you did drawings based on the
house, that's not copyright infringement because the house cannot be copyrighted
1990 Act 101- Any tangible form of expression, including plans or drawingsbut only overall
form of building is protected, not standardized features (doors, windows, etc.)
**Pictures of buildings are not infringement if they are publically visible
Owners can modify/knockdown building without architects permission
Kiosk is not a buildingmust be habitable, permanent & stationary (home, office
building.. etc)- places people enter.
Scope of Protection (Not from class) (From a supplement)
1. One must examine the work to determine if there are original design elements,
including the overall shape and interior architecture
2. If such design elements are present, one must then determine whether the elements
are functionally required.
a. If these elemetns are NOT functionally required, the work will be protected w/o
applying the physical or conceptual separability test
Subjects of Copyright: Characters
Protection of charactersif character distinctive enough, infringement can be found because
of similarity in character.
1. Visual Character are always protected.
20
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
o Winnie the pooh, Snoopy
2. Literary characters are not awarded the amount of protection because its harder
to tangibly invision the character.
Two Possible Tests
1. Story Being Told Test (WB v. Columbia)
a. If the character is the story being told, there is protection for that character. If
the character is just the vehicle, not within protection. So highly delineated.
i. Ex. Forrest Gump
2. Distinctively Delineated Testa. Character copyrighted depending on how precisely defined he is. Can also be
applied to non-central characters.
Cases
WB v. Columbia (D wins)(Story-Being Told Test)
Holding
Sam Spade lawsuit. WB held only rights to Maltese Falcon story, not to the character
WB knew that detective stories often have sequels and didnt negotiate for character
rightsas an experienced party, ambiguities were construed against them. Did not
acquire exclusive right
Anderson v. Stallone
Writer claims thought up the idea for a new rocky movie. Sues for copyright for
infringing his treatment of the film. He really did follow a lot of the elements in that
treatment.
(Fully Delineated Test): In some movies, the character is the plot. They are so highly
delineated we (court) don't care what scenario they are in. Someone cant claim in a
derivative script of the characters
o What it would mean is that no one else would be able to ever use the Rocky
character again so they rejected that argument
Gaiman v. McFarlane
Comic books. The minute it becomes pictorial you can see itthe minute they were
drawn out they became pictorial. Gaiman had partial interest in even though he only
wrote the characters and Macfarlane drew them
Characters in the Public Domain
Can Sherlock character be used If some (stories?) in the public domain, and not following
plot of the old ones?
Yes can use those characters, as long as you don't follow the stories that are still
covered under copyright. Characters are in public domain. (Klinger)
o Afraid they are going to make him sound stupid
Klinger v. Conan Doyle
Last 10 stories are in public domain. Can author use the characters?
21
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Only new story/ character trait elements from the protected stories are protected.
Everything else is in the public domainaka stock of the character.
Sound Recordings
Works that result from the fixation of a series of musical, spoken or other sounds.
Before 1972-A live performance is not covered by copyright. And recording the live
performance shouldn't be copyright. Only when it is publish.
After 1972- got sound recordings
Two Entities to be concerned with when discussing who splits the money that comes in
from sound recordings.
o The Composure
o The performer.
1976- statute- sound recordings are fixed and subject to
Newyon v. Diamond
Facts
Beastie Boys samples James Newton (Jazz composer and flautist). Had license to
recording, but not composition Three notes composed and played by Newton. Can he
have a composition interest in those three notes?
Holding
NOOits the way they were RECORDED that makes them distinctive, and since they
had rights to the recording, that was OK (de minimum) (taking was de minimis . They
simply sang those notes. Recording 3 notes is not enough to constitute infringement
Subject Matter: Government Works
No copyright for work of the U.S. government.
Every work of the U.S. govt, which is why so many companies can print SCOTUS
cases (Wheton v. Peters)
Two Limitations
(1) Not precluded from recieiving copyrights from a sign of requestget C from an
assignment
(2) If drafty of the army, anything you do is owned by govtwork for hire and since
govt cant own copyright, there was no infringement
States cants own copyrights either
Everytime state puts out an opinion, it can be copied for free (Banks v. Manchester)
o No simply refer to the blue book for the law, it is not the law though
for Sacagewea sculpture that was the basis for gold coin IS protectable because
govt inherited it by assignment.didn't originate it. (however, works for hire by govt.
are not protected)
o 105: government can receive and hold s transferred to it by assignment,
bequest or otherwise.
Briefs are Copyrightbale, but westlaws use of it was fair use.
22
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Hyman v. Rickover
Designer of Nuclear sub and navel employee) gave speech, not on command of govt,
but on govt time. Speeches not able because work of the U.S. govt they gave him
the resources to write/ give the speeches
Work of the U.S. government consists of works accomplished through government
funding, as in the government supplies the resources.
County of Suffolk v. 1st Amendment Real Estate (had enough originality)
Defendant copied official tax maps
The original maps were ableunlike judicial opinions and statutes. They are made
by the county for incomeproduced by govt. for additional financial income
Veeck v. Southern Building Code
Model bldg. code was enacted into law. Another company copies the laws. Is this
infringing on the model code?
Holding
No The model code is a copyrightable entity. But when the model code becomes the
code (the law), does it become uncopyrgithableYES
Stuff we didn't read but talked about: Public Policy
Mitchell Bros v. Cinema Adult Theater
o Are obscene movies copyrightable?
o Yes because because we are pro-creativity (not procreate.. like babies lol).
Discouraging creativity undercuts purpose of law
Works Made for Hire: Work of the U.S. government consists of works accomplished through
government funding, as in the government supplies the resources. (Hyman v. Rickover)
If Writer is an employee creating a work made for hire, her employer is deemed to be the author
and owns the copyright.
1. If the work was prepared by an employee within the scope of her employment
2. The work was specially ordered and commissioned, falls into one of several specific
categories, and the parties expressly agree in writing it is a work for hire.
NYT is author of an articlenot reporterfor purposes, if the parties expressly
agreed in written agreement that work was for hire (whether or not youre employee or
independent contractor). Same for employees on movie, etc. Owner of in a
collection has only to the collection or later revision, unless explicitly stated
otherwise in writing
o So if NYT resells article to Lexis, is this a later revision? --No, says 2 nd circuit
Friedman and others were successful author-plaintiffs. NYtimes doesn't have
the right to sell it to lexis
Martha Graham School v. Martha Graham center of Contemporary Dance
Famous dance choreographer conveyed her rights to her husband, then died. Dance
company asserted that all the dances she made while with them were works for hire
23
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Court found for the dance studiothey shouldn't have, but they did because the
husband was a real jerk.
Teachers Exception to the Work for Hire Doctrine
Teacher exception to work for hire doctrine --- teachers own their lectures, even
though they are employees of the University
o teachers work from place to place.
Duration of Copyright
Duration of Copyright
1976 ActSect. 302(a) (published on or after 1978)authors life plus 70 yrs.
(Published before 1923) public domain
o Sony Bono Extension Act Prospectivenot retroactive. So didn't apply to
works that had already lapsed
Passed in 98. Covered works that went back 75 yrs (to 23) but not
before
Under Sonny Bono, works covered for 95 yrs from publication
1923-63if published with proper noticesect. 304 of 76 actin public domain if
holder didn't renew. If did, you get 75 yrs., not 95.
1992- automatic renewal!! Covers works going back to 64. You get the full 95 yrs.
Created before 78 but not published--protects descendants ownership rights in of
ancestors unpublished works. If published it by 12/31/02, has until 12/31/2047.
(Even ancient texts!). Descendants had a 25. Yr. window to put stuff out. But if not
published by the end of 02, it went into public domain.
Sound recordings fixed before 72 were given full protection for 95 yrs. (til 2067), but
after that there is no protection.
ELDRED v. ASHCROFT (2003) (constitutionality of Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act)
In a 7-2 decision, the Supreme Court said that there was nothing unconstitutional about
extending the copyright term even though the Constitution provided for protection for
limited times
Upholds Sonny Bono extension
length of if an American published something in europe and we didnt extend our term
then Europe wouldnt recognize the extension for any America citizen so really a quid pro
qou that our authors who published works in Europe would be able to take advantage of
the 20 year extension unless we also extend our term for another 20 years. A theory is
good if falls into public domain bc more material that can be distributed to people at
24
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
cheaper prices
If constitution said give exclusive rights to writers and inventors for limited times, and if adding
another 20 years is this vioalting the limited time rule?
Each time the term was extended, there was always more years added that applied to
EXISTING and not just works t newly be create
o So if guy had 28 year protection nadn then gets another 48 years from congress,
well this guy is a happy camper
o This is to give people an incentive to create something by giving them this exclusivity
But the other prolem is they are getting more then they bargained for
Pg 394, good policy reason is that fact that the European Union had assed a satutue
extending everything for 20 years but requiring reciprocity of the authors form a nation who
did not extended it so aiding own authors by allowing extention for in Europe by extentin
our own
Craig Notes from this: (the notes I added were sent to me that day)
RBG says new extensions are valid because they apply to existing still-active s as
well as new ones
Also the fact that the EU had passed an extension means that our reciprocity is a good
move policywise, for the sake of consistency and to incentivize our authors
Breyer Dissent argues that the extension is unconstitutionalcopiers have 1 st
Amendment rights at a certain point, and this is too long
Used to have strict requirements of notice
Notice (including notice on work)
Renewal
o Theory was to help artists, who are poor at negotiation, to get a better rate later
However, artists are permitted to negotiate away the renewal term, which
defeats the purpose
Section 304 renewal option goes to author, or widow/widower/children
Rear Window Case (Abend v. Stewart)
descendents of short story writer could enjoin future distribution of derivative work, the
film
o Courts have read widow, widower OR children as meaning AND. Widow gets
50%, kids split the other 50. Crazy courts
Any kid may convey his/her share of the rights
o As a result of this case, movie companies now insist on an Abend
release some successor in interest has to sign a document
25
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
covering the renewal term so that they know that they can exploit
the movie beyond the first twenty-eight years in the event of the
copyright holders death.
Rule
A derivative work is itself a copy of the original work. When an author dies before the
renewal period arrives, his statutory successors are entitled to renewal rights even
though the author has previously assigned the renewal rights to another party. Owner
of a derivative work does NOT retain the right to exploit that work when the death of
the author causes the renewal rights in the preexisting work to revert to the statutory
successors.
Foreign Stuff
1) , owner of and date
2) requirement to renew and ceraitn time
3) manufacturing clause
o if American authorir who printed book abroad and shipped ot U.S., yo would
lose protection
simply to protect American printers
Uruguay Convention of GATT complained a lot of their natls lost US protection due
to stringent requirements
Books published abroad lost -- many foerigners lsot protection because didnt
cooperate w/ requiremetns
So we passed 104ARestoration of Copyrigth ActForeigners or Americans
abroad could get lost under one of these requirements rested upon filing NOTICE
with office.
o any person who lost protection who was at the time a national or domiciliary
of an eligible country
o this allwoed people to file a restoration notice (I was a domicialir or national of
an eligiblae foreign country) applied to americans who were abroad as well
o say lost notice in the country and now I want my rstored
o Those who relied on the work being in public domain were given 1-yr window to
continue exploiting the work.
The three excuses you could use to get your back are (From book):
o 1. Lack of relation between the country of origin and the U.S. at the time
of publication
o 2. Lack of Subject-matter protection for sound recording fixed before
1972; and
o 3. Failure to comply with U.S. statutory formalities (e.g failure to provide
notice of copyright status, or to register and renew a
26
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
REGISTRATION
Both published and unpublished works may be registered with the Copyright office.
Registration is a prerequisite for infringement of registered works.
Only the filing of the subsequent lawsuit.
The certificate of registration is prima facie evidence of the validity of the copyright,
provided the work is registered no later than five years after first publication.
Make a public record of copyright.
Advantages of registration:
1. Attorneys fees
2. Statutory damages
3. Presumption of validity and ownership of copyright.
4. Constructive notice of recorded documents.
Deposit requirements
1. One or two copies or phonorecords with the Copyright office.
2. Two copies or phonorecords with the Library of Congress
DURATION OF COPYRIGHT
Works published before 1923 are no longer under copyright in the US.
Works published between 1923 1977 may have an effective term of 95 years.
An effective term of 95 years.
Works created after 1978 have a term of at least 70 years.
Original US copyright statute provided 28 years. 14 years from publication plus a renewal
term of 14 years. (1790)
1831 42 years (28 year initial term + 14 year renewal)
All of these works are in the public domain.
1909 ACT - 28 yr limit. (67 year renewal term)
1978-1998: life + 50
1998-present:
In general: life + 70
Joint authors life of last surviving author + 70
Anonymous/pseudonymous works and works made for hire: 95 years from date of
1st publication or 120 years from creation, whichever expires first.
RENEWAL RIGHTS
Assignments of renewal rights are effective, provided that the author survived until the
time of renewal.
If the author died, all rights reverted to the authors heirs, and even derivative
works prepared during the initial term could not be disturbed or performed without
infringing copyright.
WORKS CREATED BUT NOT PUBLISHED OR COPYRIGHTED BEFORE JANUARY 1,
1978 17 USC 303(a)
In no case shall the term of copyright in such a work expire before Dec. 31,
2002, and if the work is published on or before Dec 31, 2002, the term of
27
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
copyright shall not expire before Dec 31, 2047.o Divide ownership based
on widow gets 50% and children get the rest
Formalities
1. In every other country in the world, you publish a book and you own the rights.
In the United States, even today, there are three formalities:
a. Notice ( sign, date of publication, and owner)
b. Deposit
c. Registration
Three time periods that we have to be concerned with, and depending on when
the work was published, there are different technical requirements:
d. Jurassic Age - Before January 1, 1978
e. Middle Ages - Between January 1, 1978 March 31, 1989
f. Today - April 1, 1989 to present
BEFORE JANUARY 1, 1978:
g. Publication The formalities applied only if the work was published
i. Publication is the distribution of copies.
101. DEFINITIONS.
Publication is the distribution of copies or
phonorecords of a work to the public by sale or other transfer of ownership, or by
rental, lease, or lending. The offering to distribute copies or phonorecords to a
group of persons for purposes of further distribution, public performance, or
public display, constitutes publication.
h. Limited Publication Restricted communication of the contents of a
work failure to have notice is not fatal
i. Example: The Oscar is displayed to thousands of people, but never
published only given to the winners. Failure to have notice not
fatal because this is not general publication.
i. General Publication Occurs when tangible copies of the work are
distributed to the general public in such a manner as allows the public to
exercise dominion and control over the work
ESTATE OF MARTIN LUTHER KING JR., INC. v. CBS INC. (1999) (p. 471) (I Have A
Dream speech)
j. His speech was heard everywhere, but he never published a copy. The
court found that since he did not distribute the copy, there was no
general publication and his estate still owned the copyright. Those copies
did not have proper notice
LETTER EDGED IN BLACK PRESS, INC. v. PUBLIC BLDG. COMMN OF CHICAGO
(1970) (cited in M.L.K. case) (Picasso sculpture)
k. Picasso had made a sculpture for a museum. The museum made a
postcard and distributed it to the public upon request. By allowing the
people to take pictures and allowing postcards to go out without notice,
you have distributed the work. The sculpture was thus dedicated to the
public domain. Fell into public domain
Notice
Since We Joined Bern Convention, Not mandatory to have notice.
28
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Pg 391- Sec 401 Notice of Copyright: Visually Perceptible (1978-1989)
Notice may be placedl but can be preserved with various escape hatches (today,
you don't have to at all)
Escape hatches are:
o Notice was omitted for no more than a relatively small # of copies
o Registered within 5 years of publication
o Notice omitted in violation of an express requirement in writing that, as a
condition of the authorization of the public distribution, they bear the
prescribed notice
Middle ages january 1978- march 1989--- shall became may
Hallmark Exception
o Don't need to put date on greeting card and jewelry don't want to have to say
how old jewelry is
Phonorecords of Sound Recordings- P in a circle is performance
If don't have to put the notice on, why do it?
Benefits you to to include notice because its prima facie proof of validity, a prerequisite
to civil suit, and can lead to statutory damages and attorneys fees
o Statutory damagesa set amt you can get without showing any harm at all, if
you can show infringement
403- Collection of Works by govt MAY be able if they include headnotes etc.
if you publish something that contains uncopyrightable shit of the U.S., you are
supposed to tell people what is copyrgithed and what is not so the headnotes and
such.
406- if name was improper in notice, an infringer who being undertaking of making
derivative work in reliance on the incorrect notice has a complete defense, unless proper
registration is recordedinnocent infringer
o beginning of undertakingplayfirst reading with actors; movies 1 st day of
principal photography; bookfirst publication
What happens if you don't give notice?
Now there its dif. Three escape hatches. (above)
405(b) no notice and you innocently infringed the copyright, you check shit, and then you
start to infringe, you still hve to pay actual damages. But you don't hace to pay the extra
damages under section 504
this is between the period of jan 1978- march 1989.
Example: Somebody relying on the notice (from ABC to sell the rights for the book to make a
movie), begins an undertaking. the first day of principle photography for movies is
beginning undertaking. Publishing the book is beginning undertaking
if before undertaking hasn't started, and XYZ notices and then registers so you don't
do it, there is no innocence anymore and you gonna get fucked if you make the movie.
Registration
1. its prima facie evidence to show registration
29
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
2. you cant start an infringement case without registrationregistration is a prerequisite
for filing a claim.
How to prove you created this work by a certain date
old dayssend registered letter to yourself containing the work.
Sec 411
you must register to start an infringement action
you can get statutory damages even if you cant show any damages yourselfdon't
have to prove anything if you have registered.
If you have registered before the infringement, the otherside has to pay the attorneys
fees too.
Exclusive Rights Under Copyright
106- Exclusive Rights Under Copyright
Owner of a copyright has exclusive right to (and to authorize):
i. Reproduce the copyrighted work in copies or phonorecords,
ii. Prepare derivative works based on the copyrighted work ,
iii. To distribute copies,
iv. To Perform the copyrighted work publically,
v. To display the copyrighted work publically,
vi. Perform by means of digital transmission (for sound recordings) the copyrighted work
in copies or phonorecords
Copies:
Copies are material objects other than phonorecordsfixed form, material objectthe
work can be perceived reproduced or communicated directly or with aid of machine
reproduction of copies
a. RAM- if an infringer arranges for something to appear on your screen just as
RAM, it is an infringement --- fixed enough
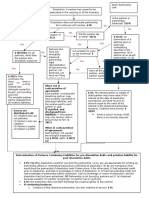
Elements of a Copyright Infringement Claim: P MUST SHOW:
1. Plaintiff must demonstrate ownership of a valid copyright
a. Must be an original work of authorship fixed in a tangible medium of expression.
b. Plaintiff must show that he owns it.
c. Timely Registration gives is to presumption that the copyright is valid and
belongs to the registrant
2. Plaintiff must show that his/her work has been COPIED: Two Ways to prove:
a. Direct Evidence of Copying- Defendant either admits that he copied it or
somebody testifies that they saw the defendant copying it.
b. Inferential or Indirect proof of copying***** (Access and Sub Similarity)
i. Access- defendant had access to the work.
1. Very loose standardit could have happened.
ii. Substantial similarity- Such similarity between the copyrighted work
and the infringing work that the similarity simply could not have come
through coincidence or other natural random causes
1. an expert can only testify on structural similarities).
30
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
2. Substantial similarity is a jury questionthey sound familiar
Cartoon Network LP v. CSC Holdings, Inc.
Rule
if someone does it as your agent it is not infrignemnt because of section 1008 audio
home recording act- 108- no action may be brought under this title alleging copyright
infringement for . For non commercial use by a consumer of such a device for
making analog copes
Holding
if you do it yourself, at home, for noncommercial reasons, you are home free.
That's why no infringement
Remote storage was doing it for you, which is functional equivalent of doing it
yourself.
Analysis
Remote storage DVRprogram content very briefly stored on remote database
specifically said theyre an exceptionAmerican Home Recording ActOK on your
own home system for own use.
2nd circuit finds Cablevision is merely the viewers agent. They provided the
technology.. the customer chooses what to record
Dish Network v. American Broadcasting Cos. Inc.
Came to same result as Cartoon Network.
DISH has no control over which programs users decide to copy. Subscriber must
decide whether she wants to use the recorder, and if she does on what programs.
Shows are stored on the personal hard drive on the Hopper (Dish Networks DVR
technology), NOT at DISH headquarters
Dish program creates the copy only in response to the users command.
Therefore, the district court did not err in concluding that the user, not dish
makes the copy
.
The Right To Make Copies
1976 Sec. 1008- Consumers can copy things for home use
If you do it yourself at home for no commercial reasons you are home free. Minute you
say you can do it yourself, if you have someone do it for you, then its not an
infringement
Blackwell v. Excell - Photocopy shops
Course on American Short Story. They are all in 10 separate books. All the books
costs $10-$20. So teacher makes copies and gives it to Kinkos to make more copies
for the students. The authors don't like this because then their books arent being
purchased. So this guy Blackwell thought of this idea where the students have to come
31
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
in and click a button and then boom ten short stories will come out in the course book.
The student has to come in an make the copy
Students may come in and print ed works from ExcelExcel stores the master.
Excel argues that students themselves create the actual reproductionthe court
rejects/doesn't buy this argument --- they are not liable. The consumer the
individual doesn't do it themselves.
Proving Infringement
Arnstein v. Porter
Facts
Arnstein claimed a few of Porters song
Issue 1:
At what stage can you dismiss this case?
o Lower court granted summary judgment
Holding
Higher court said you need to have a jury decide these issues. Ordinary observer that
decide issues of substantial similarity.
Issue 2:
How to Prove infringement?
Holding
Porter Wins. Very limited proof of the possibility of access is enough to show access
and also, even though experts may tell you something about the structure of the two
pieces of music, they cannot opine on the final question: that must be left for the jury
Analysis
Case is important for how you prove copyright infringe and what you have to show:
o 1. Show ownership of a valid copyright
Need to show you own it hasn't been assigned or a work for hire
Its valid
o 2. Access and copying
how to show copying.
1. Evidence --- defendants admission, circumstantial evidence showing
access and where a reasonable trier of fact may reasonably infer
copying
2. **Striking similarity may show accessthey are so similar he must
have looked at it
o 3. Show Substantial Similarity
if there is evidence of access and similarty, trier of fact must determine
whether similarities are sufficient to find copying
So striking you do not have to prove access
Bright Tunes Music v. Harrisongs
Access proved because Hes so Fine was in the Billboard Top 10 while Beatles were
also in the charts.
32
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Court decides Harrison subconsciously copied for My Sweet Lord
Striking Similarity: Similarities are so striking as to preclude independently arrived at same
result
Price v. Fox Entertainment (Dodgeball Case
Rule
Adopted Striking Similarity.
Analysis
Have to prove access, its easy to prove. Song, movie, book out in the public.
o Potential access established by overlap in agentswriter of the Stiller movie
then wrote his first draft with alarming speed after alleged access.
o Sent it to an agent that has access to something else. That was enough.
Movies where camera focuses on a copyrighted imagine for like a few seconds.
Why was there access? They (copier) could have heard it. Reasonable to assume
tey could have heard it.
Circumstantial Proof of Copying
Selle v. GibbBee Gees
Holding
7th Circuit rejects striking similarity test for accessthe plaintiff lost because he could
not prove access. His song was unpublished and had only been performed at
weddings and bar mitzvahs
Rule*
Court will not support a finding of infringement unless there is at least some other
evidence which would establish a reasonable possibility that the complaining work was
available to the alleged infringer.
Repp v . Weber.
Court decided jury had to decide question of similarity.
o CoA decided that there was enough contrary evidence so as to withstand
Webbers motion for summary judgment and to create a triable issue of fact.
nd
**2 circuit reiterated its view that similarity can be so striking as by itself to constitute
proof of access sufficient to withstand summary judgment
Ty, Inc. v. GMA Accessories
Reinterpreted holding in Selle (both 7th circuit cases) so as to allow a plaintiff to base
its proof of access solely on striking similarity so long as there is no earlier
exemplar, typically in the public domain, that could have independently inspired
both works.
33
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Selle required plaintiff to produce evidence of access, but in Ty, a similarity that is so
close as to be highly unlikely to have been an accident of independent creation
is evidence of access.
o A similarity may be striking without being suspicious if it is explainable because
both works copied the same thing in the public domain.so can be similar to
something in the public domain and the copyrighted product in question, but it
CANT just be similar to the copyrighted product in question.
o You can have access and copying but sometimes it is not enough similarities
between the two works must be substantial enough to under all the
circumstances, make independent creation unlikely
If similarities are so striking as to preclude the possibility that they independently
arrived as same result.
Ringgold v. BET
Holding
Camara in TV show focused on ed quilt for 26 seconds. Higher courts rejects de
minimis argument there was some copying, but it was too small.
Analysis
Says that de minimis is a subset of the 3rd point of the test (substantial similarity)fair
use factor), and thus cannot be threshold issue. There are three other fair use factors
that need to be considered and therefore, this is not enough to decide whole case --however, other circuits have found the other way
De Minimis-In the copyright context, it means a technical violation of a right so trivial that the
law will not impose legal consequences. Could mean that copying has occurred to such a
trivial extent as to fall below the quantitative threshold of substantial similarity
Distinguishing Idea and Expression
Peter Pan Fabric v. Martin Weiner-Learned hand Test
Rule
Infringement exists when: The ordinary observer, unless he set out to detect the
disparities, would be disposed to overlook them, and regard their aesthetic appeal as
the same.
o A typical observer would overlook the parts that arent identicalthe ordinary
observer doesn't take the time to pin point all the minimal details between the
two.
Herbert Rosenthal v. Kalpakian (Bee Pins)
Holding
Jeweled beecourt finds there is only one pattern either party could have used to
place the jewels on a teeny bee pin. Thus, anyone using this idea would have to copy
the execution, and thus, no infringement.
34
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
The idea and expression are indistinguishable. Obviously the jewels were going into
the bees eyes.
581: Jelly fish: no infringement with the weird jelly fish thing
SAT
SAT review courses send people in to take SATs. Job was to copy all the questions
and put that in the test materials. copyright the tests because they don't want
princeston review to immediately take the test.
The test of substantial similarity is whether the accused work is so similar to plaintiff's
work that an ordinary reasonable person would conclude that defendant unlawfully
appropriated plaintiff's protectable expression by taking material of substance and
value.
Holding: The court not convinced that ETS in the text of a question precludes a
coaching school from letting the same content in the same order as long as it doesn't
use the same or substantially similar language.
Ideas/Expressions Distinctions: Screenplays n Baes.
**NICHOLS V. UNIVERSAL PICTURES CORP.
(2nd most important cppyright case)
Rule
Learned Hand the right cannot be limited literally to the text as plagerist would
escape by immaterial variation. don't have to be copied word for word to infringe
o It is of course essential to any protection of literary property under c.l that the
right cannot be limited literally to the text, else a plagiarist would escape by
immaterial variations.
**Two ways of copying
o Copy words/dialoguefragmented literal similarity
o Copy comprehensive non literal similarity
In the series of abstrations, when they are no longer protected, something about
expression not be extended
Holding
L.Hand finds not enough similaritylovers are stock characters, jewish dads have
different personalities. Quarrel and resolution, Romeo and Juliet nonsense not enough
plot overlap
o The differences that did exist between the characters only make up a small part
of the whole of the character (the stock character).
Analysis
To say/hold infringement would be to give the plaintiff/playright the ability to prevent the
use of his ideas to which, apart from their expression, his property never extended
Takeaways From Nichols
35
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Literal Appropriation may take part of the dialog and then apply fair use doctrine or takes an
Abstract the whole thing, that makes it more difficult. The more detail you take out and use,
the more it looks like the other play.
o The details are the copyrighted shit
Two Ways to of Copying
Fragmented literal similaritydon't take all the words, just pieces of the word
paraphrasing lines. Specific words are taken from one creation to another. If that
happens, apply fair use doctrine.
Comprehensive Nonliteral Similaritycopying of structure/plot. Pattern similarity.
Stock Plot generic plot linePlot of Romeo and Juliet not copyrightable
Stock Characters- Not copyrightable.
SHELDON V. METRO-GOLDWYN PICTURES CORP. (1936)
Facts
The movie buys the rights from the book, and it can use whatever from the trial cuz its
in the public domain. It cannot use what is in the play that the play added to the trial.
Whatever the play added to the trial that is copyrightable. DC court judge and Learned
Hand have different movie interpretation
Issue
Did the movie take what was added to the trial by the play? Did the picture take new
material that was in the play but not in the novel?
Testish/Legal Analysis
(1) Whether he () used the play
(2) Whether there was an infringing use
o **Learned Hand established that in order to figure out if there is infringement,
he needs to look at the scenes/state the similarities
The poisoning scenes were basically the same
Holding
No plagiarist can excuse the wrong by showing how much his work he did NOT pirate.
----- Unconscious plagiarism is actionable quite as much as deliberate
Court concluded that the defendants motion picture tracked too much of the altogether
fictional elements contributed by the plaintiff from her imagination.
o Plaintiff actually succeeded, which is rare
Analysis
The play is the sequence of the confluents of all these means, bound together in an
inseparable unity; it may often be most effectively pirated by leaving out the speech,
for which a substitute can be found, which keeps the whole dramatic meaningthis
is exactly what the defendant did in this casethe dramatic significance of the
scenes we have recited is the same, almost to the letter.
Surely the sequence of these details is pro tanto (as far as possible) the very web of
the authors dramatic expression, and copying them is NOT fair use.
o Defendants need to steer clear of the plaintiffs expression, but could use the
general ideas.
Details in the same sequence embody more than the idea of the play; they are the
very raiment.
36
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
This case took the plot, not the linespattern similarity/Comprehensive nonliterary similarity
Judge Hand examined the similarities between the works:
Heroine
Family
background
Villain / First
Love
New Love
The blackmail
method
The method of
seduction
Ruse or
Reconciliation
Murder Method
Death Scene
Alibi
Trial
Madeleine Smith Innocent
Respectable
Ten years older
Twenty years older
not true love, just
a better match,
more $$
Letters
No seduction that
we know about
Ruse to get him
back
Arsenic in
chocolate
Not present
Innocent alibi
with sister
Play (Plaintiff)
Madeleine Cary
wanton and
corrupt
Genetic hotbloodedness
Moreno South
American
True love
Novel
Letty Lynton
wayward
Movie (Defend.)
Letty Lynton wanton
Middle-class
Hot-bloodedness
Swede
Renaul South
American
True love
Threatens to
expose relations
Gaucho song
Letters
Ruse
Ruse
Ruse
Strychnine in
coffee
Present as he dies
False sex alibi
w/Brennan
Arsenic in
chocolate
Not present
Cyclist asks for
help of passing
cyclist en route to
a party
Strychnine in wine
glass
Present
False sex alibi
Older peer, better
match
Letters
Gaucho song
Mann v. Farrer et. al. LF case
Lists movie infringement/frustrated writer cases where court didn't find infringement.
Litchfield v. Steven Spielberg
Sued by some lady regarding ET. Psychotelekinetically taking a gun away from father
(compare to bicycle); Revives father from a heart attack (Revives flower in ET); they
go back to their ship (ET goes home)
Holding
Access yes, for the purposes of summary judgment, defendants admitted to having
access.
Filtration Analysis= Learned Hands approach
How do you know if the Two plays are Substantially similar?
Need to go through the plot, the characters, particular scenes
What is the basic plot
Who are the characters
37
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Where does the action occur.
Burgess v. Chase-Ribaud
Imagined version of the meeting of Thomas Jefferson and Sally Hemmings. Someone
else copied the same scenario in a play. Court finds infringement
Followed decision from Sheldon-- Court concluded that the defendants motion picture
tracked too much of the altogether fictional elements contributed by the plaintiff from
her imagination.
Blehm v. Jacobs
Stick figure like characters with life is good slogan. Defendant has larger haead with
facial features, unlike plaintiff. Do some of the same things (giving peace symbol).
No liabilitystandard stock character.
Harney v. Sony
Facts:
Picture taken of Clark Rockefeller (the fake Rockefeller) holding daughter- was used
as have you seen this person?. TV movie used a reproduction of the saem pose
photographer sues.
Holding
The piggyback pose was NOT able because fathers often hold their daughters that
way locating the subject of a photograph in the middle of a frame is an element of
minimal originality and an insufficient basis, without more, to find substantial similarity
Additionally, subsequent events cannot fortuitously transform unoriginal elements of a
visual work into protectable subject matter. --- doesn't matter than photo became
famous
WB v. X One X Prods (supp.)
Facts
Something with Gone with the Wind-- Didn't have posters so those can be produced.
Started to put two characters together on the t-shirts
Rule
Character in movie are still protected, the minute you go beyond reproducing
the characters exactly you are going beyond your copyright permission.
Interfering with characters in the movie.
Holding
Court found the movie characters were still protected, and anything beyond
reproducing the EXACT publicity shots was infringing the movie characters.
Analysis
The characters in the movies are still protected, and the minute you start producing the
shots, you are infringing on the copyright of the movie. If they had just stuck to the old
posters/publicity flyers, would have been fine.
38
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Who is an Ordinary Observer
Ordinary observer Test- The lay person. Should be displaced ONLY when the intended
audience has specialized expertise and not merely when its tastes might differ from those of
the lay observer.
Intended Auidence Rule- similarity must be tested through the perspective of the audience for
which the products were intended.
Dawson v. Hinshaw Music
Ordinary observer of gospel musiclay listener, or choral director who would be
analyzing the sheet music more closely?
Rule
Need not be the lay person when the work is designed to appeal to an audience with
specialized knowledge
Ordinary observer Test- should be displaced ONLY when the intended audience has
specialized expertise and not merely when its tastes might differ from those of the lay
observer.
Lyons v. Morris Costumes (Barney Costumes)
What is the test? Is it the ordinary Lay person that we use in torts, or is it the audeine
of the infringing material is directed.
o The district court said it was the adults who were the intended audience. But
CoA was like nope its da children
bunch of kids yelling barney at duffy costume was very good evidence.
Substantial similarity evaluation needs to be more discerning and more refined
analysis.
Question need to ask: Whether the works are so similar that the introduction of the
alleged copy into the market will have an adverse effect on the demand for the
protected work.
Intended Auidence Rule- similarity must be tested through the perspective of the
audience for which the products were intended.
o Economically important views are those of the young children.
Approaches to Substantial Similarity
Boisson v. Banian (Infringing Quilt?)
Rule
You are not supposed to compare only the copyrightable elements you have to
compare the two taking into account the public domain elements and saying to the
observer but for the public domain elements, would an observer be inclined to
overlook the differences?
Court says Total concept and feel testwhile still using a discerning scrutiny as to
the public domain elements.
Analysis
Cant just break whole thing down into its parts extreme discerningbecause then
left with a bunch of shit that cant be copyrighted. This is too much.
39
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Need to base the comparing on the basis of the arrangement and shapes of the
letters, the colors chosen to represent the letters and other parts of the quilts, the
quilting patterns, the particular icons chosen and their placement.
Picture on 605he didn't create the scene, the scene was there.
Da Vinci Code
Sang Real author (historical theory) sues Dan Brown for Da Vinci Code
No infringement. Cant a theory, and there werent enough similarities in the story
Computers
Computer Associates v. Altai
This is the definitive decision in the copyright field (for comps)
Facts
Computer programmer copied another co.s program. The program removed him from
the project and had other programmers redesign it, scrubbing anything that was taken
directly from the original program.
Issue:
To what extent are non-literal aspects of a computer program protected by copyright?
Holding: No infringement: Substantial similarity test for comp program structure=
abstraction-filtration-comparison
Analysis
Court applies the abstraction test (Learned Hand from Nichols)remove public
domain, nonable elements, etc. Looked at all these literary cases:
1. Abstract out the utilitarian (subtract the idea)
2. Then filtrate it out subtract/eliminate like Nichols
o a. Elements dictated by efficiency- if this is the most efficient way to do
something, even if it is not necessary, subtract it out.
Nature of computer program makes this difficultan efficient computer
program will do only what its supposed to do, and such stripped-down
programming will likely be very similar to any other program designed to
do the same thing. How much was dictated solely by efficiency? Must
filter out those elements out of analysis
o b. elements dictated by external factors-- Incorporates literary elements (i.e. the
stock or standard literary devices in the Nichols case). See factors on p. 568
these are factors that are so closely associated with this particular program
and so standard that the expression of them is not copyrightable.
Standard ways of doing things/ it and therefore must examine structural
o c. Stuff in the public domain - Elements that have entered the public domain by
virtue of freely accessible program exchanges
Ultimately, on these facts, once these elements were removed, there was no
infringement
Everyone now follows this 2nd circuit formula.
40
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Steinberg v. Columbia
Moscow on the Hudson poster infringes New Yorker cover? --- myopic view of NYers
detailed views of NY with minimized landscape in the buildingone looks west, the
other looks east. All this detail of NY buildings and avenues
Yes Infringement. Same font, style.
Authors Reproducing Works in Which They No Longer Own the Copyright
Artists conveying in their own work, then redoing substantially the same work later.
Infringement?
Gross v. Seligman
If you dont won the (c) anymore (bc you sold it), you cannot copy the work.
Infringement where it was the same model posed in substantially the same way. Could
have posed the model in a different way
Franklin Mint v. Natl Wildlife Art
Artist can create a painting using the same subject matter (cardinals in trees)
No copyright infringement when you draw a cardinal why? Because pattern of
differenceevery cardinal looks the same basically
The case that did allow it was copyright infringement because can do other things than
just the one that was in the picture. The cardinal picture, cardinals mostly just sit on
branches-Friedman theorizes this is because all cardinals look alike to us, and it
would be overly restrictive to say the artist can never paint a cardinal again. Whereas,
use of the same model creates much more similarity.
Other Examples
Yes Infringement with the Santas
Tarkay- trade dress infringement
Fart Man- yes infringement
MUSIC: THE RIGHT TO MAKE PHONORECORDS
101. DEFINITIONS. Phonorecords are material objects in which sounds, other than those
accompanying a motion picture or other audiovisual work, are fixed by any method now
known or later developed, and from which the sounds can be perceived, reproduced, or
otherwise communicated, either directly or with the aid of a machine or device. The term
phonorecords includes the material object in which the sounds are first fixed.
a. Phonorecords became copyrightable subject matter in 1971. BIG DIFFERENCE
between the sound recording and the composition itself these are two separate
rights.
41
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
115 Compulsory License
Authors of literary works enjoy full rights to authorize or prohibit the creation of
recorded performances of their works.
As soon as you release a song, anyone else can make their own version of a
recording once it is out. 115 requires you serve notice w/in 30 days of creation and
BEFORE release/distribution. And pay the 9.1c.
A person wishing to obtain a compulsory license must file with the copyright owner a
(1) notice of intention to distribute phonorecords of the copyrighted work, and (2) is
to pay a royalty for each record of the work that is made and distributed.
Just record the song, contact the copyright office/ person with the copyright and pay
them for each record sold. --- Make your version of it.
Sound Recordings Generally
Sound recordings are usually about a captured performance
Sometimes they also contain original music that is being copyrighted for first time but
usually just a performance of already copyrighted music.
The right to make sound recordings is limited by two sections: 115 and 114
115 deals w/ use of the musical composition
114 deals w/ use of the sound recording
115 Compulsory License
Basics:
For a set sum of money, you have right to use music to make your own recording of
the music. Copyright owner cannot refuse.
License is not subject to individual negotiation flat rate for all.
You cannot get a license until the music is published (made public)
First recording gets made through individual negotiation
Only covers music captured in a performance and made available for sale to general
public
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS UNDER 115:
115(b) Must send a notice of intention to the owner before you distribute the work. If you
cannot identify the owner, file it with the copyright office.
Generally, one will just phone the record company and negotiate a price for less than
the 9 cents they usually do it
If you cannot do this, before distribution of the work, you must serve the notice of
intention to obtain a compulsory license under 115. If you do not do this, or if you
42
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
miss the service requirement by one day, you can be facing $150,000 in statutory
damages instead of paying 9.1 cents per record to use it.
Limitations:
Courts have been strict in applying 115 once you add visual elements to the
sound recording like w/ karaoke, it is not subject to the compulsory license.
ABKCO MUSIC, INC. v. STELLAR RECORDS, 1996) (karaoke)(limitation)
Facts:
Defendant recorded plaintiffs music onto a karaoke CD-ROM, with the lyrics scrolling
across the screen. Claimed that this was a phonorecords covered by the compulsory
license. The copyright owners claimed that it was an audiovisual work not subject to a
compulsory license.
Held:
The defendants compulsory licenses do not give it the right to publish the
compositions lyrics on a screen. Song lyrics enjoy independent copyright protection
as literary works. The karaoke CD is not within the statutory definition of
phonorecord.
DERIVATIVE WORKS: You cannot make a derivative work 115(a)(2)
You can make certain adaptations that relate to style of performer or necessity of
performance
You cannot fundamentally change melody or character
Procedures
1. Timing
2.Must give notice to copyright holder and Copyright Office
3. Accounting provisions paying royalties
Harry Fox Agency and Collective Rights Organizations
115 procedures are hard for individuals to follow so music industry came up w/
collective rights organizations to monitor
Harry Fox holds as licensee, the 115 rights of composers
So when you want a compulsory license, you go through Harry Fox and not the actual
author
HF manages the numerous small transactions
Cuts down on transaction costs of managing such small rights. The rights are only
valuable collectively.
The Harry Fox License
43
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
A large number of music publishers and copyright owners have authorized HFA to
issue licenses and collect royalties on their behalf for making and distributing
phonorecords of their musical compositions in the form of CDs, cassettes, and vinyl
records.
Harry Fox also licenses other reproduction rights outside of 115, including the use of
musical works as ringtones, and for background music and for digital jukebox services.
In 2001, the music publishers and record labels reached an agreement to license such
online description services (i.e. Rhapsody, Napster, etc.). The agreement, which was
followed by similar agreement with non-label owned music services, extends the
mechanical license to cover copies/phonorecords made as part of time-limited
downloads and on-demand digital audio streams.
Digital Performance Right in Sound Recordings Act of 1995 Digital phonograph
delivery is equivalent to the sale and distribution of a musical recording extends the
compulsory license to online downloads, or deliveries passed by congress. This never
went into effect however because there were too many peoples rights to obtain and a
government-sponsored Napster program just would not work.
Sampling
114 allows the copyright holder exclusive rights over exact reproductions and over
works in which the actual sounds fixed are rearranged, remixed, or otherwise altered
in sequence or quality. This has tended to work itself out in the industry industry
tends to allow sampling because they were sick of the litigation.
BRIDGEPORT MUSIC v. DIMENSION FILMS (2005) (sampling case)
*Court came up with Bright line test Get a license or do not sample
Audio Home Recording Act (AHRA) (p. 600) If you make a tape or a CD from a radio
broadcast for noncommercial use, that is not an infringing use.
Right to Prepare Derivative Works Under 106(2)
Derivative Work: a work based upon the copyrighted work; it must incorporate a
portion of the copyrighted work in some form. For example, if you write a novel and
somebody makes a movie about it. Sometimes it is not so easy to figure out if there is a
derivative work.
-havent recast original work and court found that it wasn't a deritative work because
the original work is still there in all its glory
106: Copyright owner and only the copyright owner has the right to prepare derivative
works. Recast transformed or adapted.
44
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Horgan v. MacMillian (Nutcracker book)
Issue
Did the photos infringe the choreography?
Holding
Court of appeals finds it may, as photos might call to mind the moments before and
after the photo; overturns court below who said that the essence of dance is
movement and thus cannot be infringed by photography
o Didn't get permission from the balancing estate he was the copyright owner fo
the ballet himself.
Lee v. Art
A.R.T purchased copies from Lee, then mounted it; they owned the copy and can do
what they want with it Mounting works on ceramic tile and reselling is not a derivative
work under the copyright actits like framing itbecause the original work still exists
wholesale
Look at technical definitions
109- the first sale doctrinethe owner of a particular copy or phonorecord lawfully
made under this title is entitled without the authority of the copyright owner to sell or
otherwise dispose of the copy.
National Geographic v. Classified
Facts:
Defendant had years worth of National Geographic articles. He took the original
articles, collected them and sorted them into different topics with related subject
matters, and sold them as compilations.
Held:
The defendants activities constituted copyright infringement. Statute gave the plaintiff
the exclusive right to compile or arrange its copyrighted articles; defendant may have
been the owner of the physical material, but not the owner of the rights to make those
kinds of unauthorized uses.
The reason it's a derivative is because it could have taken its original magazines and
taken all the shit about lakes or mountains and put it as something else. That's why
when someone else was doing it it ciolated Nat Geo BECAUSE NAT GEO WOULD
HAVE BEEN ABLE TO MAKE IT THEMSELVES IF THEY CHOSEthey have the
right to do that. NAT GEO HAS DERIVATIVE RIGHT.
o Even though other guy had a property right didn't matter because it succumbs
to the copyright law
MicroStar v. Formgen
Facts
Downloaded user-created levels of Duke Nukem and resold them on a CD-infringed
the original elements created by Formgen (Same characters, just doing different
things).
Holding
45
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Micro Star violated Formgens right to use its own characters and tell their stories.
The work that Micro Star infringes is the D/N-3D story itself in a sense, their work
acted as a sequel to Formgens. This is infringement.
Family Movie Act of 2005 Congress passed a law (110(11) which said if theres sex/violence/profanity in a movie
and you want to cut it out for the version you show your children, you are allowed to do
that
o A device that recognizes and fasts forwards sex and violence on DVDnot
recasting/derivative work because the legislature says its notbut also no
fixed copy.
Moral Rights
Berne Convention
what other countries do: independent of authors economic rights, the author shall have
the right to claim authorship (paternity right). Author has additional paternity right (after
economic rights, and even if hes transferred his economic rights) to object to any
modification of the work which would damage his honor/reputation (E.g. Leon
replacing Picassos signature with his on a painting to impress a girl; or, adding
to/changing painting.
o US enacted this in 89our 1st acknowledgment of moral rights, long after most
countries.
Policy
If I steal someones work it's an infringement, but why isnt it also moral right?
Need to use copyright as the person made it.
Gilliam v. ABC
Facts
ABC edits obscene material from Monty Pythons flying circus.
Cant call it Monty Python because what you are transmitting isnt what MP actually
was it is a false use of monty pythons name
Court found this impaired the integrity of the artists work.
o Even though this was pre-Berne Convention/Moral rights in the US, but under
Lanham Act false designation of origin, they created a false impression of the
products origin.
Rule
Must use work as it was granted, otherwise you violate copyright law by exceeding the
restrictions on the work.
Dastar
Published cut of Wm. Steigs name on bookno false designation of origin because
the publisher of the physical book WAS the originator. P
Precluded many Lanham act claims that previously would have successed. Applied
Berne convention laws.
46
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Redophsi- he brought a lawsuit. No false designation of origin.
Federal Law Protection of Moral Rights cant distort and fuck shit up
Gilliam court alluded to the continental concept of moral rights, and to the authors
prerogatives to secure proper attribution of her work and to preserve the work in the
form in which it was created.
Visual Artists Rights Act of 1990 (VARA) Added 106A to the copyright law and added a
definition of visual art to 101. VARA only protects visual arts (defined in 101 as a
painting, drawing, print, or sculpture or a still photographic image; 101 also outlines several
exclusions, including works made for hire). If it does not meet the definition of visual art in
101, can still rely on the Lanham Act and other provisions of copyright law, but there is no
protection under VARA. VARA protects both the paternity (authorship) and integrity of the
work.
Only visual works that are considered art are protectedso you cant distort, mutilate
or other modification of the work which would be prejudicial to his or her honor or
reputation.
I think this basically means you cant make derivative works of Visual Arts
This will apply to applied art and utilitarian purposes.
What is Site specific artBanksy
Part of the reason for the arts artistic appeal is the place in which it was done. This means
that you have to take into account not only the art itself, but the location of the art. (Phillips v.
Pembro Real Estate)
Only in this place
putting all kind of shit in a garden or a park
took it away from the place it was put was it a violation--- is not a violation
This is the kind of accommodations which we have for visual artists under VARA
VARA Cases
CARTER v. HELMSLEY-SPEAR, INC. (site-specific sculpture in NY building)
Facts:
Site-specific sculpture was commissioned to fill the lobby of a building and removed by
the new building owner without obtaining an agreement from the artist waiving their
rights.
Issue:
Is this applied art, which is exempted from VARA?
Held:
This is not applied art simply because components of it standing alone were applied
art. However, it was a work made for hire, so it could be taken down without violating
VARA.
o Also for applied art- nothing in VARA proscribes protection of works of visual
arts that incorporate elements of, rather than constitute, applied art.
47
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Richard Serra
Location specific art removedLeon was told he couldn't get an injunction against
U.S. Govt., only damages
Pollara v. Seymour
Banner for charity a work of art?
Court says no- It was created to draw attention to information deskcommissioned
and paid for by charity- work made for hire
Not a work of recognized statute
Phillips v. Pembro Real EstateNo violation of VARA (above)
Teaching Guidelines: Treaty Between Publishers, Authors and Teachers/Schools
Teacher can make a single copy of AN article or A chapter
o Can make no more than one copy PER STUDENT, but then must meet
standards of brevity (no more than 1000 words) and spontaneityeach must
notice of and meet cumulative test
Law is a handout
Fair Use
The most significant limitation on an authors or copyright holders prerogatives. This defense
is almost automatic. Every infringement action is going to have some fair use. The way to
resolve it is to see what the courts have decided, and see what is fair.
Fair Use
Fair use of copyrighted work
Some fair uses that are not an infringement: Criticism, news reporting, comment,
Classroom usage/teaching, scholarship, or research.
107: Factors to be included shall include: 4 factors
a. The purpose and character of the use including whether such use (by the
infringer) is of commercial nature or for nonprofit
a. Purpose and character of the use asks whether and to what extent the new
work is transformative. The more transformative of the first work the second
work is, the more likely it is that it is fair use.
b. Transformative means something that has used heavily the mind of another
person. The defendant has brought a lot to the table taken a lot of their own
brain and changed it for a purpose. (Profit making is less legitimate; education
is more legitimate.)
48
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
c. In general, commercial use tends to go against fair use and more towards
copyright infringement; non-profit/educational use is more likely to be found to
be fair use. This does not mean that if you use it for commercial purpose you
automatically lose just a factor to be considered.
b. The nature of the copyrighted work
a. Creative or factual work if its creative, go to P. If its factual go to D
c. The amount and substantiality of the portion used in relation to the copyrighted
work as a whole; and
a. Amount and substantiality -- .1% yeah not ok. Amoutn might be small but
substantial is a judgment call. Look at what is most important in the book and
see whether that was taken.
b. Look to precedent cases to see how many/much the courts allow for a
published work as well as unpublished work (depending upon which you are
dealing with) (Schloss v. Sweeney)
c.
d. The effect of the use upon the Potential mark for or value of the copyrighted
work
a. Concern is with whether the new work will become a substitute for the original;
best way to show this is to show that sales for the 2nd work increased as sales
for the first decreased
b. any market. The POTENTIAL market
i. If the plaintiff company would NOT go into the market, but the owner of
the copany could possibly want to go into the market --- NO distinction
between the company and the owner
How are the factors weighed?
a. See Leons outline at pp. 36-37. Originally, the Supreme Court (Nation) said that the
4th factor is the most important and that if you won that factor, youd only have to win
one of the others. Then in Campbell they did not mention that at all and focused on
the first factor and how transformative the use was. Now the courts all say that the 1 st
factor is the most important.
b. Judges tend to come to a conclusion; then they figure out the factors accordingly.
c. Doesn't effect the market if never meant to sell them
d. His heirs could sell it, and that's potential market
e. Salinger won
Parody
Parody has to be laughable. If not, its a derivative work.
When you have the parody, three of the factors go the other way.
Parody: factor 1 if transformative enough to make people laugh. Factor 2 not really
relevant. You need to use enough of the original to create an expectationmust
conjure up the original
CAMPBELL V. ACUFF-ROSE MUSIC, INC.(2-LIVE CREW)
First Factor
49
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Whether the new work merely supercedes the objects of the original creation, or does
it add something new, with a further purpose or a different character, altering the first
with new expression, meaning or message (Blanch v. Koons)- AKA To what extent
the new work is transformative
o Serves new/distinct purpose and character from the original
If its different from what the original used it for, its transformative. If its
transformative, you win factor one.
If you are doing a parody need to conjure up so audience laughs
Its necessary in a parody to use as much as possible to get people down that road
Leon says that as soon as defendant win 1st factor, #2 effectively disappears and
#3 diminishes in importance.
For parodies, three of the factors almost automatically go the other way
Second Factor
Factual or creative
o If its fiction, that helps plaintiff
o if nonfiction, helps defendant
Published or unpublishedo Unpublished helps P.
o Published helps D (more likely in Pub domain)
The Court found that this didn't really apply since the artistic value of parodies is often
found in their ability to invariably copy popular works of the past
Third
Need to take enough to lead people in a certain direction for parodys
The Court found that Campbell had used the 'heart' of the original work, but that
copying the 'heart' is required in order to be a successful parody. Since Campbell
substituted mostly his own lyrics, it couldn't be said that he took more of the original
work than was necessary.
For parody, you need to use enough of the original to create an expectationmust
conjure up the original
Four
Its fine if the parody makes the original seem stupidcopyright not here to protect that
2 Live Crew does not have the same audience as Orbison. And if their version injures
original by pointing out its flaws, well that's all well and good under the 1 st amendment.
That's not what the copyright law is concerned with.
Fisher v. Dees
When Sonny Gets Blue turned into When Sonny Sniffs Glue. Leons Rule for Parody- if
the judge laughs, its fair use.
Dr. Seuss Enters., L.P. v. Penguin Books USA, Inc
50
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Court ruled against the parody defense of the publisher of a book that adapted the
image and verse familiar as the Cat in the Hat to tell the tale of O.J. Simpson murder
trial in a book the cat not in the hat.
Wasnt criticizing the original. Parody needs to make fun of the original therefore
not a fair use --- NOT Transformative
Leibovitz v. Paramount
Naked Gun poster with Frank as pregnant Demi Moore is fair use parodyjust barely
Suntrust Bank v. Houghton Mifflin Co.
have to copy enough to transform what was there.
Facts
Gone with the Wind parody where slaves are intelligent and heroic, white masters are
weak and ignoarant (The Wind Done Gone). District court issued injunction because it
ripped off the full story (in the courts view) Circuit court reversed1 st amendment
concerns and lack of harm to GWTW holder
Rule
have to copy enough to transform what was there.
treat a work as a parody if its aim is to comment upon or criticize a prior work by
appropriating elements of the original in creating a new artistic as opposed to scholarly
or journalistic work.
Holding
The fact that TWDG is a commercial work is strongly overshadowed and outweighed
in view of its highly transformative use of GWTWs copyrighted elements. It does not
matter that the parody is not funny; as long as it is a transformative use and the
parodic character is clear, it will likely be found to be fair use. The minute something is
parodic or like a parody and is transformative, you win the first character
Paramount Pictures Corp. v. Carol Pubg Group, Inc (Trekkies)(P wins)
Book summarizing Star Trek for non-Star Trek fans, presented humorously, so reader
can communicate with Trekkies. Defendant (and Leon) lost they brought in a judge
from Montana who had no sense of humor
Warner Brothers v. RDR Books (Harry Potter) (P wins)
Holding
Court stressed that Ms. Rowlings rights did not entitle her to control the market for
books about Harry Potter series and its characters but that the defendants work took
too much of Rowlings original expression.
Analysis
51
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Factor 1: The book was a Derivative Work because Rowling could have published it
herself.
Factor 3- Plaintiffs amount to a substantial enough taking to tip the third factor against
a finding of fair use in view of the expressive value of the language.
Factor factor 3the Lexicon disturbs the balance and takes more than is reasonably
necessary to create a reference guide. In these instances, the Lexicon appears to retell
parts of the storyline rather than report fictional facts and where to find them.
Factor 4- Website wasn't depriving her of any income
Judges don't laugh at sexLeon Friedman
Walt Disney Prods. v. Air Pirates (dirty Disney) (P wins)
Disney characters doing obscene things. By copying the images in their entirety,
defendants took more than was necessary to place firmly in the readers mind and
parodied work and those specific attributes that are the be satirized. Defendants took
more than was necessary to call the original to mind
Mattel v. Walking Mountain Productions (whore Barbie) (D wins)
Barbie in compromising positions.Court found the amount and substantiality factor to
weigh in Forsythes favor. The defendants use was fair use. His work is a parody of
Barbie and highly transformative. The amount of Mattels figure that he used was
justified. His infringement had no discernable impact of Mattels market for derivative
uses. Finally, the benefits to the public in allowing such use are great. We do not
require parodic works to take the absolute minimum amount of the copyrighted work
possible.
Blanch v. Koons (D wins)
Facts
Koons took photo from ad, incorporated the feet (at a totally different angle) into an oil
painting amongst other feet). Was it transformative (the feet)
Holding/Rationale
Koons wins
Koons argues because one is a photo, the other is a painting. Purpose is different from
Blanchs in creating it.
Act of borrowingadvance artistic purposes. New aesthetics, new insights and
understandings.
Cariou v. Prince (D wins)
Facts
52
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
painted over some portions of the photos, over the entirety or none from Yes Rasta.
Making a collage based on the underlying pictures.
Holding
Court found it was transformative. It wasnt desired to pass truth about Rastafarians,
he had a different reason. Reasonable observer would feel that its different.
Court said this wont effect the market for the book. (factor 4)
o Prince caters to rich people (Beyonce goes to his shows and buy his paintings)
so hes not infringing on Carious market
Leon- don't call yourself an appropriation artist and then go into court and claim
you didn't steal anything.
Harper & Row Publishers, Inc. v. Nation Enterprises case is no longer the law
Facts
Nation Magazine gets advance gallery of Fords memoir, and publishes review
substantially recounting exchanges/negotiations occurring during the four days prior to
Nixons resignation. This killed the value of the first publication rights.
Analysis
1st factor-Lose first factordefendant loses
o although this may be news reporting under 107, its COMMERCIAL. So this
weighs against presumption of fair use. (Totally different from 2 Live Chains,
which was decided 10 years later)
no incidental useintended purpose of supplanting owners
commercially viable use.
nd
2 factor- Defendant loses-Nature of copyrighted work is unpublished.
o Fact that its unpublished is crucial in determining who wins the factor.
o Despite policy in favor of sharing factual works, the original was unpublished
this weighs heavily against defendant. Lose 2nd factorif unpublished, means
more effort into getting it in order to copy it.
rd
3 - Amount and Substantiality -substantiality was the most important part
o 200 words of Fords 20,000 word biography were used. However, they were the
most interesting and movie parts of the manuscript, so this WAS substantial
also, the 200 words were 1% of Fords book, but 13% of the Nations
infringing article
th
4 Factor-final factor effect on market,
o lost $37k due to loss of 1st serial rights in Time.
Afterwards, Congress added last sentence of 107 so that the unpublished nature of
an original work does not trump all the other fair use factors, the way it seems to have
in this case made it so factor 2 isnt the most important anymore.
Cambridge v. Patton
Facts
53
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Prof. puts course materials onlineeReserverather than making students buy
books. (You cant do this in hard copycant give students the Kinkos edition of the
course materials. However, is this OK on the Internet?). The minute you put it online,
you made a copy. There is no question that is a potential copyright problem
Analysis
1. Is the use transformative?- No
If yes, this factor goes to defendant. If not, theres still more analysis under the 1 st
factor
o Here, Not a transforming use. Its for educational usenoncommercial
educational use
Making copy of the entire book 2nd circuit said: the creation of a wordsearchable digital version book , is quintessentially transformative
searching is different meaning message and purpose than from the
source it took (Authors Guild v. Happy Trust)
2. Nature of the Copyrighted Work
Neutral, or weighs against fair usenot factual materials, but rather fictional stories.
Plaintiffs win here.
3. Amount Taken and Substantiality
Amount taken- this analysis must be fact-based. No blanket rule (cant say 10% is
OK in every case or one chapter is OK in every case). Remanded to lower court for
fact-finding determination. remanded
4. The use IS noncommercial and educational/ A effect on Market
Since the school isnt profiting directly by the use (only indirectly, through tuitionbut
the school is nonprofit), it falls within the congressional intent for the educational
exception, and therefore this factor goes to defendants. remanded
Wrong rule applied. Even though the defendant has the burden of proof on this elemtn,
the plaintiffs should have been required to present evidence, because they hold all the
data on this factor.
Random Examples.
Smith v. Barnes & Noble.com eBook license expired, book was no longer available
on site; but book was still findable on certain parts of the site, and users could
browse/preview the contents.
Putting photo on T shirt is fair use (7th Circ.)background was altered, face was
turned limegreen, other alterations
o Leon doesnt like this resultdoesnt this interfere with the market, because the
holder could have made shirt?
TV Eyes takes 24 hour news services (CNN, Fox News, etc.) & creates database,
allowing subscribers to track certain news items, search, etc. This was fair use.
Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings (D wins)
two copies made of her unpublished novel for librarypreservation purposes. Not
transformativebut the PURPOSE was transformative. Wasnt commercial at all in
nature. Court ruled this OK
Craft v. Kobler (P wins)
54
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
lots of quotes from Stravinskis autobiography. Too numerous with too little structural
justificationnot fair use. The copier is not @ liberty to avoid pedestrian reportage by
appropriating his subjects literary devices. court found that Kobler took too much of
Stravinskys work in the biography far too numerous and with too little instructional
justification to support the conclusion of fair use
Ads: generally not fair use because of commercial nature
Los Angeles news serv. V. Cbs broadcasting, inc.
o Police helicopter took pictures of L.A. riots and caught footage of Reginald
Denny being torn from his truck and beaten up. News channels wanted to use
that footage. Hot News Exception to fair use it is fair use if it is used
when it is very important and very vivid. But if you use the same footage a year
later, it might no longer be found to be fair use.
Showing opponents speech in political commercial is fair useits transformative
because youre using it for the opposite purpose he intendedto make him look like
an idiot
Castle Rock v. Carol Publ
Seinfeld quizbook (asking questions about plots of episodes) wasnt fair use
derivative market which NBC COULD HAVE engaged inalso could have licensed.
Also, minimal creative elements / not transformative purpose.
Clean Flix v. Soderbergh (P wins)
Congress passed home recording act so clean flix in TV is ok. But if someone takes an
edited version, like edit out all the bad sex scene, and then sells it, then they arent in
the protection of the congress.
Rule
Not permitted to create and sell censored versions of moviesnot fair use. Didn't add
anything newnot transformativejust deleted.
Analysis
Took away control element which is essential to holder
De minimis/ Decorative Use
Generally permitted (ed work briefly glimpsed/heard in movie/radio show)
But NOT where theres a callous disregard for holders interest
Ringgold v. BET
If its more than a quick pan, and the camera lingers on the object for any amt of time,
its enough to come under fair use scrutiny.
Iowa State University
3 minutes of film about a wrestler used in ABCs sideshow during Olympicscourt
didn't like this. It was for the same purpose as the original
55
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Bernard Geis
6 Seconds in Dallas book used 60 frames of Zapruder film (out of 486). Summary
judgment for the book writer (and Leon)
* this was before fair use factors, but judge felt that public policy favored spreading
knowledge to the public regarding one of the most important issues in 20 th century.
Said that the author stole the frames from Time was not a factor
o In NXIB, the court slightly weighed the propriety of defendants conduct (e.g
theftstole corp manual which he later potentially infringed)but its not given
heavy weight
Bond v. Blum- Custody battle (Wife wins)
She copied husbands biography, whole thing, to use in custody disputethat was fine.
Can copy photo if someone has done something illegal.
Sega and Electronic Cases
Sega v. Accolade co.
Facts:
Reverse engineered Sega system so could make games that are compatible . It took it
apart. You are taking it apart but making a copy of the constituent parts. It relied on the
infroamtion it gathered from the reverse engineering
Issue: Is re-compliation wrong?
Analysis
Factor 1: No dobut they made an entire copy of the original console but is its use
transformative?
Yes transformative-- use the original code to discover how to make games
compatible with this console
Factor 1 What is the prupsoe and character of the use
o The accolade took it apart to figure out how it works to figure out compatibility
with the console
Had to perform their own creative work
It wrote its own procedures
th
4 factor- They are not directly competing with sega, they are creating their own
games
1st 2nd and 4 go towards accolades
Holding
Taking apart a ed work and copying the program was fine, so long as they did it only
to ultimately use parts of the system that were NOT afforded protection and couldn't
be obtained any other way.
Sony Case (D wins)
56
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Same facts as Sega for the most part. Mechansim for allowing people to play PS
games on computer.
1st factor- Modestly transformative, new platformSimply allows you to use sony
games on a compthat's like kinda better for Sony
4th factor- extent of the harm isnt big, and not an adverse impact on the marketit
expands the market. Not competitive in anyway.
Once its transformative and theres no market impact, its fair use usually**
Application of Fair Use Doctrine to New Technologies
Photocopying machines made it easier to copy shit. Prior to them, authors werent really
worried too much about the economic impact.
Wilkin v. U.S. (early photocopying case)
Copying medical journal articles was fair sue because harm was speculative and the
use benefitted medical research. The court, which was split, went in favor of fair use
because (a) they thought this question about photocopying medical articles and such
was better left to congress to deal with AND they knew that the 1909 Copyright act
was being revised moreso in favor of fair use and (b) the harm to students not being
able to use the articles was great than the harm to the publishersplaintiff publishers
failed to show future harm.
Princeton v. Michigan Document Services (P wins)
Facts
Company producing photocopied course packs for classes. Michigan was a for profit
entity
Rule
To negate fair use, may show that the practice, if became widespread, would
adversely affect potential market (S.C. test)
Holding
Court applied the four fair use factors and found against the copiers:
o First Factor: Purpose and character You had to buy the course packet, so it
was commercial use copiers lose this factor
o Second Factor: Nature of the copyrighted works theyre short stories,
creative, and published. Copiers lose this factor too
o Third Factor: Amount & substantiality - the whole stories were copied
o Fourth Factor: Effect on potential market youre not buying the book at all!
American Geophysical Union v. Texaco
Facts
Texaco copies science journals to send to its researchers.
Difference between U.S. National institute Health and Texaco? Texaco is a big bad
company whereas NIH is a benevolent and good. This is why there is no fair use. Big
company is taking copyrightable material and archiving copies of it without giving a
profit back to the owner.
57
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Holding
No fair use even though they did similar, and in fact less, infringement than NHI in
Wilkins.
Yes there is an effect on the Market. American Geo Physical Union could get more
subscriptions.
Cambridge Uni Press v. Becker
It had to do with putting shit online for students to get. The 11th circuit reversed and
remanded abck down to the lower court. The thought the lower courts were fucking up
by weighing the factors equally and by giving too much weight to a strict quantitative
test for the 3rd factor.
Copying By End User
Test:
1. Is it (the machine/website/etc) capable of commercially significant noninfringing uses?
If yes
2. Does the use of machine/website constitute fair use and therefore not infringe?
Sony v. Universal City Studios Betamax case
Facts
Timeshifting. Sony manufactured and sold millions of Betamax video tape recorders.
When people were buying this Betamax they were copying movies and other television
shows as well as noncopyrighted programs. Disney, Universal and Sony found in
surveys that the most common use for the Betamax was time shifting.
ISSUE 1:
Is the Betamax capable of commercially significant noninfringing uses? Yes
ISSUE 2:
Does the use of the Betamax constitute fair-use and therefore not infringing upon
copyrighted material? Yes
REASONING: The court claims that the legislative intended is to motivate the creative
activity.
Sony should not be punished because the users of the machine use it to make
unauthorized reproductions.
Private time-shifting is considered non-profit and noncommercial use.
Universal needed to prove that the noncommercial use was
Harmful
That if it should become widespread, it would adversely affect the
potential market for the copyrighted work
The court weighed this in the equitable rule of reason
Can Xerox be sued for contributing to the infringementnope. Because if the machine
can be used for substantial non-infringing uses *** If a machine is capable of
substantial non-infringing uses, then you cant sue them for contributory infringement.
Doesn't hurt the producer
58
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
A&M v. Napster
Making an entire copy of the song. Literally failed all 4 fair use factors. Effect on the
market? Yes. Don't go out and buy it . Court notes that repeated and explotive copying
may be commercial even if no profits made
Obama
Obama HOPE poster copied photo of Obama. That infringed
Secondary Liability
Persons Liable
Not only is direct infringer liable (entity that copied copyrighted work), but distributor
also liable (see Ortiz-Gonzalez v. Fonovisa), as well as contributory and vicarious
infringers (See A&M Records, Inc. v. Napster).
SECONDARY LIABILITY: Somebody else is infringing, but you either help them or
encourage them and you are therefore equally liable for the infringement.
A. CONTRIBUTORY Infringer: One who with knowledge of the infringing activity, induces,
causes or materially contributes to the infringing conduct of another, may be held liable.
(Gershwin Pub. Co. v. Columbia Artists Mgmt): Knowledge. Inducement
Thus where operator of flea market was told by RIAA investigators that illegal CDs
were being sold, it had the required knowledge. Also flea market provided space,
utilities, parking, advertising, plumbing and customers, it materially contributed to the
infringement (UMG Recordings v. Sinnott).
In Grokster litigation, 9th circuit found that manufacturers of peer-to-peer filing-sharing
computer networking software were not contributory infringers since they did not
reside on distributors computers nor did they have the ability to suspend accounts. No
Knowledge THIS GETS OVER TURNED INFRA C.
B. VICARIOUS Infringer: liability extends beyond an employer/employee relationship to
cases in which a defendant has the right and ability to supervise infringing activity, and also
has a direct financial interest in such activities (Fonovisa, Inc. v. Cherry Auction, inc).
Control. Financial Interest/profit
Thus, where flea market knew of possible infringing activities and refused training to
detect which CDs were counterfeit, the first part of the test was satisfied (control).
(UMG Recordings v. Sinnott).
In addition, flea market drew extra admission fees and also made money at
concession stands. Thus financial interest part of the test was satisfied.
o Control (of premises) - were they able to stop the person from infringing
o Obtain profit
C. INDUCEMENT (GROKSTER): One who distributes a device with the object of promoting
its use to infringe , as shown by clear expression or otherwise affirmative steps taken to
foster infringement, is liable for the resulting acts of infringement by third parties.
Inducement Exists when:
1. Distribute device
59
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
2. With the object of promoting its use to infringe copyright
3. Clear intent (affirmative steps) to foster infringement.
Facilitation of Infringement by End Users: Cases:
Perfect 10 v. Visa (D wins)
Facts
Website of female models charges by credit card. Users buy images and then share
with friends. Credit card co. secondary infringer? (Perfect 10 notified Visa of its
consumers infringing uses & Visa admittedly did nothing). (Note: Perfect 10 is suing
Visa because sleazy web user is probably insolvent)
Holding
No vicariousno control over the activity; credit card has substantial legal purposes
Processing payments doesnt substantially assist infringement (unlike Google)
o That defendants have the power to undermine the commercial viability of
infringement does not demonstrate that defendants materially contribute to that
infringement
No contributorydidnt induce/cause-doesnt help locate/steal imageinfringing
activity only occurs AFTER download
Perfect 10 v. Amazon
Facts
Google Images thumbnail of image from site is transformativenot infringement. But
someone comes along and uses the Google Image thumbnail to share the
copyrighteded photo from the site.
Holding
Google isnt vicarious infringer because doesnt profit from the infringing sharing. (And
doesnt have right to directly control usersonly to affect them). And doesnt have right
to police / remove users (unlike Napster / Fonovisa)
Might be contributoryremandedCould take simple measures to stop further
damage
Distinct from Perfect 10 v. Visa because Googles search engine itself assists in
distribution of infringing content to users
Fonovisa v. Cherry Auction (P wins)
Landlord who KNOWS tenant is bootlegging music from apt. not vicarious (no profit),
not contributory (no inducement/contribution)
Flea Market: Here, you own the property and someone sells stuff but its different
because (1) theres a doc that they sign saying you have a right to control what is sold
and (2) you get a percentage of what is sold by the venders. Right to control AND
direct financial interest.
A&M v. Abdallah (P wins)
Tape provider sold tapes @ exact specified length requested by consumer.
Sometimes would even time albums so the customer would know how long a tape to
buy. This was enough knowledge (& inducement) for contributory infringement. This
60
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
was a product specifically manufactured for counterfeiting activity, rather than a
staple product
Sony v. Universal
Fulfills the factors of contributory infringement (Knowledge and financial interest)but
if the equipment has SUBSTANTIAL NONINFRINGING USES, they cant be held
liable. (Time shifting of shows is legal)
Someone makes infringing recordare ASCAP/BMI vicariously liable for profiting from
the infringing record?
o Nobenefit, but dont control the way in which the music is exploited
o No veto power over what the infringer does
A&M v. Napster
Original Napster model wasnt peer-to-peerthey actually made a copy on their server
so they were first-hand infringer.
But were also vicarious & contrib infringers:
o Control satisfied because the music went through their server. (They control &
patroland expressly reserve right to remove user, a la Fonovisa)
Capable of noninfringing uses not enough to get them off the hookunlike the
SUBSTANTIAL noninfringing uses in Betamax
MGM V. GROKSTER
Facts
Peer-to-peer site, unlike Napster. But didnt contest that they were aware users
primarily used their service to infringe. Sent email warnings to infringers, but never
blocked anyone. Trial court: No knowledgenot contrib: No controlnot vicarious
Holding: Scotus
Creates Inducement test above
Because they advertised as Cant get Napster anymore? Come to us!
Secondary Liability of ISPs
DMCA: Digital Millennium Copyright Act (98)
512(a):Safe harbor for Online Service Providersnot liable where they transmit, route,
or provide connection to content, if transmittal was initiated by another party, carried out
through automatic technical process without ISP selecting material, OSP didnt select
recipient, & not retained in OSPs system longer than is reasonable to provide the service
Must not have actual knowledge, not make a financial benefit, & act expeditiously to
remove the material if given official notice of infringement by owner (take-down
notice)
Passed 3 yrs. after Netcom case (control, but no profit)
Remedies
61
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Enforcement of Copyright
501: Infringement of Copyright: Anyone who violates any of the exclusive rights of the
copyright owner is an infringer
a. The people who can sue are a much broader group rather than the one person who
owns the copyrightmay be one legal owner of the copyright (whose name is on the
copyright certificate) but also the beneficial owner (such as someone entitled to the
movie rights, etc. or anyone else who gets $$ because the is being exploited)
11th amendment
cant sue state for money, but can enjoin them!!!
Beneficial owner Within 501e.g., publisher who holds not the in the work, but the
publishing rights; owner of film rights (anyone who is making money from some exclusive
right under the (Leon thinks that a book publisher would be able to recover against an
infringing movie production, even though they are not in direct competition).
Someone in the chain of title who will eventually have property here its like the
publisher who gets the benefit from the writers book.
A (book writer)---- B (book Publisher)
[
C (movie company) ------X (movie)
- book writer can sue movie co because book co has exclusive right to sell books
- Someone has to register the copyright--- CANNOT BRING LAWSUIT IF THE COPYRIGHT
IS NOT REGISTERED
The person who registers the copyright isnt necessarily the beneficial owner.
The beneficial owner must serve notice of the action with the copy of the complaint on
any person on the record with the . (so the people who are on the filed records). After
beneficial owner has brought action, true owner may be able to intervene.
Reversion --- If B on death bed leaves copyright to C, C is a beneficial owner
Remedies: First thing you get is injunction
502: Remedies for Infringement: Injunctions: Any Court having jurisdiction under this title
MAY grant temporary and final injunction on such terms as it may deem reasonable to
prevent or restrain infringement of a copyright
501- Court may grant injunctive reliefbut the assumption has always been that this
very nearly must, because the reputational harm/loss of good will/ difficulty of
determining potential lost profits are incalculable
o Good reasons not to enjoinif book/newspaper/magazine1 st amendment
violation
Ebay 4 Part Test (patent case): Traditional Requirements
1. Suffered irreparable injury Damage to good will.
2. Remedies available at law, such as monetary, are inadequate
a. Damages arent adequate because you will lose sales you would have had that
cant be covered by damages reputational undermine good will of the
owner of the copyright (patent). Cant trace all of the damage.
3. Considering the balance of hardships btw P and D, a remedy in equity is warranted
4. The public interest would not be disserved by an injunction
62
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Standard Today: Random House (Holden Caufield): 2nd circuit test: likelihood of
success, or in 2nd circuit, raising of substantial questions and a balance of hardship in favor of
moving party.
1. Irreparable harm AND
2(a) Likelihood of success on the merits, OR
2(b)(i) Sufficiently serious questions on the merits to make them fair grounds for
litigation AND
2(b)(ii)Balance of hardships tilts towards plaintiff
Irreperable Harm
Can usually be met by proof of a likelihood of success on the merits (ABKCO Music).
BUT since the goal of copyright is to stimulate the creation and publication of edifying
matter, Courts may wish to bear this in mind before giving an injunction (some
skepticism/discretion)
Cases
Stuart v. Abend
Rear Widow movieno injunctionwould deprive public of the movie; better to impose
reasonable royalty for plaintiff
NY Times v Tuskeenee
Tusk wrote article in the times, the times then sent it on to lexis. And it was then published on
the internet. The author claimed the tiems didn't have the right to send it on to lexis where
they would make money off this internet exploitation. Court said NYT didn't have right to
exploit your work on the internetentitled to money yes. But Court didn't grant injunction
Disney v. Powell: (P win Injunction)
Only infringe Mickey and Minnie. Disney wants to enjoin you from copying all of their
characters Yes, can get alllikely you are going to copy more in the future
Getty v. Microsoft (P no inj.)
Video clip service copyrighting news broadcast. Injunction to stop present material and
future material. Future Works in the same area Yes you can theory is this is
close enough, and since you have already done something bad, and its likely
you are going to do it in the future
Did the court issue an injunction where a big ass company like Microsoft said we
promise we don't take anymore --- Nope they didn't -- -P failed to show irreparable
harm- if Microsoft promises not to do something, they arent going to do it.
First amendment considerations
Souter said in Cambpell caseif a parody doesnt t quite make it, its still protected by
the 1st amendment. And maybe you shouldn't get an automatic injunction
Damages
504- theoretically are entitled to Injunction (A) and Actual Damages (B) and Additional
Profits (C) , OR Injunction AND Statutory Damages: ABC or AD.
63
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Actual Damages: Actual damages suffered by an owner.
One year you get 10,000. Then an infringement and now you only get 5000so actual
damage is $5000
Loss of A Licensing Fee: The reasonable cost of a license that could have been
negotiated between the parties of use of the copyrighted work (On Davis v. The Gap)
Any such lost licnese fee must be based on fair market value (Ringgold v. BET)
(Rogers v. Koons)
Profits: Successful plaintiff is entitled to receive the defendants profits attributable to the
infringement and need only present proof on infringers gross revenue.
If gross revenue is unrelated to infringement, then plaintiff must show closer
connection
o (Thus when advertisements for The Gap stores showed model wearing
plainitffs jewelry, it was not enough to show that The Gap earned an additional
$146 million in sales after the ads were published. Impossible to attribute that
increase to the use of a photograph at issue. ) (On Davis v. The Gap).
Indirect Profits- if P claims that additional indirect profits were earned by infringer, must
present some evidence of such profits to resist sum judg.
Proof of Gross Revenue: P has burden of proving gross revenue under 17 U.S.C.
504(b), and cannot merely estimate such revenue.
Statutory Damages: copyright owner must register the work BEFORE infringement (if the
work is unpublished) or within a three month grace period after the work is published
(412(2)).
412 attorneys fees= requires registration of before commencement of infringement
(for books, within 3 mos. Of publication )
Innocent Ingringer
o Min- 200
o Max- 30,000
Ordinary infringement
o Minimum 750
o Max 30,000
Willfully Infringment
o Minimum- 750
o Max- 150,000
o Not necessary to show that D was aware of Ps and consciously copied
protectable elements. Willfulness can be found if defendant was reckless in
making the inquiry.
Don't need to prove anything for statutory damages except actual infirngement
Jury decides the amount of damages
Can demand statutory damages ANYTIME before final judgmenteven while the jury
is deliberating before theyve delivered a verdict.
Davis v. Gap
64
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
You are entitled as far as infringers profits that are involved.
Frank Music Corp v. MGM
Facts
MGM grand hotel puts on music and dancing on to attract gamblers.
Holding
Kismet film can recovery for the casinos use of Kismets work in casino even though
the hotel licensed the songs, the court finds that the casinos license didn't extend to
use of the songs in the context of Kismet scenery and costumes. Are entitled to what a
reasonable licensee fee would be
Analysis on Damages
Profits of infringer Can we look at the Casinos full income, since the musical
potentially broight people into the casino to gamble. You made 24 mil because people
went to the show. What percentage would Kismat be entitled too?
o Whole show is an hour. Kismat is 5 minutes plausible argument would be 24
mil that you made, 2.4 mil is the profit, then 1/12 is what you should get as the
profit from the show. So whatever percentage of casinos profit the court
finds is attributable to the show, Kismet owners get 12%
o Problem is, people didn't pay to see hallelujah Hollywood. But gotta say that it's
a draw that brought people in who would then gamble.
Statutory Damages: Compilations/ Series of Works (TV, albums etc.)
504(c): all the parts of a compilation or derivative work constitute one work for purposes of
a single statutory damages award for all infringementswith respect to any one work.:
Bryant v. Media Rights
An album of songs was infringement of ONE work, not each individual song, because
plaintiffs had released the album as one body of work
Court said 1 it's a compilation but an infringy one
Twin Peaks
Episodes were individual works, because thats how plaintiffs release them, even though
defendants compiled scripts in one bookwhether issue works separately or together as a
unit
Ex.
Jesus Christ Superstarplaintiff registered it as three works (songs, books, and
something elsethree elements). Because plaintiff registered it this way, it was three
works, each infringed. However, the fact that defendants took their infringing
performance on the road and put it on a variety of cities counted only as one act of
infringement for each elements.
6 toys in a comic strip, and someone makes 6 toys of the characters in the comic
strips. The next year 4 different characters. Is it six infringements or 1 infringement1
infringement
3 act plays. All under 1 cover- 3 plays put in one book. Each 3 separate plays
65
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
o 1 infringement or 3 infringments
o 3 infringementseven though one book, they are separate items
TV series, each episode of a series is a different work
Clients like you moer if the otherside has to pay the fees.
COSTS AND ATTORNEYS FEES
505. REMEDIES FOR INFRINGEMENT: COSTS AND ATTORNEYS FEES. In any civil
action under this title, the court in its discretion may allow the recovery of full costs . . . the
court may also award a reasonable attorneys fee to the prevailing party as part of the costs.
FOGERTY v. FANTASY, INC. (1994) (
Said that defendants and plaintiffs are entitled to attorneys fees at the same level, rejecting
previous dual standard. Court should consider the following factors on both sides of the
equation:
i. Frivolousness
ii. Motivation
iii. Objective unreasonableness
iv. The need in certain cases to advance considerations of compensation and
deterrence
Federal Preemption of State Law: Chapter 10
Preemption 301(a): Federal laws are supreme over state. Fed law preempts state law
when there is a lw for the same thing. It must fall within the subject matter AND it must be
equivalent to those rights under 106.
Preemption 301(b): State Law Action, within the scope of copyright that come within
subject matter of copyright (look at section 102- original work of authorship that is fixedif
not, not preemptive), or if asking for relief that is equivalent to anything in 106 (equivalent
means 106are the rights you are trying to get to stop someone from copying or performing)
Not preempted if outside the subject matter of federal law AND the local law contains
an extra element --If either one is true, then the action is pre-empted
Copyright preempts any state law. Jan 1, 1978
Implied Preemption: Pervasive, dominant federal interest, or objects obtained state and
federal clash
Analysis of 301(a) and (b):
a. Works have to be fixed before any preemption is due
b. Rights or remedies under other federal statutes are saved from preemption
c. Fixation, not publication is now the dividing line between federal protection under
the statute and common law protection
State Laws Restricting Copying: What kind of rights does a person have if they object
to some book or movie or play written about them?
1. Common Law Copyright: After 1978, Fed law exists when its FIXED. If its not Fixed
(ex. Reciting a poem outloud), call it misappropriation. Cannot quote from someone
elses letter
66
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
2. Unfair Competition Misappropriation: Infringer markets a work authored by holder
while creating the impression that the infringer is the author. Allows the infringer to get
the credit (and income) for a work actually generated by another who is not known to
be the source.
a. INS v. AP: Misappropriation (fruit of labor). Cant use AP stuff until its
commercial value as news to AP and all of its members has passed away.
b. Federal common law protection for individual intellectual effort gone now
because of Erie. Misappropriation can be state claim. Preempted if:
i. Whatever you are looking at is fixed
ii. You don't have any other cause of action.
3. Privacy: Cannot use persons name , character or likeness for purposes of trade. If you
use a persons picture in an ad, and they are endorsing some product, that is a
violation of privacy because using name, person, or likelness for trade.
a. As long as you don't use persons name, there is no violation to the right to
privacy
b. New York Law--Law does not cover verbal portraits, as long as you change
the name
c. Don't fictionalize if you are using a real name of a person when writing an
unauthorized biography
4. Right to Persona: Famous people want to be paid if their images are used
a. Vanna White Case
5. Libel/Defamation: For fictional work to be actionable, the work/description must be so
close that the reader of the book linking the real person.
a. There are cases that say if you write a novel, a book about someone, and
everyone knows who it is, but you don't know name. If clearly identifiable, than
that could be libel/defamation
b. Have to change a few basic facts about a person. Add some unflattering
characteristics so nobody would want to say that's me.
i. Small penis rule no self respecting man would ever admit to being
that guy with a small penis
6. Contract: When no specific words are copied, just the idea (go up to producer, tell him
about the movie, and then he makes it). Can only sue under this cause of action if
requirements are met
a. 1. There has to be a relationship of trust and an implied in fact contract
b. 2. The idea has to be a novel idea
i. if movie is so obvious, there is NO consideration
c. I will talk to you, but you cant publish anything before I approve
7. False Advertising: Advertising that draws more than the number of people who would
respond to it that's false
8. Trade Secret: Information that is used for ones business.
Trademark Law: A title of a book, play, movie can be protected by trademark lawthe title
cannot be copyright. 4 Categories
Arbitrary and fanciful- something made up and doesnt apply to anything else
o Protected from first day of use
Suggestive marks: Suggests some quality of the product or good
67
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Descriptive: Describes the product. Need secondary meaning
How does a title develop 2ndary meaning needs to be popular enough
o Title becomes so well known it becomes known as like that book written by J.K
Rowling. Best sellers lists are evidence that secondary meaning has been
established
o Record show secondary meaning: Show sales on Billboard
o Play? : Broadway (because number of seats they have 500+ seats)
**Trial of Lee Harvey Oswalddeveloped 2ndary meaning because it
was a play that played on broadway.
Losing Trademark
Generic Trademark starts out as a trademark, but then people start to use the name
to describe the product
Dilution by Disparagement - Say something bad about a product
o Xeonon pencils dilution
Dilution by Blurring: dilute the value of the famous mark
4 SCOTUS cases
Sears v. Stiffel (preempted)
Facts
Pole lamp. Someone had designed a mechanical pole got a patent on it were not
valid patents. But the lower courts said the design of the pole name was a trade dress
(the shape of it was an indication that spiffle made it.) So it was protected under trade
dress protection
Holding
State law preempted. Problem here is giving protection under state law to something
that federal laws says cant be protected. Would give potentially infinite life protection to
something patent office rejected even given 20 years too. So, cant give state law
protection to something that federal law wont protect
Compco v. Day-Brite Lighting (preempted)
Pretty much the same outcome in Sears
Granting/applying the unfair competition law would be particularly problematic because
unfair competition law would be ongoing. It would give MORE protection than patent to
something that fed govt says doesn't merit any protection
Goldstein v. California (not preempted)
Didn't protect sound recording until 1972. Goldstein was prosecuted under state law.
Not fixed, not published, it was equivalent to a live performance.
Issue/Holding:
When say nothing, does it mean we don't want it protected, or does it say we just
didn't care, we just didn't want to put it under federal law? -- means states can protect
it. (think 10th amendment this is the constitution we are expounding)
If Federal government silent, interpret that as them not caring. Green light for state
68
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Kewanee v. Bicron
Is a trade secret claim preempted by patent?
Holding
As long as state law claim has an extra element, an extra element to prove, then can
get protection
Scope of copyright Law is broader than what is actually enforceable under the
Copyright law
o If its wiritng something that is fixed for some reason not cannot be copied it still
cannot be protected under state law bc the fed c law prempted the state law
Extra element= it was a secret.
Pg 1163- Oral works, live jazz performances, and live demonstrations or displays by cathode
rays are frequently never fixed in a tangible medium of expression. Accordingly, copyright and
other copyright-tpe uses of such material are not treated as infreingements, and state
regulaton is therefore not preempted. (Under 1101, however, incorporated in Title 17 in
1994, :bootleg recordings and broadcasts of live musical performances are now outlawed;
technicaly , they are not copyright infringements regulated udner the Copyright Clasue of the
Constitution, but are subject to copyright-like remedies. Section 1101(d) expressly provides
that state law is not preempted).
Bonita Boats v. Thunder Craft
New old or anything, as long as you copied someones thing through a direct molding
process, that would violate florida law. What is wrong with that is that the shape of a
hule is protexted by patent. To get a patent, a lot of steps and hard to get. But the
florida law is so easy
The florida law impedes the utilatiarain idea of patent.
Go to Congress and ask them to pass a new lawChaper 13 of Copyrgith law
1101-Bootlegging a live performance not technically a because its not fixedbut
legislature justifies it through commerce clause (but this doesn't pre-empt state law
1101(a) Applies retroactively and prospectivelyso for past perfroamcnes before the
law.
1101: Unauthorized Acts- Anyone, who without the consent of the performer,
1. (1) fixes the sound or sounds and images of a live musical performance in a copy or
phonorecord, or reproduces copies or phonorecords of such a performance from an
unauthorized fixation,
2. (2) transmits or otherwise communicates to the public the sounds or sound and
images of live musical performances, or
3. (3) distributes or offers to distribute, sells, or offers to sell, rents, or offers to rent, or
traffics in any copy or phonorecord fixed as described in paragraph (1), regardless of
whether fixations occurred in the United States, shall be subject to the remedies
provided in sections 502 through 505,to the same extent as an inringer of copyright.
Live performances are still protected if fit under definition of 1101
69
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
No preemption by federal statute
Hypo
Im james Brown and want to sing some wrok in the public domain. Some random
person is taking a picture of me and now they use that picture to make a movie of
James singing a PD song but is not fixed in a tangible medium
Not fixed, not in a writing, so cant rely on the constitutional copyright lawso relied on
the commerce clause
Works That Come Within The Subject of C
Whole bunch of cases that deal with right of privacy and right of publicity
Garcia (Innocence of The Muslims Film)
Muslim lady who was in the video that then was made as an anti-muslim movieher
dance itself was copyrightablethe person who took the video doesn't get itbut
court ruled for au bau review or some shit
Toney v. LOreal
Rule
Anything that identifies the individual (voice etc.) cant be used in publicity/commercial
context
Holding
Not preempted because a persons image isnt fixed
o But where the performance is entirely fixed within a copyrighted work (e.g a
song), its probably preempted
Selfie
Boyfriend who sends a self you sent him out is a violation of the right to privacy
Disclosure of intimate personal fact
Dependng on who took the picuter, you may have different rights. If you took the pic
yourself, you sue for copyright infrignemtn. If someone hacks into your system, what
can you do. (intentional infliction of emotional distress)
**Right to privacy isnt preempted because need to show extra elemtn which is name
character likeness which is misused.
Illionis right of publicity
It's a privacy issue, not a copyright issuebut it may be if you took the picture
Laws v. Sony
Sampled someones performance using her voice. Does she have a claim against the
company that sampled her? Is her voice a likeness that cant be copied by someone
else
Holding
Copyright preempts misapporopiation when the part is fully contained in (voice was
part of the recording, she didn't have an individual right to the recording)
Yululan Avalous v. IAC interactive court
70
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
Operates all kinds of dating websites
Why go through all of this when already have claim for copyright? Why go to state
court for all these unfair competition claim? BECAUSE COPYRIGHT DAMAGES ARE
VERY HARD TO GET
U.S. ex Rel Berge v. Board of Trustees of Univ. of Ala.
Research assistant for professor in Alabama. She gives her research to her
supervising professor. What he does is get a federal grant for millions based on her
research. False claims act. No dobut fraud from the guy because presented to the fed
govt materials that werent his. The fraud was his taking of her copyrighted work and
transmitting it as his own. Outside of the copyright cause wouldn't give her as many
damages
Preempted because scope and its protection are not synonymous
Ogla v. Minnesota
She brought the additional state law claims so she could go before a jury and ask for
shit like unjust enrichment and promissory estoppel
Not Equivalent: Name, likeness, character not within subject not a writing
Equivalent
Soemone steals your idea. Says going to sue you for conversion
Is that preempted?
Pg 1172- textbook says if you take my idea, it isnt protected by copyright so its ok.
AN idea is not copyrightable, but its still within the scope of copyright if it is fixed (in
writing and fixed)
Only way it can be protected is if there is a contract, because there is an extra
element in a contractyou signed it.
Implied Contractual Rights
Desny v. Wilder
If you tell a movie producer an idea, theres an implied contract that hell credit and pay
you for it (CA law) contract implied by law. If the script is used, you must be
compensated for that.
You need an extra elementneed to show that there was a promise or you told it to a
person expected to pay you, or told to a person who have a relationship of trust.
o Will you pay me if you use it
NBA v. Motorola
Facts
Reporting facts. They don't like when someone comes along and reports whats
happening Who ever control the sports want to make sure they are getting money for it
Rule
No more federal misappropriation (INS) because of Erie. BUT state misappropriation
71
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
5 elements in INS
o 1. The plaintiff generates or collects information at some cost or expense
o 2. The value of the information is highly time sensitive
o 3. The defendants use of the information constitutes free-riding on the plaintiffs
costly efforts to generate or collect it
o 4. The defendants use of the information is in direct competition with a product
or service offered by the plaintiff
o 5. The ability of other parties to free-ride on the efforts of the plaintiff would so
reduce the incentive to produce the product or service that its existence or
quality would be substantially threatened
Court tried to take principles of INS, establish new principles. Hot news
misappropriationthose 5 things and all 5 of them need to apply.
Holding
All 5 did not apply for NBA claim is not good
o Court finds no competition, and does not undermine the existence of NBA
elements 4 and 5 don't apply.
Analysis
4- direct competition? Not likely. Its not offering information about the score at any
time.
5- would undermine the existence of NBA? NOPE
NBC v. CBS Macys Day parade Case
NBC wants to stop CBS from broadcasting portions of Macys Parade. The only way
they could find to stop them was to play music that was brand new & hadnt gone
through ASCAPso there was no compulsory license.
o CBS circumvented this by playing their ow n music over the broadcast.
Misappropriation not preempted by law
Barclays v. Flyonthewall.com
Barclays advises on what stocks to purchase. Flyonthewall reports Barclays
recommendation
Holding/Analysis
The recommendation itself isnt a work of authorshipso no
o No INS-type misappropriationbecause Fly collected & collated Barclays
recommendations & properly cited to the original source. This is essentially just
collating & distributing news (Barclays recommendations are news according
to court)
ProCD v. Zeidenberg (Shrinkwrap is a contract)
Facts:
License used to appear on the outside of the box; you would tear it open and the
minute you tore it open, you showed consent to the terms. Was a proper contract
entered into?
Holding
72
If the Judge doesn't laugh, youre not going to win.
the world is divided into two kinds of rights. Rights against the world are property
rights (aka COPYRIGHT), rights from contracts are just between parties, so if dont
have right against the world, not preempted. (contracts don't create exclusive rights)
Montz v. Pilgrim
CA has Desny claimIf you tell an idea to producer/agent/someone youd expect to
compensate you [EXTRA ELEMENT preventing preemption], your expectation of
consideration is assumed & its a contract. If they steal the idea, its breach
Here, Montzs claim was too similar to --he didnt expect compensation because the
deal fell through & he retained the rights
Ehat v. Tanner
Material exposing Church of LDS stolen from office; fell into hands of some people who
published LDS pamphlets (who were NOT affiliated with the thieves)they published big
chunks of it
No misappropriationbecause this is within the scope of
73
Você também pode gostar
- Copyright Law Attack F13Documento18 páginasCopyright Law Attack F13Ilana Broad100% (1)
- Copyright Law Attack Outline 2010Documento7 páginasCopyright Law Attack Outline 2010rquinner14Ainda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento28 páginasCopyright OutlineN. M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Copyright Attack OutineDocumento17 páginasCopyright Attack Outinemyersca100% (2)
- Copyright Law OutlineDocumento55 páginasCopyright Law OutlineSos Avetisyan100% (2)
- 09patent Law - Lee - F07 - OutlineDocumento134 páginas09patent Law - Lee - F07 - OutlineansarixxxAinda não há avaliações
- Attack Sec. RegDocumento5 páginasAttack Sec. RegTroyAinda não há avaliações
- Secured Transactions Law OutlineDocumento59 páginasSecured Transactions Law OutlineAbigail ChapmanAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento39 páginasCopyright OutlineN. M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Contracts OutlineDocumento48 páginasContracts Outlinekino321100% (2)
- Business Associations OutlineDocumento114 páginasBusiness Associations Outlinecahco281760Ainda não há avaliações
- Acing BA OutlineDocumento64 páginasAcing BA OutlineStephanie PayanoAinda não há avaliações
- Information Law OutlineDocumento62 páginasInformation Law OutlineLauraChao100% (1)
- 1 January 2011: Never Published, Never Registered WorksDocumento10 páginas1 January 2011: Never Published, Never Registered Worksc133125Ainda não há avaliações
- Mass Media Outline Spring 2007Documento33 páginasMass Media Outline Spring 2007Melissa GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Remedies Goodman 2013 OutlineDocumento42 páginasRemedies Goodman 2013 OutlineCocoAinda não há avaliações
- BusAss OutlineDocumento75 páginasBusAss OutlinejryanandersonAinda não há avaliações
- SecReg Outline 1 - Stern DetailedDocumento127 páginasSecReg Outline 1 - Stern Detailedsachin_desai_9Ainda não há avaliações
- Business Associations Rough OutlineDocumento40 páginasBusiness Associations Rough OutlineGabriel C50% (2)
- Erie Flowchart 2Documento1 páginaErie Flowchart 2diannecl-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento60 páginasCopyright OutlinePatrick Paul100% (1)
- Business Organizations OutlineDocumento26 páginasBusiness Organizations OutlineMarsha Miller TerryAinda não há avaliações
- Criminal Procedure I OutlineDocumento30 páginasCriminal Procedure I OutlineJessica AehnlichAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright Law OutlineDocumento47 páginasCopyright Law OutlineRuthAinda não há avaliações
- UPA DissolutionDocumento1 páginaUPA DissolutionNiraj ThakkerAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidated TM OutlineDocumento69 páginasConsolidated TM OutlineStephanie JohnsAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Law OutlineDocumento35 páginasCyber Law OutlineBobbyCooneyAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento42 páginasCopyright Outlinevhuy12Ainda não há avaliações
- Trademark Law Beebe Fall 2013Documento45 páginasTrademark Law Beebe Fall 2013Will Xiong100% (1)
- II. Unfair Competition: Wilf Intellectual Property Spring 2016Documento35 páginasII. Unfair Competition: Wilf Intellectual Property Spring 2016TR1912Ainda não há avaliações
- Ip LawDocumento29 páginasIp LawTR1912Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Intellectual Property OutlineDocumento35 páginasFundamentals of Intellectual Property OutlineMatthew BurkettAinda não há avaliações
- My Ethics TemplatesDocumento52 páginasMy Ethics TemplatesAlejandro CuevasAinda não há avaliações
- Trademark OutliningDocumento65 páginasTrademark OutliningAna FosterAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright Attack OutlineDocumento6 páginasCopyright Attack OutlineSam Farkas100% (4)
- Condensed Equity OutlineDocumento5 páginasCondensed Equity Outlinecaribelita100% (1)
- Torts Outline-LW-CondensedDocumento8 páginasTorts Outline-LW-CondensedLarry WatkinsAinda não há avaliações
- Contracts OutlineDocumento29 páginasContracts OutlineJoeDellera75% (4)
- Con Law II OutlineDocumento27 páginasCon Law II OutlineNija Anise BastfieldAinda não há avaliações
- Torts Policy Outline - HendersonDocumento8 páginasTorts Policy Outline - HendersonYoung-Min Madison ChoAinda não há avaliações
- Civ Pro OutlineDocumento29 páginasCiv Pro OutlineZTSAinda não há avaliações
- Ethics Outline (Modern Rules For Professional Conduct)Documento12 páginasEthics Outline (Modern Rules For Professional Conduct)austinAinda não há avaliações
- Securities Regulation Outline Bancroft Fall 2011Documento33 páginasSecurities Regulation Outline Bancroft Fall 2011Erin JacksonAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento36 páginasCopyright OutlineScott SherrellAinda não há avaliações
- Last Contracts OutlineDocumento18 páginasLast Contracts Outlinerambo110Ainda não há avaliações
- Main Outline - Intl LawDocumento65 páginasMain Outline - Intl LawQuinn FultonAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright OutlineDocumento12 páginasCopyright OutlineasdfAinda não há avaliações
- White Collar Crime Outline - 4 Law School PDFDocumento73 páginasWhite Collar Crime Outline - 4 Law School PDFMissy Meyer100% (1)
- Torts Attack OutlineDocumento1 páginaTorts Attack Outlinebrittany_bisson_2Ainda não há avaliações
- Trademarks Tushnet Fall-2015 OutlineDocumento102 páginasTrademarks Tushnet Fall-2015 Outlinea thayn100% (1)
- Corporations OutlineDocumento61 páginasCorporations Outlineblessing2u100% (1)
- BA Outline - OKellyDocumento69 páginasBA Outline - OKellylshahAinda não há avaliações
- Business Associations Outline - Klein, 3rd EdDocumento75 páginasBusiness Associations Outline - Klein, 3rd Edjanklewich100% (2)
- Assignment #3 68-77 Assignment #5 106-115 Assignment #6 119-128Documento16 páginasAssignment #3 68-77 Assignment #5 106-115 Assignment #6 119-128Marco Fortades0% (1)
- Business Associations Outline Fall 2011Documento63 páginasBusiness Associations Outline Fall 2011caro6032Ainda não há avaliações
- Business Associations Guttentag Fall 2017Documento77 páginasBusiness Associations Guttentag Fall 2017Missy Meyer100% (1)
- Property Attack OutlineDocumento9 páginasProperty Attack OutlineAshley MeredithAinda não há avaliações
- Ent. Law OutlineDocumento15 páginasEnt. Law Outlinedesey9Ainda não há avaliações
- Anti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActNo EverandAnti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActAinda não há avaliações
- Business Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10No EverandBusiness Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10Ainda não há avaliações
- Night FloorsDocumento27 páginasNight FloorsDaniel FernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Conflicts of Law Outline Google DocsDocumento6 páginasConflicts of Law Outline Google DocsShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Deck of Many Things (Crossroad Angel)Documento6 páginasDeck of Many Things (Crossroad Angel)Shawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Civ. Pro II Professor DiFonzo Spring 2010Documento9 páginasCiv. Pro II Professor DiFonzo Spring 2010Shawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Section 1 Slides AgencyDocumento27 páginasChapter 1 Section 1 Slides AgencyShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- ABA Vs NY 2017Documento37 páginasABA Vs NY 2017Shawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Dolin Property OutlineDocumento164 páginasDolin Property OutlineShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Skills Master List 3.0Documento24 páginasSkills Master List 3.0Shawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Biz Orgs Albert RoadmapsDocumento13 páginasBiz Orgs Albert RoadmapsShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Property Cheat SheetDocumento46 páginasProperty Cheat SheetShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Az Copyright Short OutlineDocumento32 páginasAz Copyright Short OutlineShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Essay Question ReferenceDocumento6 páginasEssay Question ReferenceShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- CROutline F15Documento9 páginasCROutline F15Shawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Copyright Outline AGDocumento13 páginasCopyright Outline AGShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- E&E Copyright Exam StuffDocumento179 páginasE&E Copyright Exam StuffShawn AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- IMTG-PGPM Student Manual - Google DocsDocumento12 páginasIMTG-PGPM Student Manual - Google DocsNADExOoGGYAinda não há avaliações
- The Irish Chocolate CompanyDocumento7 páginasThe Irish Chocolate CompanyMaeveOSullivanAinda não há avaliações
- SOL 051 Requirements For Pilot Transfer Arrangements - Rev.1 PDFDocumento23 páginasSOL 051 Requirements For Pilot Transfer Arrangements - Rev.1 PDFVembu RajAinda não há avaliações
- Vietnam PR Agency Tender Invitation and Brief (Project Basis) - MSLDocumento9 páginasVietnam PR Agency Tender Invitation and Brief (Project Basis) - MSLtranyenminh12Ainda não há avaliações
- Rate Con PO#267800 From Parsippany - NJ To Raeford - NCDocumento2 páginasRate Con PO#267800 From Parsippany - NJ To Raeford - NCbiggbioAinda não há avaliações
- My Portfolio: Marie Antonette S. NicdaoDocumento10 páginasMy Portfolio: Marie Antonette S. NicdaoLexelyn Pagara RivaAinda não há avaliações
- Ta 9 2024 0138 FNL Cor01 - enDocumento458 páginasTa 9 2024 0138 FNL Cor01 - enLeslie GordilloAinda não há avaliações
- Public Service Application For ForgivenessDocumento9 páginasPublic Service Application For ForgivenessLateshia SpencerAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome To The Falcons School For GirlsDocumento6 páginasWelcome To The Falcons School For GirlsSowmiyiaAinda não há avaliações
- The District Governess & Other Stories by Miss Regina SnowDocumento118 páginasThe District Governess & Other Stories by Miss Regina SnowMarianne MartindaleAinda não há avaliações
- Michel Cuypers in The Tablet 19.6Documento2 páginasMichel Cuypers in The Tablet 19.6el_teologo100% (1)
- Bible Trivia Questions - Bible Challenges For KidsDocumento4 páginasBible Trivia Questions - Bible Challenges For KidsVinessa Johnson100% (1)
- Aircraft FatigueDocumento1 páginaAircraft FatigueSharan RajAinda não há avaliações
- Gerson Lehrman GroupDocumento1 páginaGerson Lehrman GroupEla ElaAinda não há avaliações
- EREMES KOOKOORITCHKIN v. SOLICITOR GENERALDocumento8 páginasEREMES KOOKOORITCHKIN v. SOLICITOR GENERALjake31Ainda não há avaliações
- Balkan Languages - Victor FriedmanDocumento12 páginasBalkan Languages - Victor FriedmanBasiol Chulev100% (1)
- Strengths Finder Book SummaryDocumento11 páginasStrengths Finder Book Summaryangelcristina1189% (18)
- Personal Data Breach Notifications in The GDPRDocumento17 páginasPersonal Data Breach Notifications in The GDPRgschandel3356Ainda não há avaliações
- Certified Data Centre Professional CDCPDocumento1 páginaCertified Data Centre Professional CDCPxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxAinda não há avaliações
- Online Advertising BLUE BOOK: The Guide To Ad Networks & ExchangesDocumento28 páginasOnline Advertising BLUE BOOK: The Guide To Ad Networks & ExchangesmThink100% (1)
- Family Code Cases Full TextDocumento69 páginasFamily Code Cases Full TextNikki AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- A Review Essay On The European GuildsDocumento11 páginasA Review Essay On The European GuildsAnonymous xDPiyEAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Energy JapanDocumento10 páginasWind Energy JapanEnergiemediaAinda não há avaliações
- Swami VivekanandaDocumento20 páginasSwami VivekanandaRitusharma75Ainda não há avaliações
- Conflict Resolution in ChinaDocumento26 páginasConflict Resolution in ChinaAurora Dekoninck-MilitaruAinda não há avaliações
- Social Dimensions OF EducationDocumento37 páginasSocial Dimensions OF Educationjorolan.annabelleAinda não há avaliações
- The Petrosian System Against The QID - Beliavsky, Mikhalchishin - Chess Stars.2008Documento170 páginasThe Petrosian System Against The QID - Beliavsky, Mikhalchishin - Chess Stars.2008Marcelo100% (2)
- Witherby Connect User ManualDocumento14 páginasWitherby Connect User ManualAshish NayyarAinda não há avaliações
- Supermarkets - UK - November 2015 - Executive SummaryDocumento8 páginasSupermarkets - UK - November 2015 - Executive Summarymaxime78540Ainda não há avaliações
- JAR66Documento100 páginasJAR66Nae GabrielAinda não há avaliações