Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CS Commerce
Enviado por
KARTHIKEYAN0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações3 páginasgvlgv
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentogvlgv
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações3 páginasCS Commerce
Enviado por
KARTHIKEYANgvlgv
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
CS - Mains - Commerce and Accountancy
Part I
Financial Accounting
Accounting as a financial information system; Impact of behavioural
sciences.
Accounting Standards e.g., accounting for depreciation, inventories,
gratuity, research and development costs, long term construction contracts,
revenue recognition, fixed assets, contingencies, foreign exchange
transactions, investments and government grants.
Advanced problems of company accounts.
Amalgamation absorption and reconstruction of companies.
Valuation of shares and goodwill.
Cost Accounting
Nature and functions of cost accounting.
Job Costing
Process Costing
Marginal Cositng; Techniques of segregating semi-variable costs into fixed
and variable costs.
Cost-volume-profit relationship; aid to decision making including pricing
decisions, shutdown etc.
Techniques of cost control and cost reduction.
Budgetary control, flexible budgets.
Standard costing and variance analysis.
Responsibility accounting, investment, profit and Cost centres.
Taxation
Definitions
Basis of charge.
Incomes which do not form part of total income.
Simple problems of computation of income under various heads, i.e.,
salaries, income from house property, profits and gains from business or
profession, capital gains, income of other persons included in assessors total
income.
Aggregation of income and set off/carry forward of loss.
Deductions to be made in computing total income.
Auditing
Audit of cash transactions, expenses, incomes, purchases, sales.
Valuation and verification of assets with special reference to fixed assets,
stocks and debts.
Verification of liabilities.
Audit of limited companies; appointment, removal, powers, duties and
liabilities of company auditor, significance of 'true and fare', MAOCARO report.
Auditor's report and qualifications therein.
Special points in the audit of different organisations like clubs, hospitals,
colleges, charitable societies.
Part II
Business Finance and Financial Institutions.
Finance Function-Nature, Scope and Objectives of Financial
Management-Risk and Return relationship.
Financial Analysis as a Diagnostic Tool.
Management of Working Capital and its Components-Forecasting working
capital needs, inventory, debtors, cash and credit management.
Investment Decisions-Nature and Scope of Capital Budgeting-Various
types of decisions including Make or Buy and Lease or Buy-Techniques of
Appraisal and their applicationConsideration of Risk and Uncertainty-Analysis of Non-financial Aspects.
Rate of Return on Investments-Required Rate of Return-its measurementCost of Capital-Weighted Average Cost-Different Weights.
Concepts of Valuation-Valuation of firm's Fixed Income Securities and
Common Stocks.
Dividend and Retention Policy-Residual Theory or Dividend Policy-Other
Models-Actual Practices.
Capital Structure-Leverages-Significance or Leverages-Theories of
Capital Structure with special reference to Modigliani and Miller approach.
Planning the Capital Structure of a Company; EBIT-EPS Analysis, Cash-flow
ability to service debt, Capital Structure Ratios, other methods.
Raising finance-short term and long term. Bank finance-norms and
conditions.
Financial Distress-Approaching BIFR under Sick Industrial Undertakings
Act : Concept of Sickness, Potential Sickness, Cash Loss, Erosion of Networth.
Money Markets-the purpose of Money markets, Money Market in IndiaOrganization and working of Capital markets in India-Organization, Structure and
Role of Financial Institutions in India. Banks and Investing Institutions-National
and International Financial Institutions-their norms and types of financial
assistance provided-inter-bank lending-its regulation, supervision and control.
System of Consortium-Supervision and regulation of banks.
Monetary and Credit policy of Reserve Bank of India.
Paper II
Part I
Organisation Theory
Nature and concept of Organisation: Organisation goals; Primary and
secondary goals, Single and multiple goals, ends means chain-Displacement,
succession, expansion and multiplication of goals-Formal organisation; Type,
Structure-Line and Staff, functional matrix, and project-Informal organisationfunctions and limitations.
Evolution of organisation theory: Classical, Neo-classical and system
approach-Bureaucracy; Nature and basis of power, sources of power, power
structure and politics-Organisational behaviour as a dynamic system:
technical, social and power systems-interrelations and interactions-PerceptionStatus system. Theoretical and empirical foundation of theories and Models of
motivation. Morale and productivity-Leadership: Theories and stylesManagement of conflicts in organisation-Transactional Analysis-Significance of
culture to organisations. Limits of rationality-Organisational change, adaptation,
growth and development, Professional management Vs. family management,
Organisational control and effectiveness.
Part II
Industrial Relations
Nature and scope of indsutrial relations, the socio-economic set-up, need
for positive approach.
Industrial labour in India and its commitment-stages of commitments.
Migratory nature-merits and shortcomings.
Theories of Unionism.
Trade Union movement in India-origin, growth and structure; Attitude and
approach of management of India-recognition. Problems before Indian Trade
Union movement.
Industrial disputes-sources; strikes and lockouts.
Compulsory adjudication and collective bargaining-approaches.
Worker's participation in management-philosophy, rationale; present day
state of affairs and future prospects.
Prevention and settlement of industrial disputes in India.
Industrial relations in Public Enterprises.
Absenteeism and labour turnover in Indian Industries-causes
Relative wages and wage differentials; wage policy.
Wage policy in India; the Bonus issue.
I.L.O. and India;
Role of Personnel Department in the Organisation.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Anti Corruption Working GuideDocumento44 páginasAnti Corruption Working GuideTiso Blackstar GroupAinda não há avaliações
- Employment Law OutlineDocumento11 páginasEmployment Law OutlineBrian McKinneyAinda não há avaliações
- Business Plan ElectricalDocumento20 páginasBusiness Plan ElectricalReynante79% (33)
- Benford 'S LawDocumento29 páginasBenford 'S LawramanathanseshaAinda não há avaliações
- Shapiro Chapter 20 SolutionsDocumento13 páginasShapiro Chapter 20 SolutionsRuiting ChenAinda não há avaliações
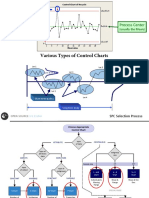
- Control Charts Are Used in Statistical Process Control (SPC)Documento23 páginasControl Charts Are Used in Statistical Process Control (SPC)KARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
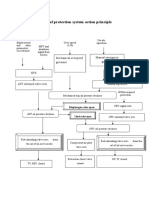
- Brief Summary of Protection System Action Principle: Mechanical Overspeed Governor Manual Emergency GovernorDocumento1 páginaBrief Summary of Protection System Action Principle: Mechanical Overspeed Governor Manual Emergency GovernorKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- BFPT Air Exhust Fan A-ADocumento20 páginasBFPT Air Exhust Fan A-AKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
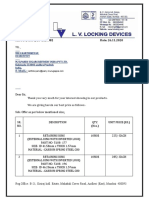
- Ref.: Lv/Igspl/20-21/3082 Date: 26.11.2020Documento2 páginasRef.: Lv/Igspl/20-21/3082 Date: 26.11.2020KARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Condensate Transportation PumpDocumento22 páginasCondensate Transportation PumpKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Equipment Details: Heat Exchanger 1Documento17 páginasEquipment Details: Heat Exchanger 1KARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of 150 Tons Sugar Storage Bin With Structural Staging by Finite Element Method (Nastran)Documento1 páginaDesign and Analysis of 150 Tons Sugar Storage Bin With Structural Staging by Finite Element Method (Nastran)KARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- GeneralDocumento1 páginaGeneralKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Henry VIII (Play) : The Famous History of The Life of King Henry The Eight Is ADocumento9 páginasHenry VIII (Play) : The Famous History of The Life of King Henry The Eight Is AKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- FloodsDocumento15 páginasFloodsKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- FuelDocumento1 páginaFuelKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- CHAP9Documento11 páginasCHAP9KARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- ReferencesDocumento1 páginaReferencesKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Forum LaDocumento3 páginasForum LaKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- CCR Operator: Job DescriptionDocumento3 páginasCCR Operator: Job DescriptionKARTHIKEYANAinda não há avaliações
- Growth of Laptop Market in India.Documento43 páginasGrowth of Laptop Market in India.dhyay100% (2)
- Assessment 1 MonthDocumento80 páginasAssessment 1 MonthnaorziAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Market Structures PDFDocumento5 páginasEconomics Market Structures PDFsourav kumar rayAinda não há avaliações
- POWER TOOLEX ExpoDocumento10 páginasPOWER TOOLEX ExpoAMARNATH KAinda não há avaliações
- Social ResponsibilityDocumento3 páginasSocial ResponsibilityMonique MalateAinda não há avaliações
- Royal EnfieldDocumento2 páginasRoyal EnfieldGopinath GovindarajAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Mutual FundsDocumento52 páginasFundamental and Technical Analysis of Mutual FundsAnnu PariharAinda não há avaliações
- MNCDocumento10 páginasMNCvinoth_17588Ainda não há avaliações
- Sub Order Labels 94ce8e7a 1b4d 4d5b Aac6 23950027e54dDocumento2 páginasSub Order Labels 94ce8e7a 1b4d 4d5b Aac6 23950027e54dDaryaee AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- WEEK 1 - COVERAGE (Article 1767-1783 of The New Civil Code) : I. Contract of PartnershipDocumento3 páginasWEEK 1 - COVERAGE (Article 1767-1783 of The New Civil Code) : I. Contract of Partnershipcarl patAinda não há avaliações
- Brandon Hina ResumeDocumento1 páginaBrandon Hina Resumeapi-490908943Ainda não há avaliações
- Use of Social Media in The Marketing of Agricultural Products and Efficiency in The Cost of Advertisement of Agricultural Products in South West NigeriaDocumento10 páginasUse of Social Media in The Marketing of Agricultural Products and Efficiency in The Cost of Advertisement of Agricultural Products in South West NigeriaEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- VC Lab Cornerstone LPADocumento34 páginasVC Lab Cornerstone LPApyrosriderAinda não há avaliações
- ADTimes 2021 ABFRLDocumento9 páginasADTimes 2021 ABFRLDIBYAJYOTI BISWALAinda não há avaliações
- Axis Long Term Equity Fund - KIMDocumento19 páginasAxis Long Term Equity Fund - KIMsurefooted1Ainda não há avaliações
- TSmunt BM 711 Ch2 HandoutDocumento3 páginasTSmunt BM 711 Ch2 HandoutShelbyAinda não há avaliações
- Crystal Rumbaugh: Career OverviewDocumento3 páginasCrystal Rumbaugh: Career Overviewapi-508568745Ainda não há avaliações
- Basic Accounting ExamDocumento8 páginasBasic Accounting ExamMikaela SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering EconomicspreboardDocumento2 páginasEngineering EconomicspreboardNUCUP Marco V.Ainda não há avaliações
- Definition of WagesDocumento8 páginasDefinition of WagesCorolla SedanAinda não há avaliações
- Ferrell 12e PPT Ch02 RevDocumento39 páginasFerrell 12e PPT Ch02 RevmichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Warranty Claim / Assessment ReportDocumento3 páginasWarranty Claim / Assessment ReportJose Antonio Andrade CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Specification 1Documento238 páginasSpecification 1Infinity SonAinda não há avaliações
- Human Relation SkillsDocumento12 páginasHuman Relation SkillsRose Deanna S. DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Lokesh Punj Cvdec2018Documento11 páginasLokesh Punj Cvdec2018LOKESH PUNJAinda não há avaliações